Competition
Diunggah oleh
Manpreet KalraDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Competition
Diunggah oleh
Manpreet KalraHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Student Notes Pages Marketing
Chapter 1: Becoming Marketing Oriented
Introduction
Marketing
Second SA edition • Importance
Charles W. Lamb, Jr. – identify threats in good time
Joseph F. Hair, Jr. – probably the most important threat for all firms
Carl McDaniel – determines the firms entire business strategy
Christo Boshoff
Nic S. Terblanche • The industry concept of competition
Chapter • Industries are classified according to:
Chapter 4:
4:
– number of sellers, barriers, cost structure, degree of
Competitive
Competitive Analysis
Analysis vertical integration, degree of globalisation
• Gives rise to four industry structures
4-1 4-2
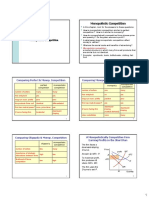
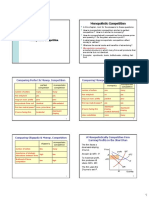
The Economics of Competition Types of Competition
Type
Type Description
Description
• The four basic industry structures are:
–Monopoly One
One Seller,
Seller, Unique
Unique Product,
Product, No
No Competitors
Competitors or
or
Monopoly
Monopoly Close
Close Substitutes
Substitutes
–Monopolistic competition Large
Monopolistic Large Number
Number of of Sellers,
Sellers, Products
Products
Monopolistic
–Oligopoly Competition
Competition
Distinguishable,
Distinguishable, Sellers
Sellers believe
believe they
they have
have
competition - including substitutes
competition - including substitutes
–Pure competition
Few
Few Sellers,
Sellers, High
High Barriers
Barriers to
to Entry,
Entry, Inelastic
Inelastic
Oligopoly
Oligopoly Demand,
Demand, Seek
Seek Non-price
Non-price Advantage
Advantage
Pure Many
Many Buyers
Buyers and
and Sellers,
Sellers, Identical
Identical Products,
Products,
Pure Full
Full knowledge,
knowledge, Easy
Easy entry,
entry, Elastic
Elastic Demand,
Demand,
Competition
Competition Focus
Focus on
on Lower
Lower Costs
Costs
4-3 4-4
Identifying Competitors Consumer-
Consumer-based Approaches to
Identify Competitors
• Consider both:
– current competitors; and
– potential new competitors • Primary competitors easy to identify
• Two ways – but competition is changing
– from a consumer’s perspective: what are the – new forms of competition are emerging
consumers’ options/choices? » customer choices
» who competes for a buyer’s choice - they are our
competitors » product-use associations
– from a firm-level perspective: what competitive
strategies are used by similar firms?
» result in groups of “similar” firms or strategic groups
4-5 4-6
© 1997 South-Western College Publishing
Student Notes Pages Marketing
Chapter 1: Becoming Marketing Oriented
The Strategic Group Approaches Understanding Potential
to Identify Competitors Competitors
• Strategic groups are firms who: • Market expansion
– use similar strategies • Product expansion
– have similar strategies • Integration
– have similar assets – forward, backward, vertical
– have similar competencies
• Export of assets or competencies
– have similar mobility barriers that prevent firms
from moving from one group to another • Retaliatory or defensive strategies
• Competing against a group more • Entry barriers
manageable than individual firms
4-7 4-8
Understanding Current Competitors Market Attractiveness
• Attractive market promises returns above
the cost of capital
• Must understand current competitors’
strengths and weaknesses • Two questions
– what factors account for the current level of
• Identify emerging threats and profitability?
opportunities – are the prospects better or worse in the future?
