Transistor As A Switch 1 Eelectronic Devices and Circuit Active Learning Assignment
Diunggah oleh
Aman0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
38 tayangan5 halamanPHYSICS INVESTIGORY
Judul Asli
Transistor as a Switch 1 Eelectronic Devices and Circuit Active Learning Assignment
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniPHYSICS INVESTIGORY
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
38 tayangan5 halamanTransistor As A Switch 1 Eelectronic Devices and Circuit Active Learning Assignment
Diunggah oleh
AmanPHYSICS INVESTIGORY
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 5
1.
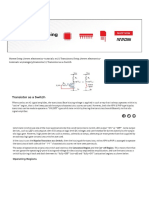
Transistor as a switch 1 Eelectronic Devices and Circuit Active Learning Assignment
2. 2. What is transistor? • When an n-type or p- type semiconductor is Connect between two p-
type or n-type semiconductor respectively then two PN junction formed. Such a two junction
device is called as TRANSISTOR • Thus transistor is a two junction , three layered, three
terminal semiconductor device. • The transistor made by Silicon , Germanium material. •
Transistor has mainly two type. 1) PNP Transistor 2) NPN Transistor
3. 3. Transistor as a Switch • When used as an AC signal amplifier, the transistors Base biasing
voltage is applied in such a way that it always operates within its “active” region, that is the
linear part of the output characteristics curves are used. However, both the NPN & PNP type
bipolar transistors can be made to operate as “ON/OFF” type solid state switches by biasing
the transistors base differently to that of a signal amplifier. • Transistor switch operating
region • NPN Transistor and PNP Transistor V-I Characteristics curves have seen in figure.
4. 4. • The areas of operation for a Transistor Switch are known as the Saturation Region and
the Cut-off Region. This means then that we can ignore the operating Q-point biasing and
voltage divider circuitry required for amplification, and use the transistor as a switch by
driving it back and forth between its “fully-OFF” (cut-off) and “fully-ON” (saturation) regions
as shown in figure. • The pink shaded area at the bottom of the curves represents the “Cut-
off” region while the blue area to the left represents the “Saturation” region of the transistor.
Both these transistor regions are defined as: 1. Cut-off Region • Then we can define the “cut-
off region” or “OFF mode” when using a bipolar transistor as a switch as being, both
junctions reverse biased, VB < 0.7v and IC = 0. For a PNP transistor, the Emitter potential
must be negative with respect to the Base.
5. 5. • Here the operating conditions of the transistor are zero input base current ( IB ), zero
output collector current ( IC ) and maximum collector voltage ( VCE ) which results in a large
depletion layer and no current flowing through the device. Therefore the transistor is
switched “Fully- OFF”. • transistor switch in cut-off
6. 6. 2. Saturation Region • Here the transistor will be biased so that the maximum amount of
base current is applied, resulting in maximum collector current resulting in the minimum
collector emitter voltage drop which results in the depletion layer being as small as possible
and maximum current flowing through the transistor. Therefore the transistor is switched
“Fully-ON”. • Saturation Characteristics • transistor switch in saturation
7. 7. • Then we can define the “saturation region” or “ON mode” when using a bipolar transistor
as a switch as being, both junctions forward biased, VB > 0.7v and IC = Maximum. For a
PNP transistor, the Emitter potential must be positive with respect to the Base. Digital Logic
Transistor Switch • Transistor switches are used for a wide variety of applications such as
interfacing large current or high voltage devices like motors, relays or lamps to low voltage
digital logic IC’s or gates like AND gates or OR gates. Here, the output from a digital logic
gate is only +5v but the device to be controlled may require a 12 or even 24 volts supply. Or
the load such as a DC Motor may need to have its speed controlled using a series of pulses
(Pulse Width Modulation). transistor switches will allow us to do this faster and more easily
than with conventional mechanical switches.
