Elc DG 401
Diunggah oleh
milecsaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Elc DG 401
Diunggah oleh
milecsaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
DATA SHEET GUIDE ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
November 1991 Page 1 of 14
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
CONTENTS
1.0 PURPOSE ............................................................................................................................3
2.0 SCOPE .................................................................................................................................3
3.0 REFERENCES.....................................................................................................................3
4.0 SEE ELECTRICAL MANUAL FOR APPLICABLE STANDARDS....................................3
5.0 USER'S DATA SHEET GUIDELINES ................................................................................3
A. Rating ....................................................................................................................................3
B. Operating Data .......................................................................................................................5
C. Construction...........................................................................................................................6
D. Data to be Provided by Vendor................................................................................................9
E. Accessories............................................................................................................................9
F. Testing................................................................................................................................. 11
G. General Specifications ..........................................................................................................14
H. Notes...................................................................................................................................14
Page 2 of 14 November 1991
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
1.0 PURPOSE
This Data Sheet Guide provides instructions on how to complete the Transformer Data Sheet (ELC-
DS-401). It helps with simple decisions. The Electrical Manual contains all data tables and
background. The section numbers of this Data Sheet Guide correspond to the Data Sheet line
numbers.
2.0 SCOPE
This Transformer Data Sheet (ELC-DS-401) covers requirements for dry-type and liquid- immersed
type transformers.
3.0 REFERENCES
ELC-DS-401 Transformer Data Sheet
C57 ANSI/EEE Standard
4.0 SEE ELECTRICAL MANUAL FOR APPLICABLE STANDARDS.
5.0 USER'S DATA SHEET GUIDELINES
Before filling out the Data Sheet, write the transformer identification number in the blank above the
columns labeled "high voltage/low voltage" (use a maximum of two transformers per Data Sheet).
A. Rating
A.1 Capacity (Continuous Self-Cooled Rating)
Normally the rating is already provided on a one-line diagram. Specify rating in kVA
(for example 1000 kVA.) See Section 100, "System Design", of the Electrical
Manual for standard kVA ratings and sizing information and Section 800,
"Transformers," of the Electrical Manual for selection and sizing information.
A.2 Rated Circuit Voltage
Secondary voltage is determined by the load characteristics, equipment availability,
and plant preference. Primary voltage is generally determined by available plant or
source voltages. Specify voltage in volts.
November 1991 Page 3 of 14
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
A.3 Connection of Windings
The recommended three-phase connection is delta primary and wye secondary. See
Section 100, "System Design," of the Electrical Manual for explanations and facts
concerning the different types of connections. This information should be on the one-
line diagram. Enter a "D" for delta and a "Y" for wye to indicate one type of
connection.
A.4 Frequency
Indicate normal operating frequency. (50 or 60 Hertz depending on country. 60 Hertz
in USA.) On isolated systems, if frequency is subject to extensive fluctuation,
indicate the plus and minus percentage of expected fluctuation from nominal
frequency. (Normally 60 3 Hz for offshore with self-generated power.)
A.5 Phase
Indicate whether the transformer is to be single-phase or three-phase. Indicate this
with the symbol 1f or 3f.
A.6 Temperature Rise
It is recommended to specify oil immersed distribution and power transformers with a
dual self-cooled temperature rise of 55/65C at full load. The 55/65C transformer
has a dual rating (for example, 1000/1120 kVA) which provides 12% more capacity
than a standard 55C rise transformer for about 5% more cost. The additional
capacity allows flexibility for future expansion.
It is recommended to specify 150C as maximum temperature rise for standard dry-
type transformers. There are also 80C and 115C rises. Make certain you do not
confuse insulation class with temperature rise. Enter the desired temperature rise in
the blank. See Section 833, "Temperature Rise," of the Electrical Manual for more
information.
A.7 Rating with Fans Installed
The fan-cooled rating should be specified on transformers purchased with cooling
fans. See Section 800, of the Electrical Manual for data on typical percentage rating
increases for forced cooling. Enter the value of the self-cooled rating (the value filled
in for A.1) times the percentage increase (See Figure 800-2). For example, 1000
kVA x 1.12 (percent increase for 55/65C transformer) = 1120 kVA is the self-cooled
rating. The same transformer with fans will be rated 1120 kVA x 1.15 = 1288 kVA
(this is the value to place in A.7 if fans are included).
Page 4 of 14 November 1991
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
A.8 Basic Impulse Level
The basic impulse level voltage (BIL) specifies the type of insulation required to
safely withstand voltage spikes due to lightning strikes or switching transients.
Standard BIL values for various nominal system voltages are listed in Section 845,
"Basic Impulse Level (BIL)" of the Electrical Manual. Enter a value from the table in
Section 845.
A.9 Impedance - Special Requirements
Typically, use standard impedance. Fill in the blank with the percent value. See
Section 100, "System Design," of the Electrical Manual for reasons to specify non-
standard values. Strike out "Special Requirements" if using standard impedance and
vice-versa for special impedance.
