Radiology Notes
Diunggah oleh
Jaymee0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
318 tayangan2 halamanRadiology notes discuss 5 key radiographic densities: metal absorbs most x-rays, air absorbs least, and calcium, fluid, fat, and soft tissue are intermediate. Understanding densities helps determine the location and composition of abnormalities.
The document also covers the silhouette sign, which occurs when two structures of the same density touch and their border disappears. Examples are given of how this sign can indicate conditions like atelectasis.
Orthogonal views, or images taken at right angles, are discussed as important for localizing lesions on conventional radiography, though modern CT and ultrasound can also be used.
Deskripsi Asli:
sadasdasds
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniRadiology notes discuss 5 key radiographic densities: metal absorbs most x-rays, air absorbs least, and calcium, fluid, fat, and soft tissue are intermediate. Understanding densities helps determine the location and composition of abnormalities.
The document also covers the silhouette sign, which occurs when two structures of the same density touch and their border disappears. Examples are given of how this sign can indicate conditions like atelectasis.
Orthogonal views, or images taken at right angles, are discussed as important for localizing lesions on conventional radiography, though modern CT and ultrasound can also be used.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
318 tayangan2 halamanRadiology Notes
Diunggah oleh
JaymeeRadiology notes discuss 5 key radiographic densities: metal absorbs most x-rays, air absorbs least, and calcium, fluid, fat, and soft tissue are intermediate. Understanding densities helps determine the location and composition of abnormalities.
The document also covers the silhouette sign, which occurs when two structures of the same density touch and their border disappears. Examples are given of how this sign can indicate conditions like atelectasis.
Orthogonal views, or images taken at right angles, are discussed as important for localizing lesions on conventional radiography, though modern CT and ultrasound can also be used.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
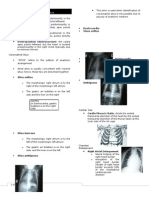
Radiology Notes
Lesson 1: 5 Radiographic Densities
A. Importance
Fundamental to understanding
Conventional radiographs
Helps tell location of ds
Helps tell what they may be
B. 5 Densities
Normal
The edge of heart can be seen as the heart and the lungs are
two different radiographic densities
Metal absorbs the most x-rays and very few reach
the film cassette
Air absorbs least x rays and most will be
reflected in the film cassette
Calcium, fluid, fat and soft tissue are
intermediate
Example
Left Lung Atelectasis
When something replaces the air in the lungs, which is the
same density of the heart, the interface b/n the left heart
border and the lung disappear
Clue as to composition of abnormality
Tell the location of the abnormality
Lesson2: Silhouette Sign
A. Definition Atelectasis of the right lower lobe
When 2 objects of the same radiographic density Normal – in the left lower lobe, the left hemidiaphragm can
touch each other, the border b/n them disappears be seen as there is air above (lungs) and below (colon)
Abonormal –at the right lower lobe, the right
B. Examples hemidiaphragm is absent caused by a something at the right
lower lobe w/ the same density as the hemiaphragm and the A. Definition
liver. To views obtained at right angle to each other
The interface b/n the R lung and R hemidiaphram B. Importance
disappear. To localize location of lesion on conventional
radiography
C. Current technology
CT and UTZ can be utilized
Right Pneumonectomy
Opacification of the right hemithorax hence the structures
on the right can no longer be seen silhouetted by the lack of
air
Leasson 4: Pulmonary Imaging Part 1
Pneumonia – Left Lower Lobe, Anterior / Lingula
Airspace density at the lower lobe is absent
Absent interface b/n L heart border and L lung must be
touching the heart since the heart is anterior it can be
anterior
