Assignment 04
Diunggah oleh
Jim BennyHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Assignment 04
Diunggah oleh
Jim BennyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
S7 ME MACHINE DESIGN - I (Contact) Assignment No. 4 To be submitted on 28-08-2017
1. A shaft made of C-40 steel and 2.2m long, is supported by two bearings, one at the left end and another at 1.7m from
the left. The shaft carries two pulleys keyed to it, one at mid-span and another at the right end. The pulleys are of
diameter 0.6m and 0.5m respectively. Input power at the left pulley is 24 kW and the power output is from the right
pulley. The input to the left pulley is horizontal and the drive from the right pulley is to a machine vertically below.
Speed of the shaft is 600 r.p.m. and the coefficient of friction is 0.3. Combined shock and fatigue factors in bending
and torsion may be taken as 2.0 and 1.5 respectively. Design the shaft assuming suitable stresses. Also, design
suitable keys for connection between the shaft and the pulleys.
2. Determine the diameter for a hollow shaft having inside diameter 0.6 times the outside diameter. The maximum
allowable shear stress for the shaft is 80 MPa. The shaft is driven by a 750mm diameter overhung pulley placed
vertically below it. The weight of the pulley is 600 N. The tensions on tight and slack sides of the belt are 3.2 kN
and 1.2 kN respectively. The overhung is 250mm. Assume angle of lap of the belt on the pulley to be 180.
3. A horizontal solid shaft is supported on two bearings 1.5 m apart. A helical gear (45 helix angle) of 20 involute
teeth and 200 mm pitch diameter is located 400 mm to the right of the left bearing. The gear is driven by a mating
gear directly behind it. A 600 mm diameter pulley is keyed to the shaft 600 mm to the left of the right bearing. The
pulley drives another pulley with a horizontal belt directly behind it. The ratio of tensions of the belt is 2.8 with the
slack side on top. The drive transmits 30 kW at 300 rpm. Design the shaft if the allowable shear stress for the shaft
material is 40 N/mm2.
4. Determine the inside and outside diameters of a hollow shaft which will replace a solid shaft of the same material.
The hollow shaft should have the same strength as that of the solid shaft, but must weigh half the solid shaft per metre
length.
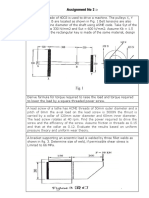
5. A 600mm pulley, P, driven by a horizontal belt transmits 20 kW of power
at 300 r.p.m. through a solid steel shaft to a 20 spur gear, G, of diameter
250 mm, which drives a mating gear directly behind it (figure-1). The
pulley weighs 1000 N and the ratio of tensions between the two sides of
the belt is 3.2. The shaft is supported between narrow bearings B 1 and B2
and both the pulley and the gear are keyed to the shaft. If commercial
steel shafting is used and the shock and fatigue factors are chosen to be
Kb = 2.0 and Kt = 1.5, determine the necessary diameter of the shaft.
Figure-1
6. A shaft and a key are made of the same material and the key width is of the shaft diameter. Considering shear
only, determine the minimum length of the key in terms of the shaft diameter. The shearing strength of the key
material is 60% of its crushing strength. Determine the thickness of the key to make the key equally strong in shear
and crushing.
7. A hollow shaft is to transmit 20 kW at 300 rpm. The loading is such that a maximum bending moment of 1000 Nm is
induced in the shaft, together with an additional axial thrust of 15 kN. The shaft is supported on bearings 1500 mm
apart. The values of shock and fatigue factors in torsion and bending (Kt and Kb) are 1.25 and 1.75 respectively. The
inside diameter is 0.8 times the outside diameter. Determine the outer diameter of the shaft if the allowable shear
stress is 60 MPa.
8. Determine the outer diameter of a hollow shaft having inside diameter 0.6 times the outside diameter. The maximum
allowable shear stress for the shaft is 85 MPa. The shaft is driven by a 900mm diameter overhung pulley placed
vertically below it. The weight of the pulley is 600 N. The tensions on tight and slack sides of the belt are 2.9 kN
and 1 kN respectively. The overhung length is 250mm. Assume angle of lap of the belt on the pulley to be 180.
