Maths & Mech Formulas
Diunggah oleh
gunasekaranHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Maths & Mech Formulas
Diunggah oleh
gunasekaranHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
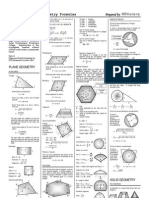
FORMULAS FOR AREA:
SQUARE
Area = a x a
Area = d x d
2
RECTANGLE
Area = a x b
PARALLELOGRAM
Area = a x b
RIGHT-ANGLED TRIANGLE
Area = a x b
2
ACTUE ANGLED TRIANGLE
Area = c x h
2
Area = s (s-a) x (s-b) x (s-c)
Where, s = (a + b + c)
OBTUSE ANGLED TRIANGLE
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
Area = b x h
2
Area = [s(s-a) x (s-b) x (s-c)]1/2
Where,
s = (a + b + c )
RIGHT ANGLE WITH 2 45 ANGLE
Area = a x a
2
b = 1.414 x a; h = 0.7071 x a;
EQUILATERIAL TRIANGLE
Area = a x h
2
h = 0.866 x a
TRAPEZOID
Area = (a + b) x h
2
REGULAR HEXAGON
A = Area
R = Radius of circumscribed circle
r = Radius of inscribed circle
A = 2.598 a2 = 2.958 R2 = 3.4654 r2
R = a = 1.155 r
REGULAR OCTAGON
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
A = Area
R = Radius of circumscribed circle
r = Radius of inscribed circle
A = 4.828 x a2 = 2.598 x R2 = 3.464 x r2
R = 1.307 x a = 1.082 x r
REGULAR POLYGON
A = Area n = Number of sides
= 360 = 180 -
n
A=nxrxa
2
R = [ r2 + a2/4]1/2 ; r = [ R2 a2/4]1/2 x a = 2 [ R2 r2]1/2
CIRCLE
Area = x r2 = x d =circumference
HALFCIRCLE OR SEMICIRCLE
Area = x r2
2
CIRCULAR SECTOR
Area = r2 x x (angle)
360
a (Arc) = r x x
180
= 57.296 x a; r = 2A
r a
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
CIRCULAR SEGMENT
A =area = Angle c = Cord
A = Area of sector area of triangle
C = 2 x r x sin /2
ELLIPSE
A = Area P = Perimeter
A=xaxb
An approximate formula for perimeter
P = x 2 ( a 2 + b2 )
ELLIPSE
Locating point on ellipse
a/b = c Ratio of minor axis to major axis
X = a2 ( 2c x Y2 )
Y = a2 x2
c
CYLINDIRICAL SURFACE
Area = 3.1416 x d x h
CONIICAL SURFACE
Area = x r x (r2 + h2)1/2
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
FRUSTUM OF CONE SURFACE
Area = 1.5708 x [ (R r)2 + h2 ] x [D + d]
SPHERE SURFACE
Area = 4 x x r2
SURFACE OF SPHERICAL SEGMENT
Area = 2 x x r x h
= (C2/4 + h2)
Where, C = 2 h(2r h)
CIRCULAR RING
Area = x (R2 r2)
= x (R + r) (R r)
= 0.7854(D2 d2)
CIRCULAR RING SECTOR
Area = x (R2 r2)
360
= x (D2 d2)
360
SPANDREL OR FILLET
Area = r2 - x r2
4
HOLLOW CIRCLE
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
Area = x (D2 d2)
4
HYPERBOLA
Area of ABC = xy _ ab x In(x/a + y/b)
2 2
PARABOLA
L = Length of arc
L = p/2 { 2x/p * ( 1 + 2x/p ) In ( 2x/p + 1 + 2x/p) }
When x is the small proportion to y, the following is a close
approximation:
L = y { 1 2/3 (x/y)2 2/5(x/y)4 } or L = y2 + 4/3 x2
Area = 2/3 * x * y
The area is equal to two third of a rectangle which has x for its base and y
for its height.