8. 8. Digital Logic Transistor Switch
9. 9. Using the transistor values from the previous tutorials of: βA Switch Example = 200, Ic
= 4mA and Ib = 20uA, find the value of the Base resistor (Rb) required to switch the load fully
“ON” when the input terminal voltage exceeds 2.5v. • Transistor Switch Base Resistance
10. 10. Application • Transistor switches can be used to switch and control lamps, relays or even
motors. • When using the bipolar transistor as a switch they must be either “fully- OFF” or
“fully-ON”. • Transistors that are fully “ON” are said to be in their Saturation region. •
Transistors that are fully “OFF” are said to be in their Cut-off region. • When using the
transistor as a switch, a small Base current controls a much larger Collector load current •
When using transistors to switch inductive loads such as relays and solenoids, a “Flywheel
Diode” is used. • When large currents or voltages need to be controlled, Darlington
Transistors can be used
11. 11. Thank you
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Class 1 Transistor As A SwitchDokumen11 halamanClass 1 Transistor As A Switchermaheshkumar4Belum ada peringkat
- Transistor As A SwitchDokumen3 halamanTransistor As A SwitchbofshafiqueBelum ada peringkat
- The Transistor As A SwitchDokumen8 halamanThe Transistor As A Switchmajstor100% (1)
- Transistor As A Switch - Using Transistor SwitchingDokumen11 halamanTransistor As A Switch - Using Transistor SwitchingDilpreet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- #12: Transistor As A Switch DiscussionDokumen1 halaman#12: Transistor As A Switch DiscussionMischelle NohayBelum ada peringkat
- BJT Transistor As A Switch 2Dokumen1 halamanBJT Transistor As A Switch 2rudranshvsingh4705Belum ada peringkat
- The Transistor As A SwitchDokumen9 halamanThe Transistor As A SwitchSoodamany Ponnu Pandian80% (5)
- Transistor As A Switch - Using Transistor SwitchingDokumen8 halamanTransistor As A Switch - Using Transistor Switchingviet triBelum ada peringkat
- Transistor As A SwitchDokumen8 halamanTransistor As A SwitchdhingrastoreBelum ada peringkat
- Ecad Exp8Dokumen7 halamanEcad Exp8Saturn MoonBelum ada peringkat
- Transistor As A SwitchDokumen7 halamanTransistor As A SwitchS GBelum ada peringkat
- To Verify The Application of Transistor As A Switch: Experiment No: 07 DATE: 14/05/2020Dokumen8 halamanTo Verify The Application of Transistor As A Switch: Experiment No: 07 DATE: 14/05/2020Kashish JainBelum ada peringkat
- Acknowledgement: The Transistor As A SwitchDokumen12 halamanAcknowledgement: The Transistor As A SwitchRamanpreet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- BJT Transistor As A SwitchDokumen12 halamanBJT Transistor As A SwitchRoaa AlfakeehBelum ada peringkat
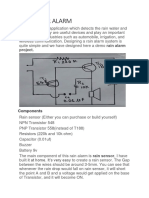
- Rain AlarmDokumen15 halamanRain AlarmTARIT DAS100% (4)
- TRANSISTORSDokumen13 halamanTRANSISTORSAbad Kurt ChristianBelum ada peringkat
- Bistable MultivibratorsDokumen9 halamanBistable MultivibratorsihtishamuddBelum ada peringkat
- Mod 2Dokumen99 halamanMod 2SREEHARI V ABelum ada peringkat
- The Bipolar Transistor As A SwitchDokumen13 halamanThe Bipolar Transistor As A Switchbarzoom007Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 2Dokumen46 halamanUnit 2Manan JainBelum ada peringkat
- Transistor As A SwitchDokumen2 halamanTransistor As A Switchjojo1216Belum ada peringkat
- Relay Switch Circuit and Relay Switching CircuitDokumen10 halamanRelay Switch Circuit and Relay Switching CircuitidatscribdBelum ada peringkat
- Thyristor Mod 1Dokumen35 halamanThyristor Mod 1Gopalakrishna Murthy C RBelum ada peringkat
- Design A Clap SwitchDokumen15 halamanDesign A Clap Switchbalvendra03Belum ada peringkat
- Transistores Como InterruptoresDokumen18 halamanTransistores Como InterruptoresSayuri CastellanosBelum ada peringkat