Lateral view
Lesson 3: Orthogonal Views
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Lung - HRCT Basic Interpretatio NDokumen19 halamanLung - HRCT Basic Interpretatio NHarsha VijaykumarBelum ada peringkat
- Basis Chest X-RayDokumen59 halamanBasis Chest X-RayadistyBelum ada peringkat
- Rapid Review of RadiologyDokumen349 halamanRapid Review of RadiologyAnka Eremia86% (28)
- Radio Logical Anatomy For FRCR Part 1Dokumen15 halamanRadio Logical Anatomy For FRCR Part 1Prashant Gupta100% (3)
- Clinical Radiology For Surgical Conditions of The AbdomenDokumen8 halamanClinical Radiology For Surgical Conditions of The AbdomenPreeti Joan Buxani100% (1)
- Aunt Minnie'sDokumen464 halamanAunt Minnie'sbabygirlmd100% (9)
- Preview PDFDokumen21 halamanPreview PDFazehboBelum ada peringkat
- Radiology Secrets - 2nd EdDokumen12 halamanRadiology Secrets - 2nd EdD T50% (8)
- (FRCR) Afaq - Succeeding in The New FRCR Part 2A Exam PDFDokumen219 halaman(FRCR) Afaq - Succeeding in The New FRCR Part 2A Exam PDFNaweed Ashraf100% (7)
- Radiology SignsDokumen99 halamanRadiology SignsPartha GanesanBelum ada peringkat
- Master Radiology Notes GIT PDFDokumen115 halamanMaster Radiology Notes GIT PDFuroshkgBelum ada peringkat
- QbasQbase Radiology3 Croppede Radiology3 CroppedDokumen175 halamanQbasQbase Radiology3 Croppede Radiology3 CroppedZubair Lone100% (4)
- Radiology Free VideoDokumen4 halamanRadiology Free VideoSecret Accord100% (2)
- PRACTICAL EXAM PPT RadiologyDokumen51 halamanPRACTICAL EXAM PPT RadiologyPartha Ganesan0% (1)
- USG ImagingDokumen26 halamanUSG ImagingskBelum ada peringkat
- Radiology PDFDokumen585 halamanRadiology PDFGilettipostino100% (3)
- 2010 Rapid Review of Radiology (2010) (True PDF) (4.5-Star) PDFDokumen353 halaman2010 Rapid Review of Radiology (2010) (True PDF) (4.5-Star) PDFtom24100% (2)
- Skull RadiographyDokumen104 halamanSkull RadiographyEzra NserekoBelum ada peringkat
- MRI BrainDokumen56 halamanMRI BrainmalaakangelBelum ada peringkat
- Radiology ExpertDokumen955 halamanRadiology ExpertAndreea Roxana100% (4)
- Emergency Radiology MAHMUOD PDFDokumen134 halamanEmergency Radiology MAHMUOD PDFCut Nonda MaraciluBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac ImagingDokumen7 halamanCardiac Imagingsarguss14Belum ada peringkat
- James Chen - Head and Neck Imaging PDFDokumen83 halamanJames Chen - Head and Neck Imaging PDFdamclf100% (1)
- Introduction To Radiology: Basic Terms and DefinitionsDokumen126 halamanIntroduction To Radiology: Basic Terms and DefinitionsChris Queiklin100% (2)
- Sample Pages of RadiologyDokumen17 halamanSample Pages of RadiologyskBelum ada peringkat
- Radiology PearlsDokumen2 halamanRadiology PearlsSalman Rashid100% (2)
- 39 RadiologyDokumen10 halaman39 RadiologyIbrahimFikry100% (1)
- Complete Revision Notes FRCRDokumen354 halamanComplete Revision Notes FRCREsraa AlmassriBelum ada peringkat
- QBASE 1 Radiology MCQs For The FRCRDokumen43 halamanQBASE 1 Radiology MCQs For The FRCRArif83% (6)
- FRCR PART 1 Revision NotesDokumen60 halamanFRCR PART 1 Revision NotesQueennie Wong86% (7)
- RadiologyDokumen29 halamanRadiologyDhon de CastroBelum ada peringkat
- FRCR Part 1 - Anatomy Mock Examinations PDFDokumen242 halamanFRCR Part 1 - Anatomy Mock Examinations PDFInnocential100% (2)
- The Essential Guide To The New FRCR Part 2A and Radiology BoardsDokumen208 halamanThe Essential Guide To The New FRCR Part 2A and Radiology Boardsbana galaxyBelum ada peringkat
- Phys-FRCR Vol 1Dokumen113 halamanPhys-FRCR Vol 1Anonymous oQtve4o100% (1)
- FRCR Clinical Radiology Lectures: 2 Diagnostic Radiology Fluoroscopy and FluorographyDokumen29 halamanFRCR Clinical Radiology Lectures: 2 Diagnostic Radiology Fluoroscopy and FluorographyDr Piyush100% (1)
- On-Call X-Rays Made Easy - NodrmDokumen305 halamanOn-Call X-Rays Made Easy - NodrmSara Navarro50% (2)
- Diagnostic Radiology MCQ Sample Exam eDokumen7 halamanDiagnostic Radiology MCQ Sample Exam eMuhammad TariqBelum ada peringkat
- Cross Sectional Imaging Made Easy® PDFDokumen207 halamanCross Sectional Imaging Made Easy® PDFsalah subbah100% (2)
- FRCR Part 1 Anatomy March 2011Dokumen2 halamanFRCR Part 1 Anatomy March 2011drramki27100% (1)