9. Design and sketch a protected type of C.I. flange coupling for a
mild steel shaft transmitting 18 kW at 200 r.p.m. Shaft and key
are of the same material. Bolts are made of alloy steel for which
the maximum shear stress should not exceed 30 MPa. The
maximum torque may be taken as 25% greater than the full-load
torque.
10. A flexible coupling (shown in figure-2) is used to transmit 15 kW
of power at 100 r.p.m. There are six pins and their pitch circle
diameter is 200 mm. The length of the pin in contact with the
left hand flange, the gap between the two flanges and the length
of bush in contact with the right hand flange are 23, 5 and 35 mm
respectively. The permissible shear and bending stresses in the
pin are 35 and 152 N/mm2 respectively. The permissible
pressure for the rubber bush is 1 N/mm2. Calculate: (i) the pin
diameter by shear consideration, (ii) the pin diameter by bending
consideration and (iii) outer diameter of the rubber bush.
Figure-2
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Mechanical Engineering Assignment on Design of Springs, Shafts, Couplings, and JointsDokumen2 halamanMechanical Engineering Assignment on Design of Springs, Shafts, Couplings, and JointsHarris ChackoBelum ada peringkat
- Final Design Work SheetDokumen7 halamanFinal Design Work SheetKINDUBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank 2 DME 1Dokumen4 halamanQuestion Bank 2 DME 1Ayush KothariBelum ada peringkat
- Unit I - Shafts: Single ElementDokumen7 halamanUnit I - Shafts: Single Elementchelam101100% (1)
- Me 6503 Design of Machine Elements QBDokumen3 halamanMe 6503 Design of Machine Elements QBDeepak SBelum ada peringkat
- Dme 2Dokumen6 halamanDme 2NITHISH KUMAR M SBelum ada peringkat
- Belt (Autosaved)Dokumen59 halamanBelt (Autosaved)Khánh NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Engine QBDokumen4 halamanEngine QBSapari VelBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank Numericals DMEDokumen3 halamanQuestion Bank Numericals DMEVanessa SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Dme Model 2Dokumen6 halamanDme Model 2YashwanthI-StyleKuttiBelum ada peringkat
- DMM I Assignment - 4Dokumen2 halamanDMM I Assignment - 4Konduru Vinay Kumar ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Design of ShaftDokumen2 halamanDesign of Shaftgourab190% (1)
- Dme Imp QuestionsDokumen9 halamanDme Imp QuestionsCAD With RaoBelum ada peringkat
- MD1 M3 Compiled Ot 1Dokumen67 halamanMD1 M3 Compiled Ot 1Jiuan AndradaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Ii Shafts and CouplingsDokumen68 halamanUnit Ii Shafts and Couplingssri guruBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment QuestionDokumen15 halamanAssignment QuestionPratik WalimbeBelum ada peringkat
- PART-B QUESTIONS STEADY STRESSES AND VARIABLE STRESSESDokumen12 halamanPART-B QUESTIONS STEADY STRESSES AND VARIABLE STRESSESMadhu MithaBelum ada peringkat
- Design of TransmissonDokumen3 halamanDesign of TransmissonrajapratyBelum ada peringkat
- DMM Question BankDokumen2 halamanDMM Question Bankzubair ahmedBelum ada peringkat
- DME 1 Question BankDokumen5 halamanDME 1 Question BankRahul YedduBelum ada peringkat
- ME3170 - Tutorial 5 ShaftsDokumen2 halamanME3170 - Tutorial 5 Shaftsme20btech11034Belum ada peringkat
- DMM-1 MID-2 Assignment QuestionsDokumen3 halamanDMM-1 MID-2 Assignment Questionsuppada AnilBelum ada peringkat
- DME - Assignment - IDokumen3 halamanDME - Assignment - ISathis KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Design ProblemsDokumen13 halamanDesign ProblemsAristotle RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Elemen MesinDokumen23 halamanElemen MesinMonika NikaBelum ada peringkat
- DME Assignment 1Dokumen2 halamanDME Assignment 1sumikannuBelum ada peringkat
