فحص بلدية دبي
Diunggah oleh
Fredj KriaaDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
فحص بلدية دبي
Diunggah oleh
Fredj KriaaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Municipality Exams
G+1 Test
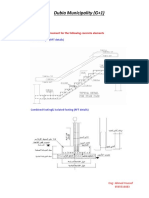
1. Draw the reinforcement for the following concrete elements
a) Staircase flight (RFT details)
b) Combined footing& isolated footing (RFT details)
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 1
c) Raft foundation (RFT details)
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 2
d) Continuous beam at least 2 spans.
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 3
e) Hollow block slab continuous from two sides.
2. What is the test before and after casting?
Before casting: Temperature test (temperature has to be less than 34) , Slump test
(the settlement not more than 11cm), cube samples for cube test which will be done
after 7 days and 28 days.
After casting: Shemidit hummer, ultra sonic, cube test (test will be done after 7 days
and 28 days), core test (will be done after cube test failed)
3. What are the cover and the de-shuttering for the following concrete elements? (footing, Tie
beam, Columns, Beams and slabs).
Footing (Cover= 5-7cm.. de-stuttering= 1 Day)
Tie Beam (Cover= 3cm.. de-stuttering= 2 Day)
Columns (Cover= 2.5-3cm.. de-stuttering= 2 Day)
Beams (Cover= 2.5cm.. de-stuttering= 14 Day (2L+2) where L the long span)
Slabs (Cover= 2.5cm.. de-stuttering= 14 Day (if L<3 after 7 day, if 3<L<6 after
10 day , if L<6 after 14 days)
4. What is the name of test which will make at site before placing footing and what is the
acceptable result?
Compaction test ( the relation between dry density and water content , result will be
95% of dry density ( also depend on specification of project)
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 4
5. Explain briefly the steps of checking for the flowing items (excavation and preparation, axes,
?)footing, col and slabs
Excavation and Preparation :
)a .
)b .
)c shoring .
)d compaction
)e back filling road base pcc .
Axis:
)a
Footing :
)a
)b
)c
)d
)e cover
)f ( ).
)g
)h
)i .
Columns :
)a
)b
)c
)d
)e
)f
)g
)h
)i
Slabs:
)a
)b
)c
)d
)e
)f
)g cover
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 5
6. What is the type of cracks may be appears in the structural elements (col and slabs) explain
?your answer with sketches
-1
:
.
: .
:
.
( : :
) ( .. :
)
-2 :
: .
.
.
?7. What is the bleeding in concrete
?8. What it mean by shotcrete concrete, self-compacted concrete
shotcrete
.
Self-compacted concrete
).Slump test = 60 cm (Dia
?9. What is the destructive test and non-destructive tests
Destructive test : . cube and core test
Non-destructive test : Ultrasonic test and loading test and
. schemidet hammer test
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 6
10. What will you do if you have a G+1 building with corrosion? How you repair the corrosion in
steel building?
remove the concrete cover
clean the steel
paint steel and old concrete with Epoxies paint
Shotcrete and cover the steel again
11. What is the acceptable result for cube test after 7 days in grade 30 and 40?
Result after 7 days not less than 75% of grade after 28 days to be successful so the result =
.75*30= 22.5 N and .75*40= 30N.
12. What is the problems maybe face for the casted concrete?
13. Draw sketch for raft foundation (plan and vertical section passing with columns)and indicate
the arrangement and position main reinforcement and extra steel top& bottom also sketch the
moment diagram on the foundation. (see Q1).
14. Draw reinforcemet details for the shown corbel and the connection between corbel and steel
section .
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 7
15. What it means by tower crane, where it locates in the building and for which kind of building
we use it?
.
. high rising construction . tower crane
Types :
1) Horizontal jib Jib moves only horizontal .
2) Luffing Jib Jib moves for both direction
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 8
6-4.
tower crane 8-6.
tower crane :
)a .
)b cranes..
