48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDF
Diunggah oleh
Sheanna May FuriaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDF
Diunggah oleh
Sheanna May FuriaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
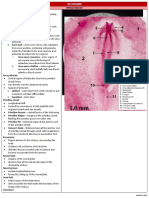
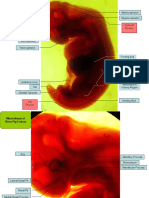
48-Hour Chick Embryo: Whole Mount splitted into two via the
Changes in the 48-hour chick embryo: stomodeum
head fold of the amnion o maxillary process
o covers the cranial half of the embryo (anterior)
o formation of amniotic fold o mandibular
head fold + lateral amniotic fold process
(posterior)
caudal fold
o establishes the caudal boundary of the body
o separates the embryo from underlying
blastoderm via subcaudal pocket
o beginning of this fold: concavity facing the
anterior end
processes involved in the 48-hour chick:
o cephalization (rapid growth of anterior
portion)
o ventral flexion (bending)
makes the half of at the anterior end of the embryo
the embryo lie on formation of a pronounced cranial
its left side while flexure (level of midbrain)
the posterior half formation of an indicated cervical
remains at the flexure (near hindbrain and spinal
original position cord)
o dextral torsion (twisting)
at the anterior end of the embryo
involves all of the head, both cranial
and cervical flexures.
heart
o elongation and twisting
o ventricle becomes posterior to the atrium (in
terms of location)
both these chambers are located
outside of the embryo
three fetal membranes that are seen:
o amnion 48-Hour Chick Embryo: Transverse Section
encircles anterior portion of embryo
consists of inner layer of ectoderm Section through the mesencephalon
& outer layer of somatic mesoderm
o yolk sac Mesencephalon
double-membrane structure oval-shaped
on left side of embryo first cavity of the brain to be seen
contains blood vessels in posterior sections, the frontal section of the
derived from endoderm and mesencephalon has several divisions
splanchnic mesoderm o due to cranial flexure
o chorion
double-membrane structure Isthmus
on right side of the embryo constriction at the lengthened section of the brain
consists of outer layer of ectoderm partially separates the mesencephalon from the
and inner layer of somatic hindbrain
mesoderm
branchial grooves and visceral arches Myelencephalon
o branchial grooves opposite to mesencephalon
white lines that radiate out from the has a thin roof
heart toward the auditory vesicle
composed of 1st, 2nd, and 3rd Metencephalon
branchial grooves underlined portion of the brain
o visceral arches
between myelencephalon and isthmus
masses of cells
composed of 1st, 2nd, and 3rd
Mesenchyme
visceral arches
depending on its order, each loose connective tissues
visceral arch is located cranial to its between brain and epidermis
corresponding branchial groove
example: 1st visceral arch Fetal Membranes
will be cranial to the 1st refer to the whole mount descriptions
branchial groove.
1st visceral arch Extraembryonic Coelom
space bounded by mesoderm
1
this space is between the chorion, yolk sac, and ganglia of cranial nerve VII and VIII
amnion
Semilunar ganglion
Section through the diencephalon dark accumulation of cells at the sides of the body
attached to the myelencephalon
Diencephalon observe: root of ganglion
when the brain separates into two cavities, it is the o pink structure
lower cavity o embedded in myelencephalon
replaces the mesencephalon in the preceding section o attached to the ganglion
Velum transversum Superior ganglion
depression on the dorsal wall of the forebrain acccumulation of cells on the sides of the
functions as a demarcation between diencephalon and myelencephalon
telencephalon can be observed when the otic vesicle is not present
anymore or it is immediately posterior to the auditory
Metencephalon vesicles
poorly defined ganglion of the glossopharyngeal (IX) nerve
anteriorly delimited by isthmus
Section through the optic cups
Myelencephalon
when the brain is divided into two cavities, this is the Optic cup
larger and upper cavity double-walled structures on the sides of the
has a thin roof diencephalon
