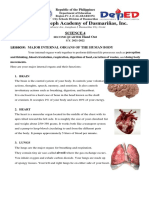
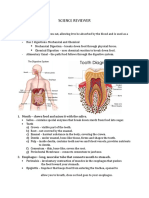
HSB Diseases
Diunggah oleh
Vivienne WrightJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
HSB Diseases
Diunggah oleh
Vivienne WrightHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
2009
ATHLETES FOOT:
Transmission:
Direct contact, as in, skin to skin contact
Walking barefoot on damp/ wet floors of changing rooms, contaminated with fungal
spores
Sharing socks / towelscontaminated with fungal spores
Skin shed from feet of infected person contains fungal spores that are picked up by
uninfected person when walking barefoot. The parasitic fungus establishes itself in
the new host.
Prevention of spread:
Well ventilated footwear/ sandals are used to inhibit fungal growth.
Wash feet thoroughly to remove sweat.
Use disinfected footbath at swimming pools.
Dry yourself thoroughly between the toesor use antifungalpowder
Change socks regularly
Fungicidal drugs and creams are used for treatment.
Wear slippers in changing rooms
Disinfect floors of changing rooms regularly
Sufferers should not use swimming pools
Dont share towels, socks, footwear to reduce the chances of cross infection.
Use disinfectant in swimming pools
Nutrition of Fungus causing Athletes Foot :
The fungus is parasitic.
It lives in the surface of the body on the damp skin between the toes.
It secretes extracellular enzymes to digest skin cells in presence of water.
The products of the digested skin are absorbed into the hyphae by diffusion
Nutrition:
Definition :A balanced diet contains all the nutrients required by the body in the right
amounts (neither omitted nor in excess). It includes fats, proteins, carbohydrates,
fibre, water, vitamins and minerals.
FATS
Use of fats in the body:
Fats act as a store of energy for use when the body requires extra energy. Fats have higher
energy value.
Fats provide electrical insulation around axons and dendrons of neurones.
Fats act a solvent for uptake of vitamins A and D to allow them to pass across cell membranes.
Fats are a component of the cell membrane, so, they are needed to form new cells.
Fats protect internal organs, for example, pericardium around the heart, protects against
mechanical injury. Kidneys are protected.
Fat layer under the skin in the hypodermis provides thermalinsulation, reducing heat loss to
the environment, thus helping maintain a constant body temperature.
Note :Eat food having lower fat content as the chances of blocking arteries / causing heart attacks is
reduced. Lower risk of obesity.
Deficiency :
The person finds it difficult to control body temperature in a coldenvironment. Fat layer
under the skin in the hypodermis provides insulation. If that layer is lost, that is, used up if
diet lacks fat, more heat is lost to the environment.
The body loses a source of energy from diet.
In Excess :
Obesity results as fat is stored around organs and under the skin.
Extra mass has to be moved around due to obesity, which puts strain on muscles, heart and
skeleton. The heart muscle must also work harder.
Increased risk of diabetes
Increased risk of coronary heart disease as deposit of saturated fat, such as, cholesterol cause
coronary arteries to be narrowed / blocked. This increases the risk of heart attack.
Problems linked to obesity :
Coronary Heart Disease
Varicose veins
Colon cancer
High blood pressure
Foot problems
Heart attacks
Increased pressure in the eye
Test for fats :
The food sample is chopped or grinded and is put in a dry test tube. Ethanol is added and the
test tube is shaken. The liquid is decanted and a drop of cold water is added to it.A cloudy
emulsion confirms the presence of fats.
Squash food on filter paper. Attempt to dry stain. If still transclucent, fat present.
Chop / squash food. Add (III or IV) dye. Leave for a few minutes and wash off. Look for
orange / red colour in food.
Differences between cells produced by mitosis and meiosis :
Mitosis Meiosis
Cells having diploid nuclei Cells having haploid nuclei
Daughter cells are genetically identical to each Daughter cells are not genetically identical
other and to the parent cell
2 cells / 2 nuclei are formed. 4 cells / 4 nuclei are formed.
Chromosome number is maintained Chromosome number is halved
Occurs in body cells Occurs in somatic cells
WATER
Uses of water in the human body :
Water is a major component of blood plasma. Water is a good solvent and hence, acts as a
transport medium. Glucose is transported in blood plasma. Oxygen dissolves in the film of
moisture in the alveolar lining, and then diffuses into red blood cells.
Water is a major component of cytoplasm.
Water causes hydrolysis of food substances during digestion, like digestion of starch.
