Prosci 2014 Best Practices Executive Overview
Diunggah oleh
mankeke19Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Prosci 2014 Best Practices Executive Overview
Diunggah oleh
mankeke19Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Best Practices in Change Executive
Overview
Management 2014 Edition
A look at Proscis latest
change management
research
In Brief: Since 1998, Prosci has conducted eight benchmarking studies to discover what works and
what doesnt when it comes to managing the people side of change. The findings from Proscis latest
2013 study have been compiled with the findings from the previous studies. The compendium
report, Best Practices in Change Management 2014 Edition, presents this data. With insights from
3400 change leaders, the report is the largest body of knowledge on change management on the
market today. This Executive Overview is a 10-page snapshot of the 250-page report.
Executive Overview
Table of Contents
Participant profile
New sections in the report
Study highlights
Further free information
2014 Prosci Inc. All rights reserved. | www.prosci.com
Prosci Best Practices in Change Management
Participant profile throughout the last five benchmarking studies.
As in the 2011 study, the top three job roles of
Eight hundred and twenty-two participants from participants were:
63 countries took part in Proscis 2013 Best Change management team leader
Practices in Change Management benchmarking External consultant
study. This report combines the findings and Project team leader
data from the 2013 study with Proscis previous
seven studies to form one of the largest bodies of
knowledge related to managing the people side of Change management team leader
change based on insights and experiences of more External consultant
than 3400 participants. Project team leader
2013 study 822 participants Change management team member
2011 study 650 participants Internal change management support staff
2009 study 575 participants Project team member
2007 study 426 participants 2013
2005 study 411 participants Human Resources
2011
2009
2003 study 288 participants Project sponsor 2007
2000 study 152 participants Other
2005
1998 study 102 participants
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50%
Percent of respondents
Figure 1 shows the geographic distribution of
participants in the 2013 study. Proportionately, Figure 2 Role of participants
participation dropped from the United States,
Africa, Latin America and Asia and Pacific
Islands. Participation increased from Australia Study objective
and New Zealand, Canada, Europe and the
Middle East. The objective of this study is to uncover lessons
learned from practitioners and consultants so
Latin America, 2% current change management teams can benefit
Asia and Pacific
Islands, 3%
Middle East, 2%
from these experiences. Emphasis is placed on
Africa, 5% what is working and what is not working in all
areas of change management. The 2014 report
also presents emerging trends in change
Europe, 14%
United States, management to identify the changes that have
34%
occurred and the future direction of the
discipline.
Because change management is a holistic system
Canada, 15%
that requires involvement by change
management practitioners, project teams,
Australia and New
executives, managers, supervisors and front-line
Zealand, 25%
employees, this report details the engagement
and role of each of these groups in change
Figure 1 Geographic distribution of
management.
participants
Study participants represented a variety of roles
in relation to the change on which they reported.
