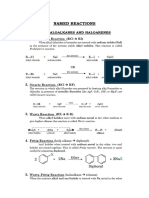
Organic Chemistry Reagents - NBS
Diunggah oleh
Pawan BabelDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Organic Chemistry Reagents - NBS
Diunggah oleh
Pawan BabelHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
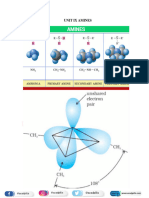
N-BROMOSUCCINIMDE
Organic Reagents
USES
Prof. Pawan Babel
TOPPERS CHOICE 0 98190 3592
Preparation of NBS
NBS is commercially available. It can also be synthesized in the laboratory. To do so, sodium
hydroxide and bromine are added to an ice-water solution of succinimide. The NBS
product precipitates and can be collected by filtration.[citation needed]
Crude NBS gives better yield in the Wohl-Ziegler reaction. In other cases, impure NBS (slightly
yellow in color) may give unreliable results. It can be purified by recrystallization from 9095 C
water (10 g of NBS for 100 mL of water).[1]
Reactions
Addition to alkenes
NBS will react with alkenes 1 in aqueous solvents to give bromohydrins 2. The preferred conditions
are the portionwise addition of NBS to a solution of the alkene in 50% aqueous DMSO, DME, THF,
or tert-butanol at 0 C.[2] Formation of a bromonium ion and immediate attack by water gives
strong Markovnikov addition and anti stereochemical selectivities.[3]
Side reactions include the formation of -bromoketones and dibromo compounds. These can be
minimized by the use of freshly recrystallized NBS.
With the addition of nucleophiles, instead of water, various bifunctional alkanes can be
synthesized.[4]
Allylic and benzylic bromination
Standard conditions for using NBS in allylic and/or benzylic bromination involves refluxing a
solution of NBS in anhydrous CCl4 with a radical initiatorusually azobisisobutyronitrile
(AIBN) or benzoyl peroxide, irradiation, or both to effect radical initiation.[5][6] The allylic and
benzylic radical intermediates formed during this reaction are more stable than other carbon
radicals and the major products are allylic and benzylic bromides. This is also called
the WohlZiegler reaction.[7][8]
The carbon tetrachloride must be maintained anhydrous throughout the reaction, as the
presence of water may likely hydrolyze the desired product.[9] Barium carbonate is often
added to maintain anhydrous and acid-free conditions.
In the above reaction, while a mixture of isomeric allylic bromide products are possible,
only one is created due to the greater stability of the 4-position radical over the methyl-
centered radical.
Bromination of carbonyl derivatives
NBS can -brominate carbonyl derivatives via either a radical pathway (as above) or via
acid-catalysis. For example, hexanoyl chloride 1 can be brominated in the alpha-position
by NBS using acid catalysis.[10]
The reaction of enolates, enol ethers, or enol acetates with NBS is the preferred
method of -bromination as it is high-yielding with few side-products. [11][12]
Bromination of aromatic derivatives]
Electron-rich aromatic compounds, such as phenols, anilines, and various
aromatic heterocycles,[13] can be brominated using NBS.[14][15] Using DMF as the
solvent gives high levels of para-selectivity.[16]
Hofmann rearrangement
NBS, in the presence of a strong base, such as DBU, reacts with primary amides to
produce a carbamate via the Hofmann rearrangement.[17]
Selective oxidation of alcohols]
It is uncommon, but possible for NBS to oxidize alcohols. E. J. Corey et
al. found that one can selectively oxidize secondary alcohols in the presence of
primary alcohols using NBS in aqueous dimethoxyethane (DME).[18]
Oxidative decarboxylation of -amino acids
NBS electrophilically brominates the amine, which is followed by
decarboxylation and release of an imine. Further hydrolysis will yield an
aldehyde and ammonia.[19][20] (cf. non-oxidative PLP dependent
decarboxylation)
Precautions
Although NBS is easier and safer to handle than bromine, precautions
should be taken to avoid inhalation. NBS should be stored in a
refrigerator. NBS will decompose over time giving off bromine. Pure
NBS is white, but it is often found to be off-white or brown colored by
bromine.
