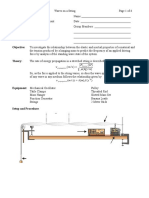
Scale Model: ∑ (−1) Π (t−n) Π (t) =1for0≤t≤T,and 0 otherwise
Diunggah oleh
Murali Kuna ShekaranJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Scale Model: ∑ (−1) Π (t−n) Π (t) =1for0≤t≤T,and 0 otherwise
Diunggah oleh
Murali Kuna ShekaranHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Scale Model
1. A beach profile is given by the equation h = Ax^(2/3), where h is the height, x is the
horizontal distance, and A is a shape parameter. If the length scaling is Nx and the height
scaling is Nh, what is the scaling for A (Na) ?
2. Determine the scaling criterion to have kinematically similar wave motion for gravity
waves. Use kinematic similarity, and assume that the wavelength is large. How does the
scaling criterion change with geometrically distorted and undistorted models ?
3. In what type of coastal engineering problems does Cauchy criterion become important ?
4. Dimensional analysis is the broad term that refers to drawing up scaling factors (or
relationships) between various forces in a phenomenon. Other than fluid modeling, what
are the other areas where dimensional analysis had been used. Why do you think it finds
more usage in fluid modeling vs other areas.
5. Use Fruode scaling and geometric similarity criterion to derive the relationship between
length and time scaling. How does it change when you use kinematic similarity (use
scaling for specific weight here).
6. Repeat this for Reynold's criterion.
7. A ship with a propeller 20 ft in diameter is designed to move at a speed of 25 ft/s, when
the propeller turns at a speed of 2 rev/s. A 1/10 scale geometrically similar model of the
hull and propeller is to be tested in water, in order to determine the thrust force of the
propeller. Viscosity is deemed to have a minor effect. What is the speed at which the model
propeller must move ?
8. A model of rubble breakwater is constructed of rocks that weight 2 lb. The rocks have
the same specific gravity as those of the prototype. Appreciable damage to the model is
observed of the wave height exceeds 1 ft. What is the minimum weight of each rock to be
used in the prototype if the prototype is to withstand geometrically similar waves 20 ft high
?
9. Two smooth balls of equal weight but different diameters are dropped from a balloon.
The ratio of diameters is 3. What is the ratio of terminal velocities ? (The terminal velocity
if the velocity at which the air resistance balances the weight).
10. The outer surface o a model airplane wing is geometrically similar to the prototype. The
scale factors for length, mass, and stiffness are 1/10, 1/100, and 1/400. What is the ratio of
natural frequencies of corresponding modes of vibration of the model and prototype.
1. Let the signal x(t) = sinc(1000t) be sampled with a sampling frequency of 2000 samples
per second. Determine the most general class of reconstruction filters for perfect
reconstruction of the signal.
2. Calculate the Fourier transform of
-- cos(t)
-- sin(t)
3. Given Fourier transform of x(t), F(x(t)) = X(f), what is F(x(at)) ?
4. Determine the Fourier series expansion for the signal
-- x(t) = n=(1)n(tn)n=(1)n(tn), where (t)=1for0tT,and 0
otherwise(t)=1for0tT,and 0 otherwise
5. What is the difference between the Fourier series, transform, and the Fast Fourier
Transform ?
6. A signal is made up of a summation of signals at frequencies 50 Hz, 100 Hz, 300 Hz, and
310 Hz. Your boss asks you to design a data acquisition system that will record the signal,
and then implement the spectrum estimation for the signal. Answer the following
-- What is the minimum sampling frequency for the system ?
-- How long would you record the signal so that all the five frequencies can be resolved.
-- If the acquisition system uses 8 byte words, what would be data capacity for your
acquisition system be in total ?
-- Which algorithm would you prefer for spectrum estimation ? The Fourier series, Fourier
Transform, DFT, or the FFT ? Why ?
1. What is the need for pre and post calibration ?
2. Explain the difference between instrument precision vs accuracy.
3. Show that the sample mean has a standard deviation that is inversely proportional to the
square root of the number of samples.
4. List the properties of the normal distribution, and the uniform distribution.
5. What is a histogram ? How can it be useful in error/data analysis ?
6. A temperature sensor records the temperature (in celsius) of the water surface on 15
different days. Test the hypothesis that the mean temperature is 29.5 celsius. The data are
26, 24, 29, 33, 25, 26, 23, 30, 31, 30, 28, 27, 29, 26, and 28.