Figure 2 shows the role of study participants
2014 Prosci Inc. All rights reserved. | www.prosci.com
Prosci Best Practices in Change Management
New sections in the report Factors for estimating change
management resource needs
New questions were added to the 2013 study to Use and sufficiency of change
expand the scope and depth of the research. management budgets
These new areas of focus include:
Factors for estimating change
Expected trends in the discipline of management budgets
change management in the coming five
years Components that make up change
management budgets
How the change management
methodology was used Change management budget profiles
Effectiveness of particular types of Prevalence of integrating change
methodologies management and project management
Rationale, steps and sources for Impacts of integrating change
internally developed methodologies management and project management
Sources and rationale for Steps for integrating change
combination/hybrid methodologies management and project management
Guidance for scaling and customizing a Reasons for integrating change
methodology for a specific change management and project management
and reasons for keeping them separate
Accommodating for organizational
culture in the change management Dimensions of change management and
approach project management integration
Action steps if change management is Tools most commonly integrated
brought on late to a project Steps for integrating change
Most important skills for a great change management and project management
management practitioner processes
Prevalence of permanent positions or job Integration across the project lifecycle
roles for change management Impact of project management maturity
Duration of permanent positions or job on change management and integration
roles Evaluating overall change readiness
Organizational locations of permanent
Evaluating group and individual
positions or job roles
readiness
Number of projects supported by change
Measuring the overall outcome of
management positions
applying change management
Annual salary of change management job
Demonstrating the value-add of applying
roles change management
Career paths in change management
Measuring and reporting on change
Change management team structures, management effectiveness
effectiveness and rationale Measuring individual transitions
Use of change agent networks
Use and sufficiency of dedicated change
management resources
2014 Prosci Inc. All rights reserved. | www.prosci.com
Prosci Best Practices in Change Management
Study highlights What to do differently on the next project
By a two-to-one margin, the top suggestion by
Greatest contributors to success participants for what they would do differently on
For the eighth consecutive study, active and their next project was to more effectively engage
visible executive sponsorship was identified as sponsors by involving them early and ensuring
the greatest contributor to success. Six of the they are active and visible throughout the
seven contributors were consistent with previous project. The next most common responses were to
studies, with a slight change in ranking. secure sufficient resources for change
Engagement and integration with project management and emphasize the preparation and
management is a new addition to the list of the planning activities.
greatest contributors to success.
1. Active and visible executive sponsorship Top trends in change management within
organizations
2. Structured change management approach
For the fourth consecutive study, the top trend
3. Dedicated change management resources identified by participants was a greater
and funding awareness of the need for and value of change
4. Frequent and open communication about management. Additional trends included the
the change and the need for change broader application of change management,
increased leadership support for change
5. Employee engagement and participation management and the establishment of dedicated
6. Engagement and integration with project functional groups or a Change Management
management Office (CMO).
7. Engagement with and support from Top trends in the discipline of change
middle management management
Greatest obstacles to success For the first time, participants in the 2013 study
identified the trends they expected in the
The top five obstacles to success identified in the discipline of change management for the coming
2013 benchmarking study are similar to findings five years. The top trend identified was the
from the 2011 study; however, poor continued maturation of the practice of change
communication was not identified as a top management, including continued formalization
obstacle. A new obstacle, division between project and evolution of the discipline and its
management and change management, was methodologies and tools. Participants also
identified. expected a greater focus on building internal
1. Ineffective change management capabilities and organizational core competencies
sponsorship in change management in the future.
2. Resistance to change from employees Change management effectiveness
3. Insufficient change management Projects with effective change management
resourcing programs were more likely to meet objectives,
4. Division between project management stay on schedule and stay on budget than those
and change management with ineffective change management. This direct
correlation mirrors the findings from the 2007,
5. Middle management resistance 2009 and 2011 studies. Projects with excellent
change management programs were six times
more likely to meet or exceed their objectives
than those with poor change management
programs.
2014 Prosci Inc. All rights reserved. | www.prosci.com
Prosci Best Practices in Change Management
100% common uses of the methodology were to provide
Percent of respondents that met
general guidance and as an activities checklist.
or exceeded project objectives
90% 96%
80%
70% 77%
Scaling and customizing the methodology
60%
50% Participants highlighted inputs used to
40% 46%
effectively scale their methodology to the
30%
particular change, including project
20%
characteristics, change management
10% 16%
assessments, organizational attributes and
0%
Poor Fair Good Excellent resource availability. When the methodology was
(n=244) (n=653) (n=834) (n=165)
scaled, participants noted a greater focus on
Overall effectiveness of change management program change management activities and on impacted
audiences.
Figure 3 Correlation of change management
effectiveness to meeting or exceeding objectives
Accommodating for organizational culture
Practitioner advice Organizational culture was accounted for by
tailoring change management activities, adapting
Experienced practitioners shared advice on how communications and seeking input and
to apply change management. Practitioners engagement from various impacted groups.
identified the three most important activities at Sponsors in various parts of the organization, as
the beginning of an engagement, with effective well as networks of key influencers, were also
communications being the top recommendation. important in accommodating for organizational
Participants identified four challenges or hurdles, culture.
the top one being ineffective sponsorship.
