NCP
Diunggah oleh
Nikki del Rosario100%(2)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (2 suara)
853 tayangan3 halamanBronchiectasis is a chronic, irreversible dilation of the bronchi and bronchioles. Each dilated tube virtually amounts to a lung abscess, the exudate which drains freely through the bronchus. The retention of secretions and subsequent obstruction ultimately cause the alveoli distal to the obstruction to collapse.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
ncp
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniBronchiectasis is a chronic, irreversible dilation of the bronchi and bronchioles. Each dilated tube virtually amounts to a lung abscess, the exudate which drains freely through the bronchus. The retention of secretions and subsequent obstruction ultimately cause the alveoli distal to the obstruction to collapse.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(2)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (2 suara)
853 tayangan3 halamanNCP
Diunggah oleh
Nikki del RosarioBronchiectasis is a chronic, irreversible dilation of the bronchi and bronchioles. Each dilated tube virtually amounts to a lung abscess, the exudate which drains freely through the bronchus. The retention of secretions and subsequent obstruction ultimately cause the alveoli distal to the obstruction to collapse.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 3
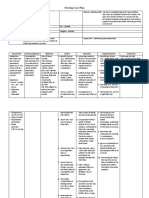
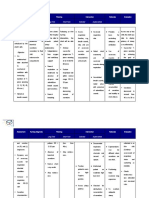
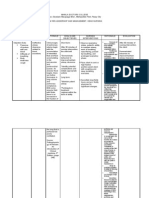
Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal & Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Ineffective airway Bronchiectasis is a Goal: After 8 hours of Independent Effectiveness:
clearance related to chronic, irreversible nursing intervention, the • Auscultate breath • The presence of After 8 hours of
retained dilation of the bronchi client will be able to sounds q 1 to 4 coarse crackles nursing
tracheobronchial and bronchioles. The maintain patent airway hours. Breath during late intervention, the
secretions inflammatory process as evidenced by sounds are normally inspiration indicates client was able to
associated with clear/clearing breath clear or scattered fluid in the airway; maintain patent
Cues: pulmonary infections sounds. fine crackles at wheezing indicates a airway as
I> damages the bronchial bases, which clear narrowed airway. evidenced by
• He complained, wall, causing a loss of with deep breathing. (Simpson, 2006) clear/clearing
“Ang hirap ilabas its supporting structure breath sounds.
nung plema, and resulting in thick • Monitor respiratory • A normal respiratory
parang matigas sputum that ultimately patterns, including rate for an adult Efficiency:
siya sa loob.” obstructs the bronchi. rate, depth, and without dyspnea is The interventions
The walls become effort. 12 to 20. With were done within
O> permanently distended secretions in the the time frame.
• At present, he and distorted, impairing Objectives: airway, the
still expectorates mucociliary clearance. After nursing respiratory rate will
sputum, however The inflammation and intervention, the client increase. (Simpson, Appropriateness:
it is lesser than infection extend to the will be able to: 2006) The interventions
before, no more peribronchial tissues; in were realistic for the
blood, but its the case of saccular • Assume an upright • Position the client to • An upright position client, the setting
color is still light bronchiectasis, each position optimize respiration allows for maximal and the time table.
yellow. dilated tube virtually lung expansion; lying
• The client’s amounts to a lung flat causes
provisional abscess, the exudate abdominal organs to Acceptability:
diagnosis is PTB which drains freely shift toward the The interventions
5 fibrothorax R through the bronchus. chest, which crowds were acceptable to
bronchiectasis, The retention of the lungs and makes the client and
and one of the secretions and it more difficult to significant others
manifestations of subsequent obstruction breathe. (Seckel,
this condition is ultimately cause the 2007)
having purulent alveoli distal to the Adequacy:
sputum. obstruction to collapse. Developmental All interventions
M> In time the patient were implemented
RR: 26 cpm develops respiratory • Restate importance • Encourage client to • Fluids help minimize accordingly.
insufficiency with of increase fluid intake mucosal drying and
reduced vital capacity, increasing fluid of up to 2500 maximize ciliary
decreased ventilation, intake
and an increased ratio mL/day within action to move
of residual volume to cardiac or renal secretions. (Smith-
total lung capacity. reserve. Sims, 2001)
There is impairment in • Restate the
the matching of importance of taking • Teach the client the • Taking the entire
ventilation to perfusion the entire course of need to take course of antibiotics
and hypoxemia. antibiotics ordered antibiotics helps to eradicate
Reference: Smeltzer, until prescription bacterial infection,
S. and Bare, B., has run out. which decreases
Brunner & lingering, chronic
Suddarth’s Textbook infection. (Donahue,
of Medical-Surgical 2002)
Nursing, 10th ed,
• Return demonstrate Supplemental
Vol.1, pp. 585-586
pursed-lip breathing • Teach the client on • Pursed lip breathing
how to do pursed-lip aims to prolong
breathing. exhalation and
• Demonstrate proper increase airway
pursed-lip breathing. pressure during
expiration, thus
reducing the amount
of trapped air and
the amount of airway
resistance.