- Fpe (1) AkDokumen39 halamanFpe (1) AkAnchal YewaleBelum ada peringkat
- Tesla Coil NPN TransistorDokumen16 halamanTesla Coil NPN TransistorRaj TokasBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2-18EE53Dokumen59 halamanModule 2-18EE53AshwiniBelum ada peringkat
- 12v DC To 220v AC Converter Circuit Using Astable MultivibratorDokumen3 halaman12v DC To 220v AC Converter Circuit Using Astable MultivibratorKïshörë0% (1)
- Push-Pull Amplifier Circuit Class A B Amp AB Amplifier CircuitsDokumen6 halamanPush-Pull Amplifier Circuit Class A B Amp AB Amplifier CircuitsDan BosakBelum ada peringkat
- Gate Driver Circuit For Three Phase InverterDokumen13 halamanGate Driver Circuit For Three Phase InverterMarc TcheukabaBelum ada peringkat
- EC6304 Uw PDFDokumen119 halamanEC6304 Uw PDFsivadhanuBelum ada peringkat
- Inverter Explanation Cd4047Dokumen7 halamanInverter Explanation Cd4047Sruthi ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Clap SwitchDokumen14 halamanClap SwitchAkilesh ArigelaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Week 03Dokumen54 halamanLecture Week 03عبدالله قيس محمود الحيدريBelum ada peringkat
- IC 555 ProjectsDokumen14 halamanIC 555 ProjectsParth Lad100% (1)
- Chapter-1 Objective: 1.1 Objective of The ProjectDokumen23 halamanChapter-1 Objective: 1.1 Objective of The ProjectPrashanth CooldudeBelum ada peringkat
- ElectronicIII - L3Dokumen14 halamanElectronicIII - L3Aya MazinBelum ada peringkat
- Aim of The Experiment:: 2.tools UsedDokumen28 halamanAim of The Experiment:: 2.tools UsedSagar SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- الكترونيك نموذجيDokumen10 halamanالكترونيك نموذجيMohammed KasimBelum ada peringkat
- EC2205 QBDokumen31 halamanEC2205 QBRaji SharmiBelum ada peringkat
- 555 Timer IC: The Important Features of The 555 Timer AreDokumen5 halaman555 Timer IC: The Important Features of The 555 Timer AreChara GalaBelum ada peringkat
- Buck ConverterDokumen13 halamanBuck ConverterDinesh MahtoBelum ada peringkat
- Gate Triggering CircuitDokumen82 halamanGate Triggering Circuitvraj loginpurposeBelum ada peringkat
- MultivibratorsDokumen6 halamanMultivibratorsWaseem AkramBelum ada peringkat
- Mini Project Report (CLAP SWITCH)Dokumen22 halamanMini Project Report (CLAP SWITCH)Om Prakash Singh100% (4)
- Aim - Theory - : Multivibrator Has Automatic Built in Triggering Which Switches It Continuously Between ItsDokumen6 halamanAim - Theory - : Multivibrator Has Automatic Built in Triggering Which Switches It Continuously Between ItsShahrukh PinjariBelum ada peringkat
- The Transistor Astable Multi VibratorDokumen6 halamanThe Transistor Astable Multi VibratorTavleen KaurBelum ada peringkat
- Ic Applications Lab NewDokumen12 halamanIc Applications Lab NewSandy RonaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Lab.5 Power ElectronicsDokumen7 halamanLab.5 Power Electronicsbaig79Belum ada peringkat
- Chap - 4 - DC Regulated Power SupplyDokumen65 halamanChap - 4 - DC Regulated Power SupplyanshikahjjpBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Instrumentation: Experiment 6 - Digital SwitchingDokumen38 halamanElectronic Instrumentation: Experiment 6 - Digital SwitchingEng-Mohammed KayedBelum ada peringkat
- Current Sensor Ic 4017Dokumen55 halamanCurrent Sensor Ic 4017Alan RejiBelum ada peringkat
- Power Diode - Lecture 2Dokumen29 halamanPower Diode - Lecture 2Akpata SamuelBelum ada peringkat
- 12V DC To 220V AC Converter CircuitDokumen3 halaman12V DC To 220V AC Converter CircuitNawaz Shariff75% (4)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Dari EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Belum ada peringkat
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Dari EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Penilaian: 2.5 dari 5 bintang2.5/5 (3)
