Parts of Speech
Diunggah oleh
Irtizahussain0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
23 tayangan2 halamankk
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inikk
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
23 tayangan2 halamanParts of Speech
Diunggah oleh
Irtizahussainkk
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
The
Eight Parts of Speech
Nouns, Pronouns, Adjectives, Verbs, Adverbs, Conjunctions, Prepositions and Interjections at
a Glance
NOUNS name people, places, things, or ideas. They can be common or proper (like teacher or Dr.
Smith) and they can also be concrete or abstract (like letter or honor). Every proper sentence has a
subject, and a subject can be a noun, or a pronoun. So what is a pronoun?
The PRONOUN is said to "take the place of a noun," although a possessive pronoun can be used as
an adjective. Just think, what if a book read: See Spot run. See Spot jump. See Spot walk. This
would be a terrible book! This is why the pronoun was invented; the usage of pronouns
dramatically decreases the number of times that you must directly refer to Spot.
Personal pronouns: I am me, you are he, we are us, they are them, etc. If you did not know who Spot
was, you could just say, He ran.
Possessive pronouns: This is my precious! Mine! It is not yours or hers or theirs! NO apostrophes
can be used with possessive personal pronouns. Think about itIt is not *your is or her is or there
is!*makes no sense.
Indefinite pronouns: Spot needs help! Somebody help! Anybody? Come on everyone, please?
Interrogative pronouns ask questions. They are: who, whom, what, which, and whose. Pretend you
are interrogating Spot. Who are you? Whom did you seek? What is his name? Whose hat is this?
Which door did you enter?
Demonstrative pronouns: This, that, these, and those (there are only four!). Pretend you are giving
a tour and demonstrating the use of certain objects. This is Spots house! That is where he prepares
for races, and these are his trophies. Oh, and those are pictures of when he was little.
The ADJECTIVE modify (describe) nouns or pronouns. For instance, we could say: Spot was brave
and victorious! or The talented and dedicated Spot ran. Possessive nouns and pronouns can be
adjectives, too; That is Spots house! or That is his house! are sentences that both use possessive
words to describe house.
Note: Articles like "the," "a," and "an" are all adjectives.
The VERB shows action, makes a statement, or shows a link between word relationships.
Action verbs show action: Spot ran.
Linking verbs make statements OR they express links and relationships. Spot is fast.
Linking verbs include: am, is, are, was, were, be, being, been, has been, have been, had been, will
be, shall be, may be, would have been, should have been, can be, should be, would be (any
combination that ENDS with be or been.) seem, and become. The words taste, feel, smell, sound,
look, appear, grow, remain, and stay may be used as action or linking verbs.
ADVERBS modify (describe!) verbs. An adverb can also modify adjectives and other adverbs.
Adverbs answer where? when? how? how often? and to what extent. Let us test these
questions:
Where is Spot? Here he is at the finish line!
When is Spot going to run? Spot will run today and tomorrow and forever in our hearts and minds.
How will Spot run? Spot will run quickly and easily. *Note the ly endings. This is common for
adverbs.
How often will Spot run? Spot will run always!
To what extent will Spot run? Spot will run really well!
The PREPOSITION shows relationship between nouns or pronouns and other words in a sentence.
Prepositional phrases usually contain the preposition and a noun that is the object of the
preposition.
Hint: One common way to check if a word is a preposition is to use the formula ______ the cloud.
Under the cloud? Beneath the cloud? To the cloud? Inside the cloud?
Be careful: Make sure that the object of a preposition is a noun. If it is a verb, you are not dealing
with a preposition.
CONJUNCTIONS are connecting words.
Coordinating conjunctions connect words, phrases, and independent clauses (a group of words
that could be a sentence by itself). Spot and I did not stop running or walking but once, for we were
not tired. (See how We were not tired is a sentence connected to a sentence with a conjunction?)
Subordinating conjunctions introduce dependent clauses (a group of words that cannot stand
alone as a proper sentence).
For instance: Although sick, Spot soldiered on.
INTERJECTIONS are exclamatory words that express strong emotion.
