Measure Sampling JCI
Diunggah oleh
Muzna IqbalHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Measure Sampling JCI
Diunggah oleh
Muzna IqbalHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Version 2.
Appendix I:
Measure Sampling
Specification Manual for the Joint Commission International Library of Measures
Version 2.0, effective for January 2013 discharges (1st Quarter 2013)
2011 Joint Commission International
1
Version 2.0
Appendix I: Measure Sampling
Introduction
Sampling is a process of selecting a representative part of the population of interest in
order to estimate the organizations performance, without collecting data for its entire
population. Using a statistically valid sample, an organization can measure its
performance in an effective and efficient manner.
Sampling is a particularly useful technique for performance measures that require
primary data collection from a source such as the medical record. Sampling should not
be used unless the organization has a large enough number of cases in the measures
initial eligible population because a fairly large number of sample cases are needed to
accurately reflect the organizations performance. Organizations with large patient
volumes may perform data collection on a sample of the total population, but sampling
is not required.
To obtain statistically valid sample data, the sample size should be carefully determined
and the sample cases should be randomly selected such that individual cases in the
population have an equal chance of being selected. Only when the sample data truly
represent the whole population can the sample-based performance measure data be
meaningful and useful. Guidelines for effective sampling procedures follow.
Sampling may be used for all measures in the Library of Measures except for I-HBIPS-
2, I-HBIPS-3, I-NCS-2, I-NSC-4 and I-NSC-5. These measures cannot be sampled
because they are event-based measures.
Sampling Availability
If an organization decides to sample a measures or measure sets initial eligible
population, sampling should be applied to all monthly discharge medical records
identified as part of the inpatient initial eligible population. Initial eligible population
criteria are described in each measure set chapter of the specification manual.
The initial eligible population should be identified by using available databases or other
information repositories that contain monthly patient discharge information, International
Classification of Diseases (ICD) diagnosis/procedure codes or patient diagnoses or
procedures, and other necessary administrative data (e.g., patient age).
Sampling should be undertaken on a monthly basis.
Specification Manual for the Joint Commission International Library of Measures
Version 2.0, effective for January 2013 discharges (1st Quarter 2013)
2011 Joint Commission International
2
Version 2.0
Appendix I: Measure Sampling
Sample Size Requirements
Hospitals selecting sample cases for Library Measures should ensure that its measures
or measure sets initial patient population(s) and sample size(s) meet the following
conditions:
The number of discharged cases to be sampled on a monthly basis is
determined in accordance with the following sampling table:
Measure Sampling Table
Total Monthly Initial Patient Population Required Monthly
Size (N) for the Selected Measure Sample Size (n)
>= 59 58
<= 58 No sampling; 100% population required
If desired, a hospital may select a larger monthly sample size.
Sample Size Examples:
A hospital has 57 discharges (N) in a month for a given measure initial patient
population. All 57 cases (100%) should be reviewed. Sampling is not
appropriate in this example.
A hospital has 128 discharges (N) in a month for a given measure initial patient
population. The sample size for this month would be 58 cases (n).
A hospital has 512 discharges (N) in a month for a given measure initial patient
population. The sample size for this month would be 58 cases (n).
A hospital has 905 discharges (N) in a month for a given measure initial patient
population. The sample size for this month would be 58 cases (n) (the maximum
required number of cases for the monthly sample size).
According to the sampling table, it is possible in the same measure to have No
sampling (<58 initial patient population discharge cases) in one month and be able to
sample with the next month of cases, if there are a sufficient number of initial patient
population discharge cases to support the sampling methodology as described.
Systematic Random Sampling Approach
Systematic random sampling requires every kth record from a population size of N in
Specification Manual for the Joint Commission International Library of Measures
Version 2.0, effective for January 2013 discharges (1st Quarter 2013)
2011 Joint Commission International
3
Version 2.0
Appendix I: Measure Sampling
such a way that a sample size of n is obtained, where k < N/n. The first sample record
(i.e., the starting point) must be randomly selected before taking every kth record. This
is a two-step process as follows:
1. Select the starting point; and
2. Then select every kth record thereafter until the selection of the sample size is
complete.
Random Selection Example: How to apply random sampling
For a measure or measure set with an initial patient population size of 360 discharges
per month (N), the sample size would be 58 (n) according to the table provided in this
section. To select a random sample of 58 cases you would implement the following
process:
1. Determine the initial patient population size N (i.e., the total number of
discharges associated with the selected measure) for the month.
2. Determine the sample size n using the above table.
3. Divide the population size N by the suggested sample size n and the quotient
is k (i.e., the resulting integer is the sampling interval k).
Example: How to get sample interval number
a. The sampling interval k = 360/58 = 6 sampling interval (k)
b. Thus, every 6th (k) patient record will be selected from the measure
population until 58 cases have been selected.