B. Operating Data
B.1 Ambient Temperature
Ambient temperatures exceeding 40C maximum and 30C average over a 24-hour
period require special design consideration. (See Section 833, "Temperature Rise,"
of the Electrical Manual.) Also, insulating liquid startup temperatures below minus
20C are not considered usual service conditions. Specify the ambient temperature in
degrees celsius.
B.2 Altitude
Due to the reduced heat transfer capability of air at higher altitudes, transformers to
be used above 3300 feet (1000 meters) must either be derated or provided with extra
cooling equipment. (See Section 834, "Altitude," of the Electrical Manual. Leave
blank if below 3300 feet.)
B.3 Average Load
The average kVA load should be the steady state load of motors (not startup loads)
and other loads. If load is intermittent or variable, use a time-weighted average. Do
not average in time when the transformer is not energized, but do include periods of
no load when the transformer remains energized. Enter the value obtained by dividing
the average load by the full load times 100%.
B.4 Evaluation Factor (EF)
Recommend using for transformers larger than 500 kVA. The Evaluation Factor (EF)
is the cost in dollars of a kilowatt of power at the installation location over the
transformer or project life.
November 1991 Page 5 of 14
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
EF = C x N x PWF
The energy cost (C) is the cost of electricity in $/KWH where the transformer is being
installed.
N equals the yearly operating time in hours that the transformer is expected to
operate.
The present worth factor (PWF) given on the Data Sheet is used to convert yearly
energy costs to a present worth basis. It is based on projected equipment life, interest
rates, inflation, and company expected return on investment. Although changes in
economic conditions can affect the present worth factor, the PWF of 4, used on the
Data Sheet, will provide consistent comparison between transformers. Enter the
calculated EF value, which will be in $/KW.
B.5 Area Classification
Specify either a nonhazardous (unclassified) area or a classified area, showing Class,
Division, and Group. To determine area classification see Section 300, "Area
Classification," of the Electrical Manual.
C. Construction
C.1 Class
Indicate the class of transformer construction required by using codes on the Data
Sheet or additional codes if needed. The first letter of the code indicates if the
transformer is a dry-type (A) or liquid immersed (O). The letter A following the first
letter indicates a self-cooled transformer (that is, cooled only by natural air
circulation). The letter W following the first letter, indicates a water-cooled
transformer.
Liquid-immersed transformers may also be forced-oil cooled (FO). Class codes
separated by a slash indicate different ratings under different conditions. For
example, OA/FA/FOA transformers have three different ratings, self cooled (A),
forced air with fans turned on (FA), and fans and oil pumps on (FOA). See Section
851, "Auxiliary Cooling," of the Electrical Manual for a list of the different classes
and their meaning. Fill in the blank with the type of class desired. (For example,
OA/FFA.)
C.2 Service
Indicate the type of transformer by crossing out the unwanted types. Some power
loads such as motors, require high starting currents and operate at a lagging power
factor. Lighting loads do not require high starting current and operate close to unity
Page 6 of 14 November 1991
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
power factor. Instrument loads are similar to lighting loads but must be segregated to
minimize electrical interference. Any other unusual applications should be noted
(such as a single motor on a captive transformer). When a captive transformer is
specified, give the number of starts per hour, motor inrush current, and kVA of the
motor. See Section 814, "Transformer Types," of the Electrical Manual.
C.3 Enclosure for Installation
State if the transformer is to be located indoors or outdoors. Additional
classifications include marine/oil rig and hazardous (classified) environments. See
ANSI/NFPA 70, Section 450 for the requirements of transformer installation in
enclosures.
C.4 High Voltage No-Load Taps (See C.14 for Load Taps)
Standard no-load tap settings consist of two 2 1/2% steps above and two 2 1/2%
steps below nominal voltage. This provides a full 5% voltage correction above and
below nominal. If required, tap settings which allow up to 10-15% voltage correction
in one direction are available. See Section 800, "Transformers," of the Electrical
Manual for further information.
Fill in the blank with the quantity of taps (normally two) above and below nominal
voltage and the percentage step of each tap. For example, one would enter two, 2
1/2% in the above blank and the same for the below blank.
C.5 Mounting
Fill in the blank with information on how the transformer is to be mounted.
C.6 Bushings
Provide information regarding whether bushings are to be mounted on the cover (or
top) of the transformer, on the wall, or on one side. Bushing location will be
determined by the conductor layout in the vicinity of the transformer. Cover bushings
are used for top connections from overhead lines. Wall bushings are used when
conduit and wire, armored cable, or bus duct connections are made.
C.7 Connectors
Spade-type connectors should be specified for medium voltage cables and low
voltage cables larger than AWG #2/0. Bolted-clamp terminals may be specified for
low voltage cables smaller than AWG #3/0. Cross out "no" if you want the
manufacturer to supply the connectors and vice versa. Fill in the blank with the type
of connector desired.