. )c
)d .
tower crane
16. Sketch the load diagram for tower crane and indicate the location of maximum load and
?minimum load
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 9
17. Draw section reinforcement of single basement wall (full details)?
18. Show position of steel splices in continuous beams (top&bot)
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 10
19. Draw the steel development for the shown systems
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 11
20. Draw the moment for the following
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 12
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 13
?21. Explain some types of concrete joints
Construction Joint :
.minimum shear
Expansion Joint :
. 2 44 64 12.
Settlement Joint : .
2 .
Isolation Joint : .
Control Joint :
.
?22. What is the difference between damp (moisture) proofing and water proofing
Damp proofing is intended to keep out soil moisture, while waterproofing keeps out both
moisture and liquid water.
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 14
23. What is the precautions during concrete casting in hot weather?
Covering water tank and aggregate
Spray water above shutter before casting
Covering the concrete and curing
Casting in night if possible
Using ice with water of mix
Maximum concrete degree should not more than 34
24. What is the types of cement used in footing and slabs
SRC (Sulphate Resistance Portland ) for footing . and OPC( Ordinary Portland cement) for slabs.
25. What are the types of shoring used in high rise buildings? Draw sketch for each type?
1- Contiguous Piles
2- Secant Piles
3- Diaphragm Walls
4- Soldger
5- H-Beams with concrete Panels
1- Contiguous Piles
5 ~ 7.5 cm gap
) 2 basements(
piles piles
2- Secant Piles
3-
piles
pile ) 3 basements (
pile
3- Diaphragm Walls
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 15
4- Soldger
5- H-Beams with concrete Panels
6 ~ 5 ) one basement (
26. Discuss the dewatering for high rising building
If the GWL is higher than the foundation level dewatering is used to pull the water 1 m below the
foundation. Removing dewatering until weight of structure is greater than the uplift pressure so that the
water doesnt affect the stability of the building.
27. What types of slabs used in high rising buildings?
Flat slab, Paneled beam, solid slab, Post tension slabs.
28. If the concrete compressive strength test after 28 days failed, what should be safety if the
structure?
. core
.
.
29. What are the minimum overlapping length under different straining action?
Columns 45D Beam& Slabs ( 60D at tension , 40D at comp.)
30. What is the difference between theodolite and total station?
Theodolite for calculation of angels only, but total station for all (angels, level and coordination)
31. Describe slump test
workability
h
.
Foundation = 2-3 (5-7 cm)
Columns =3-5 (7-13 cm)
Slabs & Beams = 2-4 (5-10 cm)
Piles = 6-8 (15-20 cm)
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 16
32. Sketch the main steel for pile cap (group of 3 piles)
33. In isolated footing, in which direction will be the main steel, why?
.
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 17
34. Draw a section in a roof water proofing system and how to test it?
35. What it means by punch and how we control it?
Punching shear will happen in flat slab, means that columns will penetrate the slabs.
It happens when the thickness of slab around columns is small and more load.
We can control it by making drop panel or column head or increase dim. of column.
36. What it mean by deflection, where it happened and how we avoid it?
:Deflection
long term ( ) short term (
) shrinking
37. What is the required depth of boreholes in different stages (isolated , combined footing, raft,
piles foundation ) as per BS?
- Isolated and combined , depth of borehole= 2 width of footing.
- Raft, depth of borehole=1.5 width of building.
- Piles, depth of borehole= length of pile+5D (where D is the damiterer of piles
Note: Depth of borehole not less than 10 m.
38. How many boreholes required for a site area 900 m2?
Minimum boreholes are 2.
- As per BS 1 borehole for each 300m2 So for area 900 m2 , required 3 boreholes.
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 18
?39. What is the different types of piles
)Classification based on load transfer: (End Bearing Piles (2~2.5 ) 0.75m
,(Friction Piles (3~5 ) 1 m),( Tension Piles).