- Radiology Notes For StudentsDokumen167 halamanRadiology Notes For Studentsmonika100% (1)
- Basic NeuroradiologyDokumen70 halamanBasic Neuroradiologyarmin_valentine50% (2)
- FRCR 2a March 2010 PapersDokumen12 halamanFRCR 2a March 2010 PapersAjay Agarwal100% (2)
- Gunn - Pearls and Pitfalls in Emergency Radiology - Variants and Other Difficult DiagnosesDokumen387 halamanGunn - Pearls and Pitfalls in Emergency Radiology - Variants and Other Difficult Diagnosesvalentina costrubscaia0% (1)
- The Final FRCR Self-AssessmentDokumen244 halamanThe Final FRCR Self-AssessmentAman KumarBelum ada peringkat
- @MedicalBooksStore Mayo Clinic Body MRI Case Review (2014) PDFDokumen881 halaman@MedicalBooksStore Mayo Clinic Body MRI Case Review (2014) PDFKahkashan Hameed100% (1)
- Digital Radiography Image CritiqueDokumen68 halamanDigital Radiography Image CritiqueNur Alam50% (2)
- Core Radiology A Visual Approach To DiagnosticDokumen1 halamanCore Radiology A Visual Approach To DiagnosticDinosaur Egg0% (1)
- FRCR Part 1 - Radiological Anatomy - New For 2013 - Set 02 PDFDokumen109 halamanFRCR Part 1 - Radiological Anatomy - New For 2013 - Set 02 PDFmohamed100% (3)
- Rotation in RadiologyDokumen6 halamanRotation in Radiologyminci sensei100% (3)
- (FRCR) Sharma - Get Through FRCR Part 2B - Reporting of Plain RadiographsDokumen249 halaman(FRCR) Sharma - Get Through FRCR Part 2B - Reporting of Plain RadiographsPankaj Nagori100% (2)
- FRCRDokumen32 halamanFRCRsarsmajor100% (8)
- Radiology Fundamentals: Introduction to Imaging & TechnologyDari EverandRadiology Fundamentals: Introduction to Imaging & TechnologyJennifer KissaneBelum ada peringkat
- Musculoskeletal Imaging: 100 Cases (Common Diseases) US, CT and MRIDari EverandMusculoskeletal Imaging: 100 Cases (Common Diseases) US, CT and MRIBelum ada peringkat
- Chest X-ray Interpretation for Radiographers, Nurses and Allied Health ProfessionalsDari EverandChest X-ray Interpretation for Radiographers, Nurses and Allied Health ProfessionalsBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic Ultrasound Imaging: Inside OutDari EverandDiagnostic Ultrasound Imaging: Inside OutPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (4)
- Atlas of Neuroradiology: 200 Common CasesDari EverandAtlas of Neuroradiology: 200 Common CasesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load of Popular Weight-Loss DietsDokumen11 halamanGlycemic Index and Glycemic Load of Popular Weight-Loss DietsJaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- OB 1.04-Maternal PhysiologyDokumen5 halamanOB 1.04-Maternal PhysiologyJaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- Docslide - Us Case Digest Legal Medicine Lucas Vs TuanoDokumen2 halamanDocslide - Us Case Digest Legal Medicine Lucas Vs TuanoJaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDokumen8 halamanNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptJaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- Neurologic ExaminationDokumen1 halamanNeurologic ExaminationJaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- Obgyne Precep 2018 1Dokumen4 halamanObgyne Precep 2018 1JaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- 820101Dokumen8 halaman820101JaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatal Infection Prevention and ControlDokumen2 halamanNeonatal Infection Prevention and ControlJaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- Table - Rheumatic DiseasesDokumen11 halamanTable - Rheumatic DiseasesJaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- Jnma00324 0037Dokumen5 halamanJnma00324 0037JaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- Updated PediatricHP 02oct2017Dokumen2 halamanUpdated PediatricHP 02oct2017JaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On Nutrition and Diet Therapy 1Dokumen1 halamanNotes On Nutrition and Diet Therapy 1Jaymee100% (6)
- SSSL Checklist Finaljun08Dokumen1 halamanSSSL Checklist Finaljun08hgcisoBelum ada peringkat
