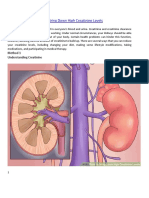
Diabetes
Diunggah oleh
BabelctgHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Diabetes
Diunggah oleh
BabelctgHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a disease that occurs when your
blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too
high. Blood glucose is your main source of
energy and comes from the food you
eat. Insulin, a hormone made by the pancreas,
helps glucose from food get into your cells to be
used for energy. Sometimes your body doesnt
make enoughor anyinsulin or doesnt use
insulin well. Glucose then stays in your blood
and doesnt reach your cells.
Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause health problems. Although
diabetes has no cure, you can take steps to manage your diabetes and stay healthy.
Sometimes people call diabetes a touch of sugar or borderline diabetes. These terms
suggest that someone doesnt really have diabetes or has a less serious case, but every
case of diabetes is serious.
What are the different types of diabetes?
The most common types of diabetes are type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes
If you have type 1 diabetes, your body does not
make insulin. Your immune system attacks and
destroys the cells in your pancreas that make
insulin. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in
children and young adults, although it can
appear at any age. People with type 1 diabetes
need to take insulin every day to stay alive.
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
Symptoms
Type 1 diabetes signs and symptoms can appear relatively suddenly and may include:
Increased thirst
Frequent urination
Bed-wetting in children who previously didn't wet
the bed during the night
Extreme hunger
Unintended weight loss
Irritability and other mood changes
Fatigue and weakness
Blurred vision
Causes
#) The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown.
Usually, the body's own immune system which
normally fights harmful bacteria and viruses
mistakenly destroys the insulin-producing (islet, or
islets of Langerhans) cells in the pancreas. Other
possible causes include:
# Genetics
# Exposure to viruses and other environmental factors
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
The role of insulin
Once a significant number of islet cells are destroyed, you'll produce little or no insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that comes from a gland situated behind and below the stomach
(pancreas).
1.The pancreas secretes insulin into the bloodstream.
2.Insulin circulates, allowing sugar to enter your cells.
3.Insulin lowers the amount of sugar in your bloodstream.
4.As your blood sugar level drops, so does the secretion of
insulin from your pancreas.
The role of glucose
Glucose a sugar is a main source of energy for the cells that make up muscles and
other tissues.
1.Glucose comes from two major sources: food and your liver.
2.Sugar is absorbed into the bloodstream, where it enters cells
with the help of insulin.
3.Your liver stores glucose as glycogen.
4.When your glucose levels are low, such as when you havent
eaten in a while, the liver breaks down the stored glycogen into
glucose to keep your glucose levels within a normal range.
In type 1 diabetes, there's no insulin to let glucose into the cells, so sugar builds up in
your bloodstream. This can cause life-threatening complications.
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
Risk factors
Some known risk factors for type 1 diabetes include:
Family history. Anyone with a parent or sibling
with type 1 diabetes has a slightly increased risk of
developing the condition.
Genetics. The presence of certain genes indicates
an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Geography. The incidence of type 1 diabetes
tends to increase as you travel away from the
equator.
Age. Although type 1 diabetes can appear at any
age, it appears at two noticeable peaks. The first
peak occurs in children between 4 and 7 years old,
and the second is in children between 10 and 14
years old.
Complications
Over time, type 1 diabetes complications can affect
major organs in your body, including heart, blood
vessels, nerves, eyes and kidneys. Maintaining a
normal blood sugar level can dramatically reduce the
risk of many complications.
Eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening.
Heart and blood vessel disease. Diabetes dramatically increases your risk of
various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain
(angina), heart attack, stroke, narrowing of the arteries (atherosclerosis) and high
blood pressure.
Nerve damage (neuropathy). Excess sugar can injure the walls of the tiny blood
vessels (capillaries) that nourish your nerves, especially in the legs. This can cause
tingling, numbness, burning or pain that usually begins at the tips of the toes or
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
fingers and gradually spreads upward. Poorly controlled blood sugar could cause
you to eventually lose all sense of feeling in the affected limbs.
