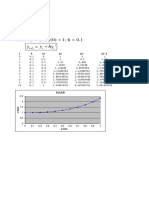
Modulation Type Description Applications: Frequency-Shift Keying)
Diunggah oleh
Renjan SolisJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Modulation Type Description Applications: Frequency-Shift Keying)
Diunggah oleh
Renjan SolisHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Table 1.
0 (Types of Digital Modulation)
MODULATION TYPE DESCRIPTION APPLICATIONS
CP-FSK (Continuous-phase It is often used to transmit Early voice-band
frequency-shift keying) digital data reliably over wire telephone line modems
line and wireless links at low use binary FSK to
data rates. Simple receivers with transmit data at 300
low error probability can be bits per second or less
built. It is a binary FSK except the and were acoustically
mark and space frequencies are coupled to the
synchronized with the input telephone handset.
binary bit rate. The mark and Some HF Radio systems
space frequencies which are use FSK to transmit
selected ensures a smooth digital data at low data
phase transition in the analog rates.
signal. The disadvantage of CP- The 3GPP Cellular Text
FSK is that it requires Telephone Modem
synchronization circuits and is (CTM) for use by the
more expensive to implement. hearing impaired over
regular cellular speech
channels uses four level
FSK.
BPSK (Binary phase-shift keying) It is the most robust digital It is used in various
modulation technique and is wireless standards such
used for long distance wireless as CDMA, WiMAX
communication. Here, two (16d,16e), WLAN 11a,
phases are possible for the 11b, 11g, 11n, Satellite,
carrier. One phase represents a DVB, Cable modem etc.
logic 1, and the other phase It is used in OFDM and
represents logic 0. As the input OFDMA to modulate
digital signal changes state, the the pilot subcarriers
phase of the output carrier shifts used for channel
between two angles that are estimation and
separated by 180. Hence, other equalization.
names for BPSK are phase
reversal keying (PRK) and
biphase modulation. It is a form
of square-wave modulation of a
continuous wave (CW) signal.
QPSK (Quaternary phase shift QPSK is bandwidth It is used in various
keying) efficient as each signal point cellular wireless
represents two bits. It is an M- standards such as GSM,
ary encoding scheme where N=2 CDMA, LTE, 802.11
and M=4. Four output phases WLAN, 802.16 fixed and
are possible for a single carrier mobile WiMAX, Satellite
frequency. Since there are four and CABLE TV
output phases, there must be applications.
four input conditions.
OQPSK (Offset Quaternary It is a modified form of It is used in biomedical
phase shift keying) QPSK where the bit waveform device applications.
on the I and Q channels are
offset or shifted in phase from
each other by one-half of a bit
time. An advantage of OQPSK is
the limited phase shift that must
be imparted during modulation.
Its disadvantage is that changes
in the output phase occur at
twice the data rate in either the
I or Q channels. OQPSK is
sometimes called OKQPSK
(offset-keyed QPSK)
8-PSK (8 phase shift keying) With this, 3 bits are Used in satellite
encoded forming tribits and broadcasting. High
producing eight different output definition programming
phases. In 8PSK, n=3, M=8, and is delivered almost
there are eight possible output exclusively in 8PSK due
phases. to the higher bitrates of
HD video and the high
Note: To encode eight different cost of satellite
phases, the incoming bits are bandwidth.
encoded in groups of three,
called tribits (23 = 8)
16-PSK (16 phase shift keying) It is an M-ary encoding It is used in most
technique where M=16 thus, 16 satellite applications.
different output phases are
possible. With 16-PSK, four bits
are combined, producing 16
different output phases. n= 4
and M=16 therefore the
minimum bandwidth and baud
equal one-fourth the bit rate
(fb/4).
8-QAM (8 Quadrature It is an M-ary encoding In 8-QAM, linear power
Amplitude Modulation) technique where M=8. Unlike 8- amplification is
PSK, the output signal from an 8- required. It is widely
QAM modulator is not a used in cable TV, Wi-Fi
constant amplitude signal. wireless local area
networks (LANs) ,
satellites and cellular
telephone systems to
produce maximum data
rate in limited
bandwidths.