- Jnma00324 0037Dokumen5 halamanJnma00324 0037JaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- PCNDokumen3 halamanPCNJaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Journal Nurse On BoardsDokumen6 halamanNursing Journal Nurse On BoardsJaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- Ethical Principles in CHNDokumen1 halamanEthical Principles in CHNJaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- En Dome Trial CancerDokumen2 halamanEn Dome Trial CancerJaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic TestingDokumen1 halamanDiagnostic TestingJaymeeBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On Nutrition and Diet TherapyDokumen1 halamanNotes On Nutrition and Diet TherapyJaymee0% (1)
- Adigwe J. C.: ATBU, Journal of Science, Technology & Education (JOSTE) Vol. 3 (1), January, 2015 ISSN: 2277-0011Dokumen16 halamanAdigwe J. C.: ATBU, Journal of Science, Technology & Education (JOSTE) Vol. 3 (1), January, 2015 ISSN: 2277-0011AnnyBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture BouffonDokumen1 halamanLecture BouffonCarlos Enrique GuerraBelum ada peringkat
- LT3845ADokumen26 halamanLT3845Asoft4gsmBelum ada peringkat
- Jy992d66901 CDokumen6 halamanJy992d66901 CMaitry ShahBelum ada peringkat
- ENSC1001 Unit Outline 2014Dokumen12 halamanENSC1001 Unit Outline 2014TheColonel999Belum ada peringkat
- Unilever PakistanDokumen26 halamanUnilever PakistanElie Mints100% (3)
- Effects of Corneal Scars and Their Treatment With Rigid Contact Lenses On Quality of VisionDokumen5 halamanEffects of Corneal Scars and Their Treatment With Rigid Contact Lenses On Quality of VisionJasmine EffendiBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Urban PlanningDokumen33 halamanWhat Is Urban PlanningDivine Grace FernandoBelum ada peringkat
- DC Generator - Construction, Working Principle, Types, and Applications PDFDokumen1 halamanDC Generator - Construction, Working Principle, Types, and Applications PDFGokul GokulBelum ada peringkat
- Linux and The Unix PhilosophyDokumen182 halamanLinux and The Unix PhilosophyTran Nam100% (1)
- Krishna TejaDokumen71 halamanKrishna TejaHimanshu GaurBelum ada peringkat
- Solid Waste Management in The World's Cities, UN-HABITAT: January 2010Dokumen17 halamanSolid Waste Management in The World's Cities, UN-HABITAT: January 2010Rajasri SBelum ada peringkat
- DIY Toolkit Arabic Web VersionDokumen168 halamanDIY Toolkit Arabic Web VersionAyda AlshamsiBelum ada peringkat
- AIP 2020 FINAL JuneDokumen5 halamanAIP 2020 FINAL JuneVINA ARIETABelum ada peringkat
- WCDMA Radio Access OverviewDokumen8 halamanWCDMA Radio Access OverviewDocMasterBelum ada peringkat
- Circuit Construction: Assignment 3Dokumen45 halamanCircuit Construction: Assignment 3ali morisyBelum ada peringkat
- EDAG0007Dokumen5 halamanEDAG0007krunalBelum ada peringkat
- P D P: C I D, C M: Design of Coastal RoadsDokumen55 halamanP D P: C I D, C M: Design of Coastal RoadsMohammedBelum ada peringkat
- CESCOM 10 - Aircraft Status Report: Maintenance InspectionsDokumen78 halamanCESCOM 10 - Aircraft Status Report: Maintenance InspectionsAlejandro BarradasBelum ada peringkat
- Cornish BoilerDokumen3 halamanCornish BoilerDeepak KV ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- 2396510-14-8EN - r1 - Service Information and Procedures Class MDokumen2.072 halaman2396510-14-8EN - r1 - Service Information and Procedures Class MJuan Bautista PradoBelum ada peringkat
- Royal British College Dancesport TeamDokumen10 halamanRoyal British College Dancesport TeamAnna rose CabatinganBelum ada peringkat
- ING C1 CO JUN2016 CorrectorDokumen6 halamanING C1 CO JUN2016 CorrectoraciameBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Second Sun of Advent (B)Dokumen4 halaman2nd Second Sun of Advent (B)Max PolakBelum ada peringkat
- FIGMADokumen22 halamanFIGMACessBelum ada peringkat
- Hackerearth Online Judge: Prepared By: Mohamed AymanDokumen21 halamanHackerearth Online Judge: Prepared By: Mohamed AymanPawan NaniBelum ada peringkat
- CH 1 Viscous Fluid Flow Part 1Dokumen29 halamanCH 1 Viscous Fluid Flow Part 1Ammar WahabBelum ada peringkat
- NamalDokumen5 halamanNamalAyusnab KarkiBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study McsDokumen4 halamanCase Study McsManjushree PatilBelum ada peringkat
- CrimDokumen29 halamanCrimkeziahmae.bagacinaBelum ada peringkat