Crystalline Solids Solid: Orthorhombic System, One of The Structural Categories Systems To
Diunggah oleh
nagatozz0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
21 tayangan1 halamanThe document describes the orthorhombic crystal system. Crystals in this system have three perpendicular axes of unequal length. The orthorhombic unit cell can be rotated 180 degrees about any of its three 2-fold symmetry axes without changing its appearance. It is characterized by right angles between axes and edges of variable length.
Deskripsi Asli:
OS
Judul Asli
Orthorhombic System
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThe document describes the orthorhombic crystal system. Crystals in this system have three perpendicular axes of unequal length. The orthorhombic unit cell can be rotated 180 degrees about any of its three 2-fold symmetry axes without changing its appearance. It is characterized by right angles between axes and edges of variable length.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
21 tayangan1 halamanCrystalline Solids Solid: Orthorhombic System, One of The Structural Categories Systems To
Diunggah oleh
nagatozzThe document describes the orthorhombic crystal system. Crystals in this system have three perpendicular axes of unequal length. The orthorhombic unit cell can be rotated 180 degrees about any of its three 2-fold symmetry axes without changing its appearance. It is characterized by right angles between axes and edges of variable length.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
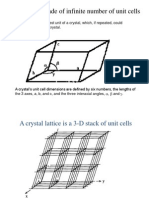
orthorhombic system, one of the structural categories systems to
which crystalline solids can be assigned. Crystals in this system are referred
to three mutually perpendicular axes that are unequal in length. If the atoms or
atom groups in the solid are represented by points and the points are
connected, the resulting lattice will consist of an orderly stacking of blocks, or
unit cells. The orthorhombic unit cell is distinguished by three lines called axes
of 2-fold symmetry about which the cell can be rotated by 180 without
changing its appearance. This characteristic requires that the angles between
any two edges of the unit cell be right angles but the edges may be any
length.
hexagonal system, one of the principal categories of structures to which a
given crystalline solid can be assigned. Components of crystals in this system
are located by reference to four axesthree of equal lengths set at 120 to
one another and a fourth, perpendicular to the plane of the other three. If the
atoms or atomic groups in the solid are represented by points and the points
are connected by line segments, the resulting lattice will define the edges of
an orderly stacking of blocks, or unit cells. The hexagonal unit cell is
distinguished by the presence of a single line, called an axis of 6-fold
symmetry, about which the cell can be rotated by either 60 or 120 without
changing its appearance.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 300+ GMAT Math Questions With Best SolutionsDokumen196 halaman300+ GMAT Math Questions With Best SolutionsKrishna ChaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- CrystallographyDokumen14 halamanCrystallographyGTU Pedia100% (1)
- Waste Incineration Bref 0806Dokumen638 halamanWaste Incineration Bref 0806Stullie100% (1)
- Chapter 2Dokumen59 halamanChapter 2Temesgen Zeleke100% (1)
- Crystal StructuresDokumen54 halamanCrystal StructuresyashvantBelum ada peringkat
- Yakubovich Diss 2008 PDFDokumen568 halamanYakubovich Diss 2008 PDFnagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- English TestDokumen6 halamanEnglish Testkaca011100% (1)
- Ma. Teresa U. Ocular, Bsce-Structural - 1 YearDokumen2 halamanMa. Teresa U. Ocular, Bsce-Structural - 1 YearMa. Teresa OcularBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal StructuresDokumen3 halamanCrystal StructuresElyanna GrefalBelum ada peringkat
- ULO2 ADokumen4 halamanULO2 AKaris DemetriaBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Types of Crystal StructureDokumen3 halaman7 Types of Crystal StructureJR Deviente50% (4)
- Physics Notes Unit 2 (Solid State)Dokumen33 halamanPhysics Notes Unit 2 (Solid State)ch215109152 B.Sc. ChemistryBelum ada peringkat
- AssignmentDokumen5 halamanAssignmentXarOonBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of MetalsDokumen29 halamanStructure of Metalsps4haris.ch3534Belum ada peringkat
- Crystal LatticeDokumen3 halamanCrystal LatticeAceeBelum ada peringkat
- The 7 Crystal Systems GuideDokumen3 halamanThe 7 Crystal Systems GuideFajar AzmiBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal SystemsDokumen2 halamanCrystal SystemseverytimeyoulieBelum ada peringkat
