And of The Inverting Amplifier: in Out
Diunggah oleh
Shakku BhaiJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
And of The Inverting Amplifier: in Out
Diunggah oleh
Shakku BhaiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
7/27/2017 361660151.
doc 1/12
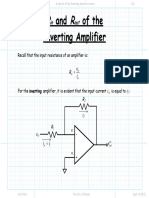
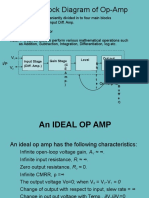
Rin and Rout of the
Inverting Amplifier
Recall that the input resistance of an amplifier is:
vin
Rin =
iin
For the inverting amplifier, it is evident that the input current iin is equal to i1 :
R2
i2
R1
v-
vin -
iin = i1 vout
oc
v+
+
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
7/27/2017 361660151.doc 2/12
Its input resistance
From Ohms Law, we know that this current is:
vin - v1
iin = i1 =
R1
The non-inverting terminal is
connected to virtual ground:
R2
v- = 0
i2
and thus the input current is:
R1
v-
vin vin -
iin = i1 =
R1 iin = i1 vout
oc
v+
We now can determine the input +
resistance:
vin R1
Rin = = vin = R1
iin vin
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
7/27/2017 361660151.doc 3/12
The input resistance of this inverting amplifier is therefore Rin = R1 !
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
7/27/2017 361660151.doc 4/12
Output resistance is harder
Now, lets attempt to determine the output resistance Rout.
Recall that we need to determine two values: the short-circuit output current
( )
iout
sc
and the open-circuit output voltage vout .
oc
( )
To accomplish this, we must replace the op-amp in the circuit with its linear
circuit model:
R2
i2
R1
vin - v-
Rout
op
vout = 0
ii = i1
+ v + i op
out iout
sc
+ -
Aop (v + - v - )
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
7/27/2017 361660151.doc 5/12
First, the short circuit output current
R2
From KCL, we find that:
i2
iout
sc
= i2 + iout
op
R1
vin - v-
where: Rout
op
vout = 0
ii = i1
-Aop v - - vout
oc
-Aop v - + v + i op
out iout
sc
iout
op
= =
Roop Roop + -
Aop (v + - v - )
and:
v - - vout
oc
v
i2 = = -
R2 R2
Therefore, the short-circuit output current is:
v - Aop v - Rout - R2 Aop Aop
op
isc
out = - op = v - @ - op v -
R2 Rout R2 Rout
op
Rout
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
7/27/2017 361660151.doc 6/12
Now, the open circuit output voltage
The open-circuit output voltage can R2
likewise be determined in terms of Aop
and v- .
i2
R1
vin - v-
iout =0
Rout
op
ii = i1
+
+ v + iout
op
+ -
Aop (v + - v - ) -
Here, it is evident that since iout = 0:
i2 = -iout
op
where we find from Ohms Law:
v - - ( - Aopv - ) 1 + Aop
i2 = = v-
R2 + Rout
op
R2 + Rout
op
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
7/27/2017 361660151.doc 7/12
The open-circuit output voltage
R2
Now from KVL:
i2
vout
oc
= v - - R2 i2
R1
vin - v-
iout =0
Rout
op
ii = i1
+
Inserting the expression for i2 : + v + i op
out
+ -
Aop (v + - v - )
1 + Aop -
v oc
out = v - - R2 v
op -
R2 + Rout
R + R op R2 1 + Aop
= 2 out
-
( )
v
R2 + Routop
R2 + Rout
op -
Roop - R2 Aop
= v -
R2 + Rout op
R2 Aop
@- v-
R2 + Rout
op
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
7/27/2017 361660151.doc 8/12
Now we find the output resistance
Now, we can find the output resistance of this amplifier:
vout
oc
Rout = sc
iout
-1
-R2 Aop - Aop
= op op
R
2 + R o Ro
R2 Roop
=
R2 + Roop
= R2 Roop
In other words, the inverting amplifier output resistance is simply equal to the
value of the feedback resistor R2 in parallel with op-amp output resistance Rout .
