Michigan 2017 CDC AR Investments
Diunggah oleh
Arielle BreenHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Michigan 2017 CDC AR Investments
Diunggah oleh
Arielle BreenHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
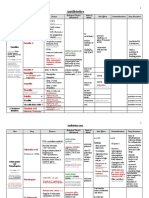
AR Solutions In Action FISCAL YEAR
CDC’s Investments to Combat Antibiotic Resistance Threats Nationwide 2017
MICHIGAN AR Lab Network’s National Tuberculosis
Molecular Surveillance Center
$3,196,689
Funding for AR Activities
Fiscal Year 2017
FUNDING TO STATE HEALTH DEPARTMENTS
AR LABORATORY NETWORK REGIONAL LABS boost state and local testing capacity and technology to detect, support
response to, and prevent AR threats across the nation—and inform new innovations to detect AR.
Added in 2017, the AR Lab Network now includes the National Tuberculosis (TB) Molecular Surveillance Center, which
$1,238,534 performs whole genome sequencing for all isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The lab is using state-of-the-art
methods to analyze TB samples. New molecular methods reduce the time needed to determine if a strain is resistant
from weeks to days.
RAPID DETECTION & RESPONSE to emerging drug-resistant germs is critical to contain the spread of these infections.
With 2016 funding, Michigan collaborated with local health departments and healthcare facilities to rapidly detect and
investigate HAI/AR cases, thereby stopping the spread of antibiotic resistance clusters and novel resistance mechanisms.
$300,974
HAI/AR PREVENTION works best when public health and healthcare facilities partner together to implement targeted,
coordinated strategies to stop infections and improve antibiotic use.
With 2016 funding, Michigan supported 40 facilities in a surveillance and prevention initiative that monitors for the
$938,507 “nightmare bacteria” CRE. These efforts reduced CRE incidence by about 30% in participating facilities and prevented
more than 300 infections.
FOOD SAFETY projects protect communities by rapidly identifying drug-resistant foodborne bacteria to stop and solve
outbreaks and improve prevention.
Michigan implemented whole genome sequencing of Listeria, Salmonella, Campylobacter and E. coli isolates submitted
$365,066 to its lab and began uploading sequence data into PulseNet for nationwide monitoring of outbreaks and trends. In
Fiscal Year 2018, Michigan will begin simultaneously monitoring these isolates for resistance genes. When outbreaks
are detected, local CDC-supported epidemiologists investigate the cases to stop spread.
FUNDING TO UNIVERSITIES & HEALTHCARE PARTNERS
REGENTS OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN: Microbiome Assessment & Intervention
Antibiotics can change the intestinal microbiome, which may increase the risk of sepsis. Researchers will extend
previous CDC-funded work to assess intestinal microbiome disruption and dominance by the Enterobacteriaceae family
$353,608 of bacteria as risk factors for sepsis.
Page 1 of 1 This data represents CDC’s largest fundng categories for AR. It shows domestic, extramural funding that supports AR activities from multiple funding lines. AR: antibiotic resistance HAI: healthcare-associated infection
CDC provides critical support to every state
to protect Americans from antibiotic resistance.
www.cdc.gov/ARinvestments
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Messer Crash 1932Dokumen5 halamanMesser Crash 1932Arielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Manistee City Council Agenda Packet InformationDokumen106 halamanManistee City Council Agenda Packet InformationArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Manistee County Public Safety Committee August AgendaDokumen20 halamanManistee County Public Safety Committee August AgendaArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Carpenter V Manistee County Release and SettlementDokumen6 halamanCarpenter V Manistee County Release and SettlementArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Civil Suit: Kelley v. Onekama Consolidated SchoolsDokumen16 halamanCivil Suit: Kelley v. Onekama Consolidated SchoolsArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 415 Manistee Junk Vehicles RulesDokumen2 halamanChapter 415 Manistee Junk Vehicles RulesArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Manistee City Council Agenda Packet April 5, 2022Dokumen167 halamanManistee City Council Agenda Packet April 5, 2022Arielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- River Street Streetscape Plan Request For Qualifications and Cost ProposalsDokumen16 halamanRiver Street Streetscape Plan Request For Qualifications and Cost ProposalsArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- David Parrott STATE OF MICHIGAN COURT OF APPEALSDokumen18 halamanDavid Parrott STATE OF MICHIGAN COURT OF APPEALSArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 650 Anti Blight in ManisteeDokumen3 halamanChapter 650 Anti Blight in ManisteeArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Impact of Recreational Cannabis Legalization in Michigan: A Baseline ReportDokumen88 halamanImpact of Recreational Cannabis Legalization in Michigan: A Baseline ReportArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Portage Lake Watershed Support Grant ApplicationDokumen9 halamanPortage Lake Watershed Support Grant ApplicationArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Carpenter V Manistee County, Et Al Final Settlement HearingDokumen1 halamanCarpenter V Manistee County, Et Al Final Settlement HearingArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Carpenter v. Manistee CountyDokumen21 halamanCarpenter v. Manistee CountyArielle Breen100% (1)