16-QAM (16 Quadrature As with the 16- PSK, 16- It can be used in PAL
Amplitude Modulation) QAM is an M-ary system where and NTSC television
M=16. The input data are acted systems where the
on in groups of four (24 = 16). different channels
Both the phase and the provided by QAM
amplitude of the transmit enable it to carry the
carrier are varied. components of chroma
or colour information.
64-QAM ( 64 Quadrature The input data are acted in It is often used in digital
Amplitude Modulation ) groups of 6 (26 = 64). Its baud cable television and
rate is fb/6 and its minimum cable modem
bandwidth is also fb/6 applications. In the UK,
it is used for digital
terrestrial television
using DVB- Digital Video
Broadcasting.
REFERENCES:
www.rfwireless-world.com/Terminology/QPSK.html
www.ni.com/tutorials/5487/en/
www.nxp.com
www.mathworks.com
www.radio-electronics.com/info/rf-technology-design/quadrature-amplitude-modulation-qam/
www.dsplog.com
www.slideshare.net/satellite-link-using-16psk
ieeexplore.ieee.org
www.electronicdesign.com
www.engineering.com
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Digital Modulation Techniques / MultiplexingDokumen3 halamanDigital Modulation Techniques / MultiplexingYzza Veah Esquivel100% (2)
- Frequency Shift Keying FSKDokumen10 halamanFrequency Shift Keying FSKapi-19937584Belum ada peringkat
- A Software Radio Development Platform PCP2000 - Partnering C6x With Virtex FPGADokumen4 halamanA Software Radio Development Platform PCP2000 - Partnering C6x With Virtex FPGAVP SengarBelum ada peringkat
- Amplitude Modulation of PSK Project ReportDokumen6 halamanAmplitude Modulation of PSK Project ReportEngr Muhammad Imran100% (2)
- PSK Phase-Shift KeyingDokumen15 halamanPSK Phase-Shift KeyingfiraszekiBelum ada peringkat
- WC Unit-3Dokumen8 halamanWC Unit-3dr.omprakash.itBelum ada peringkat
- Bit Error Rate Evaluation of IEEE 802.16 in OFDM SystemDokumen4 halamanBit Error Rate Evaluation of IEEE 802.16 in OFDM Systemabhi_rules08Belum ada peringkat
- 2009 Tayab and Walliullah IC4 Copy of The Paper PDFDokumen6 halaman2009 Tayab and Walliullah IC4 Copy of The Paper PDFtayabmemonBelum ada peringkat
- WoowoowowoowDokumen9 halamanWoowoowowoowBujji JohnBelum ada peringkat
- IJETR041769Dokumen5 halamanIJETR041769erpublicationBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 5 39191Dokumen7 halamanTutorial 5 39191ujjwal poudelBelum ada peringkat
- 2024 - 01 - 19 - Seluler - Artikel Channel Coding GSM - Group - 1 - Final - ReportDokumen26 halaman2024 - 01 - 19 - Seluler - Artikel Channel Coding GSM - Group - 1 - Final - ReportEko MarpanajiBelum ada peringkat
- DTT Principles: N. Jethi, Dir (E) DDK, BhubaneswarDokumen34 halamanDTT Principles: N. Jethi, Dir (E) DDK, BhubaneswarShishir GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Investigating 802.11A Wireless Standard For High Speed Network Using Different Modulation TechniquesDokumen5 halamanInvestigating 802.11A Wireless Standard For High Speed Network Using Different Modulation TechniqueserpublicationBelum ada peringkat
- An Allcmos Architecture For A Lowpower Frequencyhopped 900 MHZ SDokumen4 halamanAn Allcmos Architecture For A Lowpower Frequencyhopped 900 MHZ SSURAJ SINGHBelum ada peringkat
- A Survey On Digital Modulation Techniques For Software Defined Radio ApplicationsDokumen8 halamanA Survey On Digital Modulation Techniques For Software Defined Radio Applicationssreekanthreddy peramBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 3 Two Marks OneDokumen5 halamanUNIT 3 Two Marks OnerajBelum ada peringkat