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Dari EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Introduction To R: Shanti.S.Chauhan, PH.D Business Studies ShuatsDokumen53 halamanIntroduction To R: Shanti.S.Chauhan, PH.D Business Studies ShuatsShanti Swaroop ChauhanBelum ada peringkat
- Sikafloor Morritex Self-Levelling Broadcast SystemDokumen4 halamanSikafloor Morritex Self-Levelling Broadcast SystemTPBelum ada peringkat
- Tramlink Low-Floor Light Rail Vehicle: Rostocker Strassenbahn Ag, Rostock, GermanyDokumen2 halamanTramlink Low-Floor Light Rail Vehicle: Rostocker Strassenbahn Ag, Rostock, GermanyLuca Marius CristianBelum ada peringkat
- What Are The Good Research QuestionDokumen26 halamanWhat Are The Good Research Questionkavindukarunarathna100% (2)
- E3D2 1version-1Dokumen12 halamanE3D2 1version-1Nikolay NachevBelum ada peringkat
- Juniper Practice QuestionsDokumen32 halamanJuniper Practice QuestionsDasaradhiNidamarthyBelum ada peringkat
- GH13 Heavy Duty Body Installation Manual PDFDokumen132 halamanGH13 Heavy Duty Body Installation Manual PDFPrashant Sharma100% (14)
- 7-2-c Form - Gen Consultant PQ Summary Rev-0Dokumen4 halaman7-2-c Form - Gen Consultant PQ Summary Rev-0Tori SmallBelum ada peringkat
- 888 Gallant Security Services Corp NewDokumen12 halaman888 Gallant Security Services Corp Newnareyes11Belum ada peringkat
- Agroforestry: A Sustainable Land-Use System For Food and WoodDokumen72 halamanAgroforestry: A Sustainable Land-Use System For Food and WoodAlok PatraBelum ada peringkat
- Acquisition (Pagtamo) Meaning-Making (Pag-Unawa) Transfer (Paglilipat)Dokumen2 halamanAcquisition (Pagtamo) Meaning-Making (Pag-Unawa) Transfer (Paglilipat)MAY BEVERLY MORALES100% (8)
- SMDokumen36 halamanSMharan2000Belum ada peringkat
- Switch v7LAB StudentDokumen206 halamanSwitch v7LAB Studentkcf4scribdBelum ada peringkat
- Adopter CategoriesDokumen6 halamanAdopter CategoriesCaroline Mputhia100% (1)
- TDS 9-11SA Mechanical TroubleshootingDokumen34 halamanTDS 9-11SA Mechanical Troubleshootingahmed.kareem.khanjerBelum ada peringkat
- Experience The Latest & Safest in Building Circuit ProtectionDokumen28 halamanExperience The Latest & Safest in Building Circuit ProtectionYashwanth KrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- Weatherford Artificial Lifts Reciprocating Rod Lift OverviewDokumen7 halamanWeatherford Artificial Lifts Reciprocating Rod Lift OverviewKentodalBelum ada peringkat
- Lab - 17-WAN ConfigurationDokumen12 halamanLab - 17-WAN ConfigurationMuhammad Asghar Khan100% (1)
- Gen Target-2017Dokumen22 halamanGen Target-2017SundeepBelum ada peringkat
- Dutypoint BrochureDokumen24 halamanDutypoint Brochuremh wBelum ada peringkat
- Trial and Error: Failure and Innovation in Criminal Justice ReformDokumen5 halamanTrial and Error: Failure and Innovation in Criminal Justice ReformAzim MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Detail 02 Eave Gutter With Protruding Roof Detail 01-A Ridge Detail Saddle RoofDokumen1 halamanDetail 02 Eave Gutter With Protruding Roof Detail 01-A Ridge Detail Saddle Roofmin miniBelum ada peringkat
- SAP BW Basic Configuration SettingsDokumen29 halamanSAP BW Basic Configuration SettingsSIKANDARBelum ada peringkat
- Hitman Contracts PC ManualDokumen14 halamanHitman Contracts PC ManualChernoll MendoncaBelum ada peringkat
- 6400t Rev-BDokumen4 halaman6400t Rev-BGloria HamiltonBelum ada peringkat
- Product Presentation PPT NeerajDokumen8 halamanProduct Presentation PPT NeerajNeeraj UdiniyaBelum ada peringkat
- The Relevance of YS/UTS RatioDokumen21 halamanThe Relevance of YS/UTS RatiocarrespmBelum ada peringkat
- Final Project Miguel Santana GallegoDokumen44 halamanFinal Project Miguel Santana GallegoDaniel PereiraBelum ada peringkat
- NORMA TORRO Datasheet en PDFDokumen11 halamanNORMA TORRO Datasheet en PDFvikaslashkariBelum ada peringkat
- AOO Personal Information FDokumen8 halamanAOO Personal Information FOdhiambo OwinoBelum ada peringkat