Sweat is made of water. It evaporates to carry body heat away as latent heat of vapourisation.
Thus, body heat is lost. Sweat cools the body. So, water helps in temperature regulation.
DIETARY FIBRE
Source
Brown rice
Spinach
Root vegetables
Fruits
Bran / wholegrain cereal
Wholemeal bread
Functions :
Dietary fibre increases / aids peristalsis as plant cell walls contain indigestible
cellulose, which gives bulk to food. It gives grip to gut muscles as they contract during
peristalsis.
It prevents constipation as faeces are removed easily. It retains water from faeces and,
thus forms soft faeces.
It reduces risk of bowel cancer.
Less time is there for toxins to accumulate.
2009
Significance of green plants / photosynthesis :
They are called producers as they can trap sunlight, convert light energy to chemical energy. Thus,
they form the basis of food chains.
They make their own food.
They are food for other organisms as they are eaten by animals for nutrition.
They provide oxygen for respiration and maintain supply.
Benefits of photosynthesis to humans :
Glucose is converted to starch. Animals eat starch for nutrition, forming the basis of the food chain.
Photosynthesis produces oxygen needed for respiration.
WATER TREATMENT
Water is pumped from river.
It is filtered / screened through a coarse grid to remove large objects.
Aeration allows gases and smells to escape.
Suspended matter settles in settling / sedimentation tanks.
Slow sand filter :Fine sand is above gravel. Algae in water reproduce. Algae and bacteria form
a jelly like gelatinous layer on sand particles, which traps bacteria in water. Protozoa and
midge larvae feed on bacteria.
OR
Rapid sand filter :Aluminium sulphate is added to water, that forms jelly on sand particles.
Jelly traps suspended particles and bacteria. Jelly is removed periodically by forcing water
under pressure upwards from the base of the filter.
Chlorination tank :Chlorine is added to water to destroy any remaining bacteria by oxidation.
Water is stored in covered reservoirs to prevent contamination.
The purified water is distributed in closed pipes by gravity or by pumps
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- NutritionDokumen14 halamanNutritionapi-251333981Belum ada peringkat
- Integrated Science RevisionDokumen12 halamanIntegrated Science RevisionaleenawaltersBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE BiologyDokumen12 halamanIGCSE BiologyLe KhanhBelum ada peringkat
- Animal Nutrition IGSCE CIE Study NotesDokumen5 halamanAnimal Nutrition IGSCE CIE Study Notes12 kijBelum ada peringkat
- Biology-Life ProcessesDokumen60 halamanBiology-Life Processesnarayanansahaana545Belum ada peringkat
- Diet and Growth PPT Grade 7Dokumen21 halamanDiet and Growth PPT Grade 7redwannawazBelum ada peringkat
- Science f2 Jan 2010Dokumen3 halamanScience f2 Jan 2010David AntonitoBelum ada peringkat
- A Study of Alkaline Ionized Water: Educational ManualDokumen15 halamanA Study of Alkaline Ionized Water: Educational ManualJohan Korthout100% (1)
- Typhoid Fever (Mhine)Dokumen20 halamanTyphoid Fever (Mhine)Donna Salamanca DomingoBelum ada peringkat
- LN 1 FOOD PrinciplesDokumen24 halamanLN 1 FOOD PrinciplesDickson MahanamaBelum ada peringkat
- Nutrients and Their Importance: M.ANAB 11-TDokumen28 halamanNutrients and Their Importance: M.ANAB 11-TAnab ArifBelum ada peringkat
- iGCSE Biology - Food and DigestionDokumen6 halamaniGCSE Biology - Food and DigestionormattBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Notes.Dokumen8 halamanBiology Notes.Mohith ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Pe NotesDokumen29 halamanPe NotesignatiousmugovaBelum ada peringkat
- Life Process 1Dokumen4 halamanLife Process 1tanishqmalik20Belum ada peringkat
- A Balanced Diet Consists of All of The Food Groups in The Correct Proportions The Necessary Food Groups AreDokumen15 halamanA Balanced Diet Consists of All of The Food Groups in The Correct Proportions The Necessary Food Groups AreRahil BhavanBelum ada peringkat
- Functions of WaterDokumen3 halamanFunctions of WaterAbdullah Al MamunBelum ada peringkat
- Exploring Science Year 8 Summary Sheets NBNBDokumen25 halamanExploring Science Year 8 Summary Sheets NBNBHelen100% (1)
- HSBDokumen12 halamanHSBjemima MillsBelum ada peringkat
