2 Structure of Solar Cell
Diunggah oleh
Paul Ruel Gonzales Quintana0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
24 tayangan6 halamanhols
Judul Asli
2 Structure of Solar Cell.docx.Docx
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inihols
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
24 tayangan6 halaman2 Structure of Solar Cell
Diunggah oleh
Paul Ruel Gonzales Quintanahols
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 6
Structure of Solar Cell:
The most common types of materials to make solar cell are
crystalline-silicon, amorphous-silicon and thin-film
photovoltaics. Among the different materials, Crystalline-silicon
PVs (both mono and polycrystalline) currently offer the highest
efficiency, but also cost more. A Solar PV (Photovoltaic) system
is a power system that converts sunlight directly into electricity.
The basic building block of a PV sytem is the solar cell. The solar
cell is wired together to form a module and the module is then
wired together to form a solar panel. Modules come in
different sizes and typically has power output from about 20 to
300 watts in power output.
Manufacturers list the power output under "Standard Test
Conditions" (STC). It is not the same as real world conditions,
however. In actual real world environment, the energy
produced is typically 10-15% less.
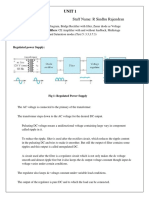
Structure of Solar Cell:
A solar cell is a solid-state electrical device (p-n junction) that
converts the energy of light directly into electricity (DC) using
the photovoltaic effect. The process of conversion first requires
a material which absorbs the solar energy (photon), and then
raises an electron to a higher energy state, and then the flow of
this high-energy electron to an external circuit. Silicon is one
such material that uses such process. A solar cell structure is
shown in figure 1 and a solar panel configuration in figure 2.
Figure 1( A Solar Cell Structure)
Figure 2(Solar Panel Configuration)
P-N junction:- It is formed by joining p-type (high concentration
of hole or deficiency of electron) and n-type (high
concentration of electron) semiconductor material. Due to this
joining, excess electrons from n-type try to diffuse with the
holes of p-type whereas excess hole from p-type try to diffuse
with the electrons of n-type. Movement of electrons to the p-
type side exposes positive ion cores in the n-type side, while
movement of holes to the n-type side exposes negative ion
cores in the p-type side, resulting in an electron field at the
junction and forming the depletion region.
Light-generated current:- Generation of current in a solar cell,
known as the “light-generated current,” involves two important
processes.
Absorption of incident photons to create electron-hole pairs.
Electron-hole pairs will generate in the solar cell provided that
the incident photon has an energy greater than that of the
band gap. However, electrons (in the p-type material), and
holes (in the n-type material) are meta-stable and will only
exist, on average, for a length of time equal to the minority
carrier lifetime before they recombine. If the carrier
recombines, then the light-generated electron-hole pair is lost
and no current or power can be generated.