4. To ensure that each patient has an equal chance of being selected,
the starting point must be randomly determined before selecting
every 6th record.
Example: How to determine starting point
a. Therefore, a simple approach to determine where to start would be to
write the numbers 1,2,3,4,5 on separate pieces of paper and
b. Then place the numbers in a container and pull one piece of paper
identifying a number to start counting the k sampling interval
i. For example, if you draw number 3, start with the 3rd case on
your list and select every 6th case after that until you reach 58
cases.
Specification Manual for the Joint Commission International Library of Measures
Version 2.0, effective for January 2013 discharges (1st Quarter 2013)
2011 Joint Commission International
4
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hospitalist Program Toolkit: A Comprehensive Guide to Implementation of Successful Hospitalist ProgramsDari EverandHospitalist Program Toolkit: A Comprehensive Guide to Implementation of Successful Hospitalist ProgramsBelum ada peringkat
- IPSG PresentationDokumen38 halamanIPSG Presentationmuhammed shamaa100% (1)
- JCI Measures For Posting2 08.04.10 PDFDokumen4 halamanJCI Measures For Posting2 08.04.10 PDFRental MegaBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar Panduan JCIDokumen12 halamanDaftar Panduan JCIEko Wahyu AgustinBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar JCI - 9 Feb 2012Dokumen16 halamanSeminar JCI - 9 Feb 2012Mahardika PertiwiBelum ada peringkat
- Joint Commission International Library of MeasuresDokumen3 halamanJoint Commission International Library of Measuresadiadi84100% (1)
- JCI International Library of Measures ANIK BUKUDokumen325 halamanJCI International Library of Measures ANIK BUKUnurulBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Analysis of Patient and Family Rights in Jci Accreditation and Cbahi Standards For HospitalsDokumen10 halamanCritical Analysis of Patient and Family Rights in Jci Accreditation and Cbahi Standards For HospitalsImpact JournalsBelum ada peringkat
- 13 Patient Saefty and Quality ImprovementDokumen36 halaman13 Patient Saefty and Quality ImprovementShafiq Ur RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- JCIADokumen100 halamanJCIAKenny JosefBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE 3 STUDENT National Patient Safety Goals 2013Dokumen15 halamanMODULE 3 STUDENT National Patient Safety Goals 2013Dewi Ratna Sari100% (1)
- 1.medication ErrorsDokumen25 halaman1.medication ErrorshussainBelum ada peringkat
- Challenges For AccreditationDokumen22 halamanChallenges For AccreditationMohammad Muntaz AliBelum ada peringkat
- JCI International Library of MeasuresDokumen261 halamanJCI International Library of Measuressarah100% (1)
- @@assessment of Medical Documentation As Per Joint Commission InternationDokumen6 halaman@@assessment of Medical Documentation As Per Joint Commission InternationNahari ArifinBelum ada peringkat
- A Proven Pathway To AccreditationDokumen25 halamanA Proven Pathway To AccreditationkukunBelum ada peringkat
- CBAhi-Quality Management & Patient SafetyDokumen14 halamanCBAhi-Quality Management & Patient SafetyJery JsBelum ada peringkat
- How To Perform Clinical AuditDokumen70 halamanHow To Perform Clinical AuditFaiq Syukri Bin SaparudinBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment and Re-Assessment of Patients According To The Scope of ServiceDokumen9 halamanAssessment and Re-Assessment of Patients According To The Scope of Servicegiya nursingBelum ada peringkat
- Epidemiology Based Market ForecastDokumen7 halamanEpidemiology Based Market Forecastkarthi339Belum ada peringkat
- Incident Reporting JciDokumen14 halamanIncident Reporting Jciakinrav100% (2)
- Information Broucher Nursing ExcellenceDokumen16 halamanInformation Broucher Nursing ExcellenceShantu Shirurmath100% (1)
- IPSG JCIA Measurable Elements and IntentsDokumen4 halamanIPSG JCIA Measurable Elements and IntentsHana Sanchez AlobaidanBelum ada peringkat