- MD1 Assign2 2023Dokumen2 halamanMD1 Assign2 2023Aditya KumarBelum ada peringkat
- 16mu315 - Machine Design Question Bank: Ut Yt B TDokumen3 halaman16mu315 - Machine Design Question Bank: Ut Yt B THarishBelum ada peringkat
- QP Pe Series 2Dokumen2 halamanQP Pe Series 2AADARS M SBelum ada peringkat
- Me8593 Iq R17Dokumen4 halamanMe8593 Iq R17Vaideesh LJBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Mechanical Design Questions For Practice 2003Dokumen4 halamanIntegrated Mechanical Design Questions For Practice 2003Mohammedraffic Noor MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Design1 SheetsDokumen9 halamanDesign1 SheetsYou channelBelum ada peringkat
- Design ExercisesDokumen13 halamanDesign ExercisesBookieeBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2Dokumen3 halamanAssignment 2sonawanepmsBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Machine Elements PC-ME 503 Assignment QuestionsDokumen5 halamanDesign of Machine Elements PC-ME 503 Assignment Questions039 Md Faizan AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Me 2303 Imp QnsDokumen3 halamanMe 2303 Imp QnsAJAY63Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 BIGDokumen3 halamanUnit 3 BIGVasanth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Imp Qoestions MDDokumen3 halamanImp Qoestions MDvenuedBelum ada peringkat
- QB Unit-3,4,5Dokumen7 halamanQB Unit-3,4,5Agranshu BhardwajBelum ada peringkat
- gupta PG - No:176) Exercise 9Dokumen3 halamangupta PG - No:176) Exercise 9mahendra babu mekalaBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Bombay: ME 423 Machine DesignDokumen1 halamanDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Bombay: ME 423 Machine DesignrahulbeniwalBelum ada peringkat
- MDDokumen5 halamanMDYogesh DanekarBelum ada peringkat
- Strength of Materials - TorsionDokumen2 halamanStrength of Materials - TorsionJan Alexis MonsaludBelum ada peringkat
- TUTORIAL 3 Design of Shaft Key and CouplingDokumen2 halamanTUTORIAL 3 Design of Shaft Key and Couplingrip111176100% (1)
- Assignment 2Dokumen1 halamanAssignment 2pethuraBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment - 2Dokumen4 halamanAssignment - 2vaijanath patilBelum ada peringkat
- Register Number NIT Mechanical Design Machine Elements ExamDokumen2 halamanRegister Number NIT Mechanical Design Machine Elements ExamdharaniventhanBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Sheet-II MEC3110/317 (Machine Design II)Dokumen4 halamanTutorial Sheet-II MEC3110/317 (Machine Design II)Prateeksha ShakyaBelum ada peringkat
- SLIDEDokumen26 halamanSLIDEThắng NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Torsion ProblemsDokumen2 halamanTorsion ProblemsSudeep magarBelum ada peringkat
- 15me53 Important Questions Paper-3Dokumen3 halaman15me53 Important Questions Paper-3Karthi SiddhBelum ada peringkat
- Machine Design 2 P1 - Review of ShaftingDokumen1 halamanMachine Design 2 P1 - Review of Shafting裴瑞尼Belum ada peringkat
- PVP Siddhartha Mech Engineering III Sem HomeworkDokumen2 halamanPVP Siddhartha Mech Engineering III Sem HomeworkNarayanarao PalagaraBelum ada peringkat
- Machine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01Dokumen10 halamanMachine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01The AIRS CreationsBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment On Shaft DesignDokumen2 halamanAssignment On Shaft DesignRitesh SinghBelum ada peringkat
- FinallDokumen175 halamanFinallremeceldo dagamac100% (1)
- 13 ME AssignmentDokumen2 halaman13 ME AssignmentMuhammad Sharif JamaliBelum ada peringkat