- 1 SMDokumen8 halaman1 SMAdhiguna MohammadBelum ada peringkat
- OFDM Performance in An Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) ChannelDokumen3 halamanOFDM Performance in An Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) ChannelerpublicationBelum ada peringkat
- CollectionDokumen15 halamanCollectionRey Maurice DonesaBelum ada peringkat
- WCDMADokumen31 halamanWCDMAHasbyNasrullohBelum ada peringkat
- EC6501 - Unit 4 & 5Dokumen13 halamanEC6501 - Unit 4 & 5menakadevieceBelum ada peringkat
- CDMA: Fundamentals: The Use of A Proper Code Allows Spreading Transmitted Signal and Despreading Received SignalDokumen31 halamanCDMA: Fundamentals: The Use of A Proper Code Allows Spreading Transmitted Signal and Despreading Received SignalGehendraSubediBelum ada peringkat
- Bit Error Rate (Ber) Comparison in Awgn Channel of BFSK and QPSK Using Matlab and SimulinkDokumen5 halamanBit Error Rate (Ber) Comparison in Awgn Channel of BFSK and QPSK Using Matlab and SimulinkGOUTAM KARBelum ada peringkat
- Digital ModulationDokumen12 halamanDigital ModulationChowneinMaioBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Modulation For Wireless CommunicationsDokumen72 halamanDigital Modulation For Wireless CommunicationslhslhinBelum ada peringkat
- 10 1109@icc 2002 996940 PDFDokumen5 halaman10 1109@icc 2002 996940 PDFMuhammadAbdullah59Belum ada peringkat
- 5 IjsrmDokumen5 halaman5 IjsrmmaxamedBelum ada peringkat
- Error Probability of Different Modulation Schemes For OFDM Based WLAN Standard IEEE 802.11aDokumen6 halamanError Probability of Different Modulation Schemes For OFDM Based WLAN Standard IEEE 802.11aaboashoorBelum ada peringkat
- Six-Port Modulator Based RF Transmission System Application in An OFDM EnviromentDokumen6 halamanSix-Port Modulator Based RF Transmission System Application in An OFDM EnviromentWalter Santiago Campos ArandaBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Modulation TechniquesDokumen14 halamanDigital Modulation Techniquesafroz_khan100% (5)
- Ofdm ProjectDokumen19 halamanOfdm ProjectSourav Pramanik0% (1)
- Digital CW Modulation Techniques: by Mrs. Leena MehtaDokumen16 halamanDigital CW Modulation Techniques: by Mrs. Leena MehtaLeena Rohan MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- A Study On The Transmission Scheme For The Advanced ISDB-T and Verification by Large-Scale Field Experiments in JapanDokumen8 halamanA Study On The Transmission Scheme For The Advanced ISDB-T and Verification by Large-Scale Field Experiments in Japanander20xBelum ada peringkat
- Unit IV 2020Dokumen78 halamanUnit IV 2020vaishnavi khilariBelum ada peringkat
- Coding and Modulation For Horrible ChannelDokumen20 halamanCoding and Modulation For Horrible ChannelAnand KharviBelum ada peringkat
- 3G Technology StudyDokumen9 halaman3G Technology StudyAbhay SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Phase-Shift Keying (PSK)Dokumen4 halamanPhase-Shift Keying (PSK)sandzzzcrazyBelum ada peringkat
- A Direct-Conversion CMOS Transceiver For The 802.11a/b/g WLAN Standard Utilizing A Cartesian Feedback TransmitterDokumen13 halamanA Direct-Conversion CMOS Transceiver For The 802.11a/b/g WLAN Standard Utilizing A Cartesian Feedback TransmitterdeviBelum ada peringkat