- 2015 Wassce - Biology 2 SolutionDokumen9 halaman2015 Wassce - Biology 2 SolutionKelvin Yeboah TenkorangBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 Notes BioDokumen9 halamanChapter 7 Notes BioArabella ShepherdBelum ada peringkat
- Personal PollutionDokumen27 halamanPersonal PollutionAngela J Brown-Rasheed0% (1)
- CHAPTER 7. Animal Nutrition (Note)Dokumen7 halamanCHAPTER 7. Animal Nutrition (Note)hongtranBelum ada peringkat
- Science Notes5Dokumen10 halamanScience Notes5abhyudai.edwardsBelum ada peringkat
- Section A 1. The Characteristics of Living Things, Cell Structure, Function and SpecializationDokumen12 halamanSection A 1. The Characteristics of Living Things, Cell Structure, Function and SpecializationJerry100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Revision NoteDokumen20 halamanPhotosynthesis Revision NoteUsman Mukhtar AbbasiBelum ada peringkat
- Discoloration of LeavesDokumen8 halamanDiscoloration of LeavesMr MusharafBelum ada peringkat
- BIOLOGYDokumen2 halamanBIOLOGYazlinaBelum ada peringkat
- SS3 Biology Lesson NoteDokumen64 halamanSS3 Biology Lesson Notepalmer okiemuteBelum ada peringkat
- Class 10 Life ProcessDokumen11 halamanClass 10 Life ProcessShubham Tiwari100% (2)
- General Biology Unit 6 (Food and Nutrition in Animals)Dokumen40 halamanGeneral Biology Unit 6 (Food and Nutrition in Animals)Jay KingBelum ada peringkat
- The Digestive SystemDokumen7 halamanThe Digestive SystemnurmeenBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 - Life ProcessesDokumen8 halamanChapter 6 - Life ProcessesManvendra Shah (B18EE026)Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 1 Life - ProcessesDokumen33 halamanChapter - 1 Life - Processesarya avyukt100% (1)
- 8 - Water & FiberDokumen33 halaman8 - Water & FiberFarhana ZolkifliBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Revision Notes Edexcel iGCSEDokumen22 halamanBiology Revision Notes Edexcel iGCSEJoshua Jones100% (2)
- Revision Notes For CBSE Class 10 Science Notes For Chapter 6 Life ProcessesDokumen71 halamanRevision Notes For CBSE Class 10 Science Notes For Chapter 6 Life Processesparashakthi PRBelum ada peringkat
- Life Process.Dokumen43 halamanLife Process.AnzarBelum ada peringkat
- Food SpoilageDokumen11 halamanFood Spoilagedinakempho3Belum ada peringkat
- Book 11 AnimalNutrition2021 Adapted 2Dokumen11 halamanBook 11 AnimalNutrition2021 Adapted 2assf7235Belum ada peringkat
- 02 Microoganisms in FoodDokumen12 halaman02 Microoganisms in FoodthinkiitBelum ada peringkat
- Science+4 +Second+Quarter+HandoutDokumen29 halamanScience+4 +Second+Quarter+HandoutJhon Manuel VelosBelum ada peringkat
- Science ReviewerDokumen15 halamanScience ReviewerCamille CaraigBelum ada peringkat
- Nutrition: What Is Malnutrition?Dokumen43 halamanNutrition: What Is Malnutrition?Starpril_88Belum ada peringkat
- Summary Notes - Topic 7 Human Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSEDokumen6 halamanSummary Notes - Topic 7 Human Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSEImran MushtaqBelum ada peringkat
- Respiration: Lack of OxygenDokumen9 halamanRespiration: Lack of OxygenTanirika rangarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 - Food and DigestionDokumen4 halamanChapter 4 - Food and DigestionAnonymous IqLK0OBBelum ada peringkat
- Bio Disc IntroDokumen19 halamanBio Disc IntroBrako Jones100% (1)
- Animal Nutrition Notes - Biology - 5090 Notes - O Level AcademyDokumen8 halamanAnimal Nutrition Notes - Biology - 5090 Notes - O Level AcademyTinotenda HelaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology 1&2 (Part 3)Dokumen124 halamanAnatomy and Physiology 1&2 (Part 3)Kleindyn Joy PeraltaBelum ada peringkat
- Name: Pavittiran A/L Gunaselan Class: P1B Topic: WaterDokumen2 halamanName: Pavittiran A/L Gunaselan Class: P1B Topic: WaterPrishitha IyerBelum ada peringkat
- Bio Notes CH 6 Class 10Dokumen14 halamanBio Notes CH 6 Class 10khushi.kashyap0468Belum ada peringkat
- Life Processes Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 6Dokumen24 halamanLife Processes Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 6Nongpok SinghaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 - Life Processes NoteDokumen22 halamanChapter 6 - Life Processes NoteJay Maki100% (1)