- Strength of Materials Unit 3 Question Bank: Jansons Institute of TechnologyDokumen3 halamanStrength of Materials Unit 3 Question Bank: Jansons Institute of TechnologyVasanth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Childhood Schizophrenia A Case of Treatment With Nicotinamide and NiacinDokumen11 halamanChildhood Schizophrenia A Case of Treatment With Nicotinamide and NiacinJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- National Institute of Technology, Calicut: Jim BennyDokumen3 halamanNational Institute of Technology, Calicut: Jim BennyJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Design 09b 2Dokumen4 halamanDesign 09b 2Jim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- 29 Sample ChapterDokumen52 halaman29 Sample ChapterJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Kerr Interview Thomas Szasz PDFDokumen11 halamanKerr Interview Thomas Szasz PDFJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Guitar Strap and Dent RepairDokumen5 halamanGuitar Strap and Dent RepairJim Benny100% (1)
- Tao of ProgrammingDokumen21 halamanTao of ProgrammingMiguel LozanoBelum ada peringkat
- The Medicalization of Everyday Life Article Szasz PDFDokumen2 halamanThe Medicalization of Everyday Life Article Szasz PDFJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- State Bank of InbbdiaDokumen1 halamanState Bank of InbbdiaJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Aniruddha Auth., Chiranjit Mukhopadhyay, K B Akhilesh, R. Srinivasan, Anjula Gurtoo, Parthasarathy Ramachandran, Parameshwar P Iyer, M Mathirajan, M H Bala Subrahmanya Eds. Driving the Economy Through Innovation and EnDokumen865 halamanAniruddha Auth., Chiranjit Mukhopadhyay, K B Akhilesh, R. Srinivasan, Anjula Gurtoo, Parthasarathy Ramachandran, Parameshwar P Iyer, M Mathirajan, M H Bala Subrahmanya Eds. Driving the Economy Through Innovation and EnJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Grade CardDokumen3 halamanGrade CardJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- New Age CalendarDokumen1 halamanNew Age CalendarJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Plan CDokumen4 halamanPlan CJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Charcoal HIV MDokumen4 halamanCharcoal HIV MShoshannah100% (1)
- 4 Discoveries JonathanDokumen68 halaman4 Discoveries JonathanJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Volume 5 Press ReleaseDokumen4 halamanVolume 5 Press ReleaseJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Will by Harold W PercivalDokumen5 halamanWill by Harold W PercivalJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Volume 4 Press ReleaseDokumen4 halamanVolume 4 Press ReleaseJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Volume 3 Press ReleaseDokumen4 halamanVolume 3 Press ReleaseJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Voltage, The Key To Rebuilding You Life PDFDokumen21 halamanVoltage, The Key To Rebuilding You Life PDFHussainBelum ada peringkat
- The Silent Ballet Volume 2Dokumen4 halamanThe Silent Ballet Volume 2Jim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Fairy Dictionary of Names and TermsDokumen35 halamanFairy Dictionary of Names and TermsKeane Raziel100% (1)
- The Silent Ballet Volume 1Dokumen4 halamanThe Silent Ballet Volume 1Jim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- JF IbogaineDokumen19 halamanJF IbogaineboninhBelum ada peringkat
- UG Special English Semester Syllabus 2015 16Dokumen9 halamanUG Special English Semester Syllabus 2015 16Jim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- National Institute of Technology Calicut: N. I. T. Campus (P. O.), Calicut - 673 601, Kerala, IndiaDokumen1 halamanNational Institute of Technology Calicut: N. I. T. Campus (P. O.), Calicut - 673 601, Kerala, IndiaJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Discoverer of LSD Reflects on its Profound ImplicationsDokumen14 halamanDiscoverer of LSD Reflects on its Profound ImplicationsJim BennyBelum ada peringkat