- Atomic and Ionic Arrangement-1Dokumen7 halamanAtomic and Ionic Arrangement-1Joseph MuhoroBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Lattice - Chemistry LibretextsDokumen3 halamanCrystal Lattice - Chemistry Libretextssafwan shafiqBelum ada peringkat
- Seven Crystal SystemDokumen15 halamanSeven Crystal SystemJakeReynaldo29Belum ada peringkat
- Crystallography Unit 1Dokumen70 halamanCrystallography Unit 1addydavid85Belum ada peringkat
- Crystal Structure - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen13 halamanCrystal Structure - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaPradeep ChaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- CrystallographyDokumen25 halamanCrystallographyAkhil Sai KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- MINERALOGYDokumen50 halamanMINERALOGYEllaine Marie PostradoBelum ada peringkat
- Homework 1 GEODokumen3 halamanHomework 1 GEOChristine Jane BarriosBelum ada peringkat
- StereochemistryDokumen11 halamanStereochemistryHaatim Ali Cader SaibBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Mineralogy and CrystallographyDokumen64 halamanPrinciples of Mineralogy and CrystallographyCamille RaboBelum ada peringkat
- 2Dokumen13 halaman2rsrinivasavaradanBelum ada peringkat
- Crystallography: Categories of Solids Based On The Solid PackDokumen21 halamanCrystallography: Categories of Solids Based On The Solid PackSomnath SahaBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal System: Crystallography Space Groups Lattices Point Groups CrystalsDokumen7 halamanCrystal System: Crystallography Space Groups Lattices Point Groups Crystalshareesh.makesuBelum ada peringkat
- Nearly Free ElectronDokumen15 halamanNearly Free ElectronJohnBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Crystal StructureDokumen7 halaman2 Crystal StructureyasinBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Structure: Unit CellDokumen4 halamanCrystal Structure: Unit CelltaufikkatiliBelum ada peringkat
- Licaros, Mary Rose S. Bsce-2ADokumen4 halamanLicaros, Mary Rose S. Bsce-2ALearn Math by mallowsBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Systems: - Sandeep Kumar Karn - 2013JE0776 - B.Tech Mining EnggDokumen11 halamanCrystal Systems: - Sandeep Kumar Karn - 2013JE0776 - B.Tech Mining EnggAkhil Sai KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal System and SymetryDokumen29 halamanCrystal System and SymetryUmairKhalidBelum ada peringkat
- MSE 101 - Lecture 4 - Crystal StructureDokumen40 halamanMSE 101 - Lecture 4 - Crystal StructureKate Lynn PabelicoBelum ada peringkat
- EMG 1204 Lecture 3Dokumen15 halamanEMG 1204 Lecture 3James musambakiBelum ada peringkat
- Crystallography 2Dokumen3 halamanCrystallography 2Akshay KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-1 1.1crystals: Fig 1.1. Structure of A CrystalDokumen44 halamanChapter-1 1.1crystals: Fig 1.1. Structure of A CrystalramBelum ada peringkat
- The Structure of Crystalline SolidsDokumen18 halamanThe Structure of Crystalline SolidsAkshay BundhooBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Structure and Crystal System: Source: Dave - Ucsc.edu/myrtreia/crystal - HTMLDokumen10 halamanCrystal Structure and Crystal System: Source: Dave - Ucsc.edu/myrtreia/crystal - HTMLJawehBelum ada peringkat
- Crystals Are Made of Infinite Number of Unit CellsDokumen8 halamanCrystals Are Made of Infinite Number of Unit Cellsshuvo134Belum ada peringkat
- Crystal Lattices and Structures-1Dokumen10 halamanCrystal Lattices and Structures-1Watyu Dennis PeterBelum ada peringkat
- CrystallographyDokumen22 halamanCrystallography4e3w21qw33Belum ada peringkat
- MaterialDokumen2 halamanMaterialAtif AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal - 1Dokumen60 halamanCrystal - 1Shivam SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Structures - Unit IDokumen16 halamanCrystal Structures - Unit Isanjay sBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Stereoisomerism NewDokumen47 halamanChapter 5 Stereoisomerism Newأسامة المنتصرBelum ada peringkat
- Crystallography and Mineralogy Shalt Am IDokumen106 halamanCrystallography and Mineralogy Shalt Am IDede TaufikBelum ada peringkat
- The Seven Crystal SystemsDokumen8 halamanThe Seven Crystal SystemsArif Siddiquie50% (2)
- Crystal StructureDokumen7 halamanCrystal StructureSREERAGHAV KBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal GeometryDokumen17 halamanCrystal GeometryNeel PatelBelum ada peringkat
- 211 3Dokumen57 halaman211 3Mada ChohBelum ada peringkat
- Isomerism: Compounds With The Same Molecular Formula But Different Structures Are IsomersDokumen15 halamanIsomerism: Compounds With The Same Molecular Formula But Different Structures Are IsomersDr-abdallah Hamdy SaeedBelum ada peringkat