(Classification based on method of installation ( Driven or displacement piles),
)replacement piles
)Classification based on Material (Steel piles),(concrete piles
Note: Piles Spacing = (2~5 )depends on soil type, piles type and piles diameter.
Piles should penetrate (2~4) inside the bearing stratum
?40. What is the different between strap beam and tie beam
?41. What the different between quality control and quality assurance
Quality control
Quality Assurance
.
?42. When we have to go for pile foundations
If the top layers of the soil are soft and good bearing stratum at a reasonable depth.
.44 .
. .
.44 7 .
28 7
28
.
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 19
45. Draw an organization chart for site project.
46. What is mean by safety third party certificate and when it finished and renewed and for which
machineries you make?
(
) 6 man lift
47. What is the additional for concrete?
waterproofing admixtures which used in tunnels, basements, swimming
pool....Example pudlow, Ash
Densifier ( ) ....Example: Micro silica
Corrosion inhibitors () .Example: calcium nitrates ()
Plasticizer () .Example: silica, FEB flow
Decrease hydration temperature & increase strength.Example GGBS
Retarders ( & ) Accelerators ()
48. What is the ratio in concrete mix design?
49. Bored Piles
The statement is to fix casing and punching it vertically by hammering and/or
drilling to specific depth and to proceed with removing the soil from inside
After finishing, steel reinforcement to be fixed in the crane and pushed down and
steel should be fixed also by dewells in the casing to prevent floating of the steel
during the concrete casting
If the ground water table is high, precaution should be taken to keep the casing full
of water up to the level of water table or even higher to prevent boiling at the scat
of the pile which is turns will cause excessive settlement (Dewatering).
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 20
:
( Auger machine( CFA
case Casing System
### Max Accepted deviation for any pile is 7cm and if we have more than that value, we have
to redesign the pile cap for this pile
50. What is the Pilling Tests?
1- Static Load Test (for 1% of the piles)
2- Dynamic Load Test (for 5% of the piles)
3- Integrity Test ( for all piles)
4- Sonic Test ( for piles more than 30 m length)
### Settlement of piles not more than 6 ~ 8 mm
### Code range of piles settlement of pile not more than 25 mm
### Piles should penetrate (2~4) inside the bearing stratum.
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 21
Static Load Test for Piles
Working piles test load = 1.5 x Design load
Total Time for the test 23 Hours
1st Cycle ( 80 minutes) - Loading
25% P 50% P 75% P 100% P
20 Minutes 20 Minutes 20 Minutes 20 Minutes
2ND Cycle (90 Minutes) Un loading
75% P 50% P 25% P 0% P
10 Minutes 10 Minutes 10 Minutes 60 Minutes
3rd Cycle (1100 Minutes) Loading Again
100% P 125% P 150% P
360 Minutes 20 Minutes 720 Minutes
4th Cycle (110 Minutes) Unloading
125% P 100% P 75% P 50% P 25% P 0% P
10 Minutes 10 Minutes 10 Minutes 10 Minutes 10 Minutes 60 Minutes
Result : Settlement of piles should not exceed 6`8 mm or 1.5mm/hr or 10% pile
### If the piles type is friction piles, then the static test must be done only after 28 days.
Sonic Test
Used for to check the pile section through the pile and no cracks or soil failure
inside the pile body
51. What is the bentonite benefits?
Used to prevent soil failure for the piles sides
Pile Caps
Caps considered as footing for columns and transfers the load through the piles
And not through the soil underneath, so compaction under pile caps is not required.
At least 60 cm from piles steel should penetrate the pile cap.
Approximately the pile cap depth is equal to double of piles diameter.
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 22
Piles reinforcement steel ratio = 0.8% piles concrete cross section .
