10 1 1 876 4751 PDF
Diunggah oleh
rockineverJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
10 1 1 876 4751 PDF
Diunggah oleh
rockineverHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Volume 3, No.
10, October 2012
Journal of Global Research in Computer Science
REVIEW ARTICLE
Available Online at www.jgrcs.info
IMPLEMENTATION OF ESSBASE APPLICATION USING ORACLE HYPERION
Varsha Bishnoi
Department of CSE & IT
Mewar University
Chittorgarh (Raj.)
varshabishnoi@yahoo.co.in
Abstract: Essbase is multidimensional database software that is optimized for planning, analysis, and management-reporting applications.
Essbase uniquely blends an innovative technical design with an open, client-server architecture. The product enables you to extend decision
support systems beyond ad hoc queries and reports on historical performance to dynamic, operational systems that combine historical
analysis and future planning .
Oracle Hyperion Essbase is the industry-leading multi-dimensional online analytical processing server, providing a rich environment for
effectively developing custom analytic and enterprise performance management applications. By leveraging its self-managed, rapid application
development capabilities, business users can quickly model complex business scenarios. In this paper we see how Oracle Hyperion Essbase
supports extremely fast query response times for vast numbers of users, large data sets, and complex business models.
Keywords: Oracle Hyperion Essbase; Multidimensional database
a familiar environment such as Microsoft Excel. Essbase can
INTRODUCTION accept data input from end users which makes it a very capable
Multidimensional Database : Multidimensional database budgeting tool in addition to its analytic capabilities. Essbase
Supprots multiple view of data sets. In multidimensional data also contains a very powerful calculation engine and is often
base data is stored in cubes not in the form of tables. In multi - used to create Profitability Costing models or other types of
dimensional database data can be analyzed from different pre analytic models that require allocations or more advanced
- spective. A multidimensional database (MDB) is a type of calculations
database that is optimized for data warehouse and online ana
lytical processing (OLAP) applications. DATA WAREHOUSE
A multidimensional database - or a multidimensional database This definition of the data warehouse focuses on data storage.
management system (MDDBMS)-implie the ability to rapidly The main source of the data is cleaned, transformed
process the data in the database so that answers can be generat catalogued,and made available for use by managers and other
- ted quickly. A number of vendors provide products that use business professionals for data mining, online analytical
multidimensional databases. Approaches to how data is stored processing, market research and decision support (Marakas &
and the user interface vary. O’Brien 2009). However, the means to retrieve and analyze
Oracle’s Hyperion Essbase allows users to model, analyze, data, to extract, transform and load data, and to manage the
and interpret the most complex business scenarios. Essbase is data dictionary are also considered essential components of a
an object oriented database that provides users with data warehousing system. Many references to data
multidimensional analysis capabilities. Essbase Databases are warehousing use this broader context. Thus, an expanded
often called “Cubes” and are defined by dimensions, which definition for data warehousing includes business intelligence
themselves are hierarchical groups of members Data is tools, tools to extract, transform and load data into the
organized into cross sectional groups that can be accessed by repository, and tools to manage and retrieve metadata.
users depending on what sections of the hierarchal dimensions
they wish to see. The Dimensions are hierarchical WHAT IS HYPERION?
representations of descriptors that business users are familiar Hyperion is a Business Intelligence (BI) and Business
with, such as a Product Hierarchy. By simply choosing any Performance Management (BPM) Tool. It’s the market leader
point in the various dimension hierarchies users are instantly in Financial, Operational and Strategic Planning. It has
presented with the data values. Users can drill up or down, or applications for Planning, Financial consolidation, and score
users can pivot different dimensions to form new cross carding, reporting, dashboards, Analysis, Workspace, Master
sections and better analyze the information. Essbase is Data Management and Foundation. Hyperion can deliver this
optimized to support On-Line Analytical Processing sort of breakthrough performance management because we
(OLAP) as opposed to the more traditional transaction offer the most comprehensive set of features, functionality and
processing (OLTP) found in relational databases. This flexibility in one system.
enables rapid response times for large volumes of users and
large volumes of information. 1. Modules of Hyperion
• Hyperion Essbase.
