C H O + A O + B NH C C H NO + D H O+eCO: Instructions
Diunggah oleh
John Paul JandayanDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
C H O + A O + B NH C C H NO + D H O+eCO: Instructions
Diunggah oleh
John Paul JandayanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CHE142 Q2
8/18/17
SCHOOL OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND CHEMISTRY. MAPAU UNIVERSITY
Instructions:
Problem Solving.
Write the necessary comments for each step of the solution in the problem solving. Indicate all
the units.
i. Write neatly and clearly by proving enough space in between each line of your solution.
If the solution is more than one page, continue on the next page, clearly indicating that
you have done so.
ii. Clearly indicate the answer you are submitting, (e.g., by circling).
This exam is worth 100 points.
Time limit: 1.5 hours
1. The enzyme, urease, is immobilized in Ca-alginate beads 4 mm in diameter. When the urea
concentration in the bulk liquid is 0.5 mM the rate of urea hydrolysis is v = 9 mM/h
diffusivity of urea in Ca-alginate beads is De = 3.5x104 cm2/sec, and the Michaelis constant
for the enzyme is Km = 0.35 mM. By neglecting the liquid film resistance on the beads (i.e.,
[So] = [Ss]) determine the following:
a. Maximum rate of hydrolysis Vm, Thiele modulus (), and effectiveness factor ().
b. What would be the Vm, , and values for a particle size of Dp = 6 mm?
Hint: Assume = 3/ for large values of ( > 2).
2. The Michaelis-Menten kinetic parameters for a soluble enzyme for a certain substrate are
found to be
Km = 0.05 mol/L
rmax=10 mol/L min.
After immobilizing this enzyme on the surface of insoluble matrix by physical adsorption, it was
found that the value was increased to 0.08 mol/L whereas the value stayed the
same as vmax. What is the effectiveness factor of the immobilized enzyme when the substrate
concentration is 1 mol/L?
1. Problem 3. Growth Stoichiometry and yield coefficient 30 pts
Aerobic degradation of an organic compound by a mixed culture of organisms in waste water
can be represented by the following reaction
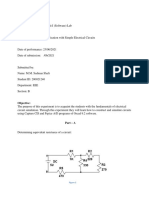
C3H6O3 + a O2 + b NH3 c C5H7NO2 + d H2O + e CO2
a) Determine a, b, c, d, and e, if YX/S =0.38 gX/gS
b) Determine the yield coefficients YX/O2 and Yx/NH3
c) Determine the degree of reductions for the substrate, bacteria, and RQ for the organisms.
Problem 3.
BIOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING| EXAM 11
CHE142 Q2
8/18/17
SCHOOL OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND CHEMISTRY. MAPAU UNIVERSITY
In a batch reactor of volume 5,000 liters, the final desired yeast concentration is 50 gdw/l.
Using the above reaction stoichiometry
a. Determine the concentration and total amount of glucose and (NH4)2SO4 in the nutrient
medium.
b. Determine the yield coefficients YX/S (biomass/glucose) and YX/O2 (biomass/oxygen).
c. Determine the total amount of oxygen required.
d. If the rate of growth at exponential phase is rx 0.7 gdw/l-h, determine the rate of oxygen
consumption (g O2/l-h).
e. Calculate the heat-removal requirements for the reactor.
BIOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING| EXAM 11
CHE142 Q2
8/18/17
SCHOOL OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND CHEMISTRY. MAPAU UNIVERSITY
BIOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING| EXAM 11
CHE142 Q2
8/18/17
SCHOOL OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND CHEMISTRY. MAPAU UNIVERSITY
BIOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING| EXAM 11
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Experiment Chemical ReactorDokumen4 halamanExperiment Chemical ReactorIboniks Beponpiks DabondatskiBelum ada peringkat
- BT 0413 BioseparationTechnologyLaboratoryDokumen21 halamanBT 0413 BioseparationTechnologyLaboratoryvijaygovindarajBelum ada peringkat
- CH371 Novel Separation ProcessDokumen3 halamanCH371 Novel Separation ProcessIrfan K MoiduBelum ada peringkat
- Rr410802 Chemical Reaction Engineering IIDokumen8 halamanRr410802 Chemical Reaction Engineering IISrinivasa Rao G100% (3)
- Microbial Growth Kinetics and BioreactorsDokumen10 halamanMicrobial Growth Kinetics and BioreactorsKareem TarekBelum ada peringkat
- Stoichiometry of Microbial Growth and Product FormationDokumen30 halamanStoichiometry of Microbial Growth and Product FormationMark GerardBelum ada peringkat
- Overall Flowsheet Simulation Benzene Cyclohexane TW6Dokumen7 halamanOverall Flowsheet Simulation Benzene Cyclohexane TW6Mitesh ParmarBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Chemical Engineering CalculationsDokumen7 halamanApplied Chemical Engineering Calculationsmbolantenaina100% (1)
- Enzyme KineticsDokumen35 halamanEnzyme KineticsFaye Y. Santiago100% (3)
- Foggler Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 3rd Edition 442 449 PDFDokumen8 halamanFoggler Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 3rd Edition 442 449 PDFJuanBelum ada peringkat
- Mass Transfer Operations II Rr320801Dokumen8 halamanMass Transfer Operations II Rr320801Nagwa MansyBelum ada peringkat
- Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Data For The SystemDokumen4 halamanVapor-Liquid Equilibrium Data For The Systemapi-3817782100% (1)
- ) Is 0.6. The Feed Stream Is SterileDokumen3 halaman) Is 0.6. The Feed Stream Is SterileAA0809Belum ada peringkat
- Reactor Design Sample ExamDokumen7 halamanReactor Design Sample ExamAugustine BrockBelum ada peringkat
- BAB 9 Rajiv DuttaDokumen86 halamanBAB 9 Rajiv DuttaYuhin meidina ocsaBelum ada peringkat
- CSTR Revised For HandoutDokumen16 halamanCSTR Revised For HandoutbagasBelum ada peringkat
- Optimal Operation of A Semi-Batch Reactive Distillation Column (2000)Dokumen7 halamanOptimal Operation of A Semi-Batch Reactive Distillation Column (2000)GodofredoBelum ada peringkat
- Chem-E-Car Sefter Conception: Muhammad Miftahur Rahman Habib Al Aziz Fitri Handayani ArcodheaDokumen16 halamanChem-E-Car Sefter Conception: Muhammad Miftahur Rahman Habib Al Aziz Fitri Handayani ArcodhearahmanBelum ada peringkat
- 5.2. Classification of FuelsDokumen16 halaman5.2. Classification of FuelsadiBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 4 Energy BalanceDokumen35 halamanCHAPTER 4 Energy BalanceZafirahAhmadFauziBelum ada peringkat
- HAFTOMDokumen67 halamanHAFTOMfanus100% (1)
- PDFDokumen88 halamanPDFMuralidharanBelum ada peringkat
- Gate 2006 PDFDokumen21 halamanGate 2006 PDFVammsy Manikanta SaiBelum ada peringkat
- RaoultDokumen11 halamanRaoultNurul AfifahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - Data InterpretationDokumen24 halamanChapter 2 - Data InterpretationPHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNBelum ada peringkat
- Isothermal Reactor Design: 1. Batch OperationDokumen3 halamanIsothermal Reactor Design: 1. Batch Operationنزار الدهاميBelum ada peringkat