SEGMENT OF PARABOLA
Area BFC = 2/3 area of parallelogram BCDE
If the FG is the height of the segment,
measured at right angles to BC then:
Area of segment BFC = 2/3 x BC x FG
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
CYCLOID
Area = 3 x x r2
= 3 x area of generating circle
Length of cycloid = 8 r = 4 d
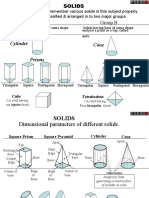
FORMULAS FOR VOLUME:
CUBE
Volume = a x a x a
a =3 Volume
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
SQUARE PRISM
Volume = a x b x c
PRISM
Volume = Height x Area of end surface
CYLINDER
Volume = 3.1416 x r2 x h
CONE
Volume = x r2 x h
3
FRUATUM OF CONE
Volume = 0.2618 x h ( D2 + D*d + d2 )
SPHERE
Volume = 4 x x r3 = x d3
3 6
SPHERICAL SECTOR
Volume = 2 x x r2 x h
3
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
SPHERICAL SEGMENT
Volume = x h2 x ( r h/3 )
= x h x ( C2/8 + h2/6 )
SPHERICAL ZONE
Volume = 0.5236 x h [ 3C12/4 + 3C22/4 + h2 ]
A = Area of spherical surface
A=2xxrxh
Where, r = C22/4 [ C22 C12 4h2 ] / 8h
SPHERICAL WEDGE
Volume = / 360 x ( 4 x x r3/3 )
A = Area of spherical surface
A = / 360 x 4r2
HOLLOW SPHERE
Volume = 4 / 3 (R3 r3)
= /6 (D3 d3 )
PORTION OF CYLINDER
Volume = 1.5708 x r2 (h1 + h2)
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
PORTION OF CYLINDER
Volume = { 2/3 x a3 b x area of ABC } x h/rb
A= Area of cylindrical surface
A = { ad b x length of arc ABC } x h/r b
Use + when base area is larger and when base area is less than one
half the base circle.
HOLLOW CYLINDER
Volume = x h ( R2 r2)
= x r x h (2R t)
= x r x h (2r + t )
= x r x h (R + r)
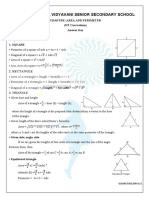
CENTER OF GRAVITY:
DEFINATION:
The center of gravity is an area or body is the point through which
about any axis the moment of the area or body is zero. If a body of
homogenous material at the center of gravity were suspended it would be
balanced in all direction.
The center of gravity of symmetrical areas as square, rectangle, circle,
etc. coincides with the geometrical center of the area. For areas which are Of
symmetry.(axis y-y)
not symmetrical or which are symmetrical about one axis only. The center of
gravity may be determined by calculation.
The center of gravity is located on the centerline
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
To determine exact location of it:
Divide the area into 3 rectangle and calculate
the area of each.(A,B,C)
Determine the center of gravity of the rectangles
and determine the distances a, b and c to a
selected axis(x-x) perpendicular to axis y-y.
Calculate distance y to locate the center of
gravity by the formula:
y = Aa + Bb + Cc
A+B+C
The area is not symmetrical about any axis. The center of gravity may be
determined by calculating the moment with reference to two selected axes.
To determine the distances of center of gravity to these axes:
Divide the area into the 3 rectangles and
calculate the areas of each(A,B,C)
Determine the center of gravity of the
rectangles and the distances a, b, and c
to x-x axis and the distances a1,b1,c1
to axis y-y.
Calculate distances x and y by the formulas:
X = Aa1 + Bb1 + Cc1
A+B+C
Y= Aa + Bb + Cc
A+B+C
PERIMETER OF A TRIANGLE
If A, B and C are the middle points of the sides of
the triangle, then the center of gravity is at the
center of the circle that the center of gravity from
side a is:
d= h(b +c)
2(a + b + c)
Where h is the height perpendicular to a.
AREA OF TRIANGLE
The center of gravity is at the intersection of
lines AD and BE, which bisect the sides BC
and AC. The perpendicular distance from the
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
center of gravity to any one of the sides is
equal to one third the height perpendicular
to that side. Hence,
A=h3
AREA OF TRAPEZOID
The center of gravity is on the line joining the
middle points of parallel lines AB and DE.
c = h(2a + 2b) d = h(2a + b)
3(a + b) 3(a + b)
e = a2 + ab + b2
3(a+b)
the trapezoid can also be divided into two
triangle. The CG is at the intersection of
the line joining the CG of the triangles,
and the middle line FG.
PARALLELOGRAM
Perimeter of a parallelogram
The CG is t intersection of diagonals.
Area of a parallelogram
The CG is t intersection of diagonals.