Damage to the nerves that affect the gastrointestinal tract can cause problems with
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. For men, erectile dysfunction may be an
issue.
Kidney damage (nephropathy). The kidneys contain millions of tiny blood vessel
clusters that filter waste from your blood. Diabetes can damage this delicate filtering
system. Severe damage can lead to kidney failure or irreversible end-stage kidney
disease, which requires dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Eye damage. Diabetes can damage the blood vessels of the retina (diabetic
retinopathy), potentially causing blindness. Diabetes also increases the risk of other
serious vision conditions, such as cataracts and glaucoma.
Foot damage. Nerve damage in the feet or poor blood flow to the feet increases the
risk of various foot complications. Left untreated, cuts and blisters can become
serious infections that may ultimately require toe, foot or leg amputation.
Skin and mouth conditions. Diabetes may leave you more susceptible to
infections of the skin and mouth, including bacterial and fungal infections. Gum
disease and dry mouth also are more likely.
Pregnancy complications. High blood sugar levels can be dangerous for both the
mother and the baby. The risk of miscarriage, stillbirth and birth defects increases
when diabetes isn't well-controlled. For the mother, diabetes increases the risk of
diabetic ketoacidosis, diabetic eye problems (retinopathy), pregnancy-induced high
blood pressure and preeclampsia.
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
Treatment :
Type 1 diabetes requires treatment to keep blood sugar levels within a target range.
Treatment includes:
Taking several insulin injections every day or using
an insulin pump.
Monitoring blood sugar levels several times a day.
Eating a healthy diet that spreads carbohydrate throughout
the day.
Regular physical activity or exercise. Exercise helps the
body to use insulin more efficiently. It may also lower your
risk for heart and bloodvessel disease.
Regular medical checkups. You will get routine screening
tests and exams to watch for signs of complications, such
as eye, kidney, heart, blood vessel, and nerve diseases.
Not smoking.
Not drinking alcohol if you are at risk for periods of low blood
sugar.
Blood sugars are easier to predict and control when mealtimes, amounts of food,
and exercise are similar every day. So getting into a daily routine helps a lot.
Type 2 diabetes
If you have type 2 diabetes, your body does not
make or use insulin well. You can develop type
2 diabetes at any age, even during childhood.
However, this type of diabetes occurs most
often in middle-aged and older people. Type 2
is the most common type of diabetes.
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowly. In fact, you can have type
2 diabetes for years and not know it. Look for:
#) Increased thirst and frequent urination. Excess
sugar building up in your bloodstream causes fluid to
be pulled from the tissues. This may leave you thirsty.
As a result, you may drink and urinate more than
usual.
#) Increased hunger. Without enough insulin to move
sugar into your cells, your muscles and organs become
depleted of energy. This triggers intense hunger.
Weight loss. Despite eating more than usual to relieve hunger, you may lose
weight. Without the ability to metabolize glucose, the body uses alternative fuels
stored in muscle and fat. Calories are lost as excess glucose is released in the urine.
Fatigue. If your cells are deprived of sugar, you may become tired and irritable.
Blurred vision. If your blood sugar is too high, fluid may be pulled from the lenses
of your eyes. This may affect your ability to focus.
Slow-healing sores or frequent infections. Type 2 diabetes affects your ability to
heal and resist infections.
Areas of darkened skin. Some people with type 2 diabetes have patches of dark,
velvety skin in the folds and creases of their bodies usually in the armpits and
neck. This condition, called acanthosis nigricans, may be a sign of insulin resistance.
Causes
Type 2 diabetes develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the
pancreas stops producing enough insulin. Exactly why this happens is unknown, although
genetics and environmental factors, such as excess weight and inactivity, seem to be
contributing factors.
How insulin works
Insulin is a hormone that comes from the gland situated behind and below the stomach
(pancreas).
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
#) The pancreas secretes insulin into the bloodstream.