op
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
7/27/2017 361660151.doc 9/12
This is zero if the op-amp is ideal
Ideally, of course, the op-amp output resistance is zero, so that the output
resistance of the inverting amplifier is likewise zero:
Rout = R2 Rout
op
= R2 0
=0
Note for this casewhere the output resistance is zerothe output voltage will
be the same, regardless of what load is attached at the output (e.g., regardless
of iout )! R 2
i2
R1
vin - v- iout 0
ii = i1
+ v + i op
out
+
+ -
Aop (v + - v - )
-
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
7/27/2017 361660151.doc 10/12
For real op-amps the
output resistance is small
Thus, if Rout = 0 , then the output voltage is equal to the open-circuit output
voltageeven when the output is not open circuited:
R2
vout = - v for all iout !!
R1 in
Recall that it is this property that made Rout = 0 an ideal amplifier
characteristic.
We will find that real (i.e., non-ideal!) op-amps typically have an output
resistance that is very small ( Rout = R2 ), so that the inverting amplifier output
op
resistance is approximately equal to the op-amp output resistance:
Rout = R2 Rout
op
Rout
op
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
7/27/2017 361660151.doc 11/12
A summary
Summarizing, we have found that for the inverting amplifier:
Rin = R1
Rout Rout
op
(ideally zero)
Thus, this inverting amplifier
R2
iin ( t )
R1
- iout ( t )
+
vin ( t ) +
- + vout ( t )
-
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
7/27/2017 361660151.doc 12/12
The inverting amp equivalent circuit
has the equivalent circuit:
iin (t ) iout (t )
+
+
R op
vin ( t )
+ out
vout ( t )
()
-
vin (t )
- R2 -
- R1
Note the input resistance and open-circuit voltage gain of the inverting
amplifier is VERY different from that of the op-amp itself!
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Multiple Linear Regression CaseDokumen7 halamanMultiple Linear Regression Casekanika07electro0% (1)
- And of The Inverting Amplifier: in OutDokumen11 halamanAnd of The Inverting Amplifier: in OutMinh NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- The Virtual Short Lecture PDFDokumen6 halamanThe Virtual Short Lecture PDFAvP AnirudhBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of The Inverting Amplifier LectureDokumen12 halamanAnalysis of The Inverting Amplifier LectureRohit PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Microelectronic Circuits I: CH 2: Operational AmplifiersDokumen15 halamanMicroelectronic Circuits I: CH 2: Operational AmplifierssimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- 073BEE Lab Sheet 4Dokumen3 halaman073BEE Lab Sheet 4Sagar UpretiBelum ada peringkat
- ESC201 UDas Lec24Corrected OpAmp Aps PDFDokumen6 halamanESC201 UDas Lec24Corrected OpAmp Aps PDFPk KumarBelum ada peringkat
- EEL 7300 - Chapter I - Operational Amplifiers 2022.2 - VisualsDokumen77 halamanEEL 7300 - Chapter I - Operational Amplifiers 2022.2 - VisualsVanderson Xavier vandilolBelum ada peringkat
- 6.2 Introduction To Op Amps: ObjectiveDokumen72 halaman6.2 Introduction To Op Amps: ObjectiveJasleen KaurBelum ada peringkat
- Operational Amplifier II & III: Measurements and Dynamics LabDokumen11 halamanOperational Amplifier II & III: Measurements and Dynamics LabHasan ToubasiBelum ada peringkat
- Today: Analog Blocks: Op Amps Conversion Noise Digital To Analog Analog To Digital Interfacing To FPGA'sDokumen25 halamanToday: Analog Blocks: Op Amps Conversion Noise Digital To Analog Analog To Digital Interfacing To FPGA'sJL CruzBelum ada peringkat