- Class 10 Science All NotesDokumen59 halamanClass 10 Science All NotesultraspacydearlizardBelum ada peringkat
- FiberDokumen5 halamanFiberapi-366449205Belum ada peringkat
- The Ultimate IGCSE Guide To BiologyDokumen53 halamanThe Ultimate IGCSE Guide To BiologyAbdul Raheem100% (1)
- Food ContaminationDokumen8 halamanFood ContaminationMabookgm MaBelum ada peringkat
- Points To Remember - Nutrition, 20.4.2022Dokumen5 halamanPoints To Remember - Nutrition, 20.4.2022janviBelum ada peringkat
- 24RoleofPolice PrisonSystem-Final PDFDokumen14 halaman24RoleofPolice PrisonSystem-Final PDFVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Type of Lesson: Discovery, Problem Solving, Web-: Teacher Instructional MaterialDokumen8 halamanSubject: Type of Lesson: Discovery, Problem Solving, Web-: Teacher Instructional MaterialVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Type of Lesson: Internet Use, Discussion, Guided: Eacher Instructional MaterialDokumen13 halamanSubject: Type of Lesson: Internet Use, Discussion, Guided: Eacher Instructional MaterialVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Type of Lesson: Web-Based, Discussion, Group Work Grade: Csec ObjDokumen11 halamanSubject: Type of Lesson: Web-Based, Discussion, Group Work Grade: Csec ObjVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- 31role of Ombudsman - FINALDokumen9 halaman31role of Ombudsman - FINALVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- 19compo Functof Exec-Final PDFDokumen13 halaman19compo Functof Exec-Final PDFVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Type of Lesson: Web Search, Concept Development, Grade: Csec ObjDokumen12 halamanSubject: Type of Lesson: Web Search, Concept Development, Grade: Csec ObjVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- 16struct Compo Function-Legis-Final PDFDokumen13 halaman16struct Compo Function-Legis-Final PDFVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Type of Lesson: Web-Based, Discussion, Group Work Grade: Csec ObjDokumen10 halamanSubject: Type of Lesson: Web-Based, Discussion, Group Work Grade: Csec ObjVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- 17law Making Process - Final PDFDokumen13 halaman17law Making Process - Final PDFVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- 21compo FunctofJudiciary-Final PDFDokumen15 halaman21compo FunctofJudiciary-Final PDFVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Type of Lesson: Web-Based, Discussion, Group Work Grade: Csec ObjDokumen9 halamanSubject: Type of Lesson: Web-Based, Discussion, Group Work Grade: Csec ObjVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Human and Social Biology Revision GuideDokumen67 halamanHuman and Social Biology Revision GuideVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- 5first Past The Post - System - PDFDokumen11 halaman5first Past The Post - System - PDFVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Type of Lesson: Web-Based, Discussion, Questioning Grade: Csec ObjDokumen11 halamanSubject: Type of Lesson: Web-Based, Discussion, Questioning Grade: Csec ObjVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Type of Lesson: Web-Based, Discussion, Group Work Grade: Csec ObjDokumen13 halamanSubject: Type of Lesson: Web-Based, Discussion, Group Work Grade: Csec ObjVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Type of Lesson: Group Work, Discussion, Internet Use Grade: Csec ObjDokumen11 halamanSubject: Type of Lesson: Group Work, Discussion, Internet Use Grade: Csec ObjVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Type of Lesson: Group Work, Discussion, Role Play Grade: Csec ObjDokumen9 halamanSubject: Type of Lesson: Group Work, Discussion, Role Play Grade: Csec ObjVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Type of Lesson: Class Discussions, Group Work,: Teacher Instructional MaterialDokumen7 halamanSubject: Type of Lesson: Class Discussions, Group Work,: Teacher Instructional MaterialVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- 6proportional Representation PDFDokumen11 halaman6proportional Representation PDFVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- E Aching Lett E: The True Heart of WorshipDokumen4 halamanE Aching Lett E: The True Heart of WorshipVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Follow Me!: Derek PrinceDokumen4 halamanFollow Me!: Derek PrinceVivienne WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Modificari Electrocardiografice in Ischemia Miocardica Acuta - PPTX 2Dokumen180 halamanModificari Electrocardiografice in Ischemia Miocardica Acuta - PPTX 2Andra RaducuBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary EdemaDokumen47 halamanPulmonary Edemamaeliszxc kimBelum ada peringkat