Communication, timing, integration with project
Change management job roles
management, building buy-in for change
management and sponsorship were the five Participants in the 2013 study reported a much
topics of advice for new practitioners. higher prevalence of change management
permanent positions or jobs roles in their
Motivation for change management organization, compared to 2011, with over half of
participants having change management job
Participants identified two primary motivations roles. Most organizations have had permanent
for applying change management. The top positions for less than three years, and less than
response was as a necessity stemming from the 20% have change management career paths,
nature of the change, including the complexity, although over 25% were developing them. The
number of people affected and breadth of impact. Project Management Office (PMO) and Human
The second primary motivator was to contribute Resources (HR) were the most common
to overall project success, as change management organizational locations for change management
was viewed as a key success factor and driver of job roles.
buy-in and adoption.
Attributes of a great team member
Use of a methodology
Communication skills and change management
The percentage of participants that reported competencies were the top attributes of a great
using a particular methodology increased to 79%, change management team member, followed by
up from 72% in 2011, 60% in 2009, 58% in 2007, flexibility and interpersonal skills.
55% in 2005 and 34% in 2003. Participants who
reported using a particular methodology reported
higher levels of overall change management
effectiveness than those who did not. The most
2014 Prosci Inc. All rights reserved. | www.prosci.com
Prosci Best Practices in Change Management
Change management team structure specific costs when estimating a change
management budget.
The most prevalent team structure in use had the
change management resource sitting on the
project team, followed by the change Integration of project management and change
management and project resources being one and management
the same. In over one-third of cases, the team Seventy-one percent of participants integrated
structure was a deliberate decision for the change management and project management on
project. Over four in five participants (81%) used their projects. Those who integrated reported
change agent networks of employees within the higher levels of change management
organization who were not considered formally effectiveness and a higher likelihood of meeting
part of the change management team to support project objectives. Working collaboratively was
their projects. viewed as key in integrating the two work
streams. Integration happened at the people,
Impacts of having a dedicated change process, methodology and tool levels. The most
management resource commonly integrated tools were the
communications plan, project plan, training plan
Just under three-quarters of participants
and schedules.
reported that their project had a dedicated
change management resource, a slight decline
from the 2011 study. The greatest advantages of Change readiness
having a dedicated change management resource In terms of evaluating readiness, 43% evaluated
were improved focus on change management and general readiness, 53% evaluated readiness for
having a single point of contact with clear the specific change, 54% evaluated readiness at
responsibility and accountability. The greatest the group level and only 33% evaluated readiness
consequence of not having a dedicated resource at the individual level.
was neglected change management activities.
Use of a dedicated change management resource
Change management measurement
correlated to more effective change management
programs. Improving employee adoption of the change and
delivering on intended project results were the
Estimating change management resource needs two primary focuses for participants measuring
the overall outcome of change management and
Participants identified a number of factors that demonstrating the value-add of applying change
went into their estimation of change management. Only 39% measured change
management resource needs, including the scale management effectiveness while 45% had to
and complexity of the change, the project plan report on change management effectiveness.
and timeline, resource availability, resource Participants provided reports on individual
capability and past experiences. employee metrics, overall project performance
metrics and change management activity
Change management budget metrics, most often to senior leaders. Speed of
adoption, ultimate utilization and proficiency
Just over one-quarter (27%) of participants had a
were measured by 24%, 39% and 30% of
dedicated change management budget. The most
participants respectively.
