Surveying
Diunggah oleh
Margie CruzHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Surveying
Diunggah oleh
Margie CruzHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
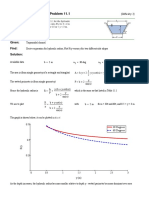
Measurement measure lay-out too long Effect of Curvature & Refraction
too long add subtract e Azimuth
Corrections too short subtract add
CD = MD (1 + )
TL hcr = 0.067K 2 from South
Due to temperature: too short
e D2
(add/subtract); measured length Probable Errors h = h2 + (h h2 ) 0.067D1 D2
CD = MD (1 ) D1 + D2 1
C = L(T2 T1 ) TL Reduction to
Probable Error (single):
Sea Level
Due to pull: Stadia Measurement Leveling
(add/subtract); measured length (x x) CD MD
E = 0.6745 Horizontal: =
(P2 P1 )L n1 Elev = Elev + R R+h
C=
EA D = d + (f + c) Inclined Upward:
Probable Error (mean):
Due to sag: error/setup = eBS + eFS
(subtract only); unsupported length D = ( )s +C Subtense Bar
E (x x) Inclined Downward:
w 2 L3 Em = = 0.6745 D = Ks + C error/setup = +eBS eFS
C= n n(n 1) D = cot
24P 2 Inclined: Total Error: 2
Proportionalities of weight, w: eT = error/setup no. of setups
Due to slope: D = Ks cos + C
(subtract only); measured length E=error; d=distance; n=no. of trials
1 1 H = D cos
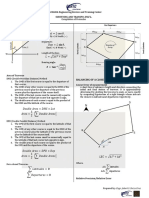
C 2 = S 2 h2 Double Meridian Distance Method DMD
V = D sin
2 DMD = Dep
Normal Tension:
DMD = DMD1 + Dep1 + Dep
0.204WAE Area of Closed Traverse Area of Irregular Boundaries
PN = DMD = Dep
PN P Trapezoidal Rule: 2A = (DMD Lat)
Lat = L cos
Dep = L sin d
A= [h + hn + 2h]
Error of Closure:
2 1 Double Parallel Distance Method DPD
Parabolic Curves Simpsons 1/3 Rule:
= L2 + D2 DPD = Lat
Symmetrical: d DPD = DPD1 + Lat 1 + Lat
Relative Error/Precision: A = [h1 + hn + 2h + 4h ]
L Error of Closure 3 DPD = Lat
H = (g1 + g 2 ) =
Perimeter Note: n must be odd 2A = (DMD Dep)
8
L 2
x 2 ( 2) 1 acre = Simple, Compound & Reverse Curves Spiral Curve
= L 4047 m2
y H 1
Unsymmetrical:
L1 L2
H= (g + g 2 )
2(L1 +L2 ) 1
g 3 (L1 +L2 ) = g1 L1 + g 2 L2
Note: Consider signs.