52. Shoring Pile Side Load Calculations
F = 1m x L x 1 ton
F* = x x L x Kp x L
Kp = 0.33
Ka = 1/Kp 3
53. What is the Foundation Types
Shallow foundations (Isolated footings, strap footings , raft footings)
Deep foundations (Piles, Caison, piers)
-: 3 30 N -
22.5 N , 27 N and 30 N
N 2665 = -
N 2565 = 44 X 4685 = %85
N 2265 = 44 X 4675 = %75
%85 <=
%75 <=
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 23
- 30 N 4 ( )cm51x51x51-:
51 52 31 04
- 25( 1 2665 = )28/2
45( 2 4465 = )44/2
= 42/2
2
4
.54 :
))(1 L.L + D.L) OR (1.25(L.L + D.L.
( )Deflection
-:
-1 < %75
> %75
?55. What is the relation between cubes and cylinder results
Cylinder strength = 0.8 cube strength
56. Dismantling of form shutters
Side forms (columns, beams sides ) after 2 days
Soffits (propped) after 7 days
Soffits (un propped) after 14 days
Cantilever (2m) after 21 days
57. What is the rings purpose
Keep vertical steel bars in position
Resist against buckling
Resist against shear force
Keep concrete cover fixed for structural element
58. Design of mix Design (example 30N) for piling
Cement = 400 kg/m3
W = 180 L
W/C = 180/400 = 0.45
Slump = 150 25 mm
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 24
59. Concrete Cover for structure elements
Beams and Slabs = 2~3 cm
Columns = 3 ~ 3.5 cm
Footings and Piles = 7.5 cm
60. Concrete Delivery Note should show the following:
Date
Truck No.
Company Name (supplier)
Main contractor Name
Site Details and Location
Type of concrete and temperature
Concrete grade
Slump value
Concrete quantities
Truck leave time
Admixtures information
Cement quantities
.61
Cubes or cylinder crush test
Core test
Loading test
Rebound hummer test
Sonic-ultra test
Types of Slabs and Usual % Reinforcement
Solid Slab (100-120) kg/m
Flat Slab (160-185) ) kg/m
Wafle Slab(160-185) ) kg/m
Hurdy Slab (160-185) )kg/m
Post Tension Slab (60-65) kg/m
Hollow core slab (Cables)
Paneled Beam Slab (150-180) kg/m
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 25
.26
.26
.
.26 slump
test
.
?65. What is the difference between target mean strength and characteristic strength for concrete
) ( Fc: Characteristic strength
) ( Fm: Target mean strength
S: Standard deviation 6.1 N/mm
K: Constant = 1.64
Fm = Fc + K x S
Example: for Fc = 30 N/mm
Fm = 30 +(1.64 x 6.1) = 40 N/mm
66. Post Tension
Dooms
post tension
Control hire cracks
To resist ve moment above columns
To resist punching or shear forces
Classes of post tension
Class (1) no cracks allowed like water tanks
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 26
Class (2) cracks limited
Class (|3) cracks allowed
Poor strip
44
.
Grouting Usage
.
Duct
duct B.M.
24~16 ( N 12~9
)
\.