#) The insulin circulates, enabling sugar to enter your
cells.
#) Insulin lowers the amount of sugar in your
bloodstream.
#) As your blood sugar level drops, so does the secretion
of insulin from your pancreas.
The role of glucose
Glucose a sugar is a main source of energy for the cells that make up muscles and
other tissues.
#) Glucose comes from two major sources: food and your
liver.
#) Sugar is absorbed into the bloodstream, where it enters
cells
with the help of insulin.
#) Your liver stores and makes glucose.
#) When your glucose levels are low, such as when you haven't eaten in a while, the
liver breaks down stored glycogen into glucose to keep your glucose level within a normal
range.
In type 2 diabetes, this process doesn't work well. Instead of moving into your cells, sugar
builds up in your bloodstream. As blood sugar levels increase, the insulin-producing beta
cells in the pancreas release more insulin, but eventually these cells become impaired
and can't make enough insulin to meet the body's demands.
In the much less common type 1 diabetes, the immune system destroys the beta cells,
leaving the body with little to no insulin.
Risk factors
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
Researchers don't fully understand why some people develop type 2 diabetes and others
don't. It's clear, however, that certain factors increase the risk, including:
Weight. Being overweight is a primary risk factor for type 2 diabetes. The more fatty
tissue you have, the more resistant your cells become to insulin. However, you don't
have to be overweight to develop type 2 diabetes.
Fat distribution. If your body stores fat primarily in your abdomen, your risk of type
2 diabetes is greater than if your body stores fat elsewhere, such as your hips and
thighs.
Inactivity. The less active you are, the greater
your risk of type 2 diabetes. Physical activity
helps you control your weight, uses up glucose
as energy and makes your cells more sensitive
to insulin.
Family history. The risk of type 2 diabetes
increases if your parent or sibling has type 2
diabetes.
Race. Although it's unclear why, people of
certain races including blacks, Hispanics,
American Indians and Asian-Americans are
more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than
whites are.
Age. The risk of type 2 diabetes increases as you get older, especially after age 45.
That's probably because people tend to exercise less, lose muscle mass and gain
weight as they age. But type 2 diabetes is also increasing dramatically among
children, adolescents and younger adults.
Prediabetes. Prediabetes is a condition in which your blood sugar level is higher
than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. Left untreated,
prediabetes often progresses to type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes. If you developed gestational diabetes when you were
pregnant, your risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases. If you gave birth to a
baby weighing more than 9 pounds (4 kilograms), you're also at risk of type 2
diabetes.
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
Polycystic ovarian syndrome. For women, having polycystic ovarian syndrome
a common condition characterized by irregular menstrual periods, excess hair
growth and obesity increases the risk of diabetes.
Complications
Type 2 diabetes can be easy to ignore, especially in the early stages when you're feeling
fine. But diabetes affects many major organs, including your heart, blood vessels, nerves,
eyes and kidneys. Controlling your blood sugar levels can help prevent these
complications.
Although long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually, they can eventually be
disabling or even life-threatening. Some of the potential complications of diabetes include:
#) Heart and blood vessel disease. Diabetes dramatically increases the risk of various
cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina),
heart attack, stroke, narrowing of arteries (atherosclerosis) and high blood pressure.
#) Nerve damage (neuropathy). Excess sugar can injure the walls of the tiny blood
vessels (capillaries) that nourish your nerves, especially in the legs. This can cause
tingling, numbness, burning or pain that usually begins at the tips of the toes or fingers
and gradually spreads upward. Poorly controlled blood sugar can eventually cause you
to lose all sense of feeling in the affected limbs. Damage to the nerves that control
digestion can cause problems with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. For men,
erectile dysfunction may be an issue.
#) Kidney damage (nephropathy). The kidneys contain millions of tiny blood vessel
clusters that filter waste from your blood. Diabetes can damage this delicate filtering
system. Severe damage can lead to kidney failure or irreversible end-stage kidney
disease, which often eventually requires dialysis or a kidney transplant.