- Arguments For Cannabis Regulation!!!Dokumen14 halamanArguments For Cannabis Regulation!!!enlightNme100% (6)
- PeripheralDokumen25 halamanPeripheralMans FansBelum ada peringkat
- Flotect Vane Operated Flow Switch: Magnetic Linkage, UL ApprovedDokumen1 halamanFlotect Vane Operated Flow Switch: Magnetic Linkage, UL ApprovedLuis GonzálezBelum ada peringkat
- LEGAL STATUs of A PersonDokumen24 halamanLEGAL STATUs of A Personpravas naikBelum ada peringkat
- 14.marifosque v. People 435 SCRA 332 PDFDokumen8 halaman14.marifosque v. People 435 SCRA 332 PDFaspiringlawyer1234Belum ada peringkat
- Apexocardiograma Precizari PracticeDokumen12 halamanApexocardiograma Precizari PracticeDaniel VelciuBelum ada peringkat
- Ra 1425 Rizal LawDokumen7 halamanRa 1425 Rizal LawJulie-Mar Valleramos LabacladoBelum ada peringkat
- Theory of Karma ExplainedDokumen42 halamanTheory of Karma ExplainedAKASH100% (1)
- Soal Ulangan Harian Smester 1 Kelas 8 SMP BAHASA INGGRISDokumen59 halamanSoal Ulangan Harian Smester 1 Kelas 8 SMP BAHASA INGGRISsdn6waykhilauBelum ada peringkat
- Society and CultureDokumen40 halamanSociety and CultureRichard AbellaBelum ada peringkat
- Hempel's Curing Agent 95040 PDFDokumen12 halamanHempel's Curing Agent 95040 PDFeternalkhut0% (1)
- Recommendation Letter - One Young WorldDokumen2 halamanRecommendation Letter - One Young WorldNabeel K. AdeniBelum ada peringkat
- The Voice of PLC 1101Dokumen6 halamanThe Voice of PLC 1101The Plymouth Laryngectomy ClubBelum ada peringkat
- Food Processing & ClassificationDokumen3 halamanFood Processing & ClassificationAzrielle JaydeBelum ada peringkat
- Metatron AustraliaDokumen11 halamanMetatron AustraliaMetatron AustraliaBelum ada peringkat
- Compatibility Testing: Week 5Dokumen33 halamanCompatibility Testing: Week 5Bridgette100% (1)
- Cultural Briefing: Doing Business in Oman and the UAEDokumen2 halamanCultural Briefing: Doing Business in Oman and the UAEAYA707Belum ada peringkat
- BLUEBOOK CITATION GUIDEDokumen12 halamanBLUEBOOK CITATION GUIDEMichaela PortarcosBelum ada peringkat
- Annex-4-JDVP Certificate of Learners MasteryDokumen1 halamanAnnex-4-JDVP Certificate of Learners MasteryZINA ARRDEE ALCANTARABelum ada peringkat
- 15-8377 - 3521 Calandria Communications L. Rivera PDFDokumen20 halaman15-8377 - 3521 Calandria Communications L. Rivera PDFRecordTrac - City of OaklandBelum ada peringkat
- History of LotteryDokumen29 halamanHistory of LotteryBala G100% (2)
- Mce Igcse Chemistry PPT c08Dokumen57 halamanMce Igcse Chemistry PPT c08Shabanito GamingBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture1 SEODokumen24 halamanLecture1 SEOUsman AnwarBelum ada peringkat
- Modern Dental Assisting 11Th Edition Bird Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokumen37 halamanModern Dental Assisting 11Th Edition Bird Test Bank Full Chapter PDFRichardThompsonpcbd100% (9)
- Subsurface Sewage DisposalDokumen174 halamanSubsurface Sewage DisposalSanthi KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Day 3Dokumen18 halamanDay 3SamBelum ada peringkat
- Factors of Cloud ComputingDokumen19 halamanFactors of Cloud ComputingAdarsh TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- AMA Manual 10th Edition PDFDokumen1.014 halamanAMA Manual 10th Edition PDFKannan Fangs S100% (2)
- Plusnet Cancellation FormDokumen2 halamanPlusnet Cancellation FormJoJo GunnellBelum ada peringkat
- Course Title: Cost Accounting Course Code:441 BBA Program Lecture-3Dokumen20 halamanCourse Title: Cost Accounting Course Code:441 BBA Program Lecture-3Tanvir Ahmed ChowdhuryBelum ada peringkat
- Minotaur Transformation by LionWarrior (Script)Dokumen7 halamanMinotaur Transformation by LionWarrior (Script)Arnt van HeldenBelum ada peringkat