Hormones Secreted by Endocrine Glands
Diunggah oleh
aditya7324Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Hormones Secreted by Endocrine Glands
Diunggah oleh
aditya7324Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Hormones secreted by the main Endocrine Glands:
Endocrine Gland Hormone(s) Secreted Function(s) of Hormones
(1) Part of the Brain: The Control and Relay Centre of the Endocrine System.
Hypothalamus
om
(2) Pituitary Known as the "Master Gland", this part of the brain consists of three lobes called
"anterior", "interior" and "posterior".
t.c
Posterior -- Oxytocin - -- Stimulates utrine contraction and brest
po
contraction for milk release.
gs
Posterior -- Anti-Diuretic Hormone -- Stimulates re-absorption of water from kidney
lo
(ADH), also known as tubules.
.b
'vasopressin'. - -- Hypo- causes Diabetes Insipidus (large
up
amounts of urine produced).
ro
Anterior -- Prolactin (PRL) - -- Production of breast milk (works in men too).
cg
Anterior * Human Growth -- Growth
ps
Hormone (HGH) - -- Hypo- Dwarfism
ap
-- Hyper- Gigantism
://
-- Thyroid Stimulating -- Stimulates the thyroid to release thyroxin.
tp
Hormone (THS) -
ht
Anterior -- Adrenocorticotrophic -- Stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce:
Hormone (ACTH) - Corticosteroids - mineral corticoids
- glucocorticoids
- cortisol (natural anti-
inflammatory)
- androgens, e.g. acdosterone.
Anterior Luteinizing Hormone -- Brings about ovulation and maintains the
-- (LH) corpus luteum.
-
Anterior -- Follicle Stimulating -- Stimulates growth--development of Graafin
Hormone (FSH) - follicles (= a mature follicle in the ovary prior to
ovulation, containing a large fluid-filled cavity
that distends the surface of the ovary) on
approx. 28 day cycle.
-- Melanin Stimulating
Hormone (MSH)
-- Gonadotrophins - -- Secondary sexual characteristics.
Anterior -- Interstitial Cell -- Works on the seminiferous tubules in the testes
Stimulating Hormone – to produce sperm – which take 21 days to
(ICSH) - mature.
(If not ejaculated within 21 days, the sperm are
re-absorbed back into the body.)
Intermediate -- Intermedin - -- Control of melanocyte production.
(2) Pineal A pea-sized mass of nerve tissue attached by a stalk to the posterior wall of the
om
third ventricle of the brain, deep between the cerebral hemispheres at the back
of the skull.
t.c
(It functions as a gland, secreting the hormone melatonin - which regulates the
po
pituitary gland and is associated with the biological clock.)
gs
-- Melatonin - -- A hormone produced by the pineal gland in
lo
darkness but not in bright light.
.b -- Melatonin receptors in the brain react to this
up
hormone and synchronize the body to the 24
hour day--night rhythm, thus informing the
ro
brain when it is day and when it is night.
cg
-- Melatonin is derived from seratonin, with which
ps
it works to regulate the sleep cycle.
ap
(3a) Thyroid Part of the Thyroid--Parathyroid Gland, which is in the neck.
Gland
://
tp
-- Thyroxin - -- Concerned with the Basal Metabolic Rate
(BMR), which is the amount of energy the
ht
body uses, just to ‘tick over’.
Hyper-Thyroidism = ‘over-active thyroid’ =
Thyrotoxicosis
Symptoms: increase in BMR; increase in heart-
rate; loss of weight; hyper-activity; insomniac;
develops bulging eyes due to accumulation of fluid
behind the eye; may develop Goitre; possible link
with Attention Deficit Disorder.
Hypo-Thyroidism
Symptoms; decrease in BMR; weight gain;
lethargy; skin becomes dry and puffy; hair
becomes thin and brittle.
Causes: Derbyshire Neck (originally due to
insufficient iodine in the soil in Derbyshire),
Graves Disease, and Cretinism (= metal and
sexual development impaired, if occurs in
children).
-- Calcitonin - -- Uptake of calcium to bone.
(3b) Parathyroid Part of the Thyroid--Parathyroid Gland, which is in the neck.
Gland
-- Parathormone - -- Associated with the growth of muscle and
bone.
-- Distribution of calcium and phosphate in
the body.
Hyper- Causes transfer of calcium from the bones
to the blood; bones become fragile & easily
broken; osteoporosis.
om
(Parathormone activity is inhibited by oestrogen.)