(Smeltzer-Bare,
2004)
• Receive postural Dependent
drainage and • Provide postural • Chest physiotherapy,
percussion as drainage and including percussion
ordered by the percussion only as and postural
physician ordered by the drainage, is
physician. important in
secretion
management.
(Smeltzer-Bare,
2004)
• Receive due
medications, most • Administer • Mucolytics help to
specifically the mucolytics as per decrease the
mucolytics doctor’s order. viscosity of the
sputum and promote
expectoration of
secretions.
(Smeltzer-Bare,
2004)
• Verbalize Collaborative
cooperation towards • Refer atypical • Maximizing nurse-
the referred health assessment findings physician
care provider to client’s attending collaboration holds
physician. promise for
improving patient
care and creating
satisfying work roles.
(www.medscape.co
m/)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDokumen2 halamanIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokumen3 halamanNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceNicholas TagleBelum ada peringkat
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Dokumen3 halamanElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliBelum ada peringkat
- PneumoniaDokumen2 halamanPneumoniaPia MedinaBelum ada peringkat
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDokumen2 halamanANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Student NurseDokumen2 halamanStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.Belum ada peringkat
- Acc Phu Case NCP HyperthermiaDokumen1 halamanAcc Phu Case NCP Hyperthermiamacy_bautistaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokumen4 halamanNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKim Gabrielle Exene LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDokumen2 halamanIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen3 halamanAssessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationAziil LiizaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisDokumen19 halamanNursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisRiza Angela BarazanBelum ada peringkat
- Date/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationDokumen2 halamanDate/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationPauleen Trisha SamparaniBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Dokumen1 halamanChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Bheru LalBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen8 halamanNCPJoseph Anthony Benitez VerzosaBelum ada peringkat
- Pain NCP BillrothDokumen2 halamanPain NCP BillrotharjayBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentDokumen2 halamanProblem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentkyawBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Map - Colon CancerDokumen2 halamanConcept Map - Colon Cancerbea pegadBelum ada peringkat
- NCP HemothoraxDokumen3 halamanNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short TermDokumen2 halamanAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short TermFrancis Xavier S. MendezBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDokumen3 halamanNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy MalaiseDokumen1 halamanNursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy Malaise06eltianBelum ada peringkat
- Medication ThalassemiaDokumen3 halamanMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For Pain (Appendicitis)Dokumen2 halamanNCP For Pain (Appendicitis)Iris BalinoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlansDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plansapi-19762967Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen4 halamanNursing Care PlanDewi PurnamasariBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For FractureDokumen4 halamanNCP For FracturejpBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokumen6 halamanNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaBelum ada peringkat
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDokumen3 halamanCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokumen5 halamanNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmm Estipona HaoBelum ada peringkat
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokumen1 halamanIneffective Airway ClearanceChristineAlaBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen2 halamanNCPShubhangi SarwanBelum ada peringkat
- Pleural Effusion FdarDokumen1 halamanPleural Effusion FdarvanessabdeveraBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlansDokumen1 halamanNursing Care Plansapplensweety100% (2)
- Cutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanDokumen2 halamanCutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanYayin Pestaño100% (1)
- NCP PTBDokumen2 halamanNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconBelum ada peringkat
- Disturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPDokumen4 halamanDisturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPSamVelascoBelum ada peringkat
- CholecystitisDokumen1 halamanCholecystitisDianne ParungaoBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKSDokumen3 halamanAssessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKStflorenzBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Acute PainDokumen3 halamanNCP Acute PainNathalie kate petallarBelum ada peringkat
- Ariane NCP 1Dokumen2 halamanAriane NCP 1Kristian Ray EraulaBelum ada peringkat