CIRCULAR ARC (approximate)
A=2xh
3
this formula is very nearly exact for all
arcs less than one-quarter of the periphery.
The error is only about one per cent for a quarter,
circle, and decreases for smaller arcs.
CIRCULAR ARC
The CG is on the line that bisects the arc, at a distance
a = r x c = c(c2 + 4h2) form the center of the circle.
l 8lh
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
For an arc equal to one-half the periphery:
a = 2r
For an arc equal to one-quarter of the periphery:
a = 2r 2
for a arc equal to one-sixth of the periphery:
a = 3r
ANY FOUR SIDES FIGURE
Two cases are possible, as show in the illustration.
To find the CG of the four-sided figure ABCD each of
the sides is divided into three equal parts. A line is then
drawn thorough each pair of division points next to the
points of intersection A, B, C and D of the sides of the
figure. These lines form a parallelogram EFGH; the
intersection of the diagonals EG and FH locates the
CG of figure.
CIRCLE SEGMENT
The distance of the CG from the center
of the circle is:
b = c3 = 2/3 x r3 sin3
12 A A
Where A = area of segment.
CIRCLE SECTOR
Distance b from CG to center of circle is:
b = 2rc = r2c
3l 3A
Where, A = area of sector , and is
expressed in degrees.
For the area of a half circle.
b = 4r 3
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
For the area of a quarter circle.
b = 42 x r 3
For the area of a sixth of a circle.
b = 2r
PART OF CIRCLE RING
Distance b from CG to center of circle is:
b = 38.197(R3 r3) sin
(R2-r2)
Angle is expressed in degree.
SPANDREL OR FILLES
Area = 0.2146R2
X = Y = 0.2234 R
SEGMENT OF AN ELLIPSE
The CG of an elliptic segments ABC.
Symmetrical about one of the axes coincides with
the center of gravity of the segment DBF of a circle,
the diameter of which is equal to that axis of the
ellipse about which the elliptic segments is
symmetrical.
PARABOLA
For the complete parabolic area , the CG
is on the center line or axis, and
a = 3h/ 5
For one-half of the parabola:
a = 3h/5 and b = 3w/8
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
For the complement area ABC:
c = 0.3 h and d = 0.75 w
SPHERICAL SURAFACE OF SEGMENTS AND ZONES OF
SPHERE:
Distance a and b which determine the CG are:
A = h/2
B = H/2
CYLINDER
The center of gravity of a solid cylinder
(or prism) with parallel end surfaces, is located
at the middle of the line that joins the centers of
gravity of the end surfaces.
The center of gravity of a cylindrical
Surface or shell. With the base or end surface
In one end is found from:
a = 2h2
4h + d
CYLINDER CUT OFF
The CG of a cylinder cut off by an inclined
Plane is located by:
a = h/2 + (r2 tan2 ) / 8h , b = r2tan /4h
where is the angle between the obliquely cut off surface & the base surface
PORTION FO CYLINDER
For a solid portion of a cylinder as shown
the center of gravity is determined by:
a = 3/16 x x r b= 3/32 x x h
For the cylinder is hollow, the CG of
The solid shell is found by:
a = 3/16 x x R4 r4
R 3 r3
PYRAMID
In a solid pyramid the center of gravity is
located on the line joining the apex with the
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
center of gravity of the base surface at a distance
from the base equal to one quarter of the
height or a = 1/3 h
The center of gravity of the triangular surfaces
forming the pyramid is located on the line joining
the apex with the center of gravity of the base
surface. At a distance from the base equal to one
third of the height or a =1/3 h.
CONE
The same rules apply as for the pyramid
For the solid cone:
-a = h
For the conical surface:
-a = 1/3 h
FRUSTUM OF PYRAMID
The center of gravity is located on the line
that joins the CG of the end surfaces.