#) Eye damage. Diabetes can damage the blood vessels of the retina (diabetic
retinopathy),potentially leading to blindness. Diabetes also increases the risk of other
serious vision conditions, such as cataracts and glaucoma.
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
#) Foot damage. Nerve damage in the
feet or poor blood flow to the feet
increases the risk of various foot
complications. Left untreated, cuts and
blisters can become serious infections,
which may heal poorly. Severe damage
might require toe, foot or leg amputation.
#)Hearing impairment. Hearing
problems are more common in people
with diabetes.
#) Skin conditions. Diabetes may leave
you more susceptible to skin problems,
including bacterial and fungal infections.
#) Alzheimer's disease. Type 2 diabetes may increase the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
The poorer your blood sugar control, the greater the risk appears to be. The exact
connection between these two conditions still remains unclear.
Prevention
Healthy lifestyle choices can help you prevent type 2 diabetes. Even if you have diabetes
in your family, diet and exercise can help you prevent the disease. If you've already
received a diagnosis of diabetes, you can use healthy lifestyle choices to help prevent
complications. And if you have prediabetes, lifestyle changes can slow or halt the
progression from prediabetes to diabetes.
Eat healthy foods. Choose foods lower in fat and calories and higher in fiber. Focus on
fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
Get physical. Aim for a minimum of 30 minutes of moderate physical activity a day. Take
a brisk daily walk. Ride a bike. Swim laps. If you can't fit in a long workout, spread 10-
minute or longer sessions throughout the day.
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
Lose excess pounds. If you're overweight,
losing 7 percent of your body weight can reduce
the risk of diabetes. To keep your weight in a
healthy range, focus on permanent changes to
your eating and exercise habits.Motivate
yourself by remembering the benefits of losing
weight, such as a healthier heart, more energy
and improved self-esteem. Sometimes
medication is an option as well. Metformin
(Glucophage, Glumetza, others), an oral
diabetes medication, may reduce the risk of type
2 diabetes but healthy lifestyle choices
remain essential.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes develops in some women
when they are pregnant. Most of the time, this
type of diabetes goes away after the baby is
born. However, if youve had gestational
diabetes, you have a greater chance of
developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Sometimes diabetes diagnosed during
pregnancy is actually type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms
Gestational diabetes symptoms can be subtleor even nonexistentand some can be
mistaken for typical side effects of pregnancy, like the urge to pee frequently. Here are
some possible signs of gestational diabetes that should be brought to your doctors
attention:
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
Blurred vision
Tingling or numbness in the hands and/or feet
Excessive thirst
Frequent urination
Sores that heal slowly
Excessive fatigue
Causes and Risk Factors
One of the gestational diabetes causes is the surge of hormones that your body produces
to help your pregnancy thrive. Those additional hormones can keep your body from using
your insulin effectively to maintain the right blood sugar levels.There are a number of risk
factors for gestational diabetes. Your ob-gyn will likely monitor you for this type of diabetes
during pregnancy if you:
Are over 25 years old
Are obese
Have a family history of diabetes
Had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy
Previously gave birth to a baby who weighed over
9.5 pounds
Previously had a stillborn baby
Are black/African-American, Latina/Hispanic,
Asian, Native American/Pacific Islander
Prevention
While theres no way to avoid gestational diabetes completely, a few things can minimize
the chances of developing the condition.
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
#) Start before youre expecting. Make a point
of eating nutritiously and reaching a healthy
weight before you even start trying to conceive.
Preparing three to six months before getting
pregnant is the first step in lowering your risk for
gestational diabetes, Ross advises. Being
overweight can affect your ability to get
pregnant and to have a healthy pregnancy.
#) Go Mediterranean. The Mediterranean diet has been embraced by the medical
community as the model of healthy living, Ross says. Plant foods, fresh fruit, whole
grains, fish, lean meats, unprocessed foods and healthy fats are the highlights of this
diet.