Essbase gets its name from Extended Spreadsheet Database Essbase is mdbms that provide multidimensional
and is commonly accessed via a spreadsheet add-in that database platform.
provides users the capability to analyze information within • Shared services
© JGRCS 2010, All Rights Reserved 52
Varsha Bishnoi, Journal of Global Research in Computer Science, 3 (10), October 2012,52-57
All the other components that are installed need to be ADMINISTRATION SERVICES ARCHITECTURE
registered with shared services .Shared Services Administration Services works with Essbase Servers in a
integrates the products to provide these three-tiered system that consists of a client user interface (UI),
functionalities: a middle-tier server, and one or more Essbase Servers. The
User provisioning. middle tier coordinates interactions and resources between the
External authentication definition. UI and Essbase Servers. The three tiers may or may not be on
Task flow management the same computer or platform. The three tiers include the
Essbase Administrative Service following components, as illustrated below:
Essbase Server
Essbase Client
INTRODUCING ESSBASE
Essbase products provide companies with the ability to
deliver critical business information to the right people when
they need it. With Essbase, companies quickly leverage and
integrate data from multiple existing data sources and
distribute filtered information to end-user communities in the
format that best meets the users’ needs. Users interact and
intuitively explore data in realtime and along familiar business
dimensions, enabling them to perform speed-of-thought
analytics. Figure: 2 Administration Services Architecture
Key Features: • Client tier (Administration Services Console): A
Essbase products provide the analytic solution that Java-based client console provides a UI to manage
integrates data from multiple sources and meets the the Essbase environment.
needs of users across an enterprise. Essbase products • Middle tier (Essbase Administration Server): A
enable the quick and easy implementation of Java-based server maintains communication,
solutions, add value to previously inaccessible data, session, and security information for connections to
and transform data into actionable information. Essbase Servers.
Essbase is a powerful multidimensional database and
• Database tier (Essbase Server): One or more
calculation engine designed to support modeling,
Essbase Servers store and process
planning, simulations, forecasting and allocations.
multidimensional database information. Essbase
It provides an integrated environment for rapidly
Servers are installed separately from
developing custom analytical and Enterprise
Administration Services.
Performance Management applications.
Essbase product Components: Essbase products incorporate PROCESS OF DESIGNING A DATABASE
powerful architectural features to handle a wide range of
analytic applications across large multi-user environments.
Figure 1 provides a high-level view of the information flow
between the source data and the product components.
Figure 3 :The Database Design Cycle
As illustrated in Figure3, designing an application is a cyclic
process that moves from a planning stage to a verification
stage.
Analyze business needs and plan:
Figure: 1 High-level Information Flow Between Product
Components Where does each department currently store data?
Is data in a form that Essbase can use?
© JGRCS 2010, All Rights Reserved 53
Varsha Bishnoi, Journal of Global Research in Computer Science, 3 (10), October 2012,52-57
Who updates the database and how frequently?
Does the data support the desired analysis and reporting
goals?
Do those who need to update data have access to it?
Creating Database outline
Most businesses analyse the following areas:
Time periods
Accounting measures
Distribution channels
Geographical regions
Business units Figure 4. Multiple Views from a Five-Dimensional
If you need to analyze a business area by classification or Database
attribute, such as by the size or color of products, you can use
A Hyperion Essbase application contains an unlimited number
attribute dimensions to represent the classification views.
of dimensions, so you can analyze large amounts of data from
multiple viewpoints.
Checking System Requirements
Now you are ready to determine the system requirements for
the database. DATABASE OUTLINES
Ensure that you have enough disk space.
Understanding the database outline is the key to understanding
Ensure that you have enough memory.
Hyperion Essbase. To define a multidimensional database, you
Ensure that your caches are set correctly.
design its database outline. The database outline contains the
database organization (structure), the database members, and
Loading Test Data the database rules, as shown in 5:
Before you can test Essbase - Calculations, consolidations,
and reports, you need data in the database. During the design
process, loading mocked-up data or a subset of real data
provides flexibility and shortens the time required to test and
analyze results.
Defining Calculations
Use the following checklist when you define a Essbase -
Calculations:
Does the default calculation logic achieve accurate results?
Which members require Essbase - Formulas?
Which members require Essbase - Two-Pass Calculations ?
Which members can be tagged as Dynamic cal ?
Defining Reports
To ensure that the design meets user information
requirements, you must view data as users view it. Users
typically view data through spreadsheets, printed reports, or
reports published on the Web.
Verifying the Design
Ensure that the database satisfies all of their goals
Do the calculations provide the information they need?
Are they able to generate reports quickly?