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDokumen2 halamanIneffective Breathing PatternjuanmarcostaglishBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokumen2 halamanIneffective Airway Clearancejancel_bollaBelum ada peringkat
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Dokumen6 halamanWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Planapi-309251523Belum ada peringkat
- NCP For TBDokumen3 halamanNCP For TBNelle Agni100% (1)
- University of Eastern Philippines: Scientific RationaleDokumen3 halamanUniversity of Eastern Philippines: Scientific RationaleJane MinBelum ada peringkat
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDokumen5 halamanDecreased Cardiac Outputshuang81Belum ada peringkat
- NCP Cad ElectiveDokumen1 halamanNCP Cad ElectivejoegeBelum ada peringkat
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDokumen6 halamanWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrBelum ada peringkat
- AAAAA Altered-Body-Temp-NCPDokumen2 halamanAAAAA Altered-Body-Temp-NCPMoi ValdozBelum ada peringkat
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDokumen2 halamanScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DBelum ada peringkat
- CopdDokumen6 halamanCopdapi-3717941100% (2)
- NCP Difficulties in BreathingDokumen4 halamanNCP Difficulties in BreathingKingJayson Pacman06Belum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen7 halamanNCPRuth MontebonBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: Short TermDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan: Short TermKristine Young100% (1)
- NCP Marilou.... SanitariumDokumen9 halamanNCP Marilou.... SanitariumJerry AbleBelum ada peringkat
- Manila Doctors College: Pres. Diosdado Macapagal BLVD., Metropolitan Park, Pasay CityDokumen3 halamanManila Doctors College: Pres. Diosdado Macapagal BLVD., Metropolitan Park, Pasay CityNichole CastleBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen9 halamanAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanBelum ada peringkat
- Ayurvedic SyllabusDokumen96 halamanAyurvedic SyllabusSumanthBelum ada peringkat
- Basic ScienceDokumen2 halamanBasic ScienceMurjanatu Saidu TiggiBelum ada peringkat
- What Is AsthmaDokumen13 halamanWhat Is AsthmaMuchlissatus Lisa MedicalbookBelum ada peringkat
- PALS Provider Manual PDFDokumen57 halamanPALS Provider Manual PDFtimie_reyes90% (21)
- Step Notes: RRC SampleDokumen9 halamanStep Notes: RRC SampleRafia 0205Belum ada peringkat
- 1ST Exam 9-10Dokumen8 halaman1ST Exam 9-10Joanne GodezanoBelum ada peringkat
- Shangrila 590 Service ManualDokumen60 halamanShangrila 590 Service ManualTuchilo Viorel100% (5)
- Pneumonia Case Study FinalllDokumen56 halamanPneumonia Case Study Finalllbethrice melegritoBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory MedicationsDokumen18 halamanRespiratory Medicationsapi-338095748Belum ada peringkat
- Australian Asthma Handbook Quick ReferenceGuide - Version1.0Dokumen44 halamanAustralian Asthma Handbook Quick ReferenceGuide - Version1.0butterwalkerBelum ada peringkat
- Pollution-Related Chronic Respiratory Disease: Dr. Dr. Agus Dwi Susanto, SP.P (K), FISR, FAPSRDokumen46 halamanPollution-Related Chronic Respiratory Disease: Dr. Dr. Agus Dwi Susanto, SP.P (K), FISR, FAPSRRosi AmaliaBelum ada peringkat
- 04 Respiration 2022 - AnswersDokumen10 halaman04 Respiration 2022 - Answersria khanBelum ada peringkat
- Concept of Disease 1.1 Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen15 halamanConcept of Disease 1.1 Anatomy and PhysiologyAulia SandraBelum ada peringkat
- Idse Unit 2Dokumen207 halamanIdse Unit 2farhan AliBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology MeaslesDokumen3 halamanAnatomy and Physiology MeaslesCamila DaludadoBelum ada peringkat
- Hand Out 3 Respiratory System Overview PDFDokumen12 halamanHand Out 3 Respiratory System Overview PDFGrape JuiceBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank Clinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease Mid PartDokumen24 halamanTest Bank Clinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease Mid Partweekup035Belum ada peringkat
- Appendix C Date/Time Soapie/R Nurse'S NotesDokumen42 halamanAppendix C Date/Time Soapie/R Nurse'S NotesedwardBelum ada peringkat
- FNCP New1Dokumen34 halamanFNCP New1Caurrine MonsaludBelum ada peringkat
- Asthma Casebook FINALDokumen55 halamanAsthma Casebook FINALBrandt CajoconBelum ada peringkat
- NCP - BronchopneumoniaDokumen11 halamanNCP - BronchopneumoniaMaria Ivy Mendoza100% (1)
- Assessment of Respiratory FunctionDokumen4 halamanAssessment of Respiratory FunctionCristine Dominique E. DonaireBelum ada peringkat
- Pranvaha - Rahim FileDokumen6 halamanPranvaha - Rahim FileRahimshaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing DiagnosisDokumen86 halamanNursing DiagnosisMarianne Gonzales100% (5)
- 365 Day of DIY 1000 Pages With Amazing Crafts Household Hacks Cleaning and Organizing HomesteadingDokumen862 halaman365 Day of DIY 1000 Pages With Amazing Crafts Household Hacks Cleaning and Organizing HomesteadingMaggieBelum ada peringkat
- Studies of The Bowen TechniqueDokumen29 halamanStudies of The Bowen TechniquefisionovaisBelum ada peringkat
- Skill 47 (1) ..Tracheostomy Tube Change PDFDokumen2 halamanSkill 47 (1) ..Tracheostomy Tube Change PDFRadhika SethuBelum ada peringkat
- Bioscience 1 NotesDokumen21 halamanBioscience 1 NotesLulu0% (1)
- Shear FlowDokumen20 halamanShear FlowHaithem HammoudaBelum ada peringkat
- URTI and AnaesthesiaDokumen6 halamanURTI and AnaesthesiaChuah Wei HongBelum ada peringkat