- James Tcheng - ACCF AHA Key Data Elements (Poster)Dokumen1 halamanJames Tcheng - ACCF AHA Key Data Elements (Poster)AMIABelum ada peringkat
- Algo FibrinolyticDokumen2 halamanAlgo FibrinolyticBobo SmithyBelum ada peringkat
- Screening For Medical Problems in Patients With Upper Extremity Signs and SymptomsDokumen23 halamanScreening For Medical Problems in Patients With Upper Extremity Signs and SymptomskerolosBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To Patient With Dyspnea & Ankle Swellling: Dr. Mudhafar Barzani MBCHB, DM, PHD, FRCP Ass. Prof. in CardiologyDokumen55 halamanApproach To Patient With Dyspnea & Ankle Swellling: Dr. Mudhafar Barzani MBCHB, DM, PHD, FRCP Ass. Prof. in CardiologyDarawan MirzaBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis Statement Heart DiseaseDokumen7 halamanThesis Statement Heart Diseasexgkeiiygg100% (2)
- Acute ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDokumen9 halamanAcute ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfZ Siclayi AtlBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Coronary Syndrome in Clinical Practice: Firman B. LeksmonoDokumen48 halamanAcute Coronary Syndrome in Clinical Practice: Firman B. Leksmonojames klemens phieter phieBelum ada peringkat
- MTB Cardiology NotesDokumen7 halamanMTB Cardiology Noteskabal321Belum ada peringkat
- English For Hospital StaffDokumen6 halamanEnglish For Hospital StaffВолодимир ТатарінBelum ada peringkat
- Suz 183Dokumen29 halamanSuz 183Benny Chris TantoBelum ada peringkat
- CHF Ec CadDokumen17 halamanCHF Ec CadAkbar IskandarBelum ada peringkat
- Oxford University Press Esc Handbook of Cardiovascular Rehabilitation 0198849303Dokumen225 halamanOxford University Press Esc Handbook of Cardiovascular Rehabilitation 0198849303ArmandoCamaraNinoBelum ada peringkat
- MrsDokumen2 halamanMrsHelen SabuquelBelum ada peringkat
- Icici Lombard Complete Health Insurance Proposal FormDokumen4 halamanIcici Lombard Complete Health Insurance Proposal FormMonal RajBelum ada peringkat
- Goldbergers Clinical Electrocardiography 9th Edition PDFDokumen360 halamanGoldbergers Clinical Electrocardiography 9th Edition PDFdr_mego75% (4)
- Anxiety R:T Death ThreatDokumen8 halamanAnxiety R:T Death ThreatAlfredo BaulaBelum ada peringkat
- Echocardiography Dissertation IdeasDokumen8 halamanEchocardiography Dissertation IdeasWhoCanWriteMyPaperForMeCanada100% (1)
- Dele PrioDokumen10 halamanDele PriomonmonBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac CatheterizationDokumen9 halamanCardiac CatheterizationAnurag Gupta100% (1)
- Emergencies in Dental Clinic: How To DealDokumen94 halamanEmergencies in Dental Clinic: How To DealhassonamonaBelum ada peringkat
- I-STAT Hospital Navigator BrochureDokumen19 halamanI-STAT Hospital Navigator BrochureClaudia SotoBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular Disease,: ObesityDokumen24 halamanCardiovascular Disease,: ObesityEmran HossainBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Decompensated Heart FailureDokumen43 halamanAcute Decompensated Heart FailureZit HibaBelum ada peringkat
- Rujuk JuniDokumen120 halamanRujuk JuniGemma AyuBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal 1Dokumen16 halamanJurnal 1tri windartiBelum ada peringkat
- Public Knowledge of The Symptoms of Myocardial Infarction: A Street Survey in Birmingham, EnglandDokumen6 halamanPublic Knowledge of The Symptoms of Myocardial Infarction: A Street Survey in Birmingham, Englandpanji satryo utomoBelum ada peringkat
- Exploring Factors Affecting Emergency Medical Services Staffs' Decision About Transporting Medical Patients To Medical Facili...Dokumen9 halamanExploring Factors Affecting Emergency Medical Services Staffs' Decision About Transporting Medical Patients To Medical Facili...mahadabrata21Belum ada peringkat
- Hypertension GuidelinesDokumen1 halamanHypertension GuidelinesJuhne GioBelum ada peringkat