will give rise to the posterior choroid plexus formed via the invagination of the optic vesicles
Semilunar ganglion fate: sensory retina (thick, inner layer) and pigmented
dark accumulation of cells on the sides of the retina (thin, outer layer)
myelencephalon parts of the optic cup:
ganglion of the trigeminal (V) cranial nerve o presumptive retina
inner layer
Jugular ganglion o presumptive pigmented epithelium
mass of cells that is: lateral to the myelencephalon outer layer
and above the anterior cardinal veins fate: pigmented layer of retina
ganglion of the X cranial nerve
Lens vesicle
Anterior cardinal vein sac-like cavity nestled within the optic cups
space that is located on each side of the formed via invagination of the ectoderm
myelencephalon
as the section moves posteriorly, this becomes long Optic stalk
spaces toward the diencephalon connects optic cup with the diencephalon
further posteriorly, this becomes more dorsal and
becomes located ventrolateral to the myelencephalon Pharynx
cavity below the notochord
Notochord triangular in shape
vacuolated cells between the myelencephalon and the o middle portion = pharynx proper
diencephalon o arms of triangle = 1st pharyngeal pouch (or
tracing posterior, splits into two due to cranial flexure hyomandibular pouch)
in succeeding structures, will eventually unite back 1st pharyngeal pouch
into one, single structure o will invaginate to form the 1st branchial
groove
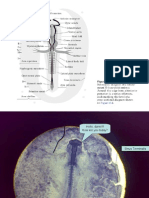
Section through the otic vesicle o the double layered membrane formed by the
invagination is called the 1st closing plate
Otic vesicle or 1st branchial plate
paired vesicle on each side of the myelencephalon
formed as an invagination of the ectoderm Preoral gut
in older specimens, an invagination at the dorsal wall anterior most part of the foregut
of the otic vesicle is the forerunner of the small circle or oval structure which is separated from
endolymphatic duct the pharynx via the oral plate
fingerlike diverticulum anterior to the future mouth
Anterior cardinal vein
pair of blood vessels Carotid loop
located on ventro-lateral to the otic vesicles extensions of the 1st aortic arches
medial to the anterior cardinal veins
Acoustico-facialis ganglion
dark accumulation of cells close to are sometimes Internal carotid arteries
attached to the otic vesicle and anterior cardinal vein paired vessels
located lateral to the myelencephalon extensions of the carotid loops
2
alongside forebrain even more posteriorly, ventral ends of the 2nd aortic
medial to the optic cups arch become continuous with the ventral aorta
Dorsal aorta 2nd pharyngeal pouch
blood vessels on the sides of the notochord outpocketing of the pharynx
above the 1st pharyngeal pouch can be seen when the otic vesicle is not seen or at the
posterior sections of the otic vesicle
First aortic arch
blood vessels below the 1st pharygneal pouch Ventral aorta
becomes located within the mandibular process blood vessels located beneath the pharynx
eventually becomes continuous with the ventral aorta the following vessels are continuous with this:
o bases of the first aortic arch
Visceral arches o ventral ends of the 2nd aortic arch
between two pharyngeal pouches o ventral ends of the 3rd aortic arches
lateral walls of the visceral arches:
o thickened
o filled with mesenchymal cells aortic ventral
arches aorta
Mandibular arch
more anterior of the rounded mesenchymal masses
between it lies the stomodeum
gives rise to the jaws
bears the first aortic arch
syn: 1st visceral arch
Section through the third aortic arch
Maxillary arch
3rd pharyngeal pouch
rounded or flattened masses
outpocketing of the pharynx
on the sides of the Rathkes pouch
pharynx + 3rd pharyngeal pouch = laterally oriented
Rathkes pouch oral cavity
small vesicle
3rd aortic arch
located between the infundibulum and the pharynx
beneath the 3rd pharyngeal pouch
arises as a dorsal evagination of the stomodeum
not well developed
fate is the hypohysis
another pair of downward extensions from the dorsal
aorta
Oral plate
ventral ends are continuous with the ventral aorta
thin line made of ectoderm and endoderm