- OpAmp CircuitsDokumen25 halamanOpAmp Circuitsrachit guptaBelum ada peringkat
- 13 Operational AmplifiersDokumen51 halaman13 Operational Amplifiers陳浚維Belum ada peringkat
- Op Amp Circuits With Finite-Gain: General SetupDokumen4 halamanOp Amp Circuits With Finite-Gain: General SetupHelloBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Op Amps AC Lecture1 Apn1Dokumen51 halamanPractical Op Amps AC Lecture1 Apn1gpay121045Belum ada peringkat
- Analog Electronics Class 2: Ideal Op-Amp AnalysisDokumen56 halamanAnalog Electronics Class 2: Ideal Op-Amp AnalysisfayazBelum ada peringkat
- Lab20 Opamps1 PDFDokumen3 halamanLab20 Opamps1 PDFgeorgeBelum ada peringkat
- OP Amp 1Dokumen14 halamanOP Amp 1Hesham EbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) : (Chapter 5)Dokumen21 halamanOperational Amplifier (Op-Amp) : (Chapter 5)syam24gmtBelum ada peringkat
- Diodes: 1 Junction Diode (P-N Junction)Dokumen13 halamanDiodes: 1 Junction Diode (P-N Junction)tiling_biling123Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 Op AmpDokumen14 halamanChapter 6 Op AmpAbdul RehmanBelum ada peringkat
- Course Coordinator:: Dr. Shilpa ShrigiriDokumen31 halamanCourse Coordinator:: Dr. Shilpa ShrigiriPaul Tan RegalaBelum ada peringkat
- Energy and PowerDokumen21 halamanEnergy and PowerJuan Camilo Guarnizo BermudezBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Block Diagram of Op-Amp: Input Stage (Diff. Amp.) Gain Stage (C E Amp.) Level Shifter Out Put Stage (Buffer)Dokumen26 halamanBasic Block Diagram of Op-Amp: Input Stage (Diff. Amp.) Gain Stage (C E Amp.) Level Shifter Out Put Stage (Buffer)Pierana PolitaniBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps)Dokumen16 halamanNotes On Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps)Venu Gopal Rao AggressBelum ada peringkat
- Ideal Op Amp ModelDokumen9 halamanIdeal Op Amp ModelAtif BhandaraBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 06Dokumen5 halamanLec 06Rajesh LkBelum ada peringkat
- Two PortsDokumen22 halamanTwo Portsvizay237_430788222Belum ada peringkat
- Operational Amplifier PDFDokumen45 halamanOperational Amplifier PDFAnonymous H6zpNuBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 9Dokumen6 halamanExperiment 9Abdullah ZubairBelum ada peringkat
- Op Amp Topologies As Excerpted From Op Amp Applications: BryantDokumen8 halamanOp Amp Topologies As Excerpted From Op Amp Applications: BryanttihomihoBelum ada peringkat
- Negative Output Cascade Boost Converters: N N N N N N N N N N N NDokumen39 halamanNegative Output Cascade Boost Converters: N N N N N N N N N N N NG JBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1 Basic ConceptsDokumen70 halamanModule 1 Basic ConceptsTanuja VBelum ada peringkat
- Source-TransformationDokumen16 halamanSource-Transformationraovinayakm2Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture28 Operational AmplifierDokumen17 halamanLecture28 Operational Amplifierwwengfei@yahoo.com100% (3)
- 741 Op AmpDokumen31 halaman741 Op AmpAhmed Mahmoud Ahmed100% (1)
- OpampsDokumen32 halamanOpampsghsalma950Belum ada peringkat
- FALLSEM2019-20 EEE3002 ETH VL2019201001056 Reference Material I 12-Jul-2019 UNIT-2-op-amp ApplicationsDokumen66 halamanFALLSEM2019-20 EEE3002 ETH VL2019201001056 Reference Material I 12-Jul-2019 UNIT-2-op-amp ApplicationsKumar RishabhBelum ada peringkat