Are they satisfied with consolidation times?
DEFINITION OF MULTIDIMENSIONAL
A dimension is a perspective or view of a specific dataset. A
different view of the same data is an alternate dimension. A
ystem that supports simultaneous, alternate views of datasets
is multidimensional. Dimensions are typically categories such
as time, accounts, product lines, markets, budgets, and so on
(see figure 3 ). Each dimension contains additional categories Figure5 : ESSBASE DATABASE OUTLINE
that have various relationships one to another. In contrast to
the multidimensional view, worksheets stores data in two The components of the database outline are the following:
dimensions, usually time and accounts, as shown in figure 4:
• Dimensions
• Members
© JGRCS 2010, All Rights Reserved 54
Varsha Bishnoi, Journal of Global Research in Computer Science, 3 (10), October 2012,52-57
• Attributes Each database member can be associated with one or more
formulas in the database outline.
• Formulas
• Aliases Aliases
Essbase supports alternative names, or aliases, for database
• Consolidations
members. Aliases are useful when various labels are used for
Refer to the following sections for descriptions of the outline the same member in various worksheets. Aliases also can be
components. used for reporting in alternative languages or for more formal
output name sets, such as account numbers.
Dimensions
Dimensions are the most basic categorical definitions of data Consolidations
within the database outline. You need at least two dimensions Consolidations in Essbase applications are defined by member
to make any meaningful reference to data; for example, a time branches. The database outline determines consolidation paths.
dimension and an accounts dimension. Other dimensions may The determination is based on the location of members within
categorize products, markets, and scenarios. Using a
dimensional organization, you can define any consolidation dimension. Indentation of one member below another
structure or any slice of data that is relevant to the application. indicates a consolidation relationship.
Hyperion Essbase supports an unlimited number of
dimensions.
RULES FILES
Members
Members are the names of the elements within a dimension. A Rules define operations that Essbase performs on data values
dimension can contain an unlimited number of members. The or on dimensions and members when it processes a data
calculation, reporting, and dimension-building facilities in source. Use rules to map data values to an Essbase database or
Hyperion Essbase use the following terms to describe to map dimensions and members to an Essbase outline Rules
members. are stored in rules files. A rules file defines which build
method to use, whether data values or members are sorted or
• Parents. A parent is a member with a consolidation in random order, and how to transform data values or members
branch below it. For example, in the illustration below, before loading them. It is best to create a separate rules file for
Qtr1 is a parent member because there is a branch each dimension.
containing monthly members below it.
• Children. A child is a member with a parent above it. For
DATA LOADING
example, Jan, Feb, and Mar are children of the parent
Qtr1. Loading data is the process of adding data values to an
• Siblings. A sibling is a child member of the same parent database from a data_source. If the data source is not perfectly
and on the same branch (same level). For example, Jan, formatted, you need a data load rules files to load the data
Feb, and Mar are siblings. Apr is not a sibling of Jan, Feb, values.
or Mar, however, because it has a different parent, Qtr2. To load data values into an Essbase database, follow these
• Descendants. A descendant is a member at any level steps:
below a parent. For example, each member that falls in • Set up the data source.
the Year branch is a descendant of Year. The following • If you are not using a rules file, you must set up the data
members are all descendants of Year: Qtr1, Jan, Feb, source outside Essbase.
Mar; Qtr2, Apr, May, Jun; Qtr3, Jul, Aug, Sep; Qtr4, Oct, • Each record in the data source must have the same number
Nov, Dec. of data value fields to perform a data load. If data values
• Ancestors. An ancestor is a member of a branch above a are missing, the data load processes incorrectly.
member. For example, Qtr2 and Year are ancestors of
Apr. For example, in figure5 the file is invalid, because there is no
• Generations. The term generation describes the branch value under Apr:
number of a member. Generations count from the root of
the tree (generation 1, which is the dimension name)
toward the leaf node.
• Levels. The term level describes the branch number of a
member. Levels count from the leaf node (level 0) toward
the root (the dimension name).
Attributes
Attributes describe characteristics of data, such as the size and
color of products. Through attributes, you can group and
analyze members of dimensions based on their characteristics.
Attribute dimensions must be associated with base
dimensions. To fix the file, insert #MISSING or #MI into the missing field:
Formulas
© JGRCS 2010, All Rights Reserved 55
Varsha Bishnoi, Journal of Global Research in Computer Science, 3 (10), October 2012,52-57
2. Outline Calculation
Outline calculation is the simplest method of calculation.