If A1 = area of base surface, and
A = area of top surface
A = h(A1 + 2 A1 x A2 + 3A2)
4 (A1 + A1 x A2 + A2)
FRUSTUM OF CONE
The same rules apply as for the frustum
of a pyramid. For a solid frustum of a
circular cone the formula:
a = h(R2 + 2Rr + 3r2)
4(r2 + Rr + r2)
The location of the CG of conical surface
of a frustum of a cone is :
a = h(R + 2r)
3(R + r)
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
WEDGE
The center of gravity line is on the line
joining the CG of the base with the
middle point of the edge and located at:
a = h(b + c)
2(2b + c)
SPHERICAL SEGEMENT
The center of gravity of a solid segment
is determined by:
a= 3(2r h)2
4(3r h)
b =h(4r h)
4(3r h)
For half sphere a = b =3/8 r
HALF OF HOLLOW SPHERE
The center of gravity is located at
a = 3(R4 r4)
8(R3 r3)
SPHERICAL SECTOR
The center of gravity is located at:
a = 3/8 ( 1 + cos) r = 3/8(2r h)
CENTER OF GRAVITY OF TWO BODIES
If the weight of the bodies are P and Q
and the distance between their CG is a, then
b = Qa c= Pa
P+Q P+Q
HEMISPHERICAL DISHED END
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
WEIGHT CALCULATION
Major formula for calculate the weight of any body, part, etc.
WEIGHT = VOLUM X SPECIFIC GRAVITY
Here some parts weight calculation is given:
RECTANGULER PLATE:
Weight = Volume x specific gravity
= length x width x thk x specific gravity
CIRCULER PLATE
Weight = Volume X specific gravity
= area of circle x thk of plate x specific gravity
SHELL COURSES
Weight = Volume of hollow cylinder x specific gravity
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
All LINEAR DIMENSION ARE IN MM.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Solid Mensuration FormulasDokumen2 halamanSolid Mensuration FormulasAllen Ang Naiba89% (70)
- Addition of Vectors: - Analytical MethodDokumen7 halamanAddition of Vectors: - Analytical MethodNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics 6 - Third Periodical TestDokumen5 halamanMathematics 6 - Third Periodical TestReichelle Flores100% (6)
- All Math FormulasDokumen27 halamanAll Math FormulasMubassher Ahmed Shoaib100% (1)
- MensurationDokumen20 halamanMensurationmaheshgullanki100% (1)
- Mathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryDokumen5 halamanMathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryabhiBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Formulae: Number and AlgebraDokumen7 halamanEssential Formulae: Number and AlgebraShinigami01001Belum ada peringkat
- Elementary Tutorial: Fundamentals of Linear VibrationsDokumen51 halamanElementary Tutorial: Fundamentals of Linear VibrationsfujinyuanBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical FormulaeDokumen1 halamanMechanical FormulaeRanjith KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Conical FrustumDokumen11 halamanConical FrustumRajaKuppanBelum ada peringkat
- Combustion Eng'g ProblemsDokumen16 halamanCombustion Eng'g ProblemsRogelyn JosolBelum ada peringkat
- 10th Maths Surface Areas and Volumes The SchoolhouseDokumen38 halaman10th Maths Surface Areas and Volumes The Schoolhouseharman161140% (5)
- Chapter Four: FuelsDokumen40 halamanChapter Four: Fuelsbiruk1Belum ada peringkat
- Steam Nozzles - Gss - Unit5 PDFDokumen41 halamanSteam Nozzles - Gss - Unit5 PDFkavya nainitaBelum ada peringkat
- Surface Area and VolumeDokumen49 halamanSurface Area and VolumeKabeer GolechhaBelum ada peringkat
- BevelDokumen11 halamanBevelsanjay aBelum ada peringkat
- Structural FormulasDokumen29 halamanStructural Formulaskevin John EstilloreBelum ada peringkat