In general, reactions involving NBS are exothermic. Therefore, extra
precautions should be taken when used on a large scale.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Organic Chemistry 12 STD Question Bank (MLM) With AnswersDokumen41 halamanOrganic Chemistry 12 STD Question Bank (MLM) With AnswersAbhiBelum ada peringkat
- Aldehyde: Structure and Bonding Physical Properties and Characterization Applications and Occurrence SynthesisDokumen9 halamanAldehyde: Structure and Bonding Physical Properties and Characterization Applications and Occurrence SynthesisEiann Jasper LongcayanaBelum ada peringkat
- Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDokumen119 halamanAldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsKashvi KhandelwalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 12 Mechanism of Reaction: Aldol CondensationDokumen17 halamanChapter 12 Mechanism of Reaction: Aldol CondensationTiya KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Name ReactionsDokumen10 halamanName ReactionsParam SoniBelum ada peringkat
- Diazonium Compound 0 1Dokumen12 halamanDiazonium Compound 0 1Marwan FarhanBelum ada peringkat
- PCM Encyclopedia Organic ReactionsDokumen10 halamanPCM Encyclopedia Organic ReactionsAbhinav SaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- Bromo AnilineDokumen6 halamanBromo AnilinebridgetteBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Project 1Dokumen12 halamanChemistry Project 1ManavBelum ada peringkat
- AminesDokumen13 halamanAminesSohamBelum ada peringkat
- MSC II SEM 2023 - 24 Organic Reagents and Modern Synthetic ReactionsDokumen51 halamanMSC II SEM 2023 - 24 Organic Reagents and Modern Synthetic Reactionsharirajans71Belum ada peringkat
- Important Organic ReagentsDokumen6 halamanImportant Organic ReagentsSajjan RajaBelum ada peringkat
- Named RXNDokumen10 halamanNamed RXNssatechies62Belum ada peringkat
- Important Name Reactions of Chemistry in Class 12th CBSE and ISC BoardDokumen11 halamanImportant Name Reactions of Chemistry in Class 12th CBSE and ISC BoardGudia kumari100% (1)
- Carboxylic AcidDokumen6 halamanCarboxylic AcidVishu AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Notes Ammines and AcidsDokumen11 halaman12 Notes Ammines and AcidsXyzdevuBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Test Paper on AminesDokumen7 halamanCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Test Paper on AminesTamil SelviBelum ada peringkat
- All Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & Isc PDFDokumen11 halamanAll Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & Isc PDFprabs2006917881% (144)
- All Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & IscDokumen11 halamanAll Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & IscAjit100% (1)
- All Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & Isc PDFDokumen11 halamanAll Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & Isc PDFzakiya100% (2)
- AldehydeDokumen159 halamanAldehydeRohit Kumar BaghelBelum ada peringkat
- Poc Unit-5Dokumen9 halamanPoc Unit-5Bintoo SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- 06 Chapter 1Dokumen63 halaman06 Chapter 1Dintakurthi PrasanthBelum ada peringkat
- Haloarenes (Aryl Halides)Dokumen11 halamanHaloarenes (Aryl Halides)A BeheraBelum ada peringkat
- Carbonyl Condensation Aldol ReactionsDokumen41 halamanCarbonyl Condensation Aldol ReactionschidambaramrBelum ada peringkat
- Single Organic Test PDFDokumen15 halamanSingle Organic Test PDFgreatBelum ada peringkat
- Tempo Reagent MechanismDokumen27 halamanTempo Reagent MechanismMd Abdullah Al NomanBelum ada peringkat
- Synthesis of 1-Bromobutane via Alcohol HalogenationDokumen10 halamanSynthesis of 1-Bromobutane via Alcohol HalogenationAmy GardnerBelum ada peringkat