Collection of these carriers by the p-n junction prevents this
recombination by using a p-n junction to spatially separate the
electron and the hole. The carriers are separated by the action
of the electric field existing at the p-n junction. If the light-
generated minority carrier reaches the p-n junction, it is swept
across the junction by the electric field at the junction, where it
is now a majority carrier. If the emitter and base of the solar
cell are connected together (i.e., if the solar cell is short-
circuited), then the light-generated carriers flow through the
external circuit.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Anselm Introduction To Semiconductor Theory MirDokumen665 halamanAnselm Introduction To Semiconductor Theory MirFabiano IshlahrBelum ada peringkat
- LASERDokumen27 halamanLASERPavan KumarBelum ada peringkat
- P Chakrabarti - Optical Fiber Communication-Mc Graw Hill India (2015) PDFDokumen600 halamanP Chakrabarti - Optical Fiber Communication-Mc Graw Hill India (2015) PDFRaja Sekhar100% (1)
- Surface, Optical and Photocatalytic Properties of RB Doped ZnO NanoparticlesDokumen16 halamanSurface, Optical and Photocatalytic Properties of RB Doped ZnO NanoparticlesCattBelum ada peringkat
- 18cs33 Module 1Dokumen145 halaman18cs33 Module 1YouBelum ada peringkat
- Sunlight Photocatalytic Performance of Mg-Doped Nickel FerriteDokumen12 halamanSunlight Photocatalytic Performance of Mg-Doped Nickel FerriteJuancho PachonBelum ada peringkat
- Physics and Technology of Semiconductor Devices - As GROVEDokumen198 halamanPhysics and Technology of Semiconductor Devices - As GROVEJerrod Rout100% (3)
- Heterojunction Solar CellDokumen6 halamanHeterojunction Solar CellYoYo ChanelBelum ada peringkat
- 2012-Nano-Photocatalytic Materials Possibilities and ChallengesDokumen23 halaman2012-Nano-Photocatalytic Materials Possibilities and ChallengesNguyen Minh Vuong TT. TNTHBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter4b 140705120937 Phpapp01Dokumen71 halamanChapter4b 140705120937 Phpapp01Rizqy FadlyBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Semiconductor Devices Module 1Dokumen4 halamanAssignment Semiconductor Devices Module 1Shivam Kumar0% (1)
- Numerical Analysis of Semiconductor PN Junctions Using MATLABDokumen15 halamanNumerical Analysis of Semiconductor PN Junctions Using MATLABMridanku PramanickBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal Resistance Analysis and Optimization of Photovoltaic-Thermoelectric Hybrid SystemDokumen15 halamanThermal Resistance Analysis and Optimization of Photovoltaic-Thermoelectric Hybrid SystemUtkarsh RajBelum ada peringkat
- Excess Carriers and Junction Concepts: Unit IIIDokumen48 halamanExcess Carriers and Junction Concepts: Unit IIIThamizharasanBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 20 21 22 EDDokumen26 halamanLec 20 21 22 EDSATYAM KUMARBelum ada peringkat
- Ec 6016Dokumen46 halamanEc 60161987parthi100% (1)
- Rau 2007Dokumen8 halamanRau 2007eniBelum ada peringkat
- 2012 ProcSPIE 8278Dokumen13 halaman2012 ProcSPIE 8278SathiyanBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Assignments SDMDokumen10 halamanSample Assignments SDMSankar SaroBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 21: Optical Properties: Issues To Address..Dokumen31 halamanChapter 21: Optical Properties: Issues To Address..Eugene Embalzado Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- An Investigation of Tio2-Znfe2o4 Nanocomposites For Visible LightDokumen124 halamanAn Investigation of Tio2-Znfe2o4 Nanocomposites For Visible LightVăn Đại - BKHN100% (1)
- Unit-2 - L-12 - Characteristics of LED, Photodiode, and LDRDokumen9 halamanUnit-2 - L-12 - Characteristics of LED, Photodiode, and LDRwebip33713Belum ada peringkat
- Course Handout KannanDokumen3 halamanCourse Handout KannanJulie JacksonBelum ada peringkat
- Mobile Charge Carrier Based Modeling of 4H21 DNTT and Structure Analysis of OTFTDokumen5 halamanMobile Charge Carrier Based Modeling of 4H21 DNTT and Structure Analysis of OTFTshubham dadhichBelum ada peringkat
- CuO Based Solar Cell With V2O5 BSF Layer - Theoretical Validation of Experimental DataDokumen12 halamanCuO Based Solar Cell With V2O5 BSF Layer - Theoretical Validation of Experimental DataNur Aisyah ShariBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 NotesDokumen33 halamanUnit 1 NotesAer ZBelum ada peringkat
- (C) Conduction BandDokumen2 halaman(C) Conduction BandBarney StinsBelum ada peringkat
- SMD TutorialDokumen8 halamanSMD TutorialAnkur ShuklaBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Optical Sources and DetectorsDokumen2 halamanTutorial Optical Sources and DetectorsMir Sameer HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Optical SourcesDokumen30 halamanOptical Sourcesomar.alamodiBelum ada peringkat