Essbase bases the calculation of the database on the
relationships between members in the database outline and on
any formulas that are associated with members in the outline.
Member Formulas
Formulas calculate relationships between member in the
database outline.
Figure 6 You can :
• apply formulas to members in the outline,
Set up the data load rule file
We can use data load rule file to load the data and also we can • or place formulas in a calculation script.
use free form loading.
Figure7 shows the Scenario dimension from the Sample Basic
1. Data Load Rules file: database. The Variance and Variance % members are
Data Load Rules file is the rules files which is involved in the calculated by using the formulas attached to them.
data load process. A data source for data load must contain
:not only the values that you want to load but also
identification of the location to which Essbase should load the
values: a data address that includes one member from every
standard dimension in your outline.
2. Free form loading:
If a Essbase - Data Source contains all of the information
required to load the data values in it into the database, you can Figure 7: Calculation of Variance and Variance %
load the data source directly in a free-form data load (without
rule file) .To load a data value successfully, Essbase must It may be more efficient to calculate some member
encounter one member from each dimension before combinations when you retrieve the data, instead of calculating
encountering the data value. For example, in the figure6, the member combinations during the regular database
Essbase loads the data value 42 into the database with the calculation. You can use dynamic calculations to calculate data
members Texas, 100-10, Jan, Sales, and Actual. at retrieval time.
3. Calculation Script
Calculation script calculation is the second method of
calculation. Using a calculation script, you can choose exactly
how to calculate a database. For example, you can calculate
part of a database or copy data values between members.
A calculation script contains a series of calculation commands,
equations, and formulas. For example, the following
Figure 7 calculation script increases the actual marketing expenses in
the New York region by 5%.
FIX (Actual, “New York”)
CALCULATIONS
Marketing = Marketing *1.05;
1. Database Calculation ENDFIX;
A database contains two types of values: CONCLUSION
• Values that you enter, which are called input data Essbase is multidimensional database application tool that lets
• Values that are calculated from input data you continually analyze and compare aspects of your business.
• For example: You enter regional sales figures for a An Essbase database works with multidimensional data and
variety of products. You calculate the total sales for rollup hierarchies within dimensions. Essbase deals with some
each product. level of sumarized data, not transaction. Essbase can be
• You enter the budget and actual values for the cost adapted to many different reporting and analysis
of goods sold for several products in several enviroment.With the help of essbase we can analyze the same
regions. You calculate the variance between budget business information from different perspectives .Essbase
and actual values for each product in each region. allow data storageand analysis to occur at different level of
• The database contains regional sales figures and detail.
prices for all products. You calculate what happens
to total profit if you increase the price of one REFERENCES
product in one region by 5%. 1. OLAP, Relational, and Multidimensional Database Systems
George Colliat Arbor Software Corporation 1325 Chcseapeakc
Terrace, Sunnyvale, CA 94089
© JGRCS 2010, All Rights Reserved 56
Varsha Bishnoi, Journal of Global Research in Computer Science, 3 (10), October 2012,52-57
2. An Overview of Data Warehousing and OLAP Technology 8. http://oracle-bpm.blogspot.com/2010/06/calculation-
Surajit Chaudhuri Umeshwar Dayal Microsoft Research, functions.html