- 9.7 A 0.33nJ/b IEEE802.15.6/Proprietary-MICS/ISM-Band Transceiver With Scalable Data-Rate From 11kb/s To 4.5Mb/s For Medical ApplicationsDokumen3 halaman9.7 A 0.33nJ/b IEEE802.15.6/Proprietary-MICS/ISM-Band Transceiver With Scalable Data-Rate From 11kb/s To 4.5Mb/s For Medical ApplicationsSaleem AzharBelum ada peringkat
- ModulationPaper ACIQR-3Dokumen85 halamanModulationPaper ACIQR-3Ryan AnchetaBelum ada peringkat
- Implementation of High Speed OFDM Transceiver Using FPGADokumen3 halamanImplementation of High Speed OFDM Transceiver Using FPGAiirBelum ada peringkat
- An Najah National University Telecommunication Engineering DepartmentDokumen29 halamanAn Najah National University Telecommunication Engineering DepartmentZahoor AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report On Performance of Digital Modulation TechniquesDokumen8 halamanProject Report On Performance of Digital Modulation Techniqueseshet chafBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Evaluation of Wimax Physical Layer: Department of Electronics &communication, Sit, Tumkur, Karnataka, IndiaDokumen4 halamanPerformance Evaluation of Wimax Physical Layer: Department of Electronics &communication, Sit, Tumkur, Karnataka, IndiaMannath SungarBelum ada peringkat
- BER Analysis and Peak To Average Power Ratio of OFDM Using QPSK and 16-QAM Digital Modulation TechniquesDokumen8 halamanBER Analysis and Peak To Average Power Ratio of OFDM Using QPSK and 16-QAM Digital Modulation TechniquesRenu PareekBelum ada peringkat
- Performance of MIMO-OFDM Systems in Rayleigh Channel: Eni Dwi Wardihani, Subuh Pramono, Nia WatoniahDokumen6 halamanPerformance of MIMO-OFDM Systems in Rayleigh Channel: Eni Dwi Wardihani, Subuh Pramono, Nia Watoniahtyas ayuBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 15Dokumen30 halamanPresentation 15Aya Abd ElmonaemBelum ada peringkat
- Polar IQ TXDokumen5 halamanPolar IQ TXjaoudeBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Analysis and Monitoring of V PDFDokumen23 halamanPerformance Analysis and Monitoring of V PDFIvan CuadrosBelum ada peringkat
- Reference 4Dokumen3 halamanReference 4Smitha C.R.Belum ada peringkat
- Introductiontoltev1 1blog 120919131414 Phpapp02Dokumen45 halamanIntroductiontoltev1 1blog 120919131414 Phpapp02Karthick VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- WC Unit 3 LectureDokumen167 halamanWC Unit 3 Lecture6027- sumanchaitanya chinniBelum ada peringkat
- ريهام خالد جوحي PskDokumen9 halamanريهام خالد جوحي Pskريهام خالد جوحيBelum ada peringkat
- Ijesat 2012 02 Si 01 02Dokumen4 halamanIjesat 2012 02 Si 01 02Ijesat JournalBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Modes OverviewDokumen22 halamanDigital Modes OverviewBenjamin DoverBelum ada peringkat
- Signal Encoding Techniques: Even The Natives Have Difficulty Mastering This Peculiar Vocabulary. - The Golden BoughDokumen56 halamanSignal Encoding Techniques: Even The Natives Have Difficulty Mastering This Peculiar Vocabulary. - The Golden BoughTadele Basazenew AyeleBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine Electronics Code - Volume 1Dokumen28 halamanPhilippine Electronics Code - Volume 1janaisha_bai7170100% (3)
- Antennas and PropagationDokumen3 halamanAntennas and PropagationAgusto PanganibanBelum ada peringkat
- Probability of Simple EventsDokumen12 halamanProbability of Simple EventsRB Astillero67% (6)
- Antennas and PropagationDokumen3 halamanAntennas and PropagationAgusto PanganibanBelum ada peringkat
- Obligations and Contracts PDFDokumen38 halamanObligations and Contracts PDFJoery Bryan BuenconsejoBelum ada peringkat