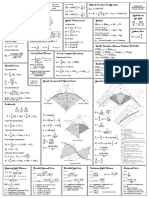
Earthworks
0
L2 180
=
f w I 2RLs
A= (d + dR ) + (fL + fR ) T = R tan
2
2 L 4 Ls 2
I i= ; p=
Volume (End Area): E = R [sec 1] 3 24R
2
L I
L3
Ve = (A1 + A2 ) m = R [1 cos ] x=
2 2 6RLs
Volume (Prismoidal): L = 2R sin
I L5 LT long tangent
ST short tangent
2 Y=L 2 R radius of simple curve
L 40R2 Ls L length of spiral from TS to any point
VP = (A1 + 4Am + A2 ) along the spiral
6 Lc = RI Ls I Ls length of spiral
180 Ts = + (R + p) tan I angle of intersection
I c angle of intersection of the simple
Prismoidal Correction: 2 2 curve
20 2R p length of throw or the distance from
= I tangent that the circular curve has been
L D 360 Es = (R + p) sec R offset
CP = (c c2 )(d1 d2 ) 2 x offset distance (right angle
12 1 1145.916 distance) from tangent to any point on
R= 0.036k 3 the spiral
xc offset distance (right angle
VP = Ve Cp D Ls = distance) from tangent to SC
R Ec external distance of the simple
Volume (Truncated): 0.0079k 2
curve
spiral angle from tangent to any
h e= point on the spiral
VT = ABase Have = A( ) R S spiral angle from tangent to SC
n i deflection angle from TS to any point
A D L on the spiral
is deflection angle from TS to SC
VT = (h1 + 2h2 + 3h3 + 4h4 ) = y distance from TS along the tangent
n DC Ls to any point on the spiral
Stopping Sight Distance Parabolic Summit Curve Parabolic Sag Curve Underpass Sight Distance Horizontal Curve
L>S
v2 L>S L>S L>S
S = vt + A(S)2
2g(f G) L= 2 A(S)2 A(S)2 h1 + h2 S2
L= L= H= C R=
a = g(f G) (deceleration) 200(h1 + h2 ) 122 + 3.5S 800H 2 8M
v L<S L<S L<S L<S
2
tb = (breaking time)
200(h1 + h2 ) 122 + 3.5S 800H L(2S L)
g(f G) L = 2(S) L = 2(S) L = 2(S) R=
A A A 8M
f
Eff = (100) L length of summit curve A algebraic difference A algebraic difference of L length of horizontal
fave S sight distance of grades, in percent grades, in percent curve
v speed in m/s h1 height of drivers eye L length of sag curve L length of sag curve S sight distance
t perception-reaction time h1 = 1.143 m or 3.75 ft S sight distance A(K)2 R radius of the curve
For passengers comfort,
f coefficient of friction h2 height of object L= where K is speed in KPH
M clearance from the
G grade/slope of road h2 = 0.15 m or 0.50 ft
395 centerline of the road
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Center: Pre-Calculus GuideDokumen7 halamanCenter: Pre-Calculus GuideLovEegnia BalbuenaBelum ada peringkat
- Surveying FormulaDokumen8 halamanSurveying FormulaJulie Ann Sta. AnaBelum ada peringkat
- Calculus 2 Cheat SheetDokumen1 halamanCalculus 2 Cheat SheetB SotoBelum ada peringkat
- Surveying and Transpo FormulaDokumen12 halamanSurveying and Transpo FormulaKent David Relatado100% (1)
- ACT Math-Ultimate Formula Sheet.Dokumen6 halamanACT Math-Ultimate Formula Sheet.Waheed ShaabanBelum ada peringkat
- Vertical Curves - Solved ExamplesDokumen6 halamanVertical Curves - Solved ExamplesShikhin Garg80% (5)
- Azimuth From South: Subtract AddDokumen1 halamanAzimuth From South: Subtract Addcristina23Belum ada peringkat
- Traversing and Traverse ComputationDokumen67 halamanTraversing and Traverse ComputationBrian Rey L. Abing100% (1)
- Different DH ConventionsDokumen20 halamanDifferent DH ConventionsomarBelum ada peringkat