Redmond Hewlett-Packard Labs, Palo Alto 9. http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E12825_01/epm.111/esb_te
3. Introduction to OLAP (A beginner's guide to OLAP & the chref/frameset.htm?launch.htm
concepts behind it) Seagate Info Technical Roadmap Series 10. http://www.scribd.com/doc/29576157/MaxL-Examples
4. Essbase Database Administrator’s Guide, 9.3.1(D_BAG) by 11. http://businessintelligencedw.blogspot.com/2009/01/security-
Oracle filter-essbase-tutorial.html
5. Oracle Essbase 9 Implementation Guide by packt publication. 12. http://www.ucertify.com/article/what-are-the-disadvantages-of-
6. Oracle Essbase Technical Reference online-transaction-processing-oltp.html
7. http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E12825_01/epm.111/esb_te 13. http://gerardnico.com/wiki/epm/essbase/development
chref/frameset.htm?launch.htm
© JGRCS 2010, All Rights Reserved 57
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- SOP Section Rolling Machine #10011234567891123Dokumen3 halamanSOP Section Rolling Machine #10011234567891123saturnelBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- As 2118.6-1995 Automatic Fire Sprinkler Systems Combined Sprinkler and HydrantDokumen7 halamanAs 2118.6-1995 Automatic Fire Sprinkler Systems Combined Sprinkler and HydrantSAI Global - APACBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Machines Principles Applications and Control Schematics 2nd Edition Dino Zorbas Solutions ManualDokumen27 halamanElectric Machines Principles Applications and Control Schematics 2nd Edition Dino Zorbas Solutions Manuallaurenstarkntmkfdjrqz100% (16)
- Sand Box Management: Sandboxes Are Enabled by MDS Reprositroy, Where All The Extenstions Are Stored and ManagedDokumen4 halamanSand Box Management: Sandboxes Are Enabled by MDS Reprositroy, Where All The Extenstions Are Stored and ManagedrockineverBelum ada peringkat
- What Is OID?: Oracle Internet Directory (OID) 11g: Part II - Requirements and ComponentsDokumen3 halamanWhat Is OID?: Oracle Internet Directory (OID) 11g: Part II - Requirements and ComponentsrockineverBelum ada peringkat
- Huawei GSM Network Energy Saving Solution (For Technical)Dokumen17 halamanHuawei GSM Network Energy Saving Solution (For Technical)c2poyraz100% (2)
- Introduction To Vault CoreDokumen25 halamanIntroduction To Vault CoreUni QloBelum ada peringkat
- Fabric Data WarehouseDokumen280 halamanFabric Data WarehouseOmarBelum ada peringkat
- CHL v4 - U1 Task 1 The Current State of The Supply Chain (CT8) - AnswersDokumen2 halamanCHL v4 - U1 Task 1 The Current State of The Supply Chain (CT8) - AnswersSara Khalil50% (2)
- QualityThought Azure SnowFlake - Data Engineer 2022Dokumen6 halamanQualityThought Azure SnowFlake - Data Engineer 2022rockineverBelum ada peringkat
- QualityThought Tableau 2022-1Dokumen4 halamanQualityThought Tableau 2022-1rockineverBelum ada peringkat
- Filter - This Is A Python Inbuilt Library That Returns Only ThoseDokumen4 halamanFilter - This Is A Python Inbuilt Library That Returns Only ThoserockineverBelum ada peringkat
- QualityThought Sales-Force 2022Dokumen6 halamanQualityThought Sales-Force 2022rockineverBelum ada peringkat
- Lamda 1Dokumen1 halamanLamda 1rockineverBelum ada peringkat
- Lamda 2Dokumen1 halamanLamda 2rockineverBelum ada peringkat
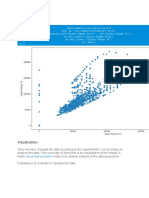
- Scatterplot: VisualizationDokumen6 halamanScatterplot: VisualizationrockineverBelum ada peringkat
- H1B Checklist 2022Dokumen2 halamanH1B Checklist 2022rockineverBelum ada peringkat
- CPAT Blocker QueriesDokumen5 halamanCPAT Blocker QueriesrockineverBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Anaconda: Data Science Machine Learning Deep LearningDokumen6 halamanIntroduction To Anaconda: Data Science Machine Learning Deep LearningrockineverBelum ada peringkat
- Oracle Epm at Oracle 1515594Dokumen21 halamanOracle Epm at Oracle 1515594rockineverBelum ada peringkat
- Python Anaconda Tutorial: Everything You Need To KnowDokumen13 halamanPython Anaconda Tutorial: Everything You Need To KnowrockineverBelum ada peringkat