Hypo- Lowers blood calcium levels, causing
t.c
tetany (which may be treated by injections of the
hormone); low calcium levels in skeletal muscle
po
(which may cause cramps).
gs
(4) Thymus The thymus gland is located straddled across the trachea & bronchi in the upper
lo
thorax (a bi-lobed organ in the root of the neck, above and in front of the heart).
.b
The thymus (a gland associated with the immune system), is enclosed in a
up
capsule and divided internally by cross-walls into many lobules (full of T-
lymphocytes). In relation to body size the thymus is largest at birth. It doubles in
ro
size by puberty, after which it gradually shrinks, its functional tissue being
cg
replaced by fatty tissue. In infancy the thymus controls the development of
ps
lymphoid tissue and the immune response to microbes and foreign proteins
(accounting for allergic response, anti immunity, and the rejection of organ
ap
transplants). T-lymphocytes migrate from the bone marrow to the thymus,
://
where they mature and differentiate until activated by antigen.
tp
-- Thymosin - -- Activates the immune system by activating the
ht
T-Cells (T-Killer Cells; T-Helper Cells; T-
Memory Cells).
-- T-Lymphocytes -- The thymus consists of lobules full of T-
lymphocytes (white blood cells associated with
antibody production).
-- T-lymphocytes migrate from the bone marrow
to the thymus, where they mature and
differentiate until activated by antigens.
(5) Pancreas The pancreas lies behind the stomach.
It is both exocrine (ducted) and endocrine (ductless).
As an exocrine gland it secrets enzymes (organic catalysts) into the small
intestine.
The enzymes are:
-- Pancreatic amylase (which breaks down polysaccharides, i.e. starch into
sugar)
-- Lipase (which breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol)
-- Proteases (which breaks down protein (polypeptide) into di-peptides).
The islets of Langerhans are within the pancreas.
Islets of Located within the pancreas. Contains groups of both Alpha- and Beta- cells.
Langerhans
Beta Cells -- Insulin - -- Conversion of glucose to glycogen.
-- Cellular up-take of Glucose.
-- Conversion of excess glucose to fat.
Hyper-
Hypo- causes Diabetes Mellitus:
Symptoms: Blood glucose levels rise
om
(hyperglycaemia). Glucose is excreted into the
urine (glycosuria) - which increases levels of
t.c
urination, causing dehydration.
po
As glucose levels in the blood increase, fats and
protein are broken-down for energy. Coma and
gs
death may follow if the symptoms are not treated.
lo
Alpha Cells -- Glucagon - .b -- Conversion of glycogen to glucose.
up
(6) Adrenal
Glands
ro
cg
Adrenal Medulla -- Adrenalin - Prepares the body for "fright, fight or flight" and
has many effects:
ps
-- Action of heart increased.
ap
-- Rate and depth of breathing increased.
://
-- Metabolic rate increased.
tp
-- Force of muscular contraction improves.
ht
-- Onset of muscular fatigue delayed.
-- Blood supply to the bladder and intestines
reduced, their muscular walls relax, the
sphincters contract.
-- Noradrenalin - Similar effects to adrenalin:
-- Constriction of small blood vessels leading to
increase in blood pressure.
-- Increased blood flow through the coronary
arteries and slowing of heart rate.
-- Increase in rate and depth of breathing.
-- Relaxation of the smooth muscle in the
intestinal walls.
Adrenal Cortex -- Corticosteroids - Glucocorticoids (e.g. cortisol, cortisone,
corticosterone)
-- Utilization of carbohydrate, fat and protein by
the body.
-- Normal response to stress.
-- Anti-inflammatory effects.
-- Hypersecretion of cortisol results in
Cushings Syndrome.
Mineralocorticoids (e.g. aldosterone)
-- Regulation of salt and water balance.
-- Hypersecretion of Alderosterone decreases
the potassium in the body (affecting nerve
impulse transmission and leading to
muscular paralysis).
om
(7) Ovaries Produce mature ova. Theoretical potential for 400-450 viable ova.
(Therefore the more and the longer pregnancies a woman has, the later her
t.c
menopause because there is no ovulation during pregnancy.)
po
-- Oestrogen - -- Break-down of the utrine wall.
gs
-- Progesterone - -- Builds up and maintains the uterus wall for
lo
embedding of fertilized egg.