- 20.1 Electrophilic Substitution and Reduction Reactions PDFDokumen21 halaman20.1 Electrophilic Substitution and Reduction Reactions PDFJoshua VincentBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 Oxidation and Reduction Reactions of Functional GroupsDokumen27 halamanChapter 4 Oxidation and Reduction Reactions of Functional GroupsBiswa Bhusan NayakBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4 Organic Chemistry ReactionsDokumen6 halamanUnit 4 Organic Chemistry ReactionsRobbing_Hood100% (1)
- Aldol CondesationDokumen13 halamanAldol CondesationRonny AlexBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohols: Methods of PreparationDokumen15 halamanAlcohols: Methods of PreparationKarthik SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Methods and Reactions of Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary AlcoholsDokumen15 halamanMethods and Reactions of Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary AlcoholsKarthik SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Carbonyl Condensation ReactionsDokumen41 halamanCarbonyl Condensation ReactionsVladislav PapperBelum ada peringkat
- Neutralization Titrations for Determining Concentrations of Acids and BasesDokumen16 halamanNeutralization Titrations for Determining Concentrations of Acids and BasesaraneyaBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohols and Ethers Nomenclature and PropertiesDokumen27 halamanAlcohols and Ethers Nomenclature and Propertiesحسين اياد الشريفيBelum ada peringkat
- Exp. 23 - Side ReactionsDokumen4 halamanExp. 23 - Side Reactionsalin444444Belum ada peringkat
- STD XII Class Note Chapter 12 13 2021 22Dokumen16 halamanSTD XII Class Note Chapter 12 13 2021 22Saurabh ShekharBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 5: The Preparation of 1-Bromobutane From 1-ButanolDokumen6 halamanExperiment 5: The Preparation of 1-Bromobutane From 1-ButanolNoor Azizah ZakariaBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDokumen40 halamanUNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsVarsha SundareswaranBelum ada peringkat
- Organic Chemistry Name ReactionsDokumen7 halamanOrganic Chemistry Name ReactionspiyashnathBelum ada peringkat
- Reduction of Aldehydes, Ketones, To: (1) Clemmsens MethodDokumen9 halamanReduction of Aldehydes, Ketones, To: (1) Clemmsens MethodHawra JawadBelum ada peringkat
- NotesDokumen10 halamanNotespovikanimathiBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 4Dokumen42 halamanLesson 4Pablo Perez lopezBelum ada peringkat
- Named Reaction TestDokumen5 halamanNamed Reaction Testaleena'Belum ada peringkat
- MSC Chemistry Paper-III Unit-9Dokumen24 halamanMSC Chemistry Paper-III Unit-9SIMARAN JAISWAL 41 M3SBelum ada peringkat
- Named ReactionsDokumen5 halamanNamed ReactionsJoshuaBelum ada peringkat
- All Named Reactions of ChemistryDokumen11 halamanAll Named Reactions of ChemistryAbhay Narayan Mishra0% (1)
- Organic Reactions and MechanismDokumen51 halamanOrganic Reactions and MechanismAbhay Kumar Nayak75% (8)
- A New Synthesis of Lysergic AcidDokumen11 halamanA New Synthesis of Lysergic AcidMiguel Lora EstradaBelum ada peringkat
- The Reactions of Adipic AcidDokumen3 halamanThe Reactions of Adipic AcidmeimeiliuBelum ada peringkat
- Formulation of Ketones, Reaction With Organocopper Compounds. Discussed in Sec 18.6Dokumen3 halamanFormulation of Ketones, Reaction With Organocopper Compounds. Discussed in Sec 18.6Rizka Hannum LubisBelum ada peringkat
- Section A: 1. Testing For Functional GroupsDokumen16 halamanSection A: 1. Testing For Functional GroupsGrace JosephBelum ada peringkat
- Organic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationDokumen9 halamanOrganic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationAtif AteeqBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisDari EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Silicon in Organic Synthesis: Butterworths Monographs in Chemistry and Chemical EngineeringDari EverandSilicon in Organic Synthesis: Butterworths Monographs in Chemistry and Chemical EngineeringBelum ada peringkat