- Calculus of Variation by GoshiDokumen34 halamanCalculus of Variation by GoshiSunkara Hemanth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Livro Hibbeler - 7 Ed Resistencia Materiais (Soluções) - 4 PDFDokumen50 halamanLivro Hibbeler - 7 Ed Resistencia Materiais (Soluções) - 4 PDFIzabel Cristina100% (1)
- Soil Prediction With R PDFDokumen370 halamanSoil Prediction With R PDFwalterdryBelum ada peringkat
- ACFrOgAeKoe92snvbBv4lCcdxTF9PzyqcDOZ02MrZTTgLuA2bvQ-1iSwmSNflyqLumBIyWZGjyShj02TH0GGn7ZuS65CCbo8 CkP5IDGy6HMGyWaL-Yv cBfwvr2LbLZ3hwe4wfA3UXsVvD20mfPDokumen1 halamanACFrOgAeKoe92snvbBv4lCcdxTF9PzyqcDOZ02MrZTTgLuA2bvQ-1iSwmSNflyqLumBIyWZGjyShj02TH0GGn7ZuS65CCbo8 CkP5IDGy6HMGyWaL-Yv cBfwvr2LbLZ3hwe4wfA3UXsVvD20mfPHamghad LambasBelum ada peringkat
- ACTMathFormulaSheetFREE 1Dokumen1 halamanACTMathFormulaSheetFREE 1segun shonaBelum ada peringkat
- Summary Chapter45Dokumen3 halamanSummary Chapter45blalllBelum ada peringkat
- Aadt or Adt ×K DHV ×D DDHVDokumen9 halamanAadt or Adt ×K DHV ×D DDHVnasserBelum ada peringkat
- Useful Aerospace FormulasDokumen1 halamanUseful Aerospace FormulasRadj90Belum ada peringkat
- Midterm 2 Cheat SheetDokumen3 halamanMidterm 2 Cheat SheetwotaddictBelum ada peringkat
- 2015Dokumen10 halaman2015ZaBelum ada peringkat
- Formula SurveyingDokumen3 halamanFormula SurveyingMerrelle Aubrey DeniegaBelum ada peringkat
- Solutions: 2017 JEE Entrance Examination Advanced/Paper 2 Code 7Dokumen14 halamanSolutions: 2017 JEE Entrance Examination Advanced/Paper 2 Code 7SUNIL KUMAR JANGRABelum ada peringkat
- PW - AITS - NT-24: Hint and Solutions PhysicsDokumen13 halamanPW - AITS - NT-24: Hint and Solutions PhysicsOfficers IasBelum ada peringkat
- Ce 201 - Fundamentals of Surveying: Cos SinDokumen2 halamanCe 201 - Fundamentals of Surveying: Cos SinDaille Wroble GrayBelum ada peringkat
- Determine The Adjusted Bearing and Lengths of The Following DataDokumen13 halamanDetermine The Adjusted Bearing and Lengths of The Following DataJoshua Onin OlivenzaBelum ada peringkat
- Formulae Part ThreeDokumen5 halamanFormulae Part ThreeShiva SeshasaiBelum ada peringkat
- MIT8 03SCF16 PracticeFinalExam1Dokumen15 halamanMIT8 03SCF16 PracticeFinalExam1Gavin BirlaBelum ada peringkat
- Poster Basics of Wettin The Young Laplace EquationDokumen1 halamanPoster Basics of Wettin The Young Laplace EquationPierre NievesBelum ada peringkat
- Integral - NEUSTDokumen3 halamanIntegral - NEUSTJohn vincent SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- Traverse SheetDokumen1 halamanTraverse Sheetjeffrobinson782Belum ada peringkat
- Act Math Formulas Interactive 1Dokumen2 halamanAct Math Formulas Interactive 1Isley Quintine YutucBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation and Design Touch and Step VoltageDokumen7 halamanCalculation and Design Touch and Step Voltagenikhilsingh1087Belum ada peringkat
- Trigonometria I.E.P. "Lord Karmel"Dokumen5 halamanTrigonometria I.E.P. "Lord Karmel"foker01Belum ada peringkat
- International Program Giaûi Tích 2: Hut - Department of Math. AppliedDokumen12 halamanInternational Program Giaûi Tích 2: Hut - Department of Math. AppliedBell PhamBelum ada peringkat
- Hezam Alasqah CHE 354 HW 7Dokumen11 halamanHezam Alasqah CHE 354 HW 7TimelessBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1Dokumen8 halamanLecture 1Khang DangBelum ada peringkat
- Metc SesiuneDokumen10 halamanMetc SesiuneRazvan 888Belum ada peringkat
- Cap. 11 PDFDokumen77 halamanCap. 11 PDFRamón RamalhoBelum ada peringkat