frequent cost components for the change
management budget were change management
resource costs, training costs and communication Sponsorship
costs. Change management budgets were Participants identified active and visible
typically comprised of between three and six line participation in the project as the most important
items. Participants considered the scale and activity for sponsors in support of change,
complexity of the change, the project plan and followed by direct communication to employees,
timeline, overall availability of resources and and building and maintaining a healthy coalition
2014 Prosci Inc. All rights reserved. | www.prosci.com
Prosci Best Practices in Change Management
of support. There was a direct correlation Project-related training
between sponsor effectiveness and meeting
project objectives. Participants engaged sponsors The most common roles played by change
in the change by holding regular meetings and management resources in project-specific
updates, outlining objectives and communicating training were design, training providers and
directly with sponsors. support, and start-to-end accountability. Face-to-
face training was the most commonly used
vehicle followed by on-the-job training. Training
Managers and supervisors
was most commonly delivered during the
Participants identified the most important implementation stage of the project.
activities for managers and supervisors during
change as communicating the change to their Resistance
direct reports and advocating for the change.
Managers and supervisors were least effective at Participants provided five tactics for identifying
coaching direct reports through change and resistance, led by observing behavior and using
managing resistance. Communicating effectively feedback tools. Resistance was most severe
and building awareness of the need for change during project implementation. The top reasons
were identified as approaches to get managers for employee resistance and manager resistance
and supervisors on board with the change so they paralleled previous studies, led by a lack of
can effectively lead their direct reports. awareness of the need for change.
Preferred senders of change messages Reinforcement and sustainment
As in previous studies, an employees supervisor Participants shared insights on how they planned
was identified as the preferred sender of personal and resourced for reinforcement and
messages, while senior leaders were identified as sustainment. Over half of participants (61%)
the preferred senders of business-level or planned for reinforcement and sustainment
organizational-level messages about why the activities, while less than half (44%) allocated
change was needed and how the change aligned resources for reinforcement and sustainment. In
with the organizations direction. both cases, those that did reported a higher
likelihood of meeting or exceeding project
objectives. Tactics were shared for sustainment,
Communication messages
individual reinforcement and group
The business reasons for the change were reinforcement, as well as using performance
identified as the most important messages for appraisals and measures to encourage adoption.
employees and the second most important for
managers and senior leaders, behind Consultants
expectations and their role in the change. Change
details were often low on the list relative to the Participants reported a slight decline in the use
reasons for change. of an external consultant for change
management, from 48% in 2011 to 46% in 2013.
Having sufficient internal capabilities was the
Use of social media
top reason for not using a consultant, while a
Just over one in four participants used social lack of internal competencies and resources was
media in communications (26%), up from 19% in the top reason for using a consultant. The most
the 2011 study. Reach and channel variety were common roles played by consultants were change
the most common drivers for using social media. management lead, advisor to the change
Over half of participants used social media only management team and provider of change
occasionally or once or twice. Nearly 40% management tools.
evaluated social media as Somewhat effective
while just under 35% evaluated it as Effective.
2014 Prosci Inc. All rights reserved. | www.prosci.com
Prosci Best Practices in Change Management
Training on change management Common and shared definition of change
management
Participants in the 2013 study reported much
higher levels of training specifically on change Participants reported that there was a more
management for groups within their common and shared definition of change
organization. The most common vehicles used to management in their organization today than
provide change management training were there was two years ago. Participants also
formal classroom training and informal identified a higher recognition of the value and
information sharing. Participants outlined the need for change management within their
common topics addressed in these training organization relative to 2011 study results.
sessions, including change management plans,
methodology, tools and change management Percent of projects applying change management
principles. Participants recommended delivering
more training than they were actually able to Overall, participants reported that 39% of
deliver. projects in their organization were applying
change management; however, nearly half of
participants (49%) stated that less than one in
Change management capability and competency
four projects in their organization applied change
building
management. Compared to the 2011 results,
Overall, participants in the 2013 study identified more projects were applying change
that their level of organizational maturity in management.
change management had increased in the past
two years. Over half of participants (53%) Justifying change management to project teams
reported that they were actively working to
deploy change management, up from 46% in Nearly two-thirds of participants (64%) had to
2011. Leadership commitment to and support of justify change management to some degree to the
change management were critical factors for project team they were engaging. The primary
building change management capabilities and focus of their justification was improvement of
competencies. project results and outcomes, increased focus on
adoption and the people side of change, and
minimized risk associated with poorly managed
Change Management Offices (CMOs)
change.