- Momentum Transport Operations External Flow Past Immersed BodiesDokumen1 halamanMomentum Transport Operations External Flow Past Immersed BodiesGerald LimBelum ada peringkat
- Research 2 Duplex Pump: GradeDokumen10 halamanResearch 2 Duplex Pump: GradeAli Requiso MahmudBelum ada peringkat
- 05 Chapter 11 (Compiled)Dokumen106 halaman05 Chapter 11 (Compiled)Haziq KhairiBelum ada peringkat
- Semi-Batch Reactor: Chemical Reaction Engineering (CRE) Is TheDokumen28 halamanSemi-Batch Reactor: Chemical Reaction Engineering (CRE) Is TheJohn Patrick DagleBelum ada peringkat
- Methanol From GlycerinDokumen5 halamanMethanol From GlycerinaudreysosoBelum ada peringkat
- CHEN3005 Process Instrumentation and ControlDokumen4 halamanCHEN3005 Process Instrumentation and ControlVincent Ys TanBelum ada peringkat
- CBB3024 Flowsheeting 1Dokumen93 halamanCBB3024 Flowsheeting 1Yunaida YusoffBelum ada peringkat
- ProblemsDokumen31 halamanProblemsAhmed Adham100% (1)
- R7222301 Mass Transfer & SeparationDokumen2 halamanR7222301 Mass Transfer & SeparationsivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1 WastewaterDokumen2 halamanTutorial 1 WastewaterAnonymous Vx9KTkM8nBelum ada peringkat
- Palaganas Hw2 Che 197Dokumen5 halamanPalaganas Hw2 Che 197Elah Palaganas100% (1)
- Perry Tabs FinalDokumen5 halamanPerry Tabs FinalCeazar Justine FuluganBelum ada peringkat
- Ex0 Questions SolutionsDokumen7 halamanEx0 Questions SolutionsBiniyam haileBelum ada peringkat
- Research Framework Siti Nur Farhanis Dialysate EffluentDokumen2 halamanResearch Framework Siti Nur Farhanis Dialysate EffluentChannis ExoBelum ada peringkat
- Diffusion Mass TransferDokumen18 halamanDiffusion Mass TransferbhuniakanishkaBelum ada peringkat
- P4E2: Kinetics of Homogeneous Reaction in Batch and Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor at Two Different TemperatureDokumen7 halamanP4E2: Kinetics of Homogeneous Reaction in Batch and Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor at Two Different TemperaturejayaprinaBelum ada peringkat
- Mass Transfer OperationsDokumen77 halamanMass Transfer OperationsNhã UyênBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1Dokumen2 halamanTutorial 1eddy50% (2)
- Step Response of First Order System Expt ChE Lab 2Dokumen5 halamanStep Response of First Order System Expt ChE Lab 2simonatics08Belum ada peringkat
- Sample Problem #14Dokumen7 halamanSample Problem #14DozdiBelum ada peringkat
- Soln Sa Adsorption PDFDokumen2 halamanSoln Sa Adsorption PDFRee ValeraBelum ada peringkat
- Module 10: Solved ProblemsDokumen2 halamanModule 10: Solved ProblemscaptainhassBelum ada peringkat
- Behavior of Excess PropertiesDokumen17 halamanBehavior of Excess PropertiesLaxmi PrasannaBelum ada peringkat
- Set8ans 10Dokumen5 halamanSet8ans 10Agustina Evania DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Solution: For A First-Order Reaction, The Following Rate Coefficients Were FoundDokumen16 halamanSolution: For A First-Order Reaction, The Following Rate Coefficients Were FoundDeepak SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- 10 PDFDokumen23 halaman10 PDFTysir SarhanBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 3.2 - Internal Diffusion and ReactionDokumen36 halamanTopic 3.2 - Internal Diffusion and ReactionHamdan Azman100% (1)
- Homework 2: U KQ Where:u Btu H FT Q FT H K ConstantDokumen6 halamanHomework 2: U KQ Where:u Btu H FT Q FT H K ConstantkatelynBelum ada peringkat
- Aeration and AgitationDokumen9 halamanAeration and AgitationKasun Prasanna SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Chlorine: International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid StateDari EverandChlorine: International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid StateBelum ada peringkat