.b -- Associated with secondary sexual
up
characteristics, e.g. body hair, breast
enlargement, changes in physical body.
ro
cg
(8) Testes Located outside the pelvic cavity.
ps
-- Testosterone - -- Development and function of male sex organs.
ap
-- Secondary sexual characteristics. e.g. body hair,
muscle development, voice change.
://
tp
ht
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- NEURODokumen201 halamanNEUROAilyn LoroBelum ada peringkat
- Sarms 1 - The Ultimate Guide To SarmsDokumen4 halamanSarms 1 - The Ultimate Guide To SarmsHumbert Gym ColombinaBelum ada peringkat
- Forensic Reports and Testimony: A Guide To Effective CommunicationDokumen2 halamanForensic Reports and Testimony: A Guide To Effective CommunicationNorfolk JournalBelum ada peringkat
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDokumen110 halamanAutonomic Nervous SystemVarsha Shende KhobragadeBelum ada peringkat
- Diaphragm Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandDiaphragm Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of The Endocrine System HypothalamusDokumen27 halamanAnatomy of The Endocrine System Hypothalamusdaphnereeze100% (1)
- AntidepresentDokumen34 halamanAntidepresentmariaBelum ada peringkat
- EndocrineDokumen144 halamanEndocrineaartiBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine SystemDokumen7 halamanEndocrine SystemMikaella Viador100% (2)
- Heart Attack & Drinking Warm WaterDokumen1 halamanHeart Attack & Drinking Warm Waterjoshua_sx180% (5)
- The Endocrine System Study Guide 101 PDFDokumen17 halamanThe Endocrine System Study Guide 101 PDFStephanie Kate PelenioBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Laboratory ValuesDokumen40 halamanNormal Laboratory ValuesPrincess Nasima M. Usngan100% (1)
- Hip Fracture of Proximal Femur SOAP COMPLETEDokumen10 halamanHip Fracture of Proximal Femur SOAP COMPLETEEj TuliaoBelum ada peringkat
- Anti Anxiety DrugsDokumen39 halamanAnti Anxiety DrugsArkene LevyBelum ada peringkat
- Vertigo Remedy EnglishDokumen4 halamanVertigo Remedy EnglishIyan Rokhadiyan100% (1)
- Scoliosis Case StudyDokumen4 halamanScoliosis Case StudysayedmBelum ada peringkat
- Stress and Adaptation & Crisis in IllnessDokumen42 halamanStress and Adaptation & Crisis in IllnessmariaBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar Stress FinalDokumen98 halamanSeminar Stress FinalSakthi DeviBelum ada peringkat
- Geriatrics 2Dokumen45 halamanGeriatrics 2Sree Latha100% (1)
- Soccer Programme U19 Pre in SeasonDokumen38 halamanSoccer Programme U19 Pre in SeasonJeffrey Peeko100% (1)
- Disoreder of PerceptionDokumen36 halamanDisoreder of PerceptionUmar Khan100% (1)
- ChemotherapyDokumen54 halamanChemotherapyPinanto IrwandyBelum ada peringkat
- Anti Depressants FinalDokumen61 halamanAnti Depressants FinalAuthor Nauman Shad100% (1)
- Health, Stress, and CopingDokumen43 halamanHealth, Stress, and CopingKar Gayee100% (1)
- Drugs Acting On The Immune SystemDokumen33 halamanDrugs Acting On The Immune SystemAnonymous iG0DCOf100% (1)
- NeurotransmittersDokumen1 halamanNeurotransmittersmegs13045Belum ada peringkat
- MH Exam 2 Study GuideDokumen24 halamanMH Exam 2 Study Guidewn4tb100% (1)
- Thorax and Lungs SGDokumen2 halamanThorax and Lungs SGDestinee Caple100% (1)
- Neurotransmitters 1Dokumen23 halamanNeurotransmitters 1Preety ShresthaBelum ada peringkat
- Legal MedDokumen42 halamanLegal Medaisajane_rmt100% (6)
- The Concepts of Conformity and ObedienceDokumen8 halamanThe Concepts of Conformity and Obedienceapi-545354167Belum ada peringkat
- Snomed CT RL (Outline)Dokumen23 halamanSnomed CT RL (Outline)kostya111Belum ada peringkat