7. A sample of size 18 has a mean of 13.55 cmcm and a variance of 6.4152 cm2cm2.
(a) Calculate the 95 % confidence interval for the population mean.
(b) How large a sample would have to be taken from this population to estimate within 1
with a 95 % confidence interval.
(c) to within 2 cmcm with 95 % confidence.
(d) to within 2 cmcm with 99 % confidence
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Unit 07. Surveying, Measuring and Setting Out Assignment 2022Dokumen8 halamanUnit 07. Surveying, Measuring and Setting Out Assignment 2022kash0% (1)
- UniversityPhysicsVolume1 Ch01Dokumen9 halamanUniversityPhysicsVolume1 Ch01stanleypitou98Belum ada peringkat
- 222 Spring 2009 PDFDokumen363 halaman222 Spring 2009 PDFcombatps1Belum ada peringkat
- Z AIAAJournal2007Dokumen5 halamanZ AIAAJournal2007engma3Belum ada peringkat
- Netting Drag CoeDokumen6 halamanNetting Drag CoeAndyBelum ada peringkat
- Which Is The Best Damping Coefficient For A Compass?Dokumen2 halamanWhich Is The Best Damping Coefficient For A Compass?Figueira, S. JalvesBelum ada peringkat
- The Effects of Transom Stern On The Resistance of High Speed CraftDokumen8 halamanThe Effects of Transom Stern On The Resistance of High Speed CraftbrsenerBelum ada peringkat
- Week11 LecturesDokumen40 halamanWeek11 LecturesMatteo RizzottoBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Iv: Results and DiscussionDokumen10 halamanUnit Iv: Results and DiscussionSuarez O.Belum ada peringkat
- 197 1 Waves On A StringDokumen6 halaman197 1 Waves On A StringRichard KelvinBelum ada peringkat
- Taylor Hypothesis and Large-Scale Coherent Structures: by K. B. M. Q. Zaman K. M. F. HussainDokumen18 halamanTaylor Hypothesis and Large-Scale Coherent Structures: by K. B. M. Q. Zaman K. M. F. Hussainamir sadighiBelum ada peringkat
- Denoising DataDokumen7 halamanDenoising DataTugba ÖzacarBelum ada peringkat
- Vibes Lab ReportDokumen13 halamanVibes Lab ReportBrian GilkeyBelum ada peringkat
- Numerical Simulations and Laboratory Measurements in Hydraulic JuDokumen9 halamanNumerical Simulations and Laboratory Measurements in Hydraulic JuBabak mahmoudiBelum ada peringkat
- Aaa MeasurementDokumen10 halamanAaa MeasurementJhane AlvaradoBelum ada peringkat
- Eerc 07 03Dokumen40 halamanEerc 07 03amirBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Transport Processes 1: 1 Course Outline and Reading MaterialDokumen29 halamanFundamentals of Transport Processes 1: 1 Course Outline and Reading MaterialAbhimanyu DubeyBelum ada peringkat
- Solids HomeworkDokumen20 halamanSolids HomeworkindiomajaderoBelum ada peringkat
- Special Lab Report 2 Simple PendulumDokumen15 halamanSpecial Lab Report 2 Simple Pendulumapi-656454154Belum ada peringkat
- محاضرة مبادئ الهندسة الكيمياوية PDFDokumen121 halamanمحاضرة مبادئ الهندسة الكيمياوية PDFKING of DARKNESSBelum ada peringkat
- 10th Grade Physics - Unit 1Dokumen25 halaman10th Grade Physics - Unit 1Alice ScarletBelum ada peringkat
- Tut BukinghamPiFermiWeek2Dokumen4 halamanTut BukinghamPiFermiWeek2Rami ChahineBelum ada peringkat
- Two Dimensional FEM Simulation of Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Isotropic Solid Media Using COMSOLDokumen12 halamanTwo Dimensional FEM Simulation of Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Isotropic Solid Media Using COMSOLHai NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Linear Diversity Combining TechniquesDokumen26 halamanLinear Diversity Combining TechniquesKash BDBelum ada peringkat
- 644 8page A Comparison of Neutral Abl Simulation Methods For Building PressuresDokumen8 halaman644 8page A Comparison of Neutral Abl Simulation Methods For Building PressuresOkke BronkhorstBelum ada peringkat
- Physics For EngineersDokumen5 halamanPhysics For EngineersKonstantinos FilippakosBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1Dokumen68 halamanChapter 1James AndeaBelum ada peringkat
- IARE EAD Lecture NotesDokumen130 halamanIARE EAD Lecture NotesTomble BravoBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Genphysics 1 UnitsDokumen38 halaman2 Genphysics 1 Unitspotato macchiatoBelum ada peringkat