- Probability of Simple EventsDokumen12 halamanProbability of Simple EventsRB Astillero67% (6)
- Rizal Summaries Chapter 1 13Dokumen3 halamanRizal Summaries Chapter 1 13Renjan Solis50% (2)
- Microwave CommunicationsDokumen43 halamanMicrowave CommunicationsShashank KothiyalBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine Electronics Code Volume 2Dokumen18 halamanPhilippine Electronics Code Volume 2JMSquaredBelum ada peringkat
- Pledge of Electronics EngineerDokumen1 halamanPledge of Electronics EngineerDanika JanBelum ada peringkat
- RA 9710 Gynecological Disorder LeaveDokumen9 halamanRA 9710 Gynecological Disorder LeaveBreth1979Belum ada peringkat
- Series and Parallel Equations From A de PerspectiveDokumen6 halamanSeries and Parallel Equations From A de PerspectivealenagroupBelum ada peringkat
- Obligations and ContractsDokumen19 halamanObligations and ContractsRenjan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1,2,3 of Jose Rizal's Life, Works, and WritingsDokumen12 halamanChapter 1,2,3 of Jose Rizal's Life, Works, and WritingsHannah Lou Paet74% (19)
- Chapter 2Dokumen22 halamanChapter 2Anne DiasBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Case StudyDokumen10 halamanEnvironmental Case StudyRenjan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- Rizal Summaries Chapter 1-13Dokumen29 halamanRizal Summaries Chapter 1-13Zamille Bernardino79% (145)
- StarcraftDokumen1 halamanStarcraftRenjan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- ProbabilityDokumen9 halamanProbabilityJaya PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Industry Protection SystemDokumen6 halamanIndustry Protection SystemRenjan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- Combined SimpsonDokumen1 halamanCombined SimpsonRenjan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- A.Data Parameter I (T) VC (T) VL (T) ValueDokumen1 halamanA.Data Parameter I (T) VC (T) VL (T) ValueRenjan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 1 Plots EZDokumen11 halamanLab 1 Plots EZRenjan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm Project Assessment RubricDokumen1 halamanMidterm Project Assessment RubricRenjan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- EULERDokumen1 halamanEULERRenjan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- ReviewerDokumen3 halamanReviewerRenjan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Problems - CircuitsDokumen10 halamanSample Problems - CircuitsRenjan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 - Direct Current CircuitDokumen53 halamanChapter 8 - Direct Current CircuitRenjan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- Modulation Type Description Applications: Frequency-Shift Keying)Dokumen4 halamanModulation Type Description Applications: Frequency-Shift Keying)Renjan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- Gauss ReductionDokumen1 halamanGauss ReductionLanz de la CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Lte Mobility: Connected Mode. The Network Controls Transition of UE Between The Idle and RRCDokumen9 halamanLte Mobility: Connected Mode. The Network Controls Transition of UE Between The Idle and RRCseeinamBelum ada peringkat
- Training Document GBSS13.0 BSC6900 (V900R013C00) VAMOS Feature Description-20110512-A-1.0Dokumen51 halamanTraining Document GBSS13.0 BSC6900 (V900R013C00) VAMOS Feature Description-20110512-A-1.0Chidhuro OwenBelum ada peringkat