#) Get moving. As little as 30 minutes of moderately intense exercise a day can improve
your health and well-being, Ross says. Exercise can reduce blood pressure, reduce
blood sugar levels, lower cholesterol levels, control body weight and body fat and lower
your risk of gestational diabetes and other pregnancy complications. Aim to work out
three to five times per week.
These lifestyle adjustments may seem basic, but science has shown they can have a
huge impact on preventing gestational diabetes. A 2016 study published in the
journal Diabetes Care found that when health-care professionals provided counseling on
diet, exercise and weight control, the occurrence of gestational diabetes in high-risk
women was reduced by 39 percent. In another studyappearing in a 2017 issue of
the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecologyobese women who exercised (in this
case, they used stationary bikes) at least 30 minutes, three times per week during
pregnancy nearly halved their risk for gestational diabetes (22 percent versus 40.6
percent).
Other types of diabetes
Less common types include monogenic diabetes, which is an inherited form of diabetes,
and cystic fibrosis-related diabetes .
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
How common is diabetes?
As of 2015, 30.3 million people in the United States, or 9.4 percent of the population, had
diabetes. More than 1 in 4 of them didnt know they had the disease. Diabetes affects 1
in 4 people over the age of 65. About 90-95 percent of cases in adults are type 2
diabetes.1
Who is more likely to develop type 2 diabetes?
You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are age 45 or older, have a family
history of diabetes, or are overweight. Physical inactivity, race, and certain health
problems such as high blood pressure also affect your chance of developing type 2
diabetes. You are also more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you have prediabetes or
had gestational diabetes when you were pregnant. Learn more about risk factors for type
2 diabetes.
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
What health problems can people with diabetes develop?
Over time, high blood glucose leads to problems such as
heart disease
stroke
kidney disease
eye problems
dental disease
nerve damage
foot problems
You can take steps to lower your chances of developing these diabetes-related health
problems.
Click to know: Doctors Reverse Type 2 Diabetes in Three Weeks
References
[1] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National diabetes statistics report, 2017.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
website. www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-statistics-
report.pdf (PDF, 1.3 MB) . Updated July, 18 2017. Accessed August 1, 2017.
[2] https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/type-1-diabetes/symptoms-
causes/syc-20353011
[3] https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/type-1-diabetes-guide/type-1-diabetes-treatment-
overview
[4] https://www.thebump.com/a/gestational-diabetes
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Diabetes Diet - The Ultimate Diabetes Diet Guide: Diabetes Diet Plan And Diabetes Diet RecipesDari EverandDiabetes Diet - The Ultimate Diabetes Diet Guide: Diabetes Diet Plan And Diabetes Diet RecipesPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- The Vital Importance of The Kidneys On Our HealthDokumen7 halamanThe Vital Importance of The Kidneys On Our HealthMus OubBelum ada peringkat
- Last Days of Diabetes Chaper 4Dokumen39 halamanLast Days of Diabetes Chaper 4vtrackBelum ada peringkat
- Resistant Hypertension. AHADokumen38 halamanResistant Hypertension. AHAEderEmmanuelMartinezRuiz100% (1)