- Oracle Weblogic Server 11G Standard Edition: Key Features and BenefitsDokumen4 halamanOracle Weblogic Server 11G Standard Edition: Key Features and BenefitsrockineverBelum ada peringkat
- Part 1 - Oracle SOA Interview Questions (Basic) : Q1. What Is SOA and Explain Its Architectural Benefits?Dokumen6 halamanPart 1 - Oracle SOA Interview Questions (Basic) : Q1. What Is SOA and Explain Its Architectural Benefits?rockineverBelum ada peringkat
- Essex CelDokumen278 halamanEssex CelrockineverBelum ada peringkat
- CERTIFIED/LICENSED SNORKEL GUIDES BY National Institute of Water Sports (NIWS), Goa List of Port Blair / Rangat / Baratang / Diglipur / Neil IslandDokumen3 halamanCERTIFIED/LICENSED SNORKEL GUIDES BY National Institute of Water Sports (NIWS), Goa List of Port Blair / Rangat / Baratang / Diglipur / Neil IslandrockineverBelum ada peringkat
- DRM HTTP Load BalancingDokumen1 halamanDRM HTTP Load BalancingrockineverBelum ada peringkat
- Expanded Functionality: Provides Master Data Management For Charts ofDokumen1 halamanExpanded Functionality: Provides Master Data Management For Charts ofrockineverBelum ada peringkat
- Locala 11B SubiectDokumen5 halamanLocala 11B SubiectAndrei SainciucBelum ada peringkat
- EU Type Examination Certificate No. DK0199.629Dokumen12 halamanEU Type Examination Certificate No. DK0199.629Ovidiu SmadiciBelum ada peringkat
- T2265 PDFDokumen0 halamanT2265 PDFMerlin PokamBelum ada peringkat
- Pa2X Loading OS and Resources PDFDokumen16 halamanPa2X Loading OS and Resources PDFAnonymous teB7D6jBelum ada peringkat
- IntroSoC Lab04Dokumen10 halamanIntroSoC Lab04Ngữ Đào DuyBelum ada peringkat
- Generic PapersizesDokumen3 halamanGeneric PapersizesConarch StudioBelum ada peringkat
- Anushree Vinu: Education Technical SkillsDokumen1 halamanAnushree Vinu: Education Technical SkillsAnushree VinuBelum ada peringkat
- Javascript NotesDokumen55 halamanJavascript NotesJony nathBelum ada peringkat
- Matlab/Simulink Modeling of Sic Power Mosfets: Paolo Giammatteo, Concettina Buccella, Carlo CecatiDokumen10 halamanMatlab/Simulink Modeling of Sic Power Mosfets: Paolo Giammatteo, Concettina Buccella, Carlo CecatiDaniel Labiano AnduezaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 - CPU Structure and Function Ver 1Dokumen43 halamanChapter 7 - CPU Structure and Function Ver 1Nurhidayatul FadhilahBelum ada peringkat
- PCM 1867Dokumen141 halamanPCM 1867pepeluis666Belum ada peringkat
- Poster Vourch Et Al IEEE Sensors 2013dDokumen1 halamanPoster Vourch Et Al IEEE Sensors 2013dMarcelo BaptistaBelum ada peringkat
- LB2-UCxx-x Premium-Sound Cabinet Loudspeaker Range Data Sheet EnUSDokumen6 halamanLB2-UCxx-x Premium-Sound Cabinet Loudspeaker Range Data Sheet EnUSvtcuongBelum ada peringkat
- An565 Rev. 7Dokumen4 halamanAn565 Rev. 7David WongBelum ada peringkat
- FHL104C User's ManualDokumen49 halamanFHL104C User's ManualChu Minh ThắngBelum ada peringkat
- Max 15.0V at 12V Max 31.5V at 24V Max 61.0V at 48V: Main FeaturesDokumen1 halamanMax 15.0V at 12V Max 31.5V at 24V Max 61.0V at 48V: Main FeaturesJoebany SaboteBelum ada peringkat
- EHT Maintenance & Troubleshooting Guide PDFDokumen7 halamanEHT Maintenance & Troubleshooting Guide PDFasdasdasdasdasdasdasdBelum ada peringkat
- Pengenalan Dan Pemanfaatan Marketplace E-Commerce Untuk Pelaku Ukm Wilayah CilegonDokumen8 halamanPengenalan Dan Pemanfaatan Marketplace E-Commerce Untuk Pelaku Ukm Wilayah CilegonPemetaanPendidikanBelum ada peringkat
- CS544 - Cloud Application DevelopmentDokumen3 halamanCS544 - Cloud Application DevelopmentMayur PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Application Note - Solaredge Inverter Support of Voltage SourcesDokumen6 halamanApplication Note - Solaredge Inverter Support of Voltage Sourcesanhthong3kBelum ada peringkat
- Manish SeminarDokumen13 halamanManish SeminarIshu RajBelum ada peringkat
- Analyzing Art Culture and Design in TheDokumen23 halamanAnalyzing Art Culture and Design in TheLívia NonatoBelum ada peringkat