- AlarmduinoDokumen6 halamanAlarmduinoMohammad HaidarBelum ada peringkat
- 1.2.4.3 Lab CiscoDokumen2 halaman1.2.4.3 Lab CiscoNicolasBelum ada peringkat
- Gigagigabyte Ga-945gcm-S2 r3.0 SchematicsDokumen34 halamanGigagigabyte Ga-945gcm-S2 r3.0 SchematicsGleison PrateadoBelum ada peringkat
- bcmwl64 Drivers DP WLAN 15055 Broadcom FORCED 81x86 BCM43 7.10.96.0Dokumen4 halamanbcmwl64 Drivers DP WLAN 15055 Broadcom FORCED 81x86 BCM43 7.10.96.0WàlÎîdBelum ada peringkat
- SReXperts Bangkok 2013 - Event Guide - 20130905 - S PDFDokumen17 halamanSReXperts Bangkok 2013 - Event Guide - 20130905 - S PDFMarco BertoliniBelum ada peringkat
- ProductSheet MCX8000121212Dokumen8 halamanProductSheet MCX8000121212alexggggBelum ada peringkat
- Lte To 3g Circuit Switched Fall Back PDFDokumen3 halamanLte To 3g Circuit Switched Fall Back PDFKarina LisbethBelum ada peringkat
- Modbus MasterDokumen3 halamanModbus MasterJaime Gutierrez MondragonBelum ada peringkat
- National Institute of Technology Calicut: Digital Communication Lab ReportDokumen7 halamanNational Institute of Technology Calicut: Digital Communication Lab ReportSaketh RaviralaBelum ada peringkat
- CCNP5Dokumen162 halamanCCNP5Camille Joy BuronBelum ada peringkat
- Xpress DR Ug LantronixDokumen149 halamanXpress DR Ug LantronixDavicho RabadánBelum ada peringkat
- BGP Route Selection: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. All Rights ReservedDokumen25 halamanBGP Route Selection: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. All Rights ReservedEDWIN GREGORIO MARIN VARGASBelum ada peringkat
- Android Phone As A VPN Gateway (Bypass Tethering Block)Dokumen6 halamanAndroid Phone As A VPN Gateway (Bypass Tethering Block)Shaza HazarulBelum ada peringkat
- LogDokumen12 halamanLog4c1kBelum ada peringkat
- 2021 03 18 - LogDokumen10 halaman2021 03 18 - LogEndri ApriliyonoBelum ada peringkat
- 6.3.2.7 Lab - Exploring Router Physical CharacteristicsDokumen9 halaman6.3.2.7 Lab - Exploring Router Physical CharacteristicsParthPatel100% (1)
- RHF2S308 WEB User Manual-V1.0Dokumen15 halamanRHF2S308 WEB User Manual-V1.0Mario Vladimir Suarez ChanchayBelum ada peringkat
- Parallel Wireless HetNet Gateway Data Sheet PDFDokumen4 halamanParallel Wireless HetNet Gateway Data Sheet PDFSamudera BuanaBelum ada peringkat
- Brocade Adapters v3.1.0.0 Admin GuideDokumen324 halamanBrocade Adapters v3.1.0.0 Admin GuideSundaresan SwaminathanBelum ada peringkat
- Shutdown Profile.4Dokumen1 halamanShutdown Profile.4Cris dlzBelum ada peringkat
- New Rock Products Catalog - VoIP Solution ProviderDokumen6 halamanNew Rock Products Catalog - VoIP Solution ProviderHanna ZhaoBelum ada peringkat
- 6.5 Dynamic NATDokumen13 halaman6.5 Dynamic NATSyifa FauziahBelum ada peringkat
- Port Security Juniper PDFDokumen298 halamanPort Security Juniper PDFroby yasirBelum ada peringkat
- MAC SublayerDokumen92 halamanMAC SublayerAlready ATracerBelum ada peringkat
- 5G Trial Offer Viettel 2019 - Scope - v1.0 - VTDokumen9 halaman5G Trial Offer Viettel 2019 - Scope - v1.0 - VTQuốc DũngBelum ada peringkat
- 7210 Sas Service-Access-Switch Amt PDFDokumen7 halaman7210 Sas Service-Access-Switch Amt PDFHector Obando VBelum ada peringkat
- v5.1.0.ERN - External v0.5Dokumen44 halamanv5.1.0.ERN - External v0.5Ashraf SaeedBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Wireless Communication - (CHAPTER 1 Introduction) PDFDokumen9 halamanFundamentals of Wireless Communication - (CHAPTER 1 Introduction) PDFJatinder KumarBelum ada peringkat