November 1991 Page 7 of 14
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
C.8 Conductors
Conductor type and size should be indicated in order for the manufacturer to supply
proper size connectors and terminations. Cross out the undesired types of conductors
and materials.
C.9 Terminal Enclosures
Indicate if a throat enclosure or a junction box is to be used. A throat is used for bus
duct connections and a junction box is used for connections with cable. The size of
the junction box must allow for cable connections without exceeding the bend radius
restrictions of the cable used. Specify the minimum distance in inches in the junction
box. API RP 14F does not allow bus duct in the Outer Continental Shelf (OCS) area.
C.10 Conduit Hubs
The number and size of the conduit hubs is determined by the number and size of
cable and conduit required to carry power to or from the transformer. If not required,
indicate "none" on the Data Sheet.
C.11 Termination
Cross out the type of terminations that are not to be used. Heat shrinkable
terminations can be used up to 15 kV. Above 15 kV, potheads are used. Dirty
environments may require special considerations. Also, indicate whether terminations
are to be supplied by the manufacturer.
C.12 Special Painting Requirements
State unusual conditions that require special paint such as marine or corrosive
environments. If a special color is required, this should be specified. If required
paint specifications are known, include this information. If there are no special paint
requirements, specify "manufacturer's standard."
C.13 Tertiary Winding
Normally not required; leave blank unless specifically required. See Section 800,
"Transformers," of the Electrical Manual for information on tertiary windings.
C.14 Load Tap Changing
Normally not required; leave blank unless specifically required. Indicate here if tap
changing under load is required. Most load tap changers vary taps in small discrete
steps. Indicate percentage range but do not include number of steps.
Page 8 of 14 November 1991
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
D. Data to be Provided by Vendor
When initially completing Data Sheet, leave this section blank. Vendor will complete this
section as part of the bid.
E. Accessories
Indicate yes or no, plus additional data for each item.
E.1 Specify the area classification (non-hazardous, Class I, Division 1, Class I, Division
2) on line B.5 in order to have the accessories mounted in the proper enclosures.
Transformers are usually installed in non-hazardous areas.
E.1.A Oil Level Gage
An oil level gage should be supplied on all oil-filled transformers. Alarm
contacts should be supplied on transformers rated 5 MVA or greater. Site
requirements for transformer reliability will determine if alarm contacts are
required on smaller transformers.
E.1.B Thermometer
A dial-type thermometer should be provided on all oil-filled transformers.
Alarm contacts should be provided on 5 MVA or greater. Expected ambient
temperatures, transformer load factor and the criticality of load served by the
transformer will determine if alarm contacts are required on smaller
transformers.
E.1.C Pressure-Vacuum Gage
A pressure-vacuum gage should be installed on all oil-filled transformers.
Alarm contacts should be provided on transformers rated 10 MVA or greater.
E.1.D Pressure-Relief Diaphragm
This is recommended on all oil-filled transformers. The pressure-relief
diaphragm prevents high pressure in oil-filled transformers from rupturing the
transformer container. Instead, the diaphragm relieves the pressure.
E.1.E Stainless Steel Diagrammatic Nameplate
Indicate whether stainless steel is to be used for nameplates.
November 1991 Page 9 of 14
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
E.1.F Sampling Device
A device for oil sampling should be required on all oil-filled transformers.
E.2.A Pressure Regulator
Specify if a continuous nitrogen blanket is required. A pressure regulating
system is usually required on transformers 10 MVA or larger.
E.2.B Provisions for Future-Cooling Fans
It is recommended to specify provisions for future-cooling fans.
Transformers normally are not specified with fans at initial installation. On
transformers of less than 1000 kVA, provisions for future-cooling fans may
not be practical and need not be specified.
E.2.C Cooling Fan Voltage
If a large transformer or unusual ambient conditions require fans, indicate
operating voltage of fan motors. As stated in instructions for Item E.2.B,
cooling fans are not normally supplied at the initial installation. Fan motor
voltage is usually determined by the voltage of the power sources convenient
to the fans and is typically 115 or 230 volts, single-phase.
If forced oil cooling is to be provided, indicate the pump voltage (with an
appropriate note). Forced oil pump motors are usually 460 volt, three-phase.
E.2.D Sudden Pressure Relay
Sudden pressure relays are recommended on transformers rated 10 MVA or
greater. A sudden pressure relay provides detection of transformer internal
faults. The relay responds to rapid increases in transformer internal pressure
caused by arcing, but is not affected by slow pressure variations due to load
changes, ambient temperature changes, system short-circuits, impulse
voltages, or inrush currents.
E.2.E Neutral CT
A bushing type current transformer should be provided on grounded three-
phase transformers when the signal from the CT is required to operate a
protective relay. The required ratio of the CT is determined when preparing
the protective relay coordination scheme. For multi-ratio (MR) CTs, all
secondaries must be wired to a terminal box and clearly tagged.