- Pituitary Gland: The Master GlandDokumen15 halamanPituitary Gland: The Master GlandMohammed ShahanewzBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology - Endocrine HormonesDokumen40 halamanPharmacology - Endocrine HormoneskpsuanBelum ada peringkat
- Transactional AnalysisDokumen12 halamanTransactional AnalysisSayan ChandraBelum ada peringkat
- Chemotherapy ReviewDokumen6 halamanChemotherapy ReviewkemisseBelum ada peringkat
- The Right Choice: Smith&nephewDokumen4 halamanThe Right Choice: Smith&nephewapi-19808945Belum ada peringkat
- Endocrine Physiology: Dale Buchanan Hales, PHD Department of Physiology & BiophysicsDokumen64 halamanEndocrine Physiology: Dale Buchanan Hales, PHD Department of Physiology & Biophysicshamako02Belum ada peringkat
- I-Recover: Management Protocol For Long Haul COVID-19 Syndrome (LHCS)Dokumen4 halamanI-Recover: Management Protocol For Long Haul COVID-19 Syndrome (LHCS)sanja vojvodić100% (1)
- Alternative & Complementary Therapies: Play Therapy, Group/Individual Therapy, Yoga, ExerciseDokumen32 halamanAlternative & Complementary Therapies: Play Therapy, Group/Individual Therapy, Yoga, ExerciseVanetBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple SclerosisDokumen6 halamanMultiple SclerosisRonnel Alvin Antonio AdrianoBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParDokumen64 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParYackson FrankBelum ada peringkat
- Siemens Mri Magnetom Mreadings Prostate PDFDokumen100 halamanSiemens Mri Magnetom Mreadings Prostate PDFnanaa02Belum ada peringkat
- Drooling PDFDokumen2 halamanDrooling PDFSuprit SnBelum ada peringkat
- Small Animals - Advances - in - Fluid, - Electrolyte, - and - Acid-Base - DisordersDokumen323 halamanSmall Animals - Advances - in - Fluid, - Electrolyte, - and - Acid-Base - Disordersprolixe108100% (1)
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing Ii: Nurse Hooman, RN 2020Dokumen130 halamanMaternal and Child Health Nursing Ii: Nurse Hooman, RN 2020Charlaine Gripal SudlaBelum ada peringkat
- Central Nervous SystemDokumen85 halamanCentral Nervous SystemmanuelBelum ada peringkat
- Anthelmintic DrugsDokumen35 halamanAnthelmintic DrugsRamla KashifBelum ada peringkat
- Physician To Population Ratios Physician Supply StandardsDokumen5 halamanPhysician To Population Ratios Physician Supply StandardsjackeldescargadorBelum ada peringkat
- Fin 20160705 Stimulants-And-Ssris PDFDokumen2 halamanFin 20160705 Stimulants-And-Ssris PDFmahesh babu100% (1)
- List of Cranial NervesDokumen2 halamanList of Cranial NervesKay Lumpas Cruda100% (1)
- SchizophreniaDokumen43 halamanSchizophreniaJun TangonanBelum ada peringkat
- Medical and Surgical Nursing Notes For NLEDokumen63 halamanMedical and Surgical Nursing Notes For NLEBel Zeta DonaireBelum ada peringkat
- Journal of Endocrine DisordersDokumen9 halamanJournal of Endocrine DisordersAustin Publishing GroupBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System Study GuideDokumen5 halamanEndocrine System Study GuideClaudia SanchezBelum ada peringkat
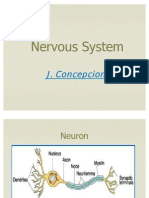
- Nervous SystemDokumen8 halamanNervous Systemfadedphotograph12340Belum ada peringkat
- Review of Endocrine SystemDokumen32 halamanReview of Endocrine SystemJames FBelum ada peringkat
- Psyche Signs and SymptomsDokumen8 halamanPsyche Signs and SymptomsLloyd Rafael EstabilloBelum ada peringkat
- Cushing Triad: Bradycardia, Wide Pulse Irregular RespirationsDokumen3 halamanCushing Triad: Bradycardia, Wide Pulse Irregular RespirationsZachary T HallBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Parameter: Management of Dementia (An Evidence-Based Review)Dokumen13 halamanPractice Parameter: Management of Dementia (An Evidence-Based Review)Jeni JimBelum ada peringkat