separates the stomodeum and pharynx 3rd visceral arch
syn: pharyngeal membrane between 2nd and 3rd pharyngeal pouch
arches that are posterior to the hyoid arch are
Infundibulum
sometimes referred to as branchial arches
arises as an evagination from the diencephalon o this is because in lower vertebrates these
extends in the direction of the foregut arches will bear the gills
later evaginate to become the posterior (neural) lobe
of pharynx Bulbus cordis
first heart cavity to be observed
Diencephalon differentiated from the ventral aorta due to the
more elongated at this level presence of both an endocardium and a myocardium
Stomodeum Dorsal mesocardium
slit-like space where the Rathkes pouch opens mesodermal stalk
attaches the stalk to the dorsal wall of the coelom
Notochord
as previously described Nasal placode
thickened skin ectoderm
Section through the thyroid rudiment and the second
lateral to the telencephalon
aortic arch
1st somite
Thyroid rudiment
compact cell masses
depression on the floor of the pharynx
composed of:
2nd aortic arch o dermatome
darkly stained cells
blood vessels beneath the 2nd pharyngeal pouch
beneath skin ectoderm
located within the 2nd visceral arch (hyoid arch) future dermis of the skin
posteriorly, extend downward from the dorsal aorta
3
o myotome Lung buds
lightly stained cells evagination on the ventro-lateral portions of the
medial to future dermatome foregut into the pleural cavity
future muscle
Pleural cavity
Anterior cardinal veins portion of coelom that is lateral to the developing lung
becomes more ventral buds
separates into two vessels: postcardinal vein (dorsal) it is continuous with the pericardial cavity
and common cardinal vein (ventral)
Transverse septum
Section through the atrium and ventricle mesenchyme surrounding the sinus venosus
from where the dorsal mesocardium connects the
Spinal cord heart to the dorsal body wall
replaces the myelencephalon at this level connected with the pleuropericardial membrane
Descending aorta Cranial liver diverticulum
fused dorsal aortae small mass of cells dorsal to the sinus venosus
lies in the transverse septum (ventral to foregut)
Dorsal intersegmented arteries a diverticulum from the wall of the gut gives rise to
small blood vessels the liver
arising at intervals from the dorsal aorta syn: dorsal diverticulum
extends dorsally between spinal cord and somite
Caudal liver rudiment
Conus arteriosus branch or branches on ventral side of cranial liver
chamber of the heart at the right side of the embryo rudiment
endocardium and myocardium are widely separated syn: ventral diverticulum
Atrium Duodenum
at the left side of the embryo when the cranial liver rudiment becomes continuous
endocardium and myocardium are in close contact with the foregut
with each other
future auricles Section through the anterior intestinal portal
Ventricle Anterior intestinal portal
large looped chamber of the heart opening of foregut to the midgut
connects the conus arteriosus and the atrium floor of midgut is the yolk
Laryngotracheal groove Vitelline veins
V-shaped depression in the floor of the foregut pair of blood vessels
develops into: larynx, trachea, and lung buds extensions of the sinus venosus
located on each side of the anterior intestinal portal
Future esophagus the left vitelline vein passes out onto the yolk first
dorsal portion of the gut before the right vitelline vein
will later differentiate from part of the foregut (which
is dorsal to the laryngotracheal groove) Peritoneal cavity
space where internal organs are located
Cardinal Veins
paired precardinal veins (or anterior cardinal veins) Paired mesonephric duct
separates into two: small tubules lateral to descending aorta
o postcardinal vein - dorsal mesonephric tubule rudiments
o common cardinal vein - ventral o medial to the mesonephric duct
o will undergo cavitation to form mesonephric
Section through the sinus venosus tubules of the paired mesonephric kidneys
formed via delamination of the nephrogenic cord
Sinus venosus (nephrotome)
portion of the heart that is attached to the foregut via
the dorsal mesocardium Section through the lateral amniotic folds