- Disease of The EarsDokumen20 halamanDisease of The EarsPrecy CoBelum ada peringkat
- Treatment and Management of Hypertension and Stroke Using Fruits and Herbs Sourced From Nigeria, AfricaDokumen44 halamanTreatment and Management of Hypertension and Stroke Using Fruits and Herbs Sourced From Nigeria, AfricaGilbert Ezengige100% (1)
- Kidney InfectionDokumen47 halamanKidney InfectionduddysinghBelum ada peringkat
- Water Borne DiseasesDokumen28 halamanWater Borne DiseasesEngr AliBelum ada peringkat
- Products Anti Diabetes For Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Natto Roots Momordica Balsamina Caju Bark Artemisia Afra TinctureDokumen5 halamanProducts Anti Diabetes For Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Natto Roots Momordica Balsamina Caju Bark Artemisia Afra TinctureNile Valley MedicineBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacovigilance DefinationsDokumen32 halamanPharmacovigilance DefinationsKadir AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Disease Stroke Cholesterol and GlutathioneDokumen10 halamanHeart Disease Stroke Cholesterol and GlutathioneRandy GroverBelum ada peringkat
- Health Psychology Assignment (MA201477)Dokumen7 halamanHealth Psychology Assignment (MA201477)Syeda DaniaBelum ada peringkat
- Resting and FastingDokumen15 halamanResting and Fastingmark ignacioBelum ada peringkat
- General Diet PlanDokumen1 halamanGeneral Diet PlanAzmat HusainBelum ada peringkat
- Key Board Short CutDokumen6 halamanKey Board Short CutChaitanya KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetes Conversation Maps: Journey To Better Diabetes EducationDokumen1 halamanDiabetes Conversation Maps: Journey To Better Diabetes EducationCenter for Managing Chronic DiseaseBelum ada peringkat
- CBC Test - What Is The Normal Range, What Do Abnormal Levels IndicateDokumen8 halamanCBC Test - What Is The Normal Range, What Do Abnormal Levels IndicateRedcliffe LabsBelum ada peringkat
- Smart Blood SugarDokumen3 halamanSmart Blood SugarSimon Josh0% (1)
- The Skin in Systemic DiseasesDokumen42 halamanThe Skin in Systemic Diseasesrainmaker77771121Belum ada peringkat
- 10 Natural Ways To Lower Your Cholesterol LevelsDokumen4 halaman10 Natural Ways To Lower Your Cholesterol LevelsKristin Gomez100% (1)
- Pituitary Gland DisordersDokumen3 halamanPituitary Gland DisordersPAPIYA BHATTACHARYABelum ada peringkat
- Daily Duas in The Month ofDokumen258 halamanDaily Duas in The Month ofTransforBelum ada peringkat
- Cystic FibrosisDokumen5 halamanCystic Fibrosisandrew_Webb92100% (2)
- NAC - Are You Ready For NACDokumen4 halamanNAC - Are You Ready For NACVickiBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Cholesterol?Dokumen21 halamanWhat Is Cholesterol?cutegal88Belum ada peringkat
- Berberine For Weight Loss: Keywords What Is Berberine?Dokumen6 halamanBerberine For Weight Loss: Keywords What Is Berberine?SuhasaGBelum ada peringkat
- Diet and Diabetes India Factsheet PDFDokumen4 halamanDiet and Diabetes India Factsheet PDFNikita ZhukBelum ada peringkat
- The Principles of A Cancer DietDokumen17 halamanThe Principles of A Cancer DietJeffrey Tan100% (1)
- A Review On Herbal Antidiabetic Drugs EditedDokumen31 halamanA Review On Herbal Antidiabetic Drugs EditedVala TejalBelum ada peringkat
- Being Well, Staying WellDokumen1 halamanBeing Well, Staying WellLizZelencich100% (1)
- Diabetic Neuropathy PPT FinalDokumen54 halamanDiabetic Neuropathy PPT FinalJenny Juniora AjocBelum ada peringkat
- Parasites CleanseDokumen3 halamanParasites CleanseAMDKKBelum ada peringkat
- Hormone Health:: How To Get Your Hormones Back in BalanceDokumen9 halamanHormone Health:: How To Get Your Hormones Back in BalanceHarindra DunuwilaBelum ada peringkat
- Liver DiseasesDokumen29 halamanLiver DiseasesRicaneth TaanBelum ada peringkat
