Tutorial 1
Diunggah oleh
ZhiTing960 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
13 tayangan2 halamanTechnology
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniTechnology
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
13 tayangan2 halamanTutorial 1
Diunggah oleh
ZhiTing96Technology
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Explain what chronic disease are and how they are linked to population ageing.
1. Long term (>1 year) and generally slow-acting, incurable (irreversible) ;
require ongoing medical attention
2. Non-infectious
o Usually due to malfunction, breakdown, or damage to body
systems/organs (essential) that occur throughout lifetime.
o Can be virus led but generally not.
3. The probability of developing chronic diseases increases with age. The
incidence rate and prevalence of chronic diseases is therefore higher
among the elder
o Common to have MCC, esp. for elderly
o Over 80% of people aged 65+ above with chronic diseases suffer
Why is the proper management of chronic diseases important?
To maintain the sustainability of future healthcare demand and spending by
proper management.
Avoid or postpone CD to develop into MCC which is more difficult and
disproportionately more expensive to treat
How does medical technology and healthcare play a role?
1. Delay the onset of chronic diseases
o Regular screening/consultations
o Education to public: promote healthy diets and lifestyles
o Most CDs are entirely preventable
2. Allow for early detection
o Diagnostic imaging
o Can prevent disease from occurring
3. Better treatment and management of symptoms
o Provide effective monitoring to slow down progression and to
prevent serious complications
4. Reduce the incidence rate and prevalence of disabilities
o Provide effective treatment which may slow down or halt the
progression of the diseases and prevent disabilities or MCCs
5. Reduce mortality
o Extend life span while at the same time preserving the quality of life
(if not might as well just die)
6. Research
o Even though research is expensive, but the technology created has
its advantages.
o Effective usage of medical resources
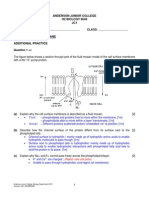
Describe the roles of colonoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal
cancer.
Colonoscopy: can check up to entire length of colon, up to the appendix,
check for cancer/ precancerous growths, ulcers, polyps (adenomatous
polyps, which is a precursor for colorectal cancer), tumours, obstruction,
pouches (diverticulosis), intestinal narrowing, areas of inflammation or
bleeding on the mucosal lining of lower gastrointestinal track
Biopsy (collection of samples from suspicious tissues/ abnormal growths) to
check for malignancy for early detection
To observe the operation in laparoscopic colectomy
Allow image capturing for future diagnostic purposes.
Describe the roles of laparoscopic colectomy in the diagnosis and treatment of
colorectal cancer.
Biopsy
What role does the optical fibre play in these procedures?
The light within the fibre will undergo total internal reflection every time to
conduct light, even when the fibre is bent or curved in the colon. All of the
light is trapped within the fibre and gets transmitted to the end of the fibre,
wherever it may be.
Enable vision (illumination)
What are some of the disadvantages and risks of these procedures?
Advantages of keyhole surgery VS open surgery
Reduced haemorrhaging-aid recovery, reduce the chance of needing a
blood transfusion
Smaller incision->faster recovery
Less pain, so less pain medication is needed
Shorter Hospital stay - faster return to normal activities and reduces the need
for overnight care in hospitals
Reduced exposure of internal organs to possible external contaminants
thereby reduced risk of acquiring infections
Better cosmetic results (less scarring)
Disadvantages of keyhole
Not all surgical procedures can be performed via keyhole
May not be suitable for all patients, depends on condition
Technologically difficult, requiring high-level of skills by trained surgeons
2D image displayed on the screen
Procedure may take longer time
Extra charge due to the use of more expensive equipment
May need to switch to open surgery in the event of complications
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Enzymes Tutorial EssayDokumen3 halamanEnzymes Tutorial EssayZhiTing96Belum ada peringkat