Anchors
Flowers
duct
67. Steel reinforcement Tests
1- Tension test
2- Bend and re-bend test
3- Chemical test
4- Yield
Used for design
5- Stain
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 27
)Modulus of Elasticity (E
Ec (Concrete) = 140 ton/cm2
Es (steel) = 2100 ton/cm2
Thermal Modulus
1 = 10 ^-5
= ( mm / m / c ) 1.2 x 10^-5
)Poissons Ratio (
For concrete = 0.15
For Steel = 0.25
Percentage of Salts in Water
1- Soluble sulphate (SO3) 0.1% or 1000 P.P.M
2- CL 0.05 % or 500 P.P.M
3- C2 CO3 0.1% or 1000 P.P.M
4- PH Value at 25 = 0.0
5- Organic Materials = 0.0
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 28
68. Draw the section for Raft or combined foundation with 16 top and bottom +
additional 25 @ 100 bottom + 20 @ 200 top
Note (Additional top between columns and additional bottom at columns)
16 both way 2 layers
20 @ 200 extra top
25 @ 200 extra bottom
16 both way 2 layers
Sec.x
69. What is the lab length splice for Bar D 40
Only using couplers (no splice)
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 29
)shear force( .04
Min. Shear Area
S/3
S/3 S/3
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 30
71. What is the connection between beam and columns for high rise building
Continuity for columns stirrups and increase columns stirrups (1m) below and above
connection
Increase beam stirrups near support (seismic zone)(L/4 or safer L/3)
1m
1m
72. From soil report we can determine and estimate
1- Bearing Capacity
2- Type of foundation
3- Type of cement
4- Expected settlement
5- Getting water table level
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 31
73. Soil Tests
1- Plate Bearing Test
75 x 75 45 x 45 30 x 30
2~1.5
12
) (
( ) =
74. For Soil Investigations
Buildings: Boreholes should be every 20m in each direction
Roads: Boreholes should be every 30m in each direction
Depth of boreholes should be (1.5~2) short raft length
: .75
Slump cone
Cubs moulds
Tedolite
Thermometer
Measuring tape
Staff level
Micrometer
Scale
Solid Block = 7N -1
Hollow BLOCK = 4.5 N -2
Hurdy Block = 5 N -4
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 32
High Rise Building Considerations:
76. What is the structure system in high rise building
For concrete (in high rise building
1- Core system
2- Core and shear walls
3- Tubular system
4- Vertical trusses for steel buildings
77. What is the scaffolding type for slab and core wall for high rise building
For slabs panel forms (DOKA :ex, the doka flex floor system for slabs)
For core climbing system with platforms.
Wind effect and seismic effect considered during design
Elevations finishing by cradles and not by traditional scaffolding
If height > 55 m hocks should be used for cradles robes
Dismantling cranes from the top of the building by special type of cranes
named (Derek) which can be fixed in the roof slab and dismantling the
main tower crane then another smaller Derek crane used to dismantle
the big Derek then the last small Derek can be transfer in the lift
Drainage cant be directly free fall (vertical u shape pipe will be each 4
floors)
( KHK )
Standard ultimate yield load = 4 tons, but we consider 600~700 kg
during design for the slab shutter
We have to consider heavy members alone as big beams which leads to
failure due to buckling of standards
We have to consider L.L values for the previous slab which will carry the
new slab during casting
Maximum opening for any base jack should not exceed 20 cm , in order
to avoid buckling for this member
Bracing to be considered and tilting with columns and walls is a must.
PREPARED BY:AHMED AMIN 33