• Try to predict their actions • Answer depends on five factors
• Identify strategic uncertainties – (1) current direct rivalry (2) bargaining power of
• Competitor actions influenced by eight suppliers (3) bargaining power of customers (4)
threat of substitutes (5) potential threat of other
factors – next slide new competitors fm related industries
4-9 4-10
Competitors’
Competitors’ Strengths and Competitive Reaction Patterns
Weaknesses
• Six competing positions to occupy in a • Not all firms respond to competition the
market: same. There are:
– the laid-back competitor
– dominant
– strong – the selective competitor
– favourable – the tiger competitor
– the stochastic competitor
– tenable
– weak
– nonviable
4-11 4-12
© 1997 South-Western College Publishing
Student Notes Pages Marketing
Chapter 1: Becoming Marketing Oriented
Direct Rivalry Selecting Competitors to Attack/Avoid
• Competitive equilibrium is:
• Attacking weak competitors is cheaper
– unstable when competitors are almost identical
– but not much to be gained
– unstable when a single factor is likely to
determine success or failure • Benchmarking and competing with strong
– fairly stable if success is determined by a competitors may enhance the firm’s
variety of factors and different firms can excel capabilities and skills
in different areas
» the fewer the number of critical factors the • Good and bad competition
fewer the number of firms that can co-exist
– stable when one firm dominates and is not
challenged
– stable when customer switching cost is high
4-13 4-14
Finding Attractive Segments Competitive Strategies in SA Retail
Market
• House brands
• Not all parts of a market are equally • No frills shopping
attractive • Extended services
• Attractive segments must be: • Credit facilities
– sufficiently distinctive • Loyalty cards
– substantial enough • Clubs for account-holders
– measurable • Use of technology
– durable • Smart cards
– identifiable
4-15 4-16
© 1997 South-Western College Publishing
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Consulting Interview Case Preparation: Frameworks and Practice CasesDari EverandConsulting Interview Case Preparation: Frameworks and Practice CasesBelum ada peringkat
- Porter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionDari EverandPorter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (10)
- Market ProfileDokumen69 halamanMarket Profileapi-374230233% (3)
- Fiction in Design Research: Report On The 6th Swiss Design Network Conference in Basle, 2010Dokumen5 halamanFiction in Design Research: Report On The 6th Swiss Design Network Conference in Basle, 2010eypmaBelum ada peringkat
- The Dynamic AAC Goals Grid 2: DAGG-2Dokumen20 halamanThe Dynamic AAC Goals Grid 2: DAGG-2DEAN MIKO BULLOBelum ada peringkat
- Retail MarketingDokumen25 halamanRetail Marketingnitinnair15Belum ada peringkat
- Pay and Allowances - Indian RailwaysDokumen94 halamanPay and Allowances - Indian RailwaysRajendra Kumar70% (10)
- Only The Paranoids Survive - Summary VersionDokumen9 halamanOnly The Paranoids Survive - Summary Versionpsthe133% (3)
- Cloud Usage in The Financial Services SectorDokumen16 halamanCloud Usage in The Financial Services SectorLlauca XavierBelum ada peringkat
- I. Market Segmentation, TARGETING &Dokumen67 halamanI. Market Segmentation, TARGETING &mano cherian mathewBelum ada peringkat
- Theory of The Firm Jan 2022Dokumen61 halamanTheory of The Firm Jan 2022Goosy GoosoBelum ada peringkat
- My Days at Lovely Professional University As A FacultyDokumen39 halamanMy Days at Lovely Professional University As A Facultybiswajitkumarchaturvedi461550% (2)
- Market SegmentationDokumen20 halamanMarket Segmentationfnab@hotmail.com100% (8)
- Digital Etiquette Lesson PlanDokumen6 halamanDigital Etiquette Lesson Planapi-281885955Belum ada peringkat
- Product Satisfying FeaturesDokumen7 halamanProduct Satisfying FeaturesFaithy CuajotorBelum ada peringkat
- Applied-Economics SHS Q1 LP-5Dokumen11 halamanApplied-Economics SHS Q1 LP-5Gladys Angela ValdemoroBelum ada peringkat
- Market Structures: An Analysis of Competition in Different MarketsDokumen3 halamanMarket Structures: An Analysis of Competition in Different Marketskaren bulauanBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2 (Operations MGT.)Dokumen15 halamanModule 2 (Operations MGT.)Nicole ReintegradoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 MEDokumen61 halamanChapter 8 MEHaryadi WidodoBelum ada peringkat