- Common Diseases, Vol II - 1223Dokumen214 halamanCommon Diseases, Vol II - 1223Farruh K100% (1)
- Foods To Aid The Kidneys To Eliminate Uric AcidDokumen25 halamanFoods To Aid The Kidneys To Eliminate Uric AcidSabbra CadabraBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension FactsheetDokumen2 halamanHypertension FactsheetPedro QuintasBelum ada peringkat
- Treatment of Hypertension by DR SarmaDokumen128 halamanTreatment of Hypertension by DR SarmaMuhammad Tariq KhanBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Things Your Eyes Say About Your HealthDokumen6 halaman4 Things Your Eyes Say About Your HealthGon FloBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetes and You: Your Guide To Better Living With DiabetesDokumen51 halamanDiabetes and You: Your Guide To Better Living With DiabetesdrjperumalBelum ada peringkat
- Dodging Diabetes ComplicationsDokumen20 halamanDodging Diabetes ComplicationsUlises MatiasBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To Back PainDokumen12 halamanApproach To Back PainSivaneasan KandiahBelum ada peringkat
- Atherosclerosis-Dyslipidaemia and Diabetes SlidesDokumen83 halamanAtherosclerosis-Dyslipidaemia and Diabetes SlidesECG17Belum ada peringkat
- (Osborn) Chapter 53 Learning Outcomes (Number and Title)Dokumen33 halaman(Osborn) Chapter 53 Learning Outcomes (Number and Title)Kitties100% (1)
- How Does The Thyroid Work? Let's Watch This Video: So Why The Big Commotion Over Such A Small Gland?Dokumen26 halamanHow Does The Thyroid Work? Let's Watch This Video: So Why The Big Commotion Over Such A Small Gland?DrRashmi MenonBelum ada peringkat
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDokumen49 halamanFluids and ElectrolytesvanessaBelum ada peringkat
- Secret Detox Drink Recipe (A Natural Detox Drink Recipe) : IngredientsDokumen7 halamanSecret Detox Drink Recipe (A Natural Detox Drink Recipe) : IngredientsBilal Masood100% (1)
- Pathogenesis of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis (Chronic Autoimmune Thyroiditis) - UpToDateDokumen22 halamanPathogenesis of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis (Chronic Autoimmune Thyroiditis) - UpToDaterazvanBelum ada peringkat
- Unlock The Secrets of Your PoopDokumen5 halamanUnlock The Secrets of Your PoopJames HudsonBelum ada peringkat
- General Principles of Malignant Tumor TreatmentDokumen33 halamanGeneral Principles of Malignant Tumor TreatmentТанмай Аасрітх Варма АйенампудіBelum ada peringkat
- HOME REMEDIES For Kidney StonesDokumen5 halamanHOME REMEDIES For Kidney StonespravanthbabuBelum ada peringkat
- DIetary Guidelines For DiabetesDokumen10 halamanDIetary Guidelines For Diabetessaipujitha1996Belum ada peringkat
- NeemDokumen21 halamanNeemprianka_padmanaban100% (1)
- Diabetic DietDokumen3 halamanDiabetic Dietmandeep axonBelum ada peringkat
- HydrotherapyDokumen7 halamanHydrotherapyGialys MoretaBelum ada peringkat
- Linco Steam Bath Sauna Bath Portable Steam CabinsDokumen17 halamanLinco Steam Bath Sauna Bath Portable Steam CabinsLinco SteamBath SaunaBathBelum ada peringkat
- How To Bring Down High Creatinine Levels PDFDokumen28 halamanHow To Bring Down High Creatinine Levels PDFAMIR100% (1)
- Piles ManagementDokumen66 halamanPiles ManagementkavindukarunarathnaBelum ada peringkat
- Glycemic IndexDokumen80 halamanGlycemic IndexdudeBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Surgery Exam 1Dokumen29 halamanOral Surgery Exam 1entistde100% (2)
- Enzymes As Targets of Drug Action: An Overview: ArticleDokumen13 halamanEnzymes As Targets of Drug Action: An Overview: ArticleSalehuddin Karaeng MattawangBelum ada peringkat
- Virology MCQ 1Dokumen21 halamanVirology MCQ 1Robert Edwards100% (9)