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Dubai Municipality Exam - G+1Dokumen32 halamanDubai Municipality Exam - G+1rabia bano60% (5)
- DM ExamDokumen4 halamanDM ExamETHANBelum ada peringkat
- Instructions For Writing Dubai Municipality Exam PDFDokumen3 halamanInstructions For Writing Dubai Municipality Exam PDFAkhil VNBelum ada peringkat
- DM Exam G+Unlimited DEQ QuestionsDokumen3 halamanDM Exam G+Unlimited DEQ QuestionsMohamed Taha100% (8)
- Subject: NOC For G+6 Exam in Dubai MunicipalityDokumen1 halamanSubject: NOC For G+6 Exam in Dubai MunicipalityZeeshan YasinBelum ada peringkat
- Ass. Sub Engineer 04 04Dokumen3 halamanAss. Sub Engineer 04 04Bipul PoudelBelum ada peringkat
- Unlimited & G+12 DM Exam-Revision-01Dokumen15 halamanUnlimited & G+12 DM Exam-Revision-01Vijith2980% (5)
- DMDokumen2 halamanDMsreedevi gummadi100% (1)
- G+4 DM QuestionsDokumen22 halamanG+4 DM QuestionsVikash Kumar100% (1)
- Dubai Unlimited & G+12 DM ExamDokumen16 halamanDubai Unlimited & G+12 DM ExamJett Aglipay88% (16)
- Syllabus For G+1 & G+4: For G+1: Questions Are Generally Asked Regarding Low-Rise Steel Structures, Both PEBDokumen1 halamanSyllabus For G+1 & G+4: For G+1: Questions Are Generally Asked Regarding Low-Rise Steel Structures, Both PEBhidayat665287Belum ada peringkat
- Dubai Municipality G 1 G 4 G 12 Exams MCQs 1690895684Dokumen20 halamanDubai Municipality G 1 G 4 G 12 Exams MCQs 1690895684osama78% (9)
- DM - Exam - Civil QuestionsDokumen1 halamanDM - Exam - Civil QuestionsSurya SundarBelum ada peringkat
- Unlimited & G+12 DM Exam Rev.01Dokumen15 halamanUnlimited & G+12 DM Exam Rev.01Lobna Tameem100% (2)
- DM ExamDokumen30 halamanDM ExamAi Lin Adarlo71% (7)
- G+12 EXAM - My ExamDokumen7 halamanG+12 EXAM - My ExamMohammed Nasih Vettathur100% (2)
- DMDokumen15 halamanDMLorraine BautistaBelum ada peringkat
- Instructions For Writing Dubai Municipality ExamDokumen3 halamanInstructions For Writing Dubai Municipality Examjinshad60% (10)
- Dubai Mnicipality G+12Dokumen4 halamanDubai Mnicipality G+12Agbanglo June75% (4)
- Dubai Municipality Exam - Civil EngineerDokumen3 halamanDubai Municipality Exam - Civil EngineerThasneem YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- (Computer Science & Engineering) Name: Subject: DM Date: Marks: 20Dokumen2 halaman(Computer Science & Engineering) Name: Subject: DM Date: Marks: 20MeeraBelum ada peringkat
- MMUP EXAM JMQDokumen3 halamanMMUP EXAM JMQmaninambiramBelum ada peringkat
- Instructions - DM TestDokumen1 halamanInstructions - DM TestmujeebscribdBelum ada peringkat
- Dubai Municipality Exam WITHOUT ANSWERSDokumen58 halamanDubai Municipality Exam WITHOUT ANSWERSW100% (1)
- Dubai Municipality Test G+12 & Unlimites - MajdDokumen19 halamanDubai Municipality Test G+12 & Unlimites - Majdmajd el chami83% (6)
- DM G+12 & Unlimited Test QuestionDokumen19 halamanDM G+12 & Unlimited Test Questionmajd el chami100% (1)
- Dubai Municipality Exam NewDokumen59 halamanDubai Municipality Exam NewMohamed Taha100% (36)
- Undertaking For DM TestDokumen1 halamanUndertaking For DM TestMuhammad Sabih ToorBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ's PADDokumen18 halamanMCQ's PADaaquib ansariBelum ada peringkat
- Steel Structure ObjectiveDokumen4 halamanSteel Structure ObjectiveImran SikandarBelum ada peringkat
- Full Mock Test Series 05Dokumen10 halamanFull Mock Test Series 05Abhilasha CIVILBelum ada peringkat
- محاضرات انشاءات معدنية د.سعد الدين مصطفيDokumen111 halamanمحاضرات انشاءات معدنية د.سعد الدين مصطفيEmad Elhussieny98% (58)