Page 10 of 14 November 1991
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
E.2.F Grounding Resistor
Three-phase wye-connected transformers with resistance grounded
secondaries should be provided with a grounding resistor rated to
continuously carry approximately five amperes for high resistance grounding
or approximately 400 amperes for 10 seconds, for low resistance grounding.
Sizing is discussed in Section 100, "System Design," of the Electrical
Manual. The grounding resistor for high resistance grounding systems is
usually provided with the switchgear or MCC.
E.2.G Three Bushing CTs
Generally, these are supplied with the switchgear except for primary CTs
used for differential relay protection or utility company metering. A current
transformer on each of the three phases is needed when the signals from the
CTs are to be used for metering or are used to operate protective relays. For
multi-ratio (MR) CTs, all secondaries must be wired to a terminal box and
clearly tagged.
E.2.H Surge Capacitors/Lightning Arrestors
Lightning arrestors should be specified on the primary of all transformers
supplied by an overhead power line and on the secondary of all transformers
feeding overhead lines. Surge capacitors may be required in high lightning
areas or on systems subject to high transients. Check local practice.
F. Testing. Indicate yes or no for each item.
F.1.A Winding Resistance
This test is recommended on all transformers. It provides information
required to calculate the I2R component of transformer losses. The
information is also used to calculate winding temperatures during the
temperature test.
F.1.B Ratio
This test should be required on all transformers. The winding ratio test
confirms that the transformer windings have the proper number of turns to
provide the voltages required. On transformers with tap changers, the ratio
test should be performed at each tap setting.
November 1991 Page 11 of 14
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
F.1.C Polarity and Phase Relationship
Polarity and phase relationship tests confirm the required phase relationship
between the primary and secondary windings. It is especially important when
two or more transformers are to be operated in parallel. These tests should
be performed on all three-phase transformers. (For single-phase transformers,
the phase relationship test is not applicable.)
F.1.D No-Load Losses and Exciting Current
This test should be performed on transformers 500 kVA or greater. The no-
load loss test is important because it measures losses in the transformer
whenever it is energized, regardless of whether it is carrying a load or not.
These losses have an impact on the economics of a transformer.
The exciting current test is used to verify that the core design and its
performance are satisfactory. The excitation current of a transformer is the
current which maintains the magnetic flux excitation in the core of the
transformer. The exciting current test and no-load loss are determined from
the same test setup.
F.1.E Impedance and Load Loss
These tests should be performed on all transformers rated greater than 500
kVA. The load loss test determines losses that are approximately
proportional to the load being carried. This also affects the economics of a
transformer. The impedance test confirms the transformer's voltage
regulation and ability to limit short-circuit current values. For transformers
rated 500 kVA or less, test data from duplicate units can substitute for
individual unit testing.
F.1.F Applied and Induced Potential
These tests should be performed on all transformers. The applied potential
test confirms the condition of the insulation between windings and between
windings and ground. The induced potential test checks the insulation
between turns on the windings.
F.1.G Temperature
This is usually not required on individual transformers. The temperature test
confirms that the transformer will carry load at the rated temperature rise.
Due to the time required for winding temperatures to stabilize and the time
for the transformer to come up to load, this is an expensive and
time-consuming test. Test data on an identical unit is acceptable.
Page 12 of 14 November 1991
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
F.2.A Impulse
Impulse tests simulate the effect of lightning strikes on the insulation of
transformers. Impulse tests are not usually performed on individual
transformers. They are used in the development of new transformers.
The full wave test is the least severe impulse test. It simulates a disturbance
some distance from the transformer that travels through the transmission line
to the transformer. If impulse testing is required, this test will usually suffice.
The chopped wave test is more severe and simulates a disturbance that
travels to the transformer and flashes over near the transformer.
Transformer reaction to the chopped wave and full wave are different. The
longer duration of the full wave induces high voltage stress throughout the
winding, turn-to-turn, layer-to-layer, as well as between the winding and
ground. The chopped wave is of shorter duration, and induces higher stresses
on insulation for the turn-to-turn and layer-to-layer.
The most severe impulse testing is front of wave. It is required only for
substation transformers subject to a direct lightning strike. The front of wave
test simulates a direct or close lightning strike with a fast voltage rise and fast
decay due to flashover. The peak amplitude of the wave is greater than both
the full and chopped wave tests.
If impulse tests are required, specify which tests are desired. New designs
should be tested by all three methods, but standard production transformers
should not require these tests unless local conditions are such that large
system disturbances are frequent.
F.2.B Insulation Resistance
The insulation test (or megohmmeter test) is required on all transformers.
The megohmmeter test should be performed on the rated voltage tap and at
the tap extremes for the first unit of a new design. This test is used as an
indication of the dryness of the insulation. This test can detect ground faults
that may exist in the transformer.