- Repaso de Reduccion de ÁngulosDokumen3 halamanRepaso de Reduccion de ÁngulosAlan CordobaBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Test - 01 - SOL - PDFDokumen13 halamanTechnical Test - 01 - SOL - PDFVamshiBelum ada peringkat
- Article 4Dokumen7 halamanArticle 4pratiksharma2828Belum ada peringkat
- Diffusion: 2.1 September 5, 2003: 1 D Cartesian and Cylindrical Steady StateDokumen20 halamanDiffusion: 2.1 September 5, 2003: 1 D Cartesian and Cylindrical Steady StateFlor MárquezBelum ada peringkat
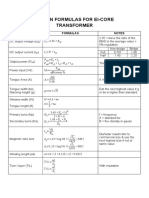
- Design Formulas For Full Wave Ei Core Transformer - NewDokumen2 halamanDesign Formulas For Full Wave Ei Core Transformer - NewViet Hoang LeBelum ada peringkat
- QM Equations and Constants Sheet NewDokumen2 halamanQM Equations and Constants Sheet NewBinh LamBelum ada peringkat
- AP Calculus BC 2006 Scoring Guidelines Form B: The College Board: Connecting Students To College SuccessDokumen7 halamanAP Calculus BC 2006 Scoring Guidelines Form B: The College Board: Connecting Students To College SuccessMr. PopoBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BDokumen11 halamanAlgebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BLaissa SerranoBelum ada peringkat
- PHL BS With Affine DivsDokumen8 halamanPHL BS With Affine DivsRaphaël FromEverBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics: Ax + by + C 0 y MX + B, y - y M (YDokumen12 halamanMathematics: Ax + by + C 0 y MX + B, y - y M (Yvzimak2355Belum ada peringkat
- Formula SheetDokumen3 halamanFormula SheetCarlos GamioBelum ada peringkat
- Cartesian 20to 20geodetic 20 - 20borkowskiDokumen2 halamanCartesian 20to 20geodetic 20 - 20borkowskiRober Ignacio GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Review 3Dokumen2 halamanReview 3xesef93262Belum ada peringkat
- 21.1 Cauchy Goursat TheoremDokumen10 halaman21.1 Cauchy Goursat TheoremNaga ArjunBelum ada peringkat
- ELEC 353 Formula Sheet - Winter 2009Dokumen1 halamanELEC 353 Formula Sheet - Winter 2009Juampi MochenBelum ada peringkat
- Please Note, This Is A Complementary Aid Only, It Is Not Allowed On Any ExamsDokumen2 halamanPlease Note, This Is A Complementary Aid Only, It Is Not Allowed On Any ExamsaradsugerdachriBelum ada peringkat
- Formula Page:: Y = X = D (1 - Cosɵ) ˙Y= V = Ωd Sinɵ Ÿ = F = Ω D CosɵDokumen5 halamanFormula Page:: Y = X = D (1 - Cosɵ) ˙Y= V = Ωd Sinɵ Ÿ = F = Ω D CosɵPhemi2580Belum ada peringkat
- Aero - Lect8 - 2019 (1) Take Off Aircraft Stability and PerformanceDokumen14 halamanAero - Lect8 - 2019 (1) Take Off Aircraft Stability and PerformanceAftab AliBelum ada peringkat
- Calculus 2 Cheat Sheet: by ViaDokumen1 halamanCalculus 2 Cheat Sheet: by ViaDauda Sulley DaudaBelum ada peringkat
- By Type: Search The World's Digital LibraryDokumen8 halamanBy Type: Search The World's Digital LibraryIbrahim ZahidBelum ada peringkat
- Relevant Charts and Formulae: e e e eDokumen4 halamanRelevant Charts and Formulae: e e e etehBelum ada peringkat
- Floating Point Arithmethic - Error AnalysisDokumen30 halamanFloating Point Arithmethic - Error AnalysisAlfreda OduroBelum ada peringkat
- Polarization: Meseret Asrat, Meseret@uchicago - Edu, 02211Dokumen3 halamanPolarization: Meseret Asrat, Meseret@uchicago - Edu, 02211MomoHinamoriChanBelum ada peringkat