Common cardinal vein Lateral amniotic folds
blood vessel to which the sinus venosus is attached elevated folds that are about to fuse
continuous with the lateral body walls
Pleuropericardial membrane consists of somatopleure
mesenchyme that encloses the common cardinal vein o forms inner amnion and outer chorion
separate pleural cavity from the pericardial region of
the coelom Vitelline blood vessels
small blood vessels within the splanchnic mesoderm
4
Paired dorsal aortae
large pair of blood vessels below the notochord
descending aorta has not formed at more caudal levels
Mesonephric tubule rudiments
round cavity medial to the mesonephric duct
Nephrostome
opening of mesonephric tubule to the coelom
Vitelline arteries
extension of dorsal aorta onto the yolk sac
Section through the tail bud
Tail bud
mass of mesenchymal cells at caudal end of the
embryo
covered by skin ectoderm
note: the tail bud is a mesoderm derived structure but it is
covered by ectoderm
Hindgut
posterior portion of the gut
now has a floor
Allantoic rudiment
endoderm lined cavity located below the tail bud
Caudal intestinal portal
space where the floor of the allantoic rudiment
disappears
opening of hindgut into the yolk
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Embryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerDokumen7 halamanEmbryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerGail AmuraoBelum ada peringkat
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabDokumen3 halaman24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- Gastrulation and Formation of Germ Layers PDFDokumen5 halamanGastrulation and Formation of Germ Layers PDFElla LagramaBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDokumen4 halamanExercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeBelum ada peringkat
- Biology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickDokumen9 halamanBiology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickPunk Midget-FairyBelum ada peringkat
- ANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Dokumen6 halamanANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Junko TsukudaBelum ada peringkat
- Dumaguit (2021)Dokumen12 halamanDumaguit (2021)Dimple May Gianne DumaguitBelum ada peringkat
- Exp 2 4.1 1Dokumen11 halamanExp 2 4.1 1Carlo MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Early DevelopmentDokumen5 halamanEarly DevelopmentMarina of The SeaBelum ada peringkat
- 33.48,72 From 2011Dokumen63 halaman33.48,72 From 2011aa628Belum ada peringkat
- DEVBIOLAB OogensisDokumen91 halamanDEVBIOLAB OogensisDimple May Gianne Dumaguit100% (1)
- 72 HR ReviewerDokumen8 halaman72 HR ReviewerAstrid AmadorBelum ada peringkat
- Skin Histology ComparisonDokumen7 halamanSkin Histology ComparisonMinamiSapphire BarbosaBelum ada peringkat
- Chick 33 HRDokumen14 halamanChick 33 HRaa628Belum ada peringkat
- 4 MM FrogDokumen5 halaman4 MM FrogMarina of The SeaBelum ada peringkat
- 24 Hour Chick EmbryoDokumen27 halaman24 Hour Chick Embryoaa6280% (1)
- 10 MM FrogDokumen23 halaman10 MM Frogfrances agulayBelum ada peringkat
- 10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory OrgansDokumen9 halaman10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory OrgansMarina of The SeaBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise 13 Serial Transverse Section of An 18 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDokumen4 halamanExercise 13 Serial Transverse Section of An 18 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela Faye100% (1)
- Ex234.1 Ascaris Eggz PDFDokumen7 halamanEx234.1 Ascaris Eggz PDFCarlo MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Pig Embryo Development StagesDokumen12 halamanPig Embryo Development StagesKarmina SantosBelum ada peringkat
- 48 Hour ChickDokumen13 halaman48 Hour ChickJowi SalBelum ada peringkat
- Urogenital SystemDokumen5 halamanUrogenital Systemstudent10100Belum ada peringkat
- Gametogenesis of Frog EmbryosDokumen21 halamanGametogenesis of Frog EmbryosNics MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- ZL 124 Lecture 7 - Gastrulation in Birds & MammalsDokumen36 halamanZL 124 Lecture 7 - Gastrulation in Birds & MammalsNestory MartineBelum ada peringkat