- An Orientation To MarketsDokumen11 halamanAn Orientation To MarketsSiddhant SaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- Dealing With Competition: Marketing Management, 13 EdDokumen32 halamanDealing With Competition: Marketing Management, 13 EdSuñđàřam JérîçøBelum ada peringkat
- Imperfect Competition: Monopolistic Competition and OligopolyDokumen45 halamanImperfect Competition: Monopolistic Competition and OligopolyRiza LugodBelum ada peringkat
- Session 11Dokumen56 halamanSession 11Ankit ChaubeyBelum ada peringkat
- Market Structures ExplainedDokumen5 halamanMarket Structures ExplainedRuby CocalBelum ada peringkat
- Micro 6 Perfect CompetitionDokumen7 halamanMicro 6 Perfect CompetitionRyanBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Monopolistic CompetitionDokumen12 halaman12 Monopolistic CompetitionMilanBelum ada peringkat
- Monopolistic CompetitionDokumen36 halamanMonopolistic CompetitionMeredithDeCastroBelum ada peringkat
- Monopolistic Competition: Chapter 16-1Dokumen36 halamanMonopolistic Competition: Chapter 16-1Naveed ShaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Monopolistic CompDokumen36 halamanMonopolistic Compsubhasispanda18Belum ada peringkat
- Monopolistic Competition: Chapter 16-1Dokumen36 halamanMonopolistic Competition: Chapter 16-1badamsmithBelum ada peringkat
- Monopolistic Competition: Chapter 16-1Dokumen36 halamanMonopolistic Competition: Chapter 16-1Gaurav AryaBelum ada peringkat
- Monopolistic CompetitionDokumen3 halamanMonopolistic Competitionjoshcastv27Belum ada peringkat
- Monopolistic Competition: Chapter 16-1Dokumen36 halamanMonopolistic Competition: Chapter 16-1Balwinder SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Monopolistic Competition: Comparing Perfect & Monop. Competition Comparing Monopoly & Monop. CompetitionDokumen4 halamanMonopolistic Competition: Comparing Perfect & Monop. Competition Comparing Monopoly & Monop. CompetitionFranco ImperialBelum ada peringkat
- Monopolistic Competition: Comparing Perfect & Monop. Competition Comparing Monopoly & Monop. CompetitionDokumen4 halamanMonopolistic Competition: Comparing Perfect & Monop. Competition Comparing Monopoly & Monop. CompetitionFranco ImperialBelum ada peringkat
- Colander ch13 MonoComp&OligopolyDokumen47 halamanColander ch13 MonoComp&OligopolyVivek SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 20: Monopolistic CompetitionDokumen17 halamanTopic 20: Monopolistic CompetitionAnnie DarkBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 9 Basic Oligopoly ModelsDokumen48 halamanLesson 9 Basic Oligopoly ModelsjantriciadBelum ada peringkat
- Monopolistic CompetitionDokumen13 halamanMonopolistic CompetitionMohit MalhotraBelum ada peringkat
- Forms of Market Micro 10Dokumen11 halamanForms of Market Micro 10sykobeats7Belum ada peringkat
- Review of Litreature PDFDokumen44 halamanReview of Litreature PDFNANDHU BMBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Economics - Quarter 1Dokumen12 halamanApplied Economics - Quarter 1Gladys Angela ValdemoroBelum ada peringkat
- Monopolistic Competition: A2 MicroDokumen29 halamanMonopolistic Competition: A2 MicroAjayGuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Micro 8 Imperfect CompetitionDokumen5 halamanMicro 8 Imperfect CompetitionRyanBelum ada peringkat
- Nature of MarketDokumen17 halamanNature of MarketShreya VengurlekarBelum ada peringkat
- Intro To Market StructuresDokumen17 halamanIntro To Market StructuresPrashantBelum ada peringkat
- Outline: Industrial Organization: From The Fundamentals of Microeconomic PrinciplesDokumen12 halamanOutline: Industrial Organization: From The Fundamentals of Microeconomic PrinciplesRoni SuhandaniBelum ada peringkat
- TZ SK 5 JVa 6Dokumen1 halamanTZ SK 5 JVa 6Kressida BanhBelum ada peringkat
- 12 MC and OligopolyDokumen33 halaman12 MC and OligopolyAMBWANI NAREN MAHESHBelum ada peringkat
- MBA-CM - ME - Lecture 16 Market Structure AnalysisDokumen11 halamanMBA-CM - ME - Lecture 16 Market Structure AnalysisSadia FerdowsiBelum ada peringkat
- The Ultimate Theory of The Marketing Mix A Proposal For Marketers and ManagersDokumen23 halamanThe Ultimate Theory of The Marketing Mix A Proposal For Marketers and ManagersNetflix ChillBelum ada peringkat
- Reviewer MECODokumen13 halamanReviewer MECOMary Tyfanie QuilantangBelum ada peringkat
- Monopolistic CompDokumen32 halamanMonopolistic Compharsh guptaBelum ada peringkat
- Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México Facultad de Química: Ingeniería Económica IDokumen10 halamanUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de México Facultad de Química: Ingeniería Económica IUriel OropezaBelum ada peringkat
- Various Market StructuresDokumen11 halamanVarious Market Structuresjandec ross joshua serranoBelum ada peringkat
- Monopolistic and Imperfect Competition EcoDokumen9 halamanMonopolistic and Imperfect Competition EcojinBelum ada peringkat
- B2B Marketing Course OverviewDokumen52 halamanB2B Marketing Course OverviewPratik PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Managerial Economics: Classification of MarketsDokumen19 halamanManagerial Economics: Classification of Marketssruthy santhoshBelum ada peringkat
- Pricing and Output DecisionDokumen19 halamanPricing and Output DecisionAnwesha KarmakarBelum ada peringkat
- MBA-CM - ME - Lecture 16 Market Structure AnalysisDokumen11 halamanMBA-CM - ME - Lecture 16 Market Structure Analysisrohan_solomonBelum ada peringkat
- Perfect CompetitionDokumen14 halamanPerfect CompetitionAman -BCOMBelum ada peringkat
- Market Structure and Price Out Determination - 20231121 - 220505 - 0000Dokumen26 halamanMarket Structure and Price Out Determination - 20231121 - 220505 - 0000CIELO ESTONANTOBelum ada peringkat
- Product Life CycleDokumen40 halamanProduct Life Cycletarrsharma100% (2)
- Market Structure and CompetitionDokumen68 halamanMarket Structure and CompetitionMeena GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Between Monopoly and Perfect Competition: OligopolyDokumen7 halamanBetween Monopoly and Perfect Competition: OligopolyGus CahBelum ada peringkat
- Focusing Marketing Strategy With Segmentation and PositioningDokumen26 halamanFocusing Marketing Strategy With Segmentation and Positioningbaongan3005Belum ada peringkat
- Trek-Worthy Journeys: April 2021Dokumen29 halamanTrek-Worthy Journeys: April 2021Winda HarahapBelum ada peringkat
- Denver City Council Bill 626Dokumen24 halamanDenver City Council Bill 626Michael_Lee_RobertsBelum ada peringkat
- Fair Trial - m12Dokumen17 halamanFair Trial - m12Digital MarketBelum ada peringkat
- Daily RoutineDokumen1 halamanDaily Routineapi-361779682Belum ada peringkat
- City Definition What Is A CityDokumen11 halamanCity Definition What Is A CityDeri SYAEFUL ROHMANBelum ada peringkat
- New Era for Nigerian FarmersDokumen3 halamanNew Era for Nigerian FarmersSimon methuselahBelum ada peringkat
- Ucsp Research GalleraDokumen13 halamanUcsp Research GalleraHannah Charis L. BarabatBelum ada peringkat
- Earlscliffe Application Form SCREENDokumen2 halamanEarlscliffe Application Form SCREENErjusXBelum ada peringkat
- Music and DanceDokumen4 halamanMusic and DanceschedrinskyBelum ada peringkat
- Topic: Presentation SkillsDokumen5 halamanTopic: Presentation Skillshanzala sheikhBelum ada peringkat
- Ericsson Et. Al. v. TCL Telecommunication Technology Holdings Et. Al.Dokumen19 halamanEricsson Et. Al. v. TCL Telecommunication Technology Holdings Et. Al.PriorSmartBelum ada peringkat
- Entrep 1Dokumen40 halamanEntrep 1shayesssBelum ada peringkat
- Human Rights and Arrest, Pre-Trial Detention and Administrative DetentionDokumen54 halamanHuman Rights and Arrest, Pre-Trial Detention and Administrative DetentionAncuta BlanariuBelum ada peringkat
- IndemitybondDokumen1 halamanIndemitybondNewTech Cyber & ServicesBelum ada peringkat
- Resume For PortfolioDokumen1 halamanResume For Portfolioapi-399897689Belum ada peringkat
- The Geneva ConventionDokumen31 halamanThe Geneva ConventionJuan FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Guidance monitoring and evaluation tool of Doña Pepeng Elementary SchoolDokumen36 halamanGuidance monitoring and evaluation tool of Doña Pepeng Elementary SchoolNhayram NaresBelum ada peringkat
- RAPSDokumen13 halamanRAPSibadwonBelum ada peringkat
- Bath Fittings and Accessories Market - IndiaDokumen9 halamanBath Fittings and Accessories Market - Indiairfanjamie1981Belum ada peringkat
- Seperation of Power.Dokumen3 halamanSeperation of Power.Subaiyal MalicBelum ada peringkat
- George W Cecil: George Woodruff Is The Name ofDokumen22 halamanGeorge W Cecil: George Woodruff Is The Name ofArmando Díaz VargasBelum ada peringkat
- Non Refoulement PDFDokumen11 halamanNon Refoulement PDFM. Hasanat ParvezBelum ada peringkat
- Sociology of LawDokumen35 halamanSociology of LawKumarBelum ada peringkat