- Quiz 1A Hema LecDokumen17 halamanQuiz 1A Hema LecAngela ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Griffiths - Are Non Speech Oro-Motor Exercises More EffectiveDokumen1 halamanGriffiths - Are Non Speech Oro-Motor Exercises More EffectiveMira AlaaBelum ada peringkat
- Examiners' Report June 2011 GCE Biology 6BI05 01Dokumen36 halamanExaminers' Report June 2011 GCE Biology 6BI05 01Annie FrancesBelum ada peringkat
- Kidney and Liver FunctionDokumen6 halamanKidney and Liver FunctionAhmad Ripani Musyaffa AhdanLabBelum ada peringkat
- Bradley Nelson - Body Code System of Natural Healing - Manual (2009) PDFDokumen514 halamanBradley Nelson - Body Code System of Natural Healing - Manual (2009) PDFJhon Talbot80% (49)
- Fab Classification of Aml PDFDokumen2 halamanFab Classification of Aml PDFBenBelum ada peringkat
- NCP DMDokumen4 halamanNCP DMStef Bernardo67% (3)
- Protective Effect of Allium Cepa L. (Onion) Against Potassium Bromate-Induced Hematological, Biochemical and Histopathological Alterations in RatsDokumen7 halamanProtective Effect of Allium Cepa L. (Onion) Against Potassium Bromate-Induced Hematological, Biochemical and Histopathological Alterations in RatsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- Anti Microbial DrugsDokumen18 halamanAnti Microbial Drugseyadballas35Belum ada peringkat
- Drosophila MelanogasterDokumen13 halamanDrosophila MelanogasterDavid MorganBelum ada peringkat
- Abdul Wahid 2019Dokumen40 halamanAbdul Wahid 2019André MesquitaBelum ada peringkat
- Genbio2 ModuleDokumen47 halamanGenbio2 ModuleAlbert Rosete100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/23Dokumen16 halamanCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/23YashodhaBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Capture - PrintableDokumen51 halamanPrinciples of Capture - PrintableNguyen Thi Phuong NhiBelum ada peringkat
- Liquid CultureDokumen30 halamanLiquid CultureSumesh ShresthaBelum ada peringkat
- Phenotypic Characterization of Class II MalocclusionDokumen88 halamanPhenotypic Characterization of Class II MalocclusionPoonam K JayaprakashBelum ada peringkat
- Module 08: Genetics: Student ObjectivesDokumen9 halamanModule 08: Genetics: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraBelum ada peringkat
- 05-Protein Structure and FunctionDokumen41 halaman05-Protein Structure and Functionصدام حسینBelum ada peringkat
- Being Left-Handed in A Right-Handed WorldDokumen3 halamanBeing Left-Handed in A Right-Handed WorldLâm Khánh TrangBelum ada peringkat
- WBI01 01 Que 20180109Dokumen24 halamanWBI01 01 Que 20180109Bekhiet AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Biacore's SPR Technology and DNA Footprinting For The Discovery and Development of New DNA-targeted Therapeutics and ReagentsDokumen4 halamanBiacore's SPR Technology and DNA Footprinting For The Discovery and Development of New DNA-targeted Therapeutics and ReagentsNkem OkonkwoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 Drug MetabolismDokumen14 halamanChapter 4 Drug MetabolismNicole AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- EwingDokumen10 halamanEwingMd Ahsanuzzaman PinkuBelum ada peringkat
- Khan Academy Notes - Biomolecules For MCATDokumen50 halamanKhan Academy Notes - Biomolecules For MCATJuanBelum ada peringkat
- Recent Advances in The Research of Milbemycin Biosynthesis and Regulation As Well As Strategies For Strain ImprovementDokumen9 halamanRecent Advances in The Research of Milbemycin Biosynthesis and Regulation As Well As Strategies For Strain Improvementneo.mx8Belum ada peringkat
- Application of The Bethesda Classification For Thyroid FNABDokumen12 halamanApplication of The Bethesda Classification For Thyroid FNABJudrelle Krizia MarianoBelum ada peringkat
- 4E64B2BA-2F81-40AF-B02D-7832121B4380Dokumen5 halaman4E64B2BA-2F81-40AF-B02D-7832121B4380John van ZylBelum ada peringkat