- Spatial Sampling Issues in FK Analysis of Surface WavesDokumen11 halamanSpatial Sampling Issues in FK Analysis of Surface WavesStefano VignaBelum ada peringkat
- A Drift Correction ProcedureDokumen7 halamanA Drift Correction ProcedureLukluk KhairiyatiBelum ada peringkat
- PHYS 51 Unit Consistency and ConversionsDokumen16 halamanPHYS 51 Unit Consistency and ConversionsjavionwhitleycBc50% (2)
- Ae2223-II Exam 150414 FinalDokumen14 halamanAe2223-II Exam 150414 FinalAhmed Valentin KassemBelum ada peringkat
- Waves On A Spring Lab v3Dokumen2 halamanWaves On A Spring Lab v3Hyun BonBelum ada peringkat
- Aero-Acoustic Modelling Using Large Eddy Simulation: Wzshen and J N SørensenDokumen9 halamanAero-Acoustic Modelling Using Large Eddy Simulation: Wzshen and J N SørensenRio RobertöBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 - MeasurementDokumen22 halamanLecture 1 - MeasurementMarjorie Jean AnogBelum ada peringkat
- Drift, Diffusion, and Recombination Lab: ObjectivesDokumen3 halamanDrift, Diffusion, and Recombination Lab: ObjectivesPrasanna Kumari MBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 6Dokumen3 halamanAssignment 6binoBelum ada peringkat
- Cantilever Project UmassDokumen5 halamanCantilever Project Umasskountryboy07Belum ada peringkat
- Time-Series Analysis of Variable Star Data: Matthew TempletonDokumen14 halamanTime-Series Analysis of Variable Star Data: Matthew TempletonSuman MaityBelum ada peringkat
- Time Frequency Reassignment: A Review and Analysis Stephen Hainsworth - Malcolm Macleod CUED/F-INFENG/TR.459Dokumen28 halamanTime Frequency Reassignment: A Review and Analysis Stephen Hainsworth - Malcolm Macleod CUED/F-INFENG/TR.459المهندس عمرانBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1. MeasurementDokumen16 halamanChapter 1. MeasurementSaad khanBelum ada peringkat
- Synthetic Seismograms: The Rayleigh Waves Modal Summation: G.F. PanzaDokumen21 halamanSynthetic Seismograms: The Rayleigh Waves Modal Summation: G.F. PanzaNajeb PendiamanBelum ada peringkat
- Theo Mo Ultra TRan Incor Sphericalresonators 2015Dokumen25 halamanTheo Mo Ultra TRan Incor Sphericalresonators 2015lavande16Belum ada peringkat
- 1718SEM1Dokumen6 halaman1718SEM1Benedict ChinBelum ada peringkat
- Standing Waves in A StringDokumen2 halamanStanding Waves in A StringJP ArtajoBelum ada peringkat
- 10 23 2021science1Dokumen3 halaman10 23 2021science1SivekiBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation of The Fracture Sizes by Using The Frequency Dependence of AnisotropyDokumen7 halamanEvaluation of The Fracture Sizes by Using The Frequency Dependence of Anisotropymsmsoft90Belum ada peringkat
- ZCA101 Chapter 01Dokumen56 halamanZCA101 Chapter 01Ren Liew Jia QingBelum ada peringkat
- Hot Wire SynjetDokumen8 halamanHot Wire SynjetDaniel SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Earthquake Design Equipment SupportsDokumen7 halamanEarthquake Design Equipment Supportsmseif1980Belum ada peringkat
- CFD Simulation and Validation of Flap Type Wave MakerDokumen7 halamanCFD Simulation and Validation of Flap Type Wave MakerTrần Văn CườngBelum ada peringkat
- Aerodynamics-II Question BankDokumen8 halamanAerodynamics-II Question Bankhamdanforaero100% (1)
- Similarity and Modelling - 2Dokumen7 halamanSimilarity and Modelling - 2Alexander MugabeBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Measurements and Uncertainties Review QuestionsDokumen2 halaman01 Measurements and Uncertainties Review QuestionsSyed ShaBelum ada peringkat
- A Semiempirical Approach To A Viscously Damped Oscillating SphereDokumen10 halamanA Semiempirical Approach To A Viscously Damped Oscillating SphereMuramasa SenpaiBelum ada peringkat
- CFD Simulation and Validation of Flap Type Wave-Maker: Anant Lal, and M. ElangovanDokumen7 halamanCFD Simulation and Validation of Flap Type Wave-Maker: Anant Lal, and M. Elangovanghanbari8668Belum ada peringkat