- Org Food1Dokumen2 halamanOrg Food1Pawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- The Nacirema Dream, You Can't Stop Destiny (2012-2015) : Television Career, Underrated (2015-Present)Dokumen2 halamanThe Nacirema Dream, You Can't Stop Destiny (2012-2015) : Television Career, Underrated (2015-Present)Pawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Projectile On Tiger: Project Tiger Is ADokumen2 halamanProjectile On Tiger: Project Tiger Is APawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- IIT 2020 JEE MAIN Test Series aITS FLT 1Dokumen6 halamanIIT 2020 JEE MAIN Test Series aITS FLT 1Pawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- 19dec 2019 Udz BdtsDokumen3 halaman19dec 2019 Udz BdtsPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- I Like Corona CORONA - ProjectDokumen1 halamanI Like Corona CORONA - ProjectPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Delhibys ProjectDokumen1 halamanDelhibys ProjectPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Students Brochure Front 2017-IaptDokumen1 halamanStudents Brochure Front 2017-IaptPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Shree Dharmachakra Parshvnath Prabhav J..Dokumen2 halamanShree Dharmachakra Parshvnath Prabhav J..Pawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Namokar Tirth, Malsane To Mangi TungiDokumen2 halamanNamokar Tirth, Malsane To Mangi TungiPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Toppers Chocie How-To-Improve-Your-MemoryDokumen12 halamanToppers Chocie How-To-Improve-Your-MemoryPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- IIT 2021 JEE MAIN Test Series Sample PAperDokumen6 halamanIIT 2021 JEE MAIN Test Series Sample PAperPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Inmo Sol 2000Dokumen5 halamanInmo Sol 2000ashu_dwy8605Belum ada peringkat
- JEE Main 2018 Online Mode 15-04-2018 Evening Shift PDFDokumen12 halamanJEE Main 2018 Online Mode 15-04-2018 Evening Shift PDFSiddharth SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Nucleophilic Substitution Questions - PKBDokumen12 halamanNucleophilic Substitution Questions - PKBPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Iap Who Wtforht 0 5 GirlsDokumen1 halamanIap Who Wtforht 0 5 GirlsPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Skill GenieDokumen46 halamanSkill GenieAnjana MaudgalyaBelum ada peringkat
- Jee Main Code BDokumen24 halamanJee Main Code BanuragBelum ada peringkat
- Students Brochure Front 2017-IaptDokumen1 halamanStudents Brochure Front 2017-IaptPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Thermo Chem Dynamics PawanDokumen4 halamanThermo Chem Dynamics PawanPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry P1&2 Mock Test 1 Sol PKBDokumen8 halamanChemistry P1&2 Mock Test 1 Sol PKBPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- JAN 2020 - Morning - Jeemains - PapernkeyDokumen36 halamanJAN 2020 - Morning - Jeemains - PapernkeyPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- QuestDokumen4 halamanQuestPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Affecting Solubility and Rate of Solution NotesDokumen3 halamanFactors Affecting Solubility and Rate of Solution NotesPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Skill GenieDokumen46 halamanSkill GenieAnjana MaudgalyaBelum ada peringkat
- Test 2 Organic Chemistry AnswersDokumen6 halamanTest 2 Organic Chemistry AnswersPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Periodictable Page 1Dokumen1 halamanPeriodictable Page 1Pawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Code: 7: Test Id: 623Dokumen30 halamanCode: 7: Test Id: 623Pawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Buffers and Titrations Student PDFDokumen20 halamanBuffers and Titrations Student PDFPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Field of a Hollow Conducting CylinderDokumen33 halamanMagnetic Field of a Hollow Conducting CylinderPawan BabelBelum ada peringkat