- Op Amp Circuits: V V V VDokumen7 halamanOp Amp Circuits: V V V VrishabhBelum ada peringkat
- Opertional Amplifiers ReviewDokumen11 halamanOpertional Amplifiers ReviewEmre ÖzerBelum ada peringkat
- ESC201T L29 Opamp Circuits 1Dokumen51 halamanESC201T L29 Opamp Circuits 1Rachit MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Unit - 1 Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps) and Its ApplicationsDokumen11 halamanUnit - 1 Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps) and Its ApplicationsVishalini PBelum ada peringkat
- AIC Basic CircuitsDokumen9 halamanAIC Basic CircuitsSAKSHI CHIKSHEBelum ada peringkat
- Operational Amplifier: Masramdhani SaputraDokumen16 halamanOperational Amplifier: Masramdhani SaputradanialBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Transistor - 1 - Resistor To Transistor ApproachDokumen59 halamanBasics of Transistor - 1 - Resistor To Transistor ApproachJoy johnsonBelum ada peringkat
- Power Topologies Quick Reference Guide PDFDokumen9 halamanPower Topologies Quick Reference Guide PDFbiosbgBelum ada peringkat
- Op Amp 2Dokumen26 halamanOp Amp 2krishBelum ada peringkat
- Note 5Dokumen9 halamanNote 5NOUARI mohamedBelum ada peringkat
- EC102 Assignment - 20095139 PDFDokumen4 halamanEC102 Assignment - 20095139 PDFMr. Nachiketa 4 Year B.Tech Chemical EngineeringBelum ada peringkat
- Op AmpDokumen57 halamanOp AmpDivyanshu Yadav100% (1)
- Electronic Instrumentation: Experiment 4Dokumen63 halamanElectronic Instrumentation: Experiment 4helenarajBelum ada peringkat
- Ri and Ro of The Inverting Amplifier LectureDokumen11 halamanRi and Ro of The Inverting Amplifier LectureVishnu Vardhan ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- 22 Op Amps1Dokumen34 halaman22 Op Amps1Mani VrsBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Power Electronics DC DC Converters: DR Taosif IqbalDokumen71 halamanAdvanced Power Electronics DC DC Converters: DR Taosif IqbalTaosif IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Chp3-Microwave Network Analysiswithexamples - Part2Dokumen30 halamanChp3-Microwave Network Analysiswithexamples - Part2Kavita KamerikarBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report Experiment 4Dokumen13 halamanLab Report Experiment 4Jake DysonBelum ada peringkat
- Home-Constructed, Building Block Op-Amp Circuits For Analog Computers Inverting IntegratorDokumen5 halamanHome-Constructed, Building Block Op-Amp Circuits For Analog Computers Inverting IntegratorMsuttonBelum ada peringkat
- Current Mirrors: Ars DiavoloDokumen50 halamanCurrent Mirrors: Ars Diavolopam_trBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2Dokumen34 halamanChapter 2Kavineel KumarBelum ada peringkat
- First Year Scheme & Syllabus 2014-15 (31.07.2014)Dokumen39 halamanFirst Year Scheme & Syllabus 2014-15 (31.07.2014)Shakku BhaiBelum ada peringkat
- ProgramDetails PDF 52Dokumen1 halamanProgramDetails PDF 52Shakku BhaiBelum ada peringkat
- Magic of KaliDokumen0 halamanMagic of KaliBala MBelum ada peringkat
- Lechlanche CellDokumen2 halamanLechlanche CellShakku BhaiBelum ada peringkat
- Generating Ideas and Their RelationshipDokumen17 halamanGenerating Ideas and Their RelationshipChenie Nhorine Fajanilan100% (1)
- UMTS CS Call Drop Analysis Guide ZteDokumen30 halamanUMTS CS Call Drop Analysis Guide Zteatungorai4234100% (11)
- DBM CSC FormDokumen4 halamanDBM CSC FormJing Goal Merit0% (1)