- Reaction Mechanisms in Environmental Engineering: Analysis and PredictionDari EverandReaction Mechanisms in Environmental Engineering: Analysis and PredictionBelum ada peringkat
- Level 2 Online BPDokumen98 halamanLevel 2 Online BProbertduvallBelum ada peringkat
- ExamDokumen12 halamanExamAidar MukushevBelum ada peringkat
- 10 TazmahalDokumen12 halaman10 TazmahalSifat E Noor SahibaBelum ada peringkat
- 7TH Maths F.a-1Dokumen1 halaman7TH Maths F.a-1Marrivada SuryanarayanaBelum ada peringkat
- Birth AsphyxiaDokumen18 halamanBirth AsphyxiaKofi Yeboah50% (2)
- EEE Sofware Lab Experiment 1, PDFDokumen11 halamanEEE Sofware Lab Experiment 1, PDF240 Sadman ShafiBelum ada peringkat
- EASA CS-22 Certification of SailplanesDokumen120 halamanEASA CS-22 Certification of SailplanessnorrigBelum ada peringkat
- 1623 Asm2Dokumen21 halaman1623 Asm2Duc Anh nguyenBelum ada peringkat
- EmbOS GenericDokumen324 halamanEmbOS Genericbogd33Belum ada peringkat
- Legal Aspects of Construction Ethics PaperDokumen11 halamanLegal Aspects of Construction Ethics PaperbikaresBelum ada peringkat
- Checkpoints Before Transformer InstallationDokumen3 halamanCheckpoints Before Transformer InstallationBeaBustosBelum ada peringkat
- 1349122940100212diggerDokumen24 halaman1349122940100212diggerCoolerAdsBelum ada peringkat
- CH 11 International TradeDokumen20 halamanCH 11 International TradeSANTU GHORAIBelum ada peringkat
- Dinengdeng RecipeDokumen1 halamanDinengdeng RecipeFuBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Statements Ias 1Dokumen34 halamanFinancial Statements Ias 1Khalid AzizBelum ada peringkat
- RTOS6Dokumen20 halamanRTOS6Krishna ChaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7Th Edition Incropera Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDokumen68 halamanFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7Th Edition Incropera Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFbrainykabassoullw100% (10)
- Quantum Data-Fitting: PACS Numbers: 03.67.-A, 03.67.ac, 42.50.DvDokumen6 halamanQuantum Data-Fitting: PACS Numbers: 03.67.-A, 03.67.ac, 42.50.Dvohenri100Belum ada peringkat
- MSDS Potassium DichromateDokumen8 halamanMSDS Potassium DichromateAyu Lakshemini OkaBelum ada peringkat
- Food Product Innovation PDFDokumen35 halamanFood Product Innovation PDFDidik HariadiBelum ada peringkat
- LGDokumen36 halamanLGNanchavisBelum ada peringkat
- Pte Lastest QuestionsDokumen202 halamanPte Lastest QuestionsIelts Guru ReviewBelum ada peringkat
- Acid Bases and Salts Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 ScienceDokumen5 halamanAcid Bases and Salts Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 Scienceclashhunting123123Belum ada peringkat
- Application of Geosynthetics in Pavement DesignDokumen7 halamanApplication of Geosynthetics in Pavement DesignAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rBelum ada peringkat
- Landis+Gyr Model EM5300 Class 0.5 Electricity Meter 14-2-63Dokumen5 halamanLandis+Gyr Model EM5300 Class 0.5 Electricity Meter 14-2-63kulukundunguBelum ada peringkat
- Pipe Support Reference 8-29-14Dokumen108 halamanPipe Support Reference 8-29-14HITESHBelum ada peringkat
- AVR On Load Tap ChangerDokumen39 halamanAVR On Load Tap ChangerInsan Aziz100% (1)
- EIC 3 Practice Exercises Unit 4Dokumen3 halamanEIC 3 Practice Exercises Unit 4Trần ChâuBelum ada peringkat
- ECE3073 P4 Bus Interfacing Answers PDFDokumen3 halamanECE3073 P4 Bus Interfacing Answers PDFkewancamBelum ada peringkat
- How To Install Mesa (OpenGL) On Linux Mint - 6 StepsDokumen2 halamanHow To Install Mesa (OpenGL) On Linux Mint - 6 Stepsankitfrnd45Belum ada peringkat