F.2.C Insulation Power Factor
This test is usually not required. The insulation power factor test is another
test of the condition of the transformer insulation. Factory test data may be
desired for comparison to field data. This test measures the capacitance
between windings and between windings and ground.
November 1991 Page 13 of 14
Chevron Data Sheet Guide ELC-DG-401
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING TRANSFORMER
DATA SHEET ELC-DS-401
F.2.D Sound Level
Noise level limitations may be required due to transformer proximity to
personnel, or to meet local noise codes. If published data on transformer
noise levels is substantially below required limits, sound level tests are not
required. If the projected noise level of the transformer is close to the noise
limits or verification of the noise level is required by local codes, sound level
tests may be required.
F.2.E Short-Circuit Capability
This test is primarily used to confirm new designs and usually is not required
on individual transformers. Short-circuit capability tests are performed to
confirm that a transformer can withstand short-circuit stresses.
F.3 Witness Test Required
The decision to witness transformer testing should be based on the size and criticality
of the transformer. Larger transformers whose failure would shut down a process,
should have tests witnessed. Load and no-load losses on larger transformers have a
large economic impact. These tests should be witnessed. Any required optional tests
in Section F2 should be witnessed. If a temperature test of the individual transformer
is required, this should be witnessed.
The testing of smaller transformers per Section F1, does not need to be witnessed.
F.4 Certified Test Results Required
Certified test results of all specified tests should be required. Test results should
include data from duplicate unit tests where this is allowed as a substitute for
individual unit tests.
G. General Specifications
Make certain that the Vendor completes Section D.
H. Notes
H.1 Use this equation to evaluate bids.
H.2 This penalty clause is used to help ensure that the Vendor meets the guaranteed
losses.
Page 14 of 14 November 1991
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Subestaciones de DistribucionDokumen18 halamanSubestaciones de Distribucionjohn pool ricaldiBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Technical Data Sheet For The 1LAP016371 - 2Dokumen1 halamanTransformer Technical Data Sheet For The 1LAP016371 - 2kongkixBelum ada peringkat
- Metal Encloced SwitchgearDokumen12 halamanMetal Encloced SwitchgearjuevesBelum ada peringkat
- Current Transformer - Rev 8 - November - 2019Dokumen21 halamanCurrent Transformer - Rev 8 - November - 2019Rukma Goud ShakkariBelum ada peringkat
- Impedance-Source Networks For Electric Power Conversion Part I: A Topological ReviewDokumen18 halamanImpedance-Source Networks For Electric Power Conversion Part I: A Topological ReviewRekhamtrBelum ada peringkat
- THE BEAM DESIGN IS ADEQUATEDokumen2 halamanTHE BEAM DESIGN IS ADEQUATEjklo12Belum ada peringkat
- 6290-A Power TransformersDokumen7 halaman6290-A Power TransformersharmlesdragonBelum ada peringkat
- USACE Design Manual 07 PDFDokumen520 halamanUSACE Design Manual 07 PDFDannyd68Belum ada peringkat
- Hoja de Cálculo para Analizar Cargas de Viento en Edificios y Estructuras de Acuerdo Al Código Asce 7-02Dokumen40 halamanHoja de Cálculo para Analizar Cargas de Viento en Edificios y Estructuras de Acuerdo Al Código Asce 7-02Orlando OtazuBelum ada peringkat
- Combined CT PT SpecificationDokumen7 halamanCombined CT PT SpecificationShajahan ShariefBelum ada peringkat
- Project Guide PDFDokumen117 halamanProject Guide PDFsuyuthikamil100% (1)
- WID Waste Incineration Directive 2000-76-ECDokumen96 halamanWID Waste Incineration Directive 2000-76-ECThomas Georg SchulzeBelum ada peringkat
- Fusing Equipment: Dual Sensing Bay-O-Net Fuse LinkDokumen6 halamanFusing Equipment: Dual Sensing Bay-O-Net Fuse Linksaniya_mirza4Belum ada peringkat
- PDVSA Technical Specification for Liquid-Immersed Transformers Up to 230 kV and 60 MVA (OADokumen24 halamanPDVSA Technical Specification for Liquid-Immersed Transformers Up to 230 kV and 60 MVA (OAzenaid vargasBelum ada peringkat