- Contact Dermatitis ModuleDokumen68 halamanContact Dermatitis Moduletimvrghs123Belum ada peringkat
- Pedia Drug Study NaproxenparacetamolDokumen3 halamanPedia Drug Study NaproxenparacetamolKuro HanabusaBelum ada peringkat
- 1.3 Blood ClottingDokumen10 halaman1.3 Blood ClottingMimie Marina Lam100% (1)
- Terminology of PsychiatryDokumen6 halamanTerminology of PsychiatryHassan.shehri100% (1)
- Schizophrenia: Vaisnvi Muthoovaloo 102011430Dokumen18 halamanSchizophrenia: Vaisnvi Muthoovaloo 102011430Vaisnavi MuthoovalooBelum ada peringkat
- Cushing'S Syndrome: Roldan, Scorch Dominique Romero, John Reden Sanchez, Tracy JoyDokumen25 halamanCushing'S Syndrome: Roldan, Scorch Dominique Romero, John Reden Sanchez, Tracy JoyGerald John PazBelum ada peringkat
- Gastro OooooDokumen11 halamanGastro OooooCHLOIE MARIE ROSALEJOSBelum ada peringkat
- Dopamin: Nur Fadhillah Khalid (P062181024) Mata Kuliah: NeurontrasmitterDokumen27 halamanDopamin: Nur Fadhillah Khalid (P062181024) Mata Kuliah: Neurontrasmitternur fadhillah khalidBelum ada peringkat
- AnxietyDokumen5 halamanAnxietyJohn HolmesBelum ada peringkat
- Health Check Consent FormDokumen4 halamanHealth Check Consent Formaxenic04Belum ada peringkat
- Vaccination or ImmunizationDokumen4 halamanVaccination or ImmunizationPrincessBelum ada peringkat
- The S.K.A.L.-Method: Out of the stress trap in just 64 seconds!Dari EverandThe S.K.A.L.-Method: Out of the stress trap in just 64 seconds!Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Therapy in Pregnancy (Soal)Dokumen6 halamanDrug Therapy in Pregnancy (Soal)Yola FebriyantiBelum ada peringkat
- LaryngitisDokumen5 halamanLaryngitisNader Smadi100% (3)
- Wolny 2018Dokumen10 halamanWolny 2018tri cahyani setyowatiBelum ada peringkat
- Part 1 - Bernal Safety - Intro and Emergencies - Powerpoint - 29mar21Dokumen34 halamanPart 1 - Bernal Safety - Intro and Emergencies - Powerpoint - 29mar21John TorrezBelum ada peringkat
- Untitled DocumentDokumen4 halamanUntitled Documentapi-388763698Belum ada peringkat
- Long-Term Prediction of Functional Outcome After Stroke Using Single Items of The Barthel Index at Discharge From Rehabilitation CentreDokumen7 halamanLong-Term Prediction of Functional Outcome After Stroke Using Single Items of The Barthel Index at Discharge From Rehabilitation CentretitinBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Aspects of Aconitum Preparations.Dokumen12 halamanClinical Aspects of Aconitum Preparations.Pablo PitrelliBelum ada peringkat
- CystosDokumen1 halamanCystosgeorgeloto12Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 014 Student HandoutsDokumen16 halamanChapter - 014 Student Handoutsebiniyam2021Belum ada peringkat
- Genetic Disorders Screening and PreventionDokumen36 halamanGenetic Disorders Screening and PreventionManovaPrasannaKumarBelum ada peringkat
- Gray On EcopsychologyDokumen10 halamanGray On EcopsychologyGiansar26Belum ada peringkat
- Dermatome Myotome SclerotomeDokumen4 halamanDermatome Myotome SclerotomeAdhya TiaraBelum ada peringkat
- Karvonen Formula Worksheet PDFDokumen2 halamanKarvonen Formula Worksheet PDFpipninjaBelum ada peringkat
- Interns 2016 DistributionDokumen13 halamanInterns 2016 DistributionKashish ChawlaBelum ada peringkat
- Seroflo 250 Synchrobreathe - View Uses, Side Effects, Price and Substitutes - 1mgDokumen10 halamanSeroflo 250 Synchrobreathe - View Uses, Side Effects, Price and Substitutes - 1mgParteek SinglaBelum ada peringkat
- FREMEC FormsDokumen1 halamanFREMEC FormsAviation MedicineBelum ada peringkat
- Kosmetik BatalDokumen5 halamanKosmetik BatalNurul AtikBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDokumen15 halamanMakalah Bahasa Inggrisfera kartikaBelum ada peringkat