- Thurber Eberhart PhillipsDokumen10 halamanThurber Eberhart PhillipsRidwan KusnandarBelum ada peringkat
- ENG60503 Lecturer 8Dokumen5 halamanENG60503 Lecturer 8Porkkodi SugumaranBelum ada peringkat
- 2020 Year 9 Physics Waves Success CriteriaDokumen2 halaman2020 Year 9 Physics Waves Success Criteriaapi-356655652Belum ada peringkat
- 9890-Article Text PDF-27824-1-10-20170629Dokumen9 halaman9890-Article Text PDF-27824-1-10-20170629Murali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Jul MeDokumen2 halaman5 Jul MeDivakar VaidyanathanBelum ada peringkat
- ErrorDokumen4 halamanErrorMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Ansys Installation InstruDokumen6 halamanAnsys Installation InstruMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- DOE: Optimization Response Surface Methods: Department of Mathematics and Computer ScienceDokumen43 halamanDOE: Optimization Response Surface Methods: Department of Mathematics and Computer ScienceMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- IHI5027982 Processed 05-Sep-2018 05:51 PM IST: Debit Account DetailsDokumen1 halamanIHI5027982 Processed 05-Sep-2018 05:51 PM IST: Debit Account DetailsMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- State Bank of IndiaDokumen1 halamanState Bank of IndiaMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment GradeDokumen1 halamanAssignment GradeMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- DiagramDokumen3 halamanDiagramMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- D 4442 - 92 R03 - Rdq0ndiDokumen6 halamanD 4442 - 92 R03 - Rdq0ndiMelgarejo AlexanderBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment GradeDokumen1 halamanAssignment GradeMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- CalenderDokumen1 halamanCalenderMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Improved BEMDokumen10 halamanImproved BEMMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Calibration of Wave Probe: Ex. No.: 1 Date: 16.07.18Dokumen2 halamanCalibration of Wave Probe: Ex. No.: 1 Date: 16.07.18Murali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Publishers: Conference Proceedings Publication ManualDokumen7 halamanIntegrated Publishers: Conference Proceedings Publication ManualMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Reduced Truck Fuel Consumption Through Aerodynamic Design: Louis L. Steers and Edwin J. SaltzmantDokumen7 halamanReduced Truck Fuel Consumption Through Aerodynamic Design: Louis L. Steers and Edwin J. SaltzmantMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- A Review of Turbine Stress AnalysisDokumen9 halamanA Review of Turbine Stress AnalysisMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- 1084790189Dokumen1 halaman1084790189Murali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Sent HilDokumen2 halamanSent HilMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Blower PDFDokumen35 halamanDesign of Blower PDFMurali Kuna Shekaran100% (1)
- Murali Oe16d017Dokumen2 halamanMurali Oe16d017Murali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Civil PDFDokumen96 halaman01 Civil PDFArjun PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- 7 IndexDokumen8 halaman7 IndexMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Untitled FormDokumen1 halamanUntitled FormMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Aero EnginesDokumen3 halamanAero EnginesMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Aircraft Structures II LabDokumen2 halamanAircraft Structures II LabMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Software Package For Solving Heat Transfer ProblemsDokumen7 halamanSoftware Package For Solving Heat Transfer ProblemsMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- FilesDokumen6 halamanFilesMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Aircraft Structures II LabDokumen2 halamanAircraft Structures II LabMurali Kuna ShekaranBelum ada peringkat
- LDA: Supply Chain Analysis, Case StudyDokumen2 halamanLDA: Supply Chain Analysis, Case StudyExperian Public SectorBelum ada peringkat