- The Inverse Geodetic Problem Using The Method by BowringDokumen2 halamanThe Inverse Geodetic Problem Using The Method by BowringRober Ignacio GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Point Function PDFDokumen1 halaman2 Point Function PDFKevin ChenBelum ada peringkat
- Comp2024 Btest-11 MathematicsDokumen16 halamanComp2024 Btest-11 MathematicsTtttBelum ada peringkat
- Cuerpo RigidoDokumen37 halamanCuerpo RigidoByron AyalaBelum ada peringkat
- NK Emt Practical PDFDokumen38 halamanNK Emt Practical PDFshubh soniBelum ada peringkat
- Nothing Is Something - by Floyd SweetDokumen12 halamanNothing Is Something - by Floyd Sweetbob13542Belum ada peringkat
- Engineering MathDokumen1 halamanEngineering MathAnil MarsaniBelum ada peringkat
- CAT Quant Questions With Solutions by Bodhee PrepDokumen12 halamanCAT Quant Questions With Solutions by Bodhee PrepDark HorseBelum ada peringkat
- Glosarry of Questions Cume 212Dokumen11 halamanGlosarry of Questions Cume 212Phenias ManyashaBelum ada peringkat
- General Linear TransformationsDokumen67 halamanGeneral Linear TransformationsJuliusBelum ada peringkat
- Capitulo 3Dokumen13 halamanCapitulo 3jenniferBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 6 TRANSFORMATIONS FINAL PLANDokumen27 halamanUnit 6 TRANSFORMATIONS FINAL PLANerdawati nurdinBelum ada peringkat
- A Study of The Motion and Stability of Torpedoes in 3 Degrees of Freedom - LeeuwenDokumen24 halamanA Study of The Motion and Stability of Torpedoes in 3 Degrees of Freedom - LeeuwenspbhavnaBelum ada peringkat
- CAD/CAM - Objective Questions - Unit2Dokumen2 halamanCAD/CAM - Objective Questions - Unit2Anonymous YkDJkSqBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - 1 Rectilinear MotionDokumen19 halamanChapter 2 - 1 Rectilinear Motiontik50100% (1)
- Physics Dp014 Tutorial 7: II III IIII III IIDokumen5 halamanPhysics Dp014 Tutorial 7: II III IIII III IIaliffBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam - Calculus - PhysicsDokumen27 halamanFinal Exam - Calculus - Physicsarvie montemayorBelum ada peringkat
- Rotational Dynamics: Angular Velocity and Angular AccelerationDokumen5 halamanRotational Dynamics: Angular Velocity and Angular AccelerationFoster TadiwanasheBelum ada peringkat
- Construction of Perpendicular Bisector - WorksheetDokumen8 halamanConstruction of Perpendicular Bisector - Worksheetbshashi9Belum ada peringkat
- Answers: Exercise 1.1Dokumen22 halamanAnswers: Exercise 1.1aeroacademicBelum ada peringkat
- 05 Finite Heisenberg SSWDokumen17 halaman05 Finite Heisenberg SSWJeoff Libo-onBelum ada peringkat
- Final - JR & SR Pre-Final Syllabus & Weightage 2020-2021Dokumen1 halamanFinal - JR & SR Pre-Final Syllabus & Weightage 2020-2021AbhiBelum ada peringkat
- Drawing Instruments and Their Uses: Chapter - 1ADokumen71 halamanDrawing Instruments and Their Uses: Chapter - 1AAttaUrRahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Diff Calc 1Dokumen3 halamanDiff Calc 1Jirah GicangaoBelum ada peringkat
- Up GeoinformaticsDokumen105 halamanUp GeoinformaticsSharadBelum ada peringkat
- Vector AlgebraDokumen14 halamanVector AlgebraShang Divina EbradaBelum ada peringkat
- Evan Dummit - Multiple - Integration - Calculus III - 2018 PDFDokumen24 halamanEvan Dummit - Multiple - Integration - Calculus III - 2018 PDFogasofotiniBelum ada peringkat
- Enhancement Activity/Outcome (Lesson 1) : No Answers YetDokumen3 halamanEnhancement Activity/Outcome (Lesson 1) : No Answers YetWinxPink 17Belum ada peringkat