- 2 CorrectionDokumen37 halaman2 CorrectionJeah Joyce LagrimasBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set For Work ProblemsDokumen2 halamanProblem Set For Work ProblemsMaria Jessa BruzaBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics - Lecture Notes - Unit 4Dokumen71 halamanFluid Mechanics - Lecture Notes - Unit 4Mohan Prasad.MBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 PDFDokumen7 halamanChapter 11 PDFKshitij SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- 8-6 TrapezoidsDokumen12 halaman8-6 TrapezoidsGem Lam SenBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes in Fluid MechanicDokumen49 halamanLecture Notes in Fluid MechanicflashtronBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Fabrication of Plastic Bottle and Can Crusher For Recycling PurposeDokumen3 halamanDesign and Fabrication of Plastic Bottle and Can Crusher For Recycling PurposeInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2. Vector Operation in Analytical and Graphical MethodDokumen7 halamanChapter 2. Vector Operation in Analytical and Graphical MethodRampage YT100% (1)
- Coal Miners SuitDokumen4 halamanCoal Miners SuitSudipta BainBelum ada peringkat
- Let 8 ArDokumen7 halamanLet 8 ArAmro TajBelum ada peringkat
- Gear Ratio CalculationDokumen6 halamanGear Ratio CalculationvenkateswaranBelum ada peringkat
- CHE 111 Tutorial 2 Semester I 2021Dokumen4 halamanCHE 111 Tutorial 2 Semester I 2021Pasmore ndelekiBelum ada peringkat
- Traverse Point For MeasurementDokumen2 halamanTraverse Point For MeasurementsudheerBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment 3 Problem SolvingDokumen3 halamanAssessment 3 Problem Solvinglaurence Dave Belason100% (1)
- CH 14Dokumen11 halamanCH 14hirenpatel_universalBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1 MATH13Dokumen52 halamanLesson 1 MATH13Randel Boris de Ocampo100% (4)
- DynamicsDokumen3 halamanDynamicsjj012586Belum ada peringkat
- Surveying Lecture 100620Dokumen2 halamanSurveying Lecture 100620John Dalton ValenciaBelum ada peringkat
- Mobile Lubrication Bijur DelimonDokumen12 halamanMobile Lubrication Bijur DelimonFAVIOBelum ada peringkat
- Balance Sheet AnsDokumen6 halamanBalance Sheet Ansيوسف عبدالرحمن رمضانBelum ada peringkat
- A Prism Is A 3D Shape That Has A Constant: Cross-Section Along Its LengthDokumen14 halamanA Prism Is A 3D Shape That Has A Constant: Cross-Section Along Its Lengthzhu qingBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Terminology - PDF Version 1 PDFDokumen31 halamanEngineering Terminology - PDF Version 1 PDFAjayBravoBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1 Metal RemovalDokumen40 halaman3.1 Metal RemovalMichael Kearney50% (2)
- Unit 14 Areas and Volumes (Word Problems)Dokumen13 halamanUnit 14 Areas and Volumes (Word Problems)bemdasBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Analytic TrigonometryDokumen20 halamanChapter 1 - Analytic Trigonometrysimsonisna100% (1)
- Height of Instrument MethodDokumen17 halamanHeight of Instrument MethodkoppolusrinivasuluBelum ada peringkat
- Anallytic Geometry LarinDokumen3 halamanAnallytic Geometry LarinanjoBelum ada peringkat
- Mesl Elements 3Dokumen227 halamanMesl Elements 3Barb BarianBelum ada peringkat
- BouyancyDokumen2 halamanBouyancyEugine Balomaga0% (1)
- Design of ChainDokumen9 halamanDesign of ChainArun Pravin APBelum ada peringkat
- CHPT 7Dokumen51 halamanCHPT 7jimbob7410Belum ada peringkat
- Saint Louis College: College of Engineering and ArchitectureDokumen3 halamanSaint Louis College: College of Engineering and ArchitectureRhey LuceroBelum ada peringkat
- Problems Quiz PROB and STAT CHE With Answer KeyDokumen2 halamanProblems Quiz PROB and STAT CHE With Answer KeyInah KurtBelum ada peringkat
- Ajide Oluwamayowa Oluwatobi 12-30gd017Dokumen103 halamanAjide Oluwamayowa Oluwatobi 12-30gd017Aina Praise OluwashogoBelum ada peringkat
- Bangun RuangDokumen17 halamanBangun Ruangsam_raunayBelum ada peringkat
- Trigonometry PresentationDokumen55 halamanTrigonometry PresentationNazir PriceBelum ada peringkat
- Ball MillDokumen4 halamanBall MillGM MalikBelum ada peringkat
- Key Formulas MathsDokumen7 halamanKey Formulas MathsAdil Ghaznavi50% (2)
- Grade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet Area and Perimeter Answer KeyDokumen7 halamanGrade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet Area and Perimeter Answer Keygeetha100% (1)