- The Road Final Essay AssignmentDokumen5 halamanThe Road Final Essay Assignmentapi-302574650Belum ada peringkat
- Paper Presentation FMCGDokumen22 halamanPaper Presentation FMCGAyesha SheikhBelum ada peringkat
- Chrysopogon Aciculatus: F Yi N × 100Dokumen4 halamanChrysopogon Aciculatus: F Yi N × 100Yuyeen FarhanahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10 Sampling Strategies EditedDokumen23 halamanChapter 10 Sampling Strategies EditedAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadBelum ada peringkat
- Ergonomic Assessment ToolkitDokumen75 halamanErgonomic Assessment Toolkitmustafa el refaey67% (3)
- Practical Research 2: Quarter 1 - Module 3Dokumen42 halamanPractical Research 2: Quarter 1 - Module 3Daven McstrongBelum ada peringkat
- MR - Loyalty-Cards-Chapter 1-5Dokumen56 halamanMR - Loyalty-Cards-Chapter 1-5Krisel Ibanez100% (1)
- A Study On Customer Preference of Induction CookerDokumen60 halamanA Study On Customer Preference of Induction Cookervineet lalmuniBelum ada peringkat
- IBM SPSS Statistics 23 Part 1 - Descriptive StatisticsDokumen18 halamanIBM SPSS Statistics 23 Part 1 - Descriptive StatisticsRitesh SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- The Quantitative Measurement of Organizational CommitmentDokumen23 halamanThe Quantitative Measurement of Organizational CommitmentMitch-Eugene Jacob Binas-PaglingayenBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Statment Analysis.Dokumen7 halamanFinancial Statment Analysis.narendermbaBelum ada peringkat
- A Study of Different Compensation Plans at PTCL and Their Effect On EmployeeDokumen38 halamanA Study of Different Compensation Plans at PTCL and Their Effect On Employeeabdulsaqib0% (1)
- (A) The Abstract For 500-1000 Words: 7. Writing The Dissertation WorkDokumen2 halaman(A) The Abstract For 500-1000 Words: 7. Writing The Dissertation WorkPramit Babai NagBelum ada peringkat
- Goal Free EvaluationDokumen12 halamanGoal Free EvaluationDivya NenaBelum ada peringkat
- ESSnet Culture Final Report PDFDokumen556 halamanESSnet Culture Final Report PDFderoryBelum ada peringkat
- Mba Strategic Management Midterm ExamDokumen3 halamanMba Strategic Management Midterm Examlea bantingBelum ada peringkat
- 08PR001C - Risk ManagementDokumen22 halaman08PR001C - Risk Managementfadli.lpgBelum ada peringkat
- Stat QuizDokumen105 halamanStat QuizAllen Jerry AriesBelum ada peringkat
- BRM Quiz 1 - 26 04 2020 - 19BM61K15Dokumen4 halamanBRM Quiz 1 - 26 04 2020 - 19BM61K15Saikat SarkarBelum ada peringkat
- A Guide To The Project Management Body of Knowledg... - (APPENDIX X6 TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES)Dokumen10 halamanA Guide To The Project Management Body of Knowledg... - (APPENDIX X6 TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES)Milton R. GutierrezBelum ada peringkat
- A Study On Effectiveness of Training and Development in Ashok Leyland All Over IndiaDokumen12 halamanA Study On Effectiveness of Training and Development in Ashok Leyland All Over IndiaMukesh kannan MahiBelum ada peringkat
- b1900942 - Loh Chong King - mgt400 ProposalDokumen13 halamanb1900942 - Loh Chong King - mgt400 ProposalKing LohBelum ada peringkat
- Blessed Christian School de Santa Rosa - Inc: The Learners Should Be Able ToDokumen6 halamanBlessed Christian School de Santa Rosa - Inc: The Learners Should Be Able ToAngelyn LingatongBelum ada peringkat
- Perceived TrustDokumen13 halamanPerceived Trustneil aivan PatulayinBelum ada peringkat
- CH 11Dokumen111 halamanCH 11lana del reyBelum ada peringkat
- Level of Satisfaction On K-12 Curriculum Among K-12 GraduatesDokumen6 halamanLevel of Satisfaction On K-12 Curriculum Among K-12 GraduatesKrishel GabucoBelum ada peringkat
- Creative & Critical Thinking Lecture 1Dokumen42 halamanCreative & Critical Thinking Lecture 1Mark MumbaBelum ada peringkat
- Avoiding Cost Overruns in Construction PDokumen11 halamanAvoiding Cost Overruns in Construction Pnasru hajiBelum ada peringkat