- JCI Standard Manual Guide For QM and Medical DirectorDokumen1 halamanJCI Standard Manual Guide For QM and Medical DirectorCyrene Diane Riego Roxas-ManzanoBelum ada peringkat
- Improve Care.: Empower ChangeDokumen13 halamanImprove Care.: Empower Changekukun67% (3)
- Clinical AuditDokumen5 halamanClinical AuditdrskumarBelum ada peringkat
- Hakim Seikh CaseDokumen14 halamanHakim Seikh Caseronn13nBelum ada peringkat
- Patient Safety: What Should We Be Trying To Communicate?Dokumen32 halamanPatient Safety: What Should We Be Trying To Communicate?cicaklomenBelum ada peringkat
- 450-JCI Library of Measures Consultant Practicum Sept 2011Dokumen26 halaman450-JCI Library of Measures Consultant Practicum Sept 2011h1m4w4nBelum ada peringkat
- Joint Commission International: Nepomuceno, Rose Ann TDokumen42 halamanJoint Commission International: Nepomuceno, Rose Ann TRoan Nepomuceno - Joaquin100% (1)
- Safety Event Reporting PolicyDokumen10 halamanSafety Event Reporting PolicypatientsafetyBelum ada peringkat
- Joint Commission TST Hand Hygiene Data Collection Tool PDFDokumen5 halamanJoint Commission TST Hand Hygiene Data Collection Tool PDFJoel Guillen JulianBelum ada peringkat
- Jci Manual ItDokumen20 halamanJci Manual ItNAIMUL ISLAM100% (1)
- Organizational Chart Cbahi ThemeDokumen8 halamanOrganizational Chart Cbahi ThemeVelmurugan KumarasamyBelum ada peringkat
- كيف تجتاز jciDokumen379 halamanكيف تجتاز jciwaleed fangaryBelum ada peringkat
- STAN5 JCI AccreditationDokumen57 halamanSTAN5 JCI AccreditationYulinur FirdausBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Audit GuideDokumen13 halamanClinical Audit Guidewassie gebiBelum ada peringkat
- National Core Standards 2011 1Dokumen52 halamanNational Core Standards 2011 1yos_peace86Belum ada peringkat
- Ways To Improve The Health SystemDokumen18 halamanWays To Improve The Health SystemB I N SBelum ada peringkat
- JCI International Library of MeasuresDokumen261 halamanJCI International Library of MeasuresDedy Haris DeswandarBelum ada peringkat
- Quality Control & Quality Improvement: Under SupervisionDokumen20 halamanQuality Control & Quality Improvement: Under Supervisionheba abd elazizBelum ada peringkat
- A New Drug-Shelf Arrangement For Reducing MedicatiDokumen9 halamanA New Drug-Shelf Arrangement For Reducing MedicatiEmmanuel LawerBelum ada peringkat
- Uhmb Quality ImprovementDokumen44 halamanUhmb Quality Improvementeloxs100% (1)
- Mod2 - Ch3 - Health IndicatorsDokumen13 halamanMod2 - Ch3 - Health IndicatorsSara Sunabara100% (1)
- Feedback FormDokumen1 halamanFeedback Formsubhan takildarBelum ada peringkat
- NEW: 7th Edition of JCI Accreditation Standards For Hospitals ManualDokumen4 halamanNEW: 7th Edition of JCI Accreditation Standards For Hospitals ManualOmar AlkahloutBelum ada peringkat
- StandardsDokumen68 halamanStandardsAnan Aghbar100% (1)
- Joint Commission International (JCI) Requirements Related To Safe SurgeryDokumen16 halamanJoint Commission International (JCI) Requirements Related To Safe Surgeryngurah_wardanaBelum ada peringkat
- The Importance of CBAHI Accreditation: Saudi ArabiaDokumen32 halamanThe Importance of CBAHI Accreditation: Saudi ArabiaMohamad HssanBelum ada peringkat
- Patient Identification SOPDokumen7 halamanPatient Identification SOPIrma Nech100% (1)
- Fppe Focused EvaluationDokumen1 halamanFppe Focused EvaluationLOVI KRISSADIBelum ada peringkat
- Tubing Misconnections Self Assessment For Healthcare FacilitiesDokumen38 halamanTubing Misconnections Self Assessment For Healthcare FacilitiesAle Gastelum100% (1)
- Adverse EventDokumen5 halamanAdverse EventumeshbhartiBelum ada peringkat
- JCIA Handbook 2020Dokumen61 halamanJCIA Handbook 2020WAQASBelum ada peringkat
- Sampling Chapter TJC (V2020a1)Dokumen18 halamanSampling Chapter TJC (V2020a1)Eman SherifBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-1 Statistical Quality Control: Learning ObjectivesDokumen69 halamanUnit-1 Statistical Quality Control: Learning ObjectivesHarnitBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Exercise No 3BDokumen6 halamanLaboratory Exercise No 3BMichael AbeledaBelum ada peringkat