- Table of Concrete Design Properties Including Strength PropertiesDokumen7 halamanTable of Concrete Design Properties Including Strength PropertiesselinaBelum ada peringkat
- HP steam turbine drain manualDokumen1 halamanHP steam turbine drain manualryan hardiantoBelum ada peringkat
- Diseño de Subestaciones Eléctricas de DistribuciónDokumen87 halamanDiseño de Subestaciones Eléctricas de Distribuciónjonathan cruzBelum ada peringkat
- l2330h Project Guide PDFDokumen292 halamanl2330h Project Guide PDFMuhammad Tri KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- UKPN G81 Design Planning Appendix v1.0 KK 040711Dokumen20 halamanUKPN G81 Design Planning Appendix v1.0 KK 040711Sandeep LallBelum ada peringkat
- Voltage Sag and Harmonics Mitigation Using Distributed Power Flow ControllerDokumen7 halamanVoltage Sag and Harmonics Mitigation Using Distributed Power Flow ControllerAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Steam Engine Generator Capacity Calculation 3.9.1 Normal OperationDokumen31 halaman1 Steam Engine Generator Capacity Calculation 3.9.1 Normal OperationIlham Rahmat KurniaBelum ada peringkat
- KKS Handbook Edition 07Dokumen126 halamanKKS Handbook Edition 07Hüseyin ÖnözBelum ada peringkat
- Nxair enDokumen28 halamanNxair endmglennonBelum ada peringkat
- VGB-B 106 e ContentDokumen5 halamanVGB-B 106 e ContentVictor Hugo Huaman PalominoBelum ada peringkat
- Pool Design Construction GuideDokumen16 halamanPool Design Construction Guidekkundan52Belum ada peringkat
- Cane Shredder 2Dokumen9 halamanCane Shredder 2Dirajen Pullay MardayBelum ada peringkat
- Site Explanation For Mechanical WorkDokumen36 halamanSite Explanation For Mechanical WorkĐình Nam0% (1)
- Cdna07135enc 001Dokumen248 halamanCdna07135enc 001NeerajaBelum ada peringkat
- Surge CapacitorDokumen2 halamanSurge CapacitorvyroreiBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Issues On Distributed Generation (DG) Connection and GuidelinesDokumen4 halamanTechnical Issues On Distributed Generation (DG) Connection and GuidelinesKristiano RonaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Analog IO Module 1746 Installation ManualDokumen28 halamanAnalog IO Module 1746 Installation ManualWilBert Alcántara MatosBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Technical Data Sheet For The 1LAP016413 PDFDokumen1 halamanTransformer Technical Data Sheet For The 1LAP016413 PDFsanBelum ada peringkat
- Simulationof Single Phase Full Bridge Converter Using PSPICEDokumen10 halamanSimulationof Single Phase Full Bridge Converter Using PSPICEDhivya NBelum ada peringkat
- York Budgetary Price Non-Ducted 070712 (I)Dokumen3 halamanYork Budgetary Price Non-Ducted 070712 (I)daveleyconsBelum ada peringkat
- SIEMENS The H Class To Korea BrochureDokumen8 halamanSIEMENS The H Class To Korea Brochurelink2u_007Belum ada peringkat
- Spec PipingDokumen354 halamanSpec PipingBhaveshBelum ada peringkat
- Selecting Control and Balancing Valves in A Variable Flow System - ASHRAe Journal - Jun 1997Dokumen10 halamanSelecting Control and Balancing Valves in A Variable Flow System - ASHRAe Journal - Jun 1997Vince DavidBelum ada peringkat
- Distribution Substation Design Code of PracticeDokumen95 halamanDistribution Substation Design Code of PracticeKei WongBelum ada peringkat
- Flex Tube Boiler BookDokumen38 halamanFlex Tube Boiler BookrasheedillikkalBelum ada peringkat
- 2020 Nec Significant ChangesDokumen7 halaman2020 Nec Significant ChangesSatriaBelum ada peringkat
- Nfpa-220 (2006)Dokumen22 halamanNfpa-220 (2006)Counter RoverBelum ada peringkat
- 2.panelboard Spec ChartDokumen2 halaman2.panelboard Spec ChartangelBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Energy Steam LeaksDokumen2 halamanDepartment of Energy Steam Leaksz_sadiqBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar Wind LoadDokumen18 halamanSeminar Wind LoadKaustubh JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Oil Separator DimensionDokumen2 halamanOil Separator DimensionislamakthamBelum ada peringkat
- National Grid Blue Book 2009Dokumen232 halamanNational Grid Blue Book 2009KiddBelum ada peringkat
- HVACS Errata ForWeb Updated01042010xDokumen12 halamanHVACS Errata ForWeb Updated01042010xAldrin AbuegBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer DS - JSPLDokumen11 halamanTransformer DS - JSPLpromiseajayBelum ada peringkat