- Iiyama 19LJ2 Service ManualDokumen41 halamanIiyama 19LJ2 Service ManualRoger Martínez BermúdezBelum ada peringkat
- Meteor F8 FR9 ManualDokumen29 halamanMeteor F8 FR9 ManualAceBelum ada peringkat
- Informacion TransferenciaDokumen4 halamanInformacion TransferenciaHector Lizardo AndinoBelum ada peringkat
- GT-POWER Engine Simulation Software: HighlightsDokumen2 halamanGT-POWER Engine Simulation Software: HighlightsIrfan ShaikhBelum ada peringkat
- 1000 VA UPS: For Marine Dynamic Positioning and Vessel Control Systems Model ALS 210Dokumen16 halaman1000 VA UPS: For Marine Dynamic Positioning and Vessel Control Systems Model ALS 210Rodrigo100% (3)
- Accurate and Cost-Effective Mini CNC Plotter: Sara Raad Qasim Haider Mohammad Mustafa FalahDokumen6 halamanAccurate and Cost-Effective Mini CNC Plotter: Sara Raad Qasim Haider Mohammad Mustafa FalahRamleelakal OfficialBelum ada peringkat
- Megger FRAX 101 Sweep Frequency Response Analyser User Manual PDFDokumen97 halamanMegger FRAX 101 Sweep Frequency Response Analyser User Manual PDFMujahid Ahmed FadelBelum ada peringkat
- Piper PA-46-350P Malibu Mirage N186CB 11-16Dokumen30 halamanPiper PA-46-350P Malibu Mirage N186CB 11-16Antonio Cesar de Sa LeitaoBelum ada peringkat
- RRU-Remote Radio Unit: Function, Concept, Details: 1.: Definition and OverviewDokumen4 halamanRRU-Remote Radio Unit: Function, Concept, Details: 1.: Definition and OverviewJosé Angel Santiesteban RicardoBelum ada peringkat
- Crown StandardTCP IPPortDokumen5 halamanCrown StandardTCP IPPortDavid Alejandro Quijada GilBelum ada peringkat
- Dell s2421hn Monitor Users GuideDokumen56 halamanDell s2421hn Monitor Users GuideKatarina SimovicBelum ada peringkat
- Update LogsDokumen170 halamanUpdate Logsconeinha123Belum ada peringkat
- Particle Flow OrbazDokumen159 halamanParticle Flow OrbazAna QuintanaBelum ada peringkat
- REAA - CPPREP4004 - Personal Profile Template v1.1Dokumen4 halamanREAA - CPPREP4004 - Personal Profile Template v1.1Michael ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Hum102 Report of ProjectDokumen19 halamanHum102 Report of ProjectSamiullah MalhiBelum ada peringkat
- MBA Project Report of ICFAI Distance Learning ProgramsDokumen4 halamanMBA Project Report of ICFAI Distance Learning ProgramsPrakashB144Belum ada peringkat
- Simulaids 2011 CatalogDokumen68 halamanSimulaids 2011 CatalogAlfred De Jesús ToledoBelum ada peringkat
- CECS Class Schedule and Google Classroom Codes For The 1st Semester, AY2020-2021Dokumen13 halamanCECS Class Schedule and Google Classroom Codes For The 1st Semester, AY2020-2021Balot PenoyBelum ada peringkat
- Chi Square DistributionDokumen4 halamanChi Square DistributionIziBelum ada peringkat
- Folleto. GA1-240202501-AA1-EV03.Dokumen1 halamanFolleto. GA1-240202501-AA1-EV03.alfonso vanderley velascoBelum ada peringkat
- Poweredge r910 Technical GuideDokumen78 halamanPoweredge r910 Technical GuidePhani KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Python Interview Questions PDFDokumen6 halamanPython Interview Questions PDFAsh McGowenBelum ada peringkat
- TestNG NotesDokumen23 halamanTestNG Notesvishal sonwaneBelum ada peringkat
- 1945 To Spy Chase TutorialDokumen21 halaman1945 To Spy Chase TutorialMagda GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Network Virtualization Dummies GuideDokumen81 halamanNetwork Virtualization Dummies GuideUmme KulsumBelum ada peringkat
- BDC OldDokumen5 halamanBDC OldDora BabuBelum ada peringkat