Ouch! My shoulder is killing me, Crikey, this is a big crocodile, Fail! I was so close to winning,
Alas, Spot is with us no more,
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Determination of Caffeine in Beverages by HPLCDokumen3 halamanDetermination of Caffeine in Beverages by HPLCIvelisse03120% (1)
- Oxford TCC ExamDokumen36 halamanOxford TCC ExamLolaBelum ada peringkat
- Writing Feature Stories - How To Research and Write Newspaper and Magazine ArticlesDokumen301 halamanWriting Feature Stories - How To Research and Write Newspaper and Magazine ArticlesGCala666100% (5)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Sith LanguageDokumen6 halamanSith LanguageMáirtín Ó hUallacháin100% (2)
- Poetry Terms Scavenger HuntDokumen3 halamanPoetry Terms Scavenger Huntapi-248420848Belum ada peringkat
- Reading Meeting Me and Uncle Romie Day 2Dokumen3 halamanReading Meeting Me and Uncle Romie Day 2api-252145631100% (1)
- Performance Tasks For English Language ArtsDokumen20 halamanPerformance Tasks For English Language ArtsMelisa StoccoBelum ada peringkat
- Flywheel: Flywheels-Function Need and OperationDokumen11 halamanFlywheel: Flywheels-Function Need and OperationKristian John B Rabino100% (2)
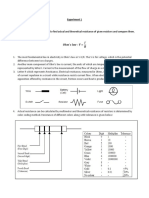
- The Purpose of This Experiment Is To Find Actual and Theoretical Resistance of Given Resistors and Compare ThemDokumen10 halamanThe Purpose of This Experiment Is To Find Actual and Theoretical Resistance of Given Resistors and Compare ThemIrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- Newton's "Derivation" of The Inverse Square Law of GravityDokumen7 halamanNewton's "Derivation" of The Inverse Square Law of GravityIrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- GIKIAA FA 2013-14 - v3.7 - (Reg No) - (Full Name)Dokumen10 halamanGIKIAA FA 2013-14 - v3.7 - (Reg No) - (Full Name)IrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- MathematicsDokumen30 halamanMathematicsIrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- Necessary Data Pertaining To Engineering Programs: FOR Electrical Engineering ProgramDokumen10 halamanNecessary Data Pertaining To Engineering Programs: FOR Electrical Engineering ProgramIrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- Application Form USAID Funded Merit & Need Based Scholarship For Regular Mba Students Seeking Admission in Fall 2014Dokumen13 halamanApplication Form USAID Funded Merit & Need Based Scholarship For Regular Mba Students Seeking Admission in Fall 2014IrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- Ex 6 4 FSC Part2 Ver 2 1 1Dokumen13 halamanEx 6 4 FSC Part2 Ver 2 1 1Sikandar KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Sr. # Reg. No. Name Faculty Hostel # Room #. TypeDokumen14 halamanSr. # Reg. No. Name Faculty Hostel # Room #. TypeIrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- Compound Pendulum0001 PDFDokumen8 halamanCompound Pendulum0001 PDFIrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- AssignmentDokumen6 halamanAssignmentIrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- Gessen, Masha - The Memory Keeper (New Yorker, 26 Oct 2015)Dokumen6 halamanGessen, Masha - The Memory Keeper (New Yorker, 26 Oct 2015)Hudson RabeloBelum ada peringkat
- Alexievich, Svetlana - The Man Who Flew (NYRB, 19 Nov 2015)Dokumen3 halamanAlexievich, Svetlana - The Man Who Flew (NYRB, 19 Nov 2015)IrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- DN 22Dokumen7 halamanDN 22rehmania78644Belum ada peringkat
- Faculty Positions On Website July 2017Dokumen5 halamanFaculty Positions On Website July 2017HaseebPirachaBelum ada peringkat
- Mill ML', 13 (1/2.: June 23, 1964Dokumen9 halamanMill ML', 13 (1/2.: June 23, 1964IrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- Texas Instruments Activity #10 Title: Exploring Taylor's Integrals Author: Charles P. Kost II Estimated Time: 40-50 Minutes NCTM StandardsDokumen4 halamanTexas Instruments Activity #10 Title: Exploring Taylor's Integrals Author: Charles P. Kost II Estimated Time: 40-50 Minutes NCTM StandardsIrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- 501 Critical Reading QuestionsDokumen283 halaman501 Critical Reading Questionsapi-3813392100% (9)