- Crystallographyand Mineralogy ShaltamiDokumen106 halamanCrystallographyand Mineralogy Shaltamiabhinandpradeep2000Belum ada peringkat
- Unit V Crystal PhysicsDokumen7 halamanUnit V Crystal Physicssmileofsun4656Belum ada peringkat
- UnitDokumen51 halamanUnitlijyohannesmekonnen7Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment Crystallography AhmadhDokumen12 halamanAssignment Crystallography AhmadhAhmadhAzharBelum ada peringkat
- The Structure of Crystalline SolidsDokumen40 halamanThe Structure of Crystalline SolidsAsif AliBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-1 1.1crystals: Fig 1.1. Structure of A CrystalDokumen10 halamanChapter-1 1.1crystals: Fig 1.1. Structure of A CrystalramBelum ada peringkat
- Review of CrystallographyDokumen20 halamanReview of CrystallographyGilda AvendañoBelum ada peringkat
- TJ No.99Dokumen1 halamanTJ No.99nagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Parallel Session ICMIA Update 12 NovDokumen4 halamanParallel Session ICMIA Update 12 NovnagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- 300 GMAT CR Questions With Best SolutionsDokumen186 halaman300 GMAT CR Questions With Best SolutionsRakesh RajagopalBelum ada peringkat
- To Enable The Command Console You First Need To Do Some Tweaking in Your SettingsDokumen7 halamanTo Enable The Command Console You First Need To Do Some Tweaking in Your SettingsnagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Force Sensitive Resistor FSRDokumen25 halamanForce Sensitive Resistor FSRnagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Crystalline Solids Solid: Orthorhombic System, One of The Structural Categories Systems ToDokumen1 halamanCrystalline Solids Solid: Orthorhombic System, One of The Structural Categories Systems TonagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Guide For Author ROMANIAN JOURNALDokumen2 halamanGuide For Author ROMANIAN JOURNALnagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- WF312Dokumen4 halamanWF312t0p5ooBelum ada peringkat
- SEKRETARIATDokumen1 halamanSEKRETARIATnagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Crystalline Solids Solid: Orthorhombic System, One of The Structural Categories Systems ToDokumen1 halamanCrystalline Solids Solid: Orthorhombic System, One of The Structural Categories Systems TonagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Materials Research Bulletin: Activated Carbon Aerogel Containing Graphene As Electrode Material For SupercapacitorDokumen8 halamanMaterials Research Bulletin: Activated Carbon Aerogel Containing Graphene As Electrode Material For SupercapacitornagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Does Burning Garbage To Produce Electricity Make SenseDokumen4 halamanDoes Burning Garbage To Produce Electricity Make SensenagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- LaPlata2014 4 SpaceGroups StudentsDokumen63 halamanLaPlata2014 4 SpaceGroups StudentsnagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- How To Work CrystalMakerDokumen5 halamanHow To Work CrystalMakernagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Baco3 + Cuo + Nd2O3 + O2 Ndba2Cu3O7 + Co2 Penyetaraan Reaksi 8 Baco + 2 ND O + 12 Cuo + O 4 Ndba Cu O + 8 CoDokumen1 halamanBaco3 + Cuo + Nd2O3 + O2 Ndba2Cu3O7 + Co2 Penyetaraan Reaksi 8 Baco + 2 ND O + 12 Cuo + O 4 Ndba Cu O + 8 ConagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Force Sensitive Resistor FSRDokumen25 halamanForce Sensitive Resistor FSRnagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- EticketDokumen2 halamanEticketnagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Log Book Kuliah Kerja Nyata Universitas Negeri Makassar 2015Dokumen6 halamanLog Book Kuliah Kerja Nyata Universitas Negeri Makassar 2015nagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- AplikasiDOSDokumen63 halamanAplikasiDOSnagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Instrumental MotivatedDokumen1 halamanInstrumental MotivatednagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Syntheses of New Rare-Earth Rhodium Borocarbides: SciencedirectDokumen4 halamanSyntheses of New Rare-Earth Rhodium Borocarbides: SciencedirectnagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Baco3 + Cuo + Nd2O3 + O2 Ndba2Cu3O7 + Co2 Penyetaraan Reaksi Baco + ND O + Cuo + O Ndba Cu O + CoDokumen1 halamanBaco3 + Cuo + Nd2O3 + O2 Ndba2Cu3O7 + Co2 Penyetaraan Reaksi Baco + ND O + Cuo + O Ndba Cu O + ConagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Baco3 + Cuo + Nd2O3 + O2 Ndba2Cu3O7 + Co2 Penyetaraan Reaksi Baco + ND O + Cuo + O Ndba Cu O + CoDokumen1 halamanBaco3 + Cuo + Nd2O3 + O2 Ndba2Cu3O7 + Co2 Penyetaraan Reaksi Baco + ND O + Cuo + O Ndba Cu O + ConagatozzBelum ada peringkat
- Force Sensitive Resistor FSRDokumen25 halamanForce Sensitive Resistor FSRnagatozzBelum ada peringkat