- Prime Continuous Power vs. Standby Backup PowerDokumen5 halamanPrime Continuous Power vs. Standby Backup PowerOsama ShalabyBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Design EngineerDokumen4 halamanMechanical Design Engineerapi-79066865Belum ada peringkat
- SmartPlant Instrumentation 2013 UpgradationDokumen11 halamanSmartPlant Instrumentation 2013 UpgradationVeeraVenkateshBelum ada peringkat
- ACS+6000+EN+Rev+F LowresDokumen20 halamanACS+6000+EN+Rev+F Lowreslujohn28Belum ada peringkat
- Selkirk PS/IPSDokumen8 halamanSelkirk PS/IPSMel MudhookBelum ada peringkat
- Project Planni NG - AS Appli ED I N Engi Neeri NG AND Constructi ON FOR Capi TAL ProjectsDokumen20 halamanProject Planni NG - AS Appli ED I N Engi Neeri NG AND Constructi ON FOR Capi TAL ProjectsBrajan Esteban Nieto EspinozaBelum ada peringkat
- G210154Dokumen19 halamanG210154Balan PalaniappanBelum ada peringkat
- Relay Setting For 7ut51 Differential Protection RelayDokumen12 halamanRelay Setting For 7ut51 Differential Protection Relayyesrojas100% (1)
- Chap 12Dokumen18 halamanChap 12Jarrett MathewsBelum ada peringkat
- DC-DC Converter ApplicationsDokumen33 halamanDC-DC Converter ApplicationsRuben Juan JuanBelum ada peringkat
- Pages From Handbook of Electrical Engineering For Practitioners in The Oil Gas & Petrochemical Industry (Alan L. Sheldrake)Dokumen4 halamanPages From Handbook of Electrical Engineering For Practitioners in The Oil Gas & Petrochemical Industry (Alan L. Sheldrake)Sandeep PanigrahiBelum ada peringkat
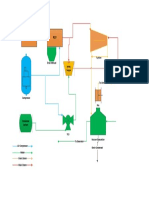
- Appendix A. Mean Temperature Difference Charts: Tower ManualDokumen21 halamanAppendix A. Mean Temperature Difference Charts: Tower ManualmilecsaBelum ada peringkat
- 2000 Process Equipment: 2010 Pumps 2000-3Dokumen36 halaman2000 Process Equipment: 2010 Pumps 2000-3milecsaBelum ada peringkat
- 500 Utility Gases: 510 500-3 520 Air Systems 500-3Dokumen40 halaman500 Utility Gases: 510 500-3 520 Air Systems 500-3milecsaBelum ada peringkat
- PMP 200Dokumen103 halamanPMP 200milecsaBelum ada peringkat
- FFM50 Using This Manual PDFDokumen4 halamanFFM50 Using This Manual PDFThiruThirunavukkarasuBelum ada peringkat
- Using this Manual: An SEO-Optimized GuideDokumen8 halamanUsing this Manual: An SEO-Optimized Guidelosmoscasbr-1Belum ada peringkat
- 3050 Using This Manual: Chevron Corporation 3050-1 August 1999Dokumen8 halaman3050 Using This Manual: Chevron Corporation 3050-1 August 1999milecsa100% (1)
- Fire Protection Guidelines for New ProjectsDokumen68 halamanFire Protection Guidelines for New ProjectsmilecsaBelum ada peringkat
- 1200 Automatic Tank GaugingDokumen28 halaman1200 Automatic Tank GaugingmilecsaBelum ada peringkat
- Tank Manual 50 Using This ManualDokumen4 halamanTank Manual 50 Using This ManualmilecsaBelum ada peringkat
- 1000 Tank Types and CalibrationDokumen24 halaman1000 Tank Types and CalibrationmilecsaBelum ada peringkat
- Appendix A. Conversion TablesDokumen18 halamanAppendix A. Conversion TablesmilecsaBelum ada peringkat
- CatalogoDokumen153 halamanCatalogomilecsaBelum ada peringkat
- PIM300 Piping System Design PDFDokumen66 halamanPIM300 Piping System Design PDFmika cabelloBelum ada peringkat
- 2000 Automatics Sprinklers PDFDokumen94 halaman2000 Automatics Sprinklers PDFmilecsaBelum ada peringkat
- FFM TocDokumen1 halamanFFM TocmilecsaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Instrumentation Measuring Devices and Basic Pid ControlDokumen125 halamanBasic Instrumentation Measuring Devices and Basic Pid ControlCuong Nguyen ChiBelum ada peringkat
- 3990 Less or Nonflammable TransformersDokumen16 halaman3990 Less or Nonflammable TransformersmilecsaBelum ada peringkat
- Asme 19.2 1987Dokumen145 halamanAsme 19.2 1987Popescu Alin100% (3)
- COSASCO - Catalogo-Rev. B5 PDFDokumen492 halamanCOSASCO - Catalogo-Rev. B5 PDFmilecsa100% (1)
- Todo BonsaiDokumen39 halamanTodo BonsaiElvis Medardo Cano LaymeBelum ada peringkat
- COSASCO - Catalogo-Rev. B5 PDFDokumen492 halamanCOSASCO - Catalogo-Rev. B5 PDFmilecsa100% (1)
- Erosion Guidelines Rev 2 - 1Dokumen15 halamanErosion Guidelines Rev 2 - 1milecsaBelum ada peringkat
- 1100 Manual Tank GaugingDokumen35 halaman1100 Manual Tank GaugingmilecsaBelum ada peringkat