- Grade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet 2 Area and PerimeterDokumen8 halamanGrade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet 2 Area and PerimetergeethaBelum ada peringkat
- Mensuration of Formulary For SSS3Dokumen5 halamanMensuration of Formulary For SSS3Imumonlen OHIS PETERBelum ada peringkat
- Math Formula Chart: Perimeter CircumferenceDokumen4 halamanMath Formula Chart: Perimeter CircumferenceBhushan SrivatsaBelum ada peringkat
- Engr DiaryDokumen168 halamanEngr DiaryGunaBelum ada peringkat
- MensurationDokumen0 halamanMensurationBalabhadruni SowmyaBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 8-Development of SurfacesDokumen2 halamanTutorial 8-Development of SurfacesrudranshBelum ada peringkat
- Williams Ground Anchor SystemsDokumen76 halamanWilliams Ground Anchor SystemsVigneshBelum ada peringkat
- Ee324 Hw#6 Spring12Dokumen11 halamanEe324 Hw#6 Spring12Jobayer AhamedBelum ada peringkat
- 4024 s11 QP 22 PDFDokumen24 halaman4024 s11 QP 22 PDFMuhammad WajdanBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Drawing Textbook Intro by N D BhattDokumen11 halamanEngineering Drawing Textbook Intro by N D BhattAizaz Shamshad100% (1)
- Projection of SolidsDokumen23 halamanProjection of SolidsUsama AnsariBelum ada peringkat
- Math6 Week8Dokumen10 halamanMath6 Week8Donna Lornne CabutajeBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematical Studies Paper 1 TZ1 SLDokumen20 halamanMathematical Studies Paper 1 TZ1 SLAbid_raufBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge O Level: Mathematics (Syllabus D) 4024/22Dokumen20 halamanCambridge O Level: Mathematics (Syllabus D) 4024/22محمد مجتبی راحیلBelum ada peringkat
- Exam 3 Review SlidesDokumen75 halamanExam 3 Review Slidesnael94Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorial-2 Surface IntegralDokumen1 halamanTutorial-2 Surface IntegralKathiravanHaridasBelum ada peringkat
- PDC Bit Design: Bit Profile and Cutter OrientationDokumen23 halamanPDC Bit Design: Bit Profile and Cutter OrientationFarouq Eng100% (1)
- Unit 3 Projection of SolidsDokumen58 halamanUnit 3 Projection of SolidsShokeen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering GraphicsDokumen1 halamanEngineering GraphicsPrabaakaran KandasamyBelum ada peringkat
- Third Periodical Test in Math 6Dokumen5 halamanThird Periodical Test in Math 6BERNADETTE TADURANBelum ada peringkat
- June 2018 QP - C4 EdexcelDokumen9 halamanJune 2018 QP - C4 EdexcelВася МищенкоBelum ada peringkat
- ST - Stephen - Girl - College - F3 Math P1 17 18 Final ExamDokumen13 halamanST - Stephen - Girl - College - F3 Math P1 17 18 Final ExamTommy UwuuwuBelum ada peringkat
- Maths 1Dokumen61 halamanMaths 1Zulhanif IdrisBelum ada peringkat
- AnalyticDokumen49 halamanAnalyticEdelyn Lindero AmbosBelum ada peringkat
- Graduate School: Final Examination For The 1 Semester of School Year 2020 - 2021Dokumen1 halamanGraduate School: Final Examination For The 1 Semester of School Year 2020 - 2021Jemar Quezon LifanaBelum ada peringkat
- Dyanmic Cone Penetrometer (DCP) Test MS WORDDokumen5 halamanDyanmic Cone Penetrometer (DCP) Test MS WORDAvinash LalBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/04Dokumen64 halamanCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/04lhaBelum ada peringkat
- PT - Mathematics 5 - Q3Dokumen6 halamanPT - Mathematics 5 - Q3Jessmiel Labis100% (1)
- Conic Section PDFDokumen22 halamanConic Section PDFishad satyen100% (2)
- EG Unit 1Dokumen7 halamanEG Unit 1Jayakrishna KandasamyBelum ada peringkat
- (A Treatise On Natural Philosophy 2 (Kelvin Tait 1912)Dokumen560 halaman(A Treatise On Natural Philosophy 2 (Kelvin Tait 1912)LurzizareBelum ada peringkat
- Volumes and Surface Area Homework 1Dokumen9 halamanVolumes and Surface Area Homework 1swati goelBelum ada peringkat
- All Subject Module 2023 g6Dokumen31 halamanAll Subject Module 2023 g6charene bolfangoBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge O Level: Mathematics (Syllabus D) 4024/11Dokumen20 halamanCambridge O Level: Mathematics (Syllabus D) 4024/11Everything EverythingBelum ada peringkat