- 18 Hour Chick EmbryoDokumen7 halaman18 Hour Chick Embryoaa628100% (2)
- Ex4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoDokumen14 halamanEx4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoNexie100% (1)
- 10mm Frog TadpoleDokumen30 halaman10mm Frog TadpoleSarah Margaret Chong33% (3)
- Lbybio4 Label 00Dokumen12 halamanLbybio4 Label 00Eunice ChingBelum ada peringkat
- 10mm Pig Embryo Whole Mount with Labeled StructuresDokumen34 halaman10mm Pig Embryo Whole Mount with Labeled StructuresVanessa CarinoBelum ada peringkat
- Histology of Glands: Dr. Zana TahseenDokumen28 halamanHistology of Glands: Dr. Zana TahseenAhmed JawdetBelum ada peringkat
- Embryo Lab Org 2Dokumen14 halamanEmbryo Lab Org 2pauBelum ada peringkat
- Chick Embryo 72 HoursDokumen48 halamanChick Embryo 72 HoursogheeluvBelum ada peringkat
- 33 hour Chick Embryo Development StagesDokumen36 halaman33 hour Chick Embryo Development StagesSasha GutierrezBelum ada peringkat
- Echinoderm Class IdentificationDokumen13 halamanEchinoderm Class IdentificationFernando Martin BarbaBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory System: StructureDokumen29 halamanRespiratory System: StructureDr. Abir Ishtiaq100% (1)
- ANATOMY: Pelvic 2Dokumen16 halamanANATOMY: Pelvic 2Nur Liyana MohamadBelum ada peringkat
- 7 MM FrogDokumen28 halaman7 MM FrogNiki Reroll04Belum ada peringkat
- Chick 72 HR DDokumen35 halamanChick 72 HR Daa628Belum ada peringkat
- Chick GastrulationDokumen6 halamanChick GastrulationAlyssa Gail de VeraBelum ada peringkat
- Early Chick Embryo Development StagesDokumen74 halamanEarly Chick Embryo Development StagesMinette EmmanuelBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report 4 GametogenesisDokumen13 halamanLab Report 4 GametogenesisWnz NaiveBelum ada peringkat
- Gastrulation in Amphibians and AvesDokumen20 halamanGastrulation in Amphibians and AvesAnonymous mpD5IsJvaBelum ada peringkat
- 72 HrsDokumen35 halaman72 HrsChristalie Bea FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- 33-Hour Chick ReviewerDokumen5 halaman33-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatriceBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 1: Frog's Egg, Cleavage, and Blastulation: Late-Yolk-Plug-4x-Ss - JPGDokumen7 halamanActivity 1: Frog's Egg, Cleavage, and Blastulation: Late-Yolk-Plug-4x-Ss - JPGIvanBelum ada peringkat
- Early Development in BirdsDokumen53 halamanEarly Development in BirdsMuqaddas NadeemBelum ada peringkat
- Spermatogenesis ReviewerDokumen8 halamanSpermatogenesis ReviewerJowi Sal100% (1)
- Chick Embryo ReviewerDokumen9 halamanChick Embryo ReviewerKeana TapangBelum ada peringkat
- Gastrulation in Frog, Chick and Human ComparedDokumen1 halamanGastrulation in Frog, Chick and Human ComparedClaire BolalinBelum ada peringkat
- Seed Germination Experiment Revised Final Copy 2Dokumen8 halamanSeed Germination Experiment Revised Final Copy 2sally ngBelum ada peringkat
- 48 Hour Chick LabelledDokumen89 halaman48 Hour Chick LabelledSasha Gutierrez100% (1)
- Chick Embryo DevelopmentDokumen5 halamanChick Embryo DevelopmentPaula Manalo-SuliguinBelum ada peringkat
- 96-Hour Chick Embryo Development Stages in SectionsDokumen7 halaman96-Hour Chick Embryo Development Stages in Sectionsfrances agulayBelum ada peringkat
- Development of Frog EmbryoDokumen13 halamanDevelopment of Frog EmbryoNexieBelum ada peringkat
- BIOLAB FROG Organ HistologyDokumen7 halamanBIOLAB FROG Organ HistologyCloie Anne Rabinetas100% (1)
- 7 MM Frog EmbryoDokumen20 halaman7 MM Frog EmbryoCourtneyBelum ada peringkat
- Metamorphosis in InsectsDokumen13 halamanMetamorphosis in InsectsAnupam GhoshBelum ada peringkat
- 24-Hr Chick EmbryoDokumen8 halaman24-Hr Chick EmbryopauBelum ada peringkat
- 48-Hour Chick Embryo: ST ND RDDokumen29 halaman48-Hour Chick Embryo: ST ND RDFerhaeeza KalayakanBelum ada peringkat
- Tubulointerstitial Nephritis - 161269200418Dokumen12 halamanTubulointerstitial Nephritis - 161269200418ተሣለነ ወልድBelum ada peringkat