- Protein Synthesis ACEDokumen14 halamanProtein Synthesis ACEZhiTing96Belum ada peringkat
- Structure N Functions of CSMDokumen68 halamanStructure N Functions of CSMZhiTing96Belum ada peringkat
- Additional and Challenging Qns CSMDokumen5 halamanAdditional and Challenging Qns CSMZhiTing96Belum ada peringkat
- Photosynthesis ACEDokumen7 halamanPhotosynthesis ACEZhiTing96Belum ada peringkat
- GP Question Analysis - All Words MatterDokumen5 halamanGP Question Analysis - All Words MatterZhiTing96Belum ada peringkat
- APGPDokumen11 halamanAPGPZhiTing96Belum ada peringkat
- What Kinds of Examples Can I Use? Howdoi Incorporate Them Into My Essay?Dokumen15 halamanWhat Kinds of Examples Can I Use? Howdoi Incorporate Them Into My Essay?ZhiTing96Belum ada peringkat
- Mathematical Induction ACEDokumen9 halamanMathematical Induction ACEZhiTing96Belum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1091)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDokumen3 halamanInflammatory Bowel DiseaseDivine ParagasBelum ada peringkat
- 6.3 FA#3.B (Staffing) : Attempt HistoryDokumen8 halaman6.3 FA#3.B (Staffing) : Attempt HistoryGil GanibanBelum ada peringkat
- Radial Neck Fractures in ChildrenDokumen4 halamanRadial Neck Fractures in ChildrenAndikaBelum ada peringkat
- PostureDokumen20 halamanPostureBalram Jha100% (1)
- Client Soap NoteDokumen2 halamanClient Soap Noteapi-335875079Belum ada peringkat
- Surgical Audit and Peer Review Guide 2014Dokumen54 halamanSurgical Audit and Peer Review Guide 2014juweriyBelum ada peringkat
- Management of A Case of Acute PoisoningDokumen36 halamanManagement of A Case of Acute PoisoningIndranil KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Anger Aggression ManagementDokumen37 halamanAnger Aggression ManagementAashish Parihar100% (2)
- Adrenal Cortex Case StudyDokumen21 halamanAdrenal Cortex Case StudyMaya Vil0% (1)
- Laryngeal Trauma: Dr. Ida Sjailandrawati Harahap, SP.T.H.T.K.LDokumen19 halamanLaryngeal Trauma: Dr. Ida Sjailandrawati Harahap, SP.T.H.T.K.LNoni100% (1)
- Fluid Calculation For Iv InfusionDokumen8 halamanFluid Calculation For Iv InfusionAsma SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- NLE Compilation 1 Q PDFDokumen67 halamanNLE Compilation 1 Q PDFKc Orense100% (3)
- Isolation PrecautionsDokumen3 halamanIsolation PrecautionsAntonette Y. AlbaricoBelum ada peringkat
- What Are H2 Blockers?Dokumen3 halamanWhat Are H2 Blockers?Alexandra FeherBelum ada peringkat
- Overdentures and Implants-HandoutDokumen38 halamanOverdentures and Implants-HandoutliudifairBelum ada peringkat
- EKG StripsDokumen10 halamanEKG StripsSaidel ElizondoBelum ada peringkat
- ISTDP Coughlin KatzmanDokumen4 halamanISTDP Coughlin Katzmanmilane84Belum ada peringkat
- PCNE Classification V6-2Dokumen9 halamanPCNE Classification V6-2Mo'men El-MassryBelum ada peringkat
- The Use of Blenderized Tube Feeding in Pediatric Patients: Evidence and Guidelines For Dietetic PracticeDokumen31 halamanThe Use of Blenderized Tube Feeding in Pediatric Patients: Evidence and Guidelines For Dietetic PracticeLaura Schoenfeld, MPH, RD100% (1)
- Performing Nasotracheal SuctionDokumen1 halamanPerforming Nasotracheal SuctionSITTIE JOBAISAH TOMINAMAN ALIBelum ada peringkat
- System: Total Solution For Value-Based Healthcare PurchasingDokumen17 halamanSystem: Total Solution For Value-Based Healthcare PurchasingmochkurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Emergency NursingDokumen96 halamanEmergency NursingNimrod100% (3)
- Potts DiseaseDokumen3 halamanPotts DiseasePaul Stephen PinedaBelum ada peringkat
- Kelly Morrison Edited ResumeDokumen2 halamanKelly Morrison Edited Resumeapi-355985174Belum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology Toxicology Case StudiesDokumen134 halamanPharmacology Toxicology Case StudiesMae Quenie Abadingo Tiro56% (9)
- Orebro Musculoskeletal Pain Questionnaire FinalDokumen4 halamanOrebro Musculoskeletal Pain Questionnaire FinalIntan SafitriBelum ada peringkat
- HematuriaDokumen42 halamanHematuriaWasim R. IssaBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Emergency Medicine PDFDokumen589 halamanPractical Emergency Medicine PDFendermen minecraft100% (7)
- 2019 AFK Protocol - Revised 12102018 PDFDokumen10 halaman2019 AFK Protocol - Revised 12102018 PDFsBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory Failure S/T HCAPDokumen50 halamanRespiratory Failure S/T HCAPElaine Jean UayanBelum ada peringkat