Thirty-eight percent of participants reported
having a functional group or Change Justifying change management to senior leaders
Management Office, an increase from 36% in the
2011 study. Participants identified the Three in five study participants had to justify
responsibilities of this group, with the most change management to senior leadership teams.
common being owning and maintaining the Impact on benefit realization, financial outcome,
change management methodology, owning and project results and risk mitigation were the most
maintaining change management tools, and common ways change management was justified
providing consultative support to resources on to senior leaders.
project teams. The Project Management Office
(PMO) was the most common location for the Change saturation and portfolio management
CMO, followed by Human Resources (HR) and
More participants reported being near, at or past
Organizational Development (OD). Over three-
the point of saturation than in previous studies
quarters of participants (77%) reported having
(77% of participants in 2013, 73% in 2011, 66% in
the group in a single organizational location
2009 and 59% in 2007). Forty-eight percent
while 16% reported having it in two locations.
reported saturation universal across the
Participants outlined the advantages of having
organization while 37% reported localized
the CMO in different locations within the
saturation. Participants outlined several specific
organization.
change management tactics for their particular
project to address the organizational level of
2014 Prosci Inc. All rights reserved. | www.prosci.com
Prosci Best Practices in Change Management
saturation. Less than one-third (32%) reported
that they were actively managing the portfolio of
change and only 20% reported that there was a
high or extremely high interest in addressing the
portfolio of change. The top motivator for those
managing the portfolio of change was to mitigate
and alleviate change saturation.
Unique change types
Participants identified specific change
management issues and provided
recommendations for seven unique change types.
1. Changes that spanned wide geographic
areas
2. Changes that had impact across various
cultures
3. Changes that occurred over a long time
frame
4. Changes that had little or no whats in it
for me? (WIIFM)
5. Changes that occurred in a union
environment
6. Changes that had layoffs or significant
staff reduction
7. Changes that involved a merger or
acquisition
Aligning change management with specific
approaches
Participants identified action steps and
recommendations for aligning change
management with several specific approaches.
1. Program-management
2. Continuous Process Improvement (CPI)
3. Lean
4. Agile
5. Six Sigma
2014 Prosci Inc. All rights reserved. | www.prosci.com
Prosci Best Practices in Change Management
Get your copy of Proscis Best Practices in Change Management 2014 Edition and
Immediately start applying the new insights into your change management applications.
Further Free Information
Learn more and register for Prosci's 2014 Best Practices Webinars and participate interactively with peers
and the latest research findings.
Attend world-leading change management training programs that are based on Prosci's 16 years of
research with over 3,400 change leaders.
Sign up for Prosci's 2014 Top Contributors to Success eCourse email series and start receiving in-depth
insights to the top contributors of success to change management.
Receive engaging tutorials straight to your inbox on all the hottest topics in change management.
Contact us
Prosci Inc.