- TISSEEL Fibrin Sealant Prescribing InformationDokumen3 halamanTISSEEL Fibrin Sealant Prescribing InformationCBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Embolism Postpartum PIH 2022Dokumen19 halamanPulmonary Embolism Postpartum PIH 2022Nikky SilvestreBelum ada peringkat
- The Excretory System Revision WorksheetDokumen7 halamanThe Excretory System Revision WorksheetAryan KhemaniBelum ada peringkat
- CABG Beats PCI for Left Main DiseaseDokumen44 halamanCABG Beats PCI for Left Main DiseaseAnindyaSarkar100% (1)
- IRIS 2017 DOG Treatment Recommendations 09may18Dokumen15 halamanIRIS 2017 DOG Treatment Recommendations 09may18crilala23Belum ada peringkat
- Barrett's Esophagus: What You Need To Know About This Precancerous Condition - Kaizen Gastro CareDokumen2 halamanBarrett's Esophagus: What You Need To Know About This Precancerous Condition - Kaizen Gastro CareKaizen Gastro CareBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S2468054023000239 MainDokumen9 halaman1 s2.0 S2468054023000239 MainSyarifa Syafira Al BahasyimBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy MCQ PDFDokumen73 halamanAnatomy MCQ PDFSmart NemoBelum ada peringkat
- Combination of Lisinopril and Nifedipine GITS.10Dokumen7 halamanCombination of Lisinopril and Nifedipine GITS.10Andi PermanaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokumen2 halamanDrug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheryhan Tahir BayleBelum ada peringkat
- Kristian Karl Bautista Kiw-Is - Class Activity Cardivascular With Case Study 2020Dokumen6 halamanKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-Is - Class Activity Cardivascular With Case Study 2020Kristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Coronary Artery DiseaseDokumen103 halamanManaging Coronary Artery DiseasePeter InocandoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care of Clients Before and After CABGDokumen46 halamanNursing Care of Clients Before and After CABGshejila c hBelum ada peringkat
- HeartIndia54157-4958724 134627 PDFDokumen3 halamanHeartIndia54157-4958724 134627 PDFGagandeep Singh ShergillBelum ada peringkat
- Risk of OSA in DM Type 2 PatientsDokumen9 halamanRisk of OSA in DM Type 2 Patientskryshna maqBelum ada peringkat
- Dr. Navas Kizhakkayil: SUBJECT: Application To Doctor VacancyDokumen3 halamanDr. Navas Kizhakkayil: SUBJECT: Application To Doctor VacancyNasih TrBelum ada peringkat
- NCM of Clients With Endocrine DisordersDokumen24 halamanNCM of Clients With Endocrine DisordersArgee Alonsabe100% (1)
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDokumen29 halamanAdrenergic AntagonistsBenedict Brashi100% (1)
- Mechanisms and lifelong management of Turner syndromeDokumen15 halamanMechanisms and lifelong management of Turner syndromekirki pBelum ada peringkat
- How To Manage Coagulopathies in Critically Ill Patients: ReviewDokumen18 halamanHow To Manage Coagulopathies in Critically Ill Patients: ReviewDaniel Balderas Anzures100% (2)
- AIAPGET 2017 Homoeopathy Question PaperDokumen24 halamanAIAPGET 2017 Homoeopathy Question PaperShubhanshi Bhasin100% (2)
- BPJS Apotek Kimia Farma KetanggunganDokumen8 halamanBPJS Apotek Kimia Farma KetanggunganputriBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of Blood Vessels - StationsDokumen6 halamanStructure of Blood Vessels - StationsRamya MalariniBelum ada peringkat
- ANAPHY Lec Session #22 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Dokumen9 halamanANAPHY Lec Session #22 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Extremity Anatomy LectureDokumen15 halamanUpper Extremity Anatomy LectureNoreen Hannah GabrielBelum ada peringkat
- Elektro Fisika Dan Sumber Fisis 1 Pertemuan 1Dokumen16 halamanElektro Fisika Dan Sumber Fisis 1 Pertemuan 1Amethysa DiaryBelum ada peringkat
- The Small Intestine - Duodenum - Jejunum - Ileum - TeachMeAnatomyDokumen4 halamanThe Small Intestine - Duodenum - Jejunum - Ileum - TeachMeAnatomyFelix Oriono100% (1)
- Assessing Endothelial Function: Overview and Scientific Validation of EndoPATDokumen12 halamanAssessing Endothelial Function: Overview and Scientific Validation of EndoPATEndo-PATBelum ada peringkat
- AmiodaroneDokumen2 halamanAmiodaroneEmmil BernardoBelum ada peringkat