- RP 4-6 Procedure For The Design of Buildings Subject To Blast LoadingDokumen31 halamanRP 4-6 Procedure For The Design of Buildings Subject To Blast Loadingmilecsa100% (1)
- TM 2000-19 PDFDokumen22 halamanTM 2000-19 PDFmilecsaBelum ada peringkat
- Corrosion Prediction Modelling PDFDokumen102 halamanCorrosion Prediction Modelling PDFmilecsa100% (1)
- Erosion Guidelines Rev 2 - 1Dokumen33 halamanErosion Guidelines Rev 2 - 1milecsaBelum ada peringkat
- Solenoid Valves BasicsDokumen47 halamanSolenoid Valves BasicsGary8100% (6)
- Approach Aeroport LightingDokumen6 halamanApproach Aeroport LightingAzizullahBelum ada peringkat
- Installation 2127 PDFDokumen136 halamanInstallation 2127 PDFMichael SezeniasBelum ada peringkat
- Accounting Information SystemDokumen2 halamanAccounting Information SystemRosee D.Belum ada peringkat
- Em Lab-Ii ManualDokumen32 halamanEm Lab-Ii ManualKUMAR SBelum ada peringkat
- SQL Server 2019 Editions DatasheetDokumen3 halamanSQL Server 2019 Editions DatasheetKeluarga ZulfanBelum ada peringkat
- BSNL Performance ScorecardDokumen1 halamanBSNL Performance ScorecardpokharnapokarBelum ada peringkat
- Project SpecificationDokumen8 halamanProject SpecificationYong ChengBelum ada peringkat
- Microdis IPC 2.0Dokumen16 halamanMicrodis IPC 2.0jimBelum ada peringkat
- Exploring Citizenship: Doing Something About The Mess We're inDokumen38 halamanExploring Citizenship: Doing Something About The Mess We're inJohn Humphrey Centre for Peace and Human RightsBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Computing Applied Business Tools and TechnologiesDokumen9 halamanIntroduction To Computing Applied Business Tools and TechnologiesClaire CarpioBelum ada peringkat
- Notifier FTM 1 Firephone Control ModuleDokumen2 halamanNotifier FTM 1 Firephone Control Modulejhon bayonaBelum ada peringkat
- BCS English Preparation Fill in The Appropriate Preposition PDFDokumen3 halamanBCS English Preparation Fill in The Appropriate Preposition PDFRasel Islam100% (1)
- Topic 1 - Information Assurance PrinciplesDokumen21 halamanTopic 1 - Information Assurance PrinciplesMathavan KrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- Smart Automated Irrigation System Seminar ReportDokumen30 halamanSmart Automated Irrigation System Seminar ReportSCOC53 Parth NegiBelum ada peringkat
- Weight Reduction Design of Military Vehicle SubframeDokumen28 halamanWeight Reduction Design of Military Vehicle SubframeSANATHBelum ada peringkat
- 360bind For SAP BusinessObjects Automated Regression TestingDokumen16 halaman360bind For SAP BusinessObjects Automated Regression Testinggoiffon sebastienBelum ada peringkat
- C1362Dokumen8 halamanC1362Lucas CamposBelum ada peringkat
- Catalogue MidlandDokumen94 halamanCatalogue MidlandzffryfvxBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Construction Standards For Kiosk Type SubstationsDokumen37 halamanDesign and Construction Standards For Kiosk Type SubstationsFlo MircaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical SubstationsDokumen16 halamanElectrical SubstationsEngr Syed Numan ShahBelum ada peringkat
- HB2300 ProGrafNT PG - Konfig enDokumen78 halamanHB2300 ProGrafNT PG - Konfig enBojan MilovanovicBelum ada peringkat
- Genesys Logic GL823 - C48653Dokumen21 halamanGenesys Logic GL823 - C48653casaswqBelum ada peringkat
- Power Line Carrier CommunicationDokumen11 halamanPower Line Carrier Communicationthe_ray004100% (1)
- Alseca Innovation Mar2021 15Dokumen20 halamanAlseca Innovation Mar2021 15Gabriel BodeaBelum ada peringkat
- Best Digital Marketing Course in Udaipur.Dokumen33 halamanBest Digital Marketing Course in Udaipur.Eduwigs IndiaBelum ada peringkat
- Santosh KumarDokumen4 halamanSantosh KumarNagaraju kBelum ada peringkat
- Firmware Update Sinamics Chassis V25 EngDokumen15 halamanFirmware Update Sinamics Chassis V25 Engalpha1ahBelum ada peringkat
- Steam - Receipt For Key SubscriptionDokumen1 halamanSteam - Receipt For Key SubscriptionLuis Felipe BuenoBelum ada peringkat
- Expt - 1 - Verification of Superposition Theorem For Ac CircuitsDokumen3 halamanExpt - 1 - Verification of Superposition Theorem For Ac CircuitsChaitanya Vivek Deshpande100% (1)
- Christensen CS3001Dokumen2 halamanChristensen CS3001Julio Jesus Quijano VargasBelum ada peringkat