- Dubai Engineering Qualifications Individuals Services V4.5Dokumen62 halamanDubai Engineering Qualifications Individuals Services V4.5Dream Homes100% (1)
- Pad Footing BS8110Dokumen1 halamanPad Footing BS8110Asif BillalBelum ada peringkat
- Dubai Municipality - Building Code RegulationsDokumen34 halamanDubai Municipality - Building Code RegulationsHany dowedarBelum ada peringkat
- DUBAI MUNICIPALITY - Regulations On Building Conditions & SpecificationsDokumen90 halamanDUBAI MUNICIPALITY - Regulations On Building Conditions & Specificationsscribduserforever71% (7)
- نوتة حسابية كاملة لمبنى فيلاDokumen87 halamanنوتة حسابية كاملة لمبنى فيلاWalif Dababat95% (22)
- Adel Mohamed Dubai Municipality 2Dokumen43 halamanAdel Mohamed Dubai Municipality 2ALPHYL BALASABAS100% (2)
- ShoringDokumen8 halamanShoringJeo LawrenceBelum ada peringkat
- Types of ShoringDokumen9 halamanTypes of ShoringAzil14100% (10)
- Dubai Municipality Exam Solution g4Dokumen9 halamanDubai Municipality Exam Solution g4santhi peddannaBelum ada peringkat
- SHORINGDokumen10 halamanSHORINGIzzuddin ShahidanBelum ada peringkat
- أعمال البناءDokumen115 halamanأعمال البناءWalif Dababat100% (5)
- Dubai Engineering StanderDokumen193 halamanDubai Engineering Standermzafarnawaz80% (5)
- 1500 سؤال QuesDokumen1.867 halaman1500 سؤال Quesamin alzuraiki97% (31)
- Fig. 1. Plan View of Typical Frame Layout: ASCE Wind LoadsDokumen1 halamanFig. 1. Plan View of Typical Frame Layout: ASCE Wind Loadscewaleed2590Belum ada peringkat
- Deshuttering Time For Slabs, Beams and Columns As Per IS CodeDokumen5 halamanDeshuttering Time For Slabs, Beams and Columns As Per IS Codesrinivasyadav4Belum ada peringkat
- DM ExamDokumen4 halamanDM Examyayooo2004100% (1)
- Dubai Municipality Building Code RegulationsDokumen93 halamanDubai Municipality Building Code RegulationsRajesh K Narayanan100% (2)
- أعمال اللياسةDokumen91 halamanأعمال اللياسةWalif Dababat100% (5)
- Dubai Municipality Building Regulations: Translated by Santis HSE Group 2309 Al-Shatha Tower DMC-Dubai UAEDokumen74 halamanDubai Municipality Building Regulations: Translated by Santis HSE Group 2309 Al-Shatha Tower DMC-Dubai UAEAhamed Ashith100% (2)
- What Is The Test Before and After Casting?: TH TH TH THDokumen7 halamanWhat Is The Test Before and After Casting?: TH TH TH THMohammad UmmerBelum ada peringkat
- Uganda Technical College - Lira: IMPORTANT SAMPLE QUESTIONS (Design of Concrete Structures To Eurocode 2)Dokumen38 halamanUganda Technical College - Lira: IMPORTANT SAMPLE QUESTIONS (Design of Concrete Structures To Eurocode 2)Mugara Waitega PeterBelum ada peringkat
- ROB Design 35 Deg Skew - SuperstructureDokumen25 halamanROB Design 35 Deg Skew - SuperstructureAnonymous sfkedkymBelum ada peringkat
- Method Statement of AbutmentDokumen8 halamanMethod Statement of AbutmentSaeed Ahmed SoomroBelum ada peringkat
- Performance of Joints in Reinforced Concrete (Filigree) Slabs For Two-Way Spanning Action (Stehle 2011)Dokumen13 halamanPerformance of Joints in Reinforced Concrete (Filigree) Slabs For Two-Way Spanning Action (Stehle 2011)Eli WallachBelum ada peringkat
- 5958r09-Earthquake Resistant Design of BuildingsDokumen2 halaman5958r09-Earthquake Resistant Design of BuildingsSagarBelum ada peringkat
- Pa&d JalanDokumen9 halamanPa&d JalanIkram MuzhaffarBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Drawing HRS.: of StructuresDokumen2 halamanDesign and Drawing HRS.: of StructureskarthiksampBelum ada peringkat
- Civil Work Specification Part 15Dokumen10 halamanCivil Work Specification Part 15mr.xinbombayBelum ada peringkat