- Fifth Elephant 2013Dokumen15 halamanFifth Elephant 2013jose5000@latinmail.comBelum ada peringkat
- Algorithmic Mathematics PDFDokumen167 halamanAlgorithmic Mathematics PDFIrtizahussain50% (2)
- GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology - Time Table Fall 2017Dokumen3 halamanGIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology - Time Table Fall 2017doctorsur7Belum ada peringkat
- Req GridDokumen19 halamanReq GridIrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- Drinking Water and Infectious Disease - Paul Raymond Hunter Et Al. (CRC, 2003)Dokumen254 halamanDrinking Water and Infectious Disease - Paul Raymond Hunter Et Al. (CRC, 2003)IrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- Ap Suggested Reading ListDokumen6 halamanAp Suggested Reading Listapi-290988513Belum ada peringkat
- Como Dibujar Comics y Caricaturas - (By Karnatoons, 1997 36 Pages)Dokumen34 halamanComo Dibujar Comics y Caricaturas - (By Karnatoons, 1997 36 Pages)rcruces100% (5)
- Anexo Sistema+politico+y+estructura+de+pakistan Ang PDFDokumen8 halamanAnexo Sistema+politico+y+estructura+de+pakistan Ang PDFIrtaza AkramBelum ada peringkat
- Bearings Higher HomeworkDokumen10 halamanBearings Higher HomeworkBecca RickwoodBelum ada peringkat
- Hand Out 2014Dokumen67 halamanHand Out 2014IrtizahussainBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine Linguistics: The State of The Art: 1970-1980Dokumen49 halamanPhilippine Linguistics: The State of The Art: 1970-1980Roc-Haidee Guro BantogBelum ada peringkat
- English Paper I - Trial '10Dokumen4 halamanEnglish Paper I - Trial '10Roshan P NairBelum ada peringkat
- Bing 1Dokumen62 halamanBing 1Vania VasthiiBelum ada peringkat
- Metaphor Lesson PlanDokumen4 halamanMetaphor Lesson Planapi-316482781Belum ada peringkat
- PKBK3073 ELTM Topic4Dokumen12 halamanPKBK3073 ELTM Topic4Fadhila NadiaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 NotesDokumen2 halamanUnit 2 NotesSonam BaghaBelum ada peringkat
- Diessel 2011-De Dónde Provienen Los Morfemas GramaticalesDokumen18 halamanDiessel 2011-De Dónde Provienen Los Morfemas GramaticalesCristian OyarzoBelum ada peringkat
- Project On ICTDokumen59 halamanProject On ICTVinayPawarBelum ada peringkat
- Principal Parts of The Verb and Their FunctionsDokumen2 halamanPrincipal Parts of The Verb and Their FunctionsJuanmiguel Ocampo Dion SchpBelum ada peringkat
- Gender NounDokumen4 halamanGender NounAien Ghazali100% (1)
- Mission EssentialDokumen44 halamanMission EssentialfraudblawgBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet 2-Digital MarketingDokumen3 halamanWorksheet 2-Digital MarketingAbhishekBelum ada peringkat
- Analizing MeaningDokumen502 halamanAnalizing MeaningEmmanuel Hurtado100% (1)
- Well, Very Well, A LittleDokumen5 halamanWell, Very Well, A Littlevaleria saltosBelum ada peringkat
- Planificare Clasa A VII A EnglezaDokumen7 halamanPlanificare Clasa A VII A EnglezaȘtefana StefiBelum ada peringkat
- The Importance of SLA (Introduction)Dokumen3 halamanThe Importance of SLA (Introduction)Rizky Allivia LarasatiBelum ada peringkat
- Have Have GotDokumen3 halamanHave Have GotManuel Garcia GrandyBelum ada peringkat
- 9 London Bydayandby NightDokumen2 halaman9 London Bydayandby NightOana DuricanBelum ada peringkat
- English Q1 M2Dokumen27 halamanEnglish Q1 M2Rosie Florante0% (1)
- Quiz 1 Inlges 4Dokumen5 halamanQuiz 1 Inlges 4juan vargasBelum ada peringkat
- PMR English Marking CriteriaDokumen5 halamanPMR English Marking CriteriaTeoWC100% (1)
- HandoutsDokumen42 halamanHandoutsChen VillarinBelum ada peringkat
- Ankur's Sentence Correction Notes - V1.0Dokumen133 halamanAnkur's Sentence Correction Notes - V1.0Ali Aljuboori100% (2)
- The Sounds of English and Their RepresentationDokumen5 halamanThe Sounds of English and Their RepresentationbelbachirBelum ada peringkat