1367 South Garfield Avenue
Loveland, CO 80537 USA
www.prosci.com
changemanagement@prosci.com
+1 970-203-9332
2014 Prosci Inc. All rights reserved. | www.prosci.com
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Moving Average Guide: Periods, Signals & StrategiesDokumen9 halamanMoving Average Guide: Periods, Signals & StrategiesNavdeep GopamwarBelum ada peringkat
- General ManagerDokumen14 halamanGeneral Managerdamianuskrowin100% (1)
- Akl Soal 3 - Kelompok 2Dokumen9 halamanAkl Soal 3 - Kelompok 2M KhairiBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Marketing Proposal for Udzungwa Falls LodgeDokumen25 halamanDigital Marketing Proposal for Udzungwa Falls LodgeLouis Fanuel100% (1)
- SAP Business One Implementation GuideDokumen20 halamanSAP Business One Implementation GuideJesus A Roque Ortiz100% (1)
- Companies Act 2013 HighlightsDokumen9 halamanCompanies Act 2013 Highlightsashishbajaj007100% (2)
- Case Chapter 5Dokumen3 halamanCase Chapter 5Laras Dwi ArofatinBelum ada peringkat
- Rfli Midterm ReviewerDokumen20 halamanRfli Midterm ReviewerKatrina PaquizBelum ada peringkat
- Reliance Gadimoga PO For Spill KitsDokumen4 halamanReliance Gadimoga PO For Spill KitsProject Sales CorpBelum ada peringkat
- Inymart AcademyDokumen10 halamanInymart AcademySmash HulkBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3 - Managing The Customer JourneyDokumen28 halamanLesson 3 - Managing The Customer JourneyNora Abdulhakim S ALHAIDARBelum ada peringkat
- Gov Uscourts Mad 246980 61 0Dokumen102 halamanGov Uscourts Mad 246980 61 0bruhBelum ada peringkat
- Syed H S Finance 2018Dokumen71 halamanSyed H S Finance 2018Venki GajaBelum ada peringkat
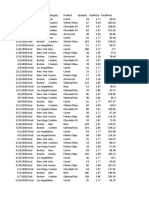
- SampledatafoodsalesDokumen10 halamanSampledatafoodsalesMunish RanaBelum ada peringkat
- Final Effects of Product PacakgingDokumen11 halamanFinal Effects of Product PacakgingMa Angeli GomezBelum ada peringkat
- PDF Credit Analysis of Personal Loan HDFC Bank Specialisation ProjectDokumen89 halamanPDF Credit Analysis of Personal Loan HDFC Bank Specialisation ProjectTejas BhavsarBelum ada peringkat
- Cpa2901us2-Ver41 Online FarDokumen35 halamanCpa2901us2-Ver41 Online Faralik711698100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 Group No.1Dokumen227 halamanCHAPTER 2 Group No.1Pavan KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Duracell'S Acquisition by Berkshire Hathaway: A Case StudyDokumen19 halamanDuracell'S Acquisition by Berkshire Hathaway: A Case Studytanya batraBelum ada peringkat
- May 28, 2015-CH 10-Basic Income Tax Patterns-Valencia & RoxasDokumen18 halamanMay 28, 2015-CH 10-Basic Income Tax Patterns-Valencia & RoxasgoerginamarquezBelum ada peringkat
- Dba 5002 - ConsumerbehaviourDokumen92 halamanDba 5002 - ConsumerbehaviourKathiresan NarayananBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment One Name: Hussein Abdulkadir Ibrahim (Allauun)Dokumen2 halamanAssignment One Name: Hussein Abdulkadir Ibrahim (Allauun)Hussein Abdulkadir IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- 5s PrincipleDokumen22 halaman5s PrincipleamaliaBelum ada peringkat
- Emily A. Moore: Audit Test - October 9 PayrollDokumen3 halamanEmily A. Moore: Audit Test - October 9 PayrollJoel Christian MascariñaBelum ada peringkat
- ENM 301 Speaking Examination - SVDokumen1 halamanENM 301 Speaking Examination - SVBích NgânBelum ada peringkat
- Accounting and Management Problems of SmallDokumen128 halamanAccounting and Management Problems of SmallelohoBelum ada peringkat
- OB Case Study - Lenovo IBMDokumen16 halamanOB Case Study - Lenovo IBMNithi HariBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 5 Strategic ImplementationDokumen94 halamanLesson 5 Strategic ImplementationMahlet AbrahaBelum ada peringkat
- Information Management PRELIM QUIZ 1Dokumen8 halamanInformation Management PRELIM QUIZ 1Nicoco LocoBelum ada peringkat
- Sap FSVDokumen7 halamanSap FSVJaved IqbalBelum ada peringkat