- Manistee Kids Count 2021Dokumen2 halamanManistee Kids Count 2021Arielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Manistee Recycling Center Guide at A GlanceDokumen1 halamanManistee Recycling Center Guide at A GlanceArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Michigan Deer Harvest Report 2020Dokumen77 halamanMichigan Deer Harvest Report 2020Arielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Residential Target Market Analysis Manistee CountyDokumen48 halamanResidential Target Market Analysis Manistee CountyArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Impact of Recreational Cannabis Legalization in Michigan: A Baseline ReportDokumen88 halamanImpact of Recreational Cannabis Legalization in Michigan: A Baseline ReportArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Manistee County Public Safety Committee Meeting February 2021Dokumen20 halamanManistee County Public Safety Committee Meeting February 2021Arielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Joint Land Use Draft ReportDokumen152 halamanJoint Land Use Draft ReportArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Attorney General vs. AmeriGas PropaneDokumen44 halamanAttorney General vs. AmeriGas PropaneArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Joint Land Use Handout April 2018Dokumen6 halamanJoint Land Use Handout April 2018Arielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Gaylord Community Schools Sinking Fund PamphletDokumen2 halamanGaylord Community Schools Sinking Fund PamphletArielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- Installation Environmental Noise Management Plan 2001Dokumen90 halamanInstallation Environmental Noise Management Plan 2001Arielle BreenBelum ada peringkat
- 2017 Annual SANE ReportDokumen24 halaman2017 Annual SANE ReportArielle Breen0% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1091)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Hepatitis B: Pathophysiology and TransmissionDokumen6 halamanHepatitis B: Pathophysiology and TransmissionEndrianus Jaya PutraBelum ada peringkat
- Omicron Webinar AHSDokumen16 halamanOmicron Webinar AHSDian AkbariBelum ada peringkat
- Mohamad Hamad Infection Control in DentalDokumen25 halamanMohamad Hamad Infection Control in DentalMohamad Hamad100% (1)
- Cataloguenew 121215100406 Phpapp02Dokumen12 halamanCataloguenew 121215100406 Phpapp02sidomoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical and Etiological Profile of Acute Febrile Encephalopathy in Eastern NepalDokumen3 halamanClinical and Etiological Profile of Acute Febrile Encephalopathy in Eastern NepalNeha OberoiBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation of Antibiotic Sensitivity Pattern in Acute TonsillitisDokumen5 halamanEvaluation of Antibiotic Sensitivity Pattern in Acute TonsillitisyoanaBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Acute Exacerbation of Copd: Dr. Fanny WS KoDokumen3 halamanManagement of Acute Exacerbation of Copd: Dr. Fanny WS KoCalca NeusBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Un Bahasa Inggris Xii (Lat 22)Dokumen10 halamanSoal Un Bahasa Inggris Xii (Lat 22)hasanlina2007100% (1)
- Microbiology Newlab سالى ابو السعود 0864986Dokumen1 halamanMicrobiology Newlab سالى ابو السعود 0864986Mohammed TahounBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Surgical Nursing - IDokumen97 halamanMedical Surgical Nursing - IGuruKPO80% (10)
- Anti Rabies CampaignDokumen3 halamanAnti Rabies CampaignJoey YusingcoBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic Microbiology and Laboratory MethodsDokumen70 halamanDiagnostic Microbiology and Laboratory MethodsArulmany SelliahBelum ada peringkat
- Digitale Einreiseanmeldung: Für Die Zuständige Behörde/ For The Responsible AuthorityDokumen3 halamanDigitale Einreiseanmeldung: Für Die Zuständige Behörde/ For The Responsible AuthorityNelson CardosoBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Rickettsia Chlamydia, MycoplasmaDokumen49 halamanLecture Rickettsia Chlamydia, MycoplasmaHabeeb Ali Baig100% (3)
- Gentamicin SulfateDokumen4 halamanGentamicin Sulfateapi-3797941Belum ada peringkat
- Cable Abbreviations With Woven Cable PatternDokumen2 halamanCable Abbreviations With Woven Cable PatterntritidiefBelum ada peringkat
- Indonesia National Immunization Program:: Dr. Prima Yosephine Epi Manager Moh IndonesiaDokumen19 halamanIndonesia National Immunization Program:: Dr. Prima Yosephine Epi Manager Moh IndonesiaAstri KhairanaBelum ada peringkat
- NVI Product Catalog 4 1Dokumen40 halamanNVI Product Catalog 4 1Ayele Bizuneh100% (4)
- Quick Quiz: Number of Yeast CellsDokumen2 halamanQuick Quiz: Number of Yeast CellsVictor Barber SanchisBelum ada peringkat
- Antimicrobial Drugs TableDokumen19 halamanAntimicrobial Drugs TableLaylee ClareBelum ada peringkat
- USMLE - VirusesDokumen120 halamanUSMLE - Viruseszeal7777100% (1)
- Im SQ Admin PDFDokumen2 halamanIm SQ Admin PDFAlvin JjBelum ada peringkat
- Reading - Fill in The BlankDokumen8 halamanReading - Fill in The BlankHoa TruongBelum ada peringkat
- Notice 503943616Dokumen2 halamanNotice 503943616abreu2021Belum ada peringkat
- 5096 s13 QP 13Dokumen20 halaman5096 s13 QP 13mstudy123456Belum ada peringkat
- Strunk's Criminal Complaint Charges To Each New York 62 Subdivision Sheriffs and Department of Health 8-12-2021Dokumen24 halamanStrunk's Criminal Complaint Charges To Each New York 62 Subdivision Sheriffs and Department of Health 8-12-2021kris strunk100% (1)
- Activity 3 - Inventory Converstions Using Metric SystemsDokumen2 halamanActivity 3 - Inventory Converstions Using Metric SystemsshayBelum ada peringkat
- Aerobic Non-Spore Forming Gram-Positive BacilliDokumen31 halamanAerobic Non-Spore Forming Gram-Positive BacilliCagar Irwin TaufanBelum ada peringkat
- Evans SyndromeDokumen13 halamanEvans SyndromerizeviBelum ada peringkat
- Human & Social Biology School Based AssessmentDokumen10 halamanHuman & Social Biology School Based AssessmentShaunielle ReidBelum ada peringkat