- A Brief History of Indian Alchemy Covering Transi-Tional and Tantric Periods (Circa 800 A.D. - 1300 A. D)Dokumen27 halamanA Brief History of Indian Alchemy Covering Transi-Tional and Tantric Periods (Circa 800 A.D. - 1300 A. D)neelakantasiddaBelum ada peringkat
- Properties of Ionic Compounds and Covalent CompoundsDokumen6 halamanProperties of Ionic Compounds and Covalent Compoundsnoraini nasikinBelum ada peringkat
- Water Treatment Plant1Dokumen15 halamanWater Treatment Plant1Mhssp Co 5 IBelum ada peringkat
- Deicing Salt - Recognizing The Corrosion ThreatDokumen11 halamanDeicing Salt - Recognizing The Corrosion ThreatMilanBelum ada peringkat
- Ethylene Polymers LLDPE PDFDokumen42 halamanEthylene Polymers LLDPE PDFDadadaBelum ada peringkat
- Cold Sintered Ceramic Nanocomposites of 2D MXene and Zinc OxideDokumen6 halamanCold Sintered Ceramic Nanocomposites of 2D MXene and Zinc OxideYuxiang GanBelum ada peringkat
- Baranowski2002 - XRF Soil ChemicalDokumen10 halamanBaranowski2002 - XRF Soil ChemicalElisangela SordiBelum ada peringkat
- Dyeing Lab Department Calculation and Others - TEXTILE TECHNOLOGY ( ) PDFDokumen10 halamanDyeing Lab Department Calculation and Others - TEXTILE TECHNOLOGY ( ) PDFshakilsai100% (1)
- The Performance of Stainless Steels in Concentrated Sulphuric AcidDokumen4 halamanThe Performance of Stainless Steels in Concentrated Sulphuric AcidAlvaro JaraBelum ada peringkat
- CarbofilDokumen3 halamanCarbofilBranko FerenčakBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Lab - 15 - Solubility Curve For KNO3Dokumen4 halamanChemistry Lab - 15 - Solubility Curve For KNO3Nader AwadBelum ada peringkat
- DIN 51825 German Grease Classification System PDFDokumen1 halamanDIN 51825 German Grease Classification System PDFsoumya ghoshBelum ada peringkat
- Polymer Chemistry: Structure and Properties of PolyethyleneDokumen19 halamanPolymer Chemistry: Structure and Properties of PolyethyleneSumedha ThakurBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan Acid N BaseDokumen3 halamanLesson Plan Acid N BasedediyanBelum ada peringkat
- Light and electron configurationDokumen23 halamanLight and electron configurationHayley AndersonBelum ada peringkat
- Shieldmaster Brochure by Manuli HydraulicsDokumen12 halamanShieldmaster Brochure by Manuli HydraulicsPawan ChaturvediBelum ada peringkat
- 18-Noyori Asymmetric Hydrogenation ReactionDokumen11 halaman18-Noyori Asymmetric Hydrogenation ReactionImdadur RahamanBelum ada peringkat
- Frank D Gunstone - Lipid Technologi PDFDokumen849 halamanFrank D Gunstone - Lipid Technologi PDFFachri Bachtiar100% (1)
- ACGDokumen10 halamanACGrishichauhan25Belum ada peringkat
- ASTM E353-93 Standard Test Methods For Chemical Analysis ofDokumen33 halamanASTM E353-93 Standard Test Methods For Chemical Analysis ofAvishek guptaBelum ada peringkat
- Pricelist CAT, 010921, Naik Harga, GreenDokumen8 halamanPricelist CAT, 010921, Naik Harga, GreenIham ELbusyra satu'GeBelum ada peringkat
- Cidox Chlorine Dioxide Disinfection Tablets BrochureDokumen6 halamanCidox Chlorine Dioxide Disinfection Tablets BrochureOso Casa50% (2)
- Modern Steelmaking TechnologyDokumen8 halamanModern Steelmaking Technologylakon 22Belum ada peringkat
- Ferrous Alloys: Author: KattusDokumen19 halamanFerrous Alloys: Author: KattussunsirBelum ada peringkat
- BIODEDokumen17 halamanBIODEBayikati PavaniBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 4 (Recrystallization) PDFDokumen7 halamanExperiment 4 (Recrystallization) PDFanon_733744716Belum ada peringkat
- Un NoDokumen64 halamanUn Noapi-127528443Belum ada peringkat
- Ajaykumar Tiwari: Engineers TeamDokumen2 halamanAjaykumar Tiwari: Engineers TeamAjay TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Phytochemical and Antioxidant Activity of Avocado Leaf Extract (Persea Americana Mill.)Dokumen1 halamanPhytochemical and Antioxidant Activity of Avocado Leaf Extract (Persea Americana Mill.)Jeff AlbaBelum ada peringkat
- Mass Balance Examples4Dokumen8 halamanMass Balance Examples4Darel Williams100% (2)