- Statatistical InferencesDokumen22 halamanStatatistical InferencesBlen tesfayeBelum ada peringkat
- Internet Marketing and E-Commerce: Session 12Dokumen38 halamanInternet Marketing and E-Commerce: Session 12sudhanshuBelum ada peringkat
- 13.375 CASING Tally KH #C Wspace OutDokumen14 halaman13.375 CASING Tally KH #C Wspace OutnabiBelum ada peringkat
- Automotive SPICE - Guidelines - 1. Edition 2017 - English - PDF - Automotive SPICE - Guidelines - 1. Edition 2017 - EnglishDokumen312 halamanAutomotive SPICE - Guidelines - 1. Edition 2017 - English - PDF - Automotive SPICE - Guidelines - 1. Edition 2017 - EnglishVesna Mićić100% (3)
- EPIC32BDokumen1 halamanEPIC32BAnyie EliasBelum ada peringkat
- Answers 1: CS 161 Computer Security Spring 2010 Paxson/Wagner January 26, 2010Dokumen3 halamanAnswers 1: CS 161 Computer Security Spring 2010 Paxson/Wagner January 26, 2010alishBelum ada peringkat
- YALE (D810) GLP040SVX LIFT TRUCK Service Repair Manual PDFDokumen18 halamanYALE (D810) GLP040SVX LIFT TRUCK Service Repair Manual PDFjkdmsmemmd0% (1)
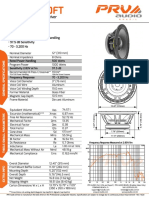
- PRV Audio 12MB1000FT DatasheetDokumen1 halamanPRV Audio 12MB1000FT DatasheetGilberto MontaniBelum ada peringkat
- 2 - Transformers - FIDPDokumen12 halaman2 - Transformers - FIDPLoumarie C. ZepedaBelum ada peringkat
- The Display Centre S Fairfield Display Collection-1Dokumen52 halamanThe Display Centre S Fairfield Display Collection-1RichardBelum ada peringkat
- Taboola Education Industry Benchmark ReportDokumen38 halamanTaboola Education Industry Benchmark ReportRonaldo RibeiroBelum ada peringkat
- Tech30 2022 by YourStoryDokumen62 halamanTech30 2022 by YourStoryAnkitBelum ada peringkat
- Dacs Standards Brochure 1Dokumen23 halamanDacs Standards Brochure 1Quy VănBelum ada peringkat
- Whitehat Revenue: by FlupherDokumen23 halamanWhitehat Revenue: by FlupherkerasaktibangetBelum ada peringkat
- COMPRO PT Elning Heksa Karya - 2021 UpdatedDokumen24 halamanCOMPRO PT Elning Heksa Karya - 2021 UpdatedEngineering AstonBelum ada peringkat
- Sample - China Digital Freight Forwarding Maeket (2020 - 2025) - Mordor IntelligenceDokumen47 halamanSample - China Digital Freight Forwarding Maeket (2020 - 2025) - Mordor IntelligenceredejavoeBelum ada peringkat
- Employee Referral Bonus Program (Erbp)Dokumen49 halamanEmployee Referral Bonus Program (Erbp)kprabhu19Belum ada peringkat
- Kyplot Research PDFDokumen10 halamanKyplot Research PDFTakkas FernandoBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Networks - ANUDokumen2 halamanComputer Networks - ANUMike MikkelsenBelum ada peringkat
- Ciclo Di Verniciatura: Technical PropertiesDokumen1 halamanCiclo Di Verniciatura: Technical PropertiesMaffone NumerounoBelum ada peringkat
- DBF-Proposal Final FinalDokumen5 halamanDBF-Proposal Final FinalSaif RezaBelum ada peringkat
- MOT - Week 14 - Assignment - Group 7Dokumen10 halamanMOT - Week 14 - Assignment - Group 7vian100% (2)
- Module-3a-Knhs AnswersDokumen32 halamanModule-3a-Knhs AnswersJobellyn May AguirreBelum ada peringkat
- Emailing Fortan - NotesDokumen110 halamanEmailing Fortan - NotesnirjalBelum ada peringkat
- AMF 2.0 User Manual - ENDokumen16 halamanAMF 2.0 User Manual - ENRodrigo GoeringBelum ada peringkat
- NATIONAL FOOD AUTHORITY-Accounts Analyst PDFDokumen1 halamanNATIONAL FOOD AUTHORITY-Accounts Analyst PDFJake ScotBelum ada peringkat
- MyPhp MaterialsDokumen233 halamanMyPhp MaterialsJai DanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Alibaba Retail TechnologyDokumen28 halamanAlibaba Retail TechnologyHomer SimpBelum ada peringkat
- CSD Registration Summary Report: Supplier IdentificationDokumen3 halamanCSD Registration Summary Report: Supplier IdentificationmorutibBelum ada peringkat
- A Tertiary Study: Experiences of Conducting Systematic Literature Reviews in Software EngineeringDokumen4 halamanA Tertiary Study: Experiences of Conducting Systematic Literature Reviews in Software EngineeringsalmaimtiazBelum ada peringkat
- Benchmark H4000 Hotplate Stirrer Instruction ManualDokumen1 halamanBenchmark H4000 Hotplate Stirrer Instruction ManualKenneth SaganBelum ada peringkat