Elastic Stability of Plates (Plate Buckling Analysis
Diunggah oleh
ruhul72Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Elastic Stability of Plates (Plate Buckling Analysis
Diunggah oleh
ruhul72Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
WORKSHOP 5
Elastic Stability of Plates
(Plate Buckling Analysis)
100 psi 100 psi
8 in
20 in
Objectives:
■ Create a geometric representation of a plate.
■ Apply a compression load to two opposite sides of the
plate.
■ Run a buckling analysis of the plate.
MSC.Nastran for Windows 105 Exercise Workbook 5-1
5-2 MSC.Nastran for Windows 105 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 5 Elastic Stability of Plates
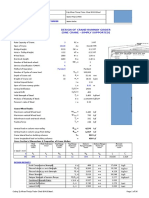
Model Description:
Below is a finite element representation of a rectangular plate under
equal, uniform compression on two opposite edges. Assume that all
edges are simply supported.
Figure 5.1 - Load Conditions
100psi 100 psi
8 in
20 in
Table 5.1 - Material Properties
Youngs Modulus: 29E+06 psi
Poisson’s Ratio 0.3
Plate Thickness: 0.01 in
MSC.Nastran for Windows 105 Exercise Workbook 5-3
Exercise Procedure:
1. Start up MSC.Nastran for Windows V4.0 and begin to create a new
model.
Double click on the icon labeled MSC.Nastran for Windows V4.0.
On the Open Model File form, select New Model.
Open Model File: New Model
2. Create a material called mat_1.
From the pulldown menu, select Model/Material.
Model/Material...
Title: mat_1
Youngs Modulus: 29E6
Poisson’s Ratio: 0.3
OK
Cancel
3. Create a property called prop_1 to apply to the members of the plate
itself.
From the pulldown menu, select Model/Property.
Model/Property...
Title: prop_1
To select the material, click on the list icon next to the databox and
select mat_1.
Material: 1..mat_1
Thickness, Tavg or T1: 0.01
OK
Cancel
4. Create the MSC.Nastran geometry for the plate.
5-4 MSC.Nastran for Windows 105 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 5 Elastic Stability of Plates
Make the geometry in standard form.
Tools/Advanced Geometry...
Geometry Engine: ● Standard
OK
Geometry/Surface/Corners...
X: Y: Z:
Corner 1 0 0 0
OK
Repeat this process for the other 3 corners.
X: Y: Z:
20 0 0 OK
20 8 0 OK
0 8 0 OK
Cancel
To fit the display onto the screen, use the Autoscale feature.
View/Autoscale (Ctrl-A)
5. Place mesh seeds on the newly created surface.
Mesh/Mesh Control/Mapped Divisions on Surface...
Select All
OK
s t
Number of Elements: 10 4
MSC.Nastran for Windows 105 Exercise Workbook 5-5
Bias: 1. 1. OK
Cancel
6. Create the appropriate elements on the surface of the plate.
Mesh/Geometry/Surface...
Select All
OK
Property: 1..prop_1
OK
Turn off the workplane.
Tools/Workplane... (F2)
Draw Workplane
Done
View/Regenerate... (Ctrl-G)
7. Create the constraints for the model.
Before creating the appropriate constraints, a constraint set needs to
be created. Do so by performing the following:
Model/Constraint/Set...
Title: constraint_1
OK
Now define the relevant constraint for the model.
Model/Constraint/Nodal...
Select all 5 nodes on the left edge.
HINT: Use
Method ^
On Curve
5-6 MSC.Nastran for Windows 105 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 5 Elastic Stability of Plates
to easily select the nodes on the left edge.
OK
On the DOF box, select all translations.
TX TY TZ
OK
Now select all 5 nodes on the right edge.
OK
On the DOF box, select the following translations.
TY TZ
OK
Finally, select the nodes on the top and bottom edges without
selecting the corner nodes.
OK
On the DOF box, select the following translation.
TZ
OK
Cancel
8. Create the appropriate model loading.
Like the constraints, a load set must first be created before creating
the appropriate model loading.
Model/Load/Set...
Title: load_1
OK
MSC.Nastran for Windows 105 Exercise Workbook 5-7
Next, convert the edge pressure of 100 psi to appropriate nodal force.
Total edge force will be (100 psi) x (0.01 in) x (8 in) = 8 lb. Thus, 2
lb each will be used for the 3 middle nodes and 1 lb each will be used
for the 2 corner nodes.
Model/Load/Nodal...
Select the middle 3 nodes of right edge
OK
Highlight Force.
Force
FX -2
OK
Now select the top and bottom nodes of right edge
OK
Highlight Force.
Force
FX -1
OK
Cancel
This will put a total of 8 lb along the right edge.
9. Create the input file and run the analysis.
File/Export/Analysis Model...
Analysis Format/Type: 7..Buckling
OK
Change the directory to C:\temp.
File Name: plbuck
Write
5-8 MSC.Nastran for Windows 105 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 5 Elastic Stability of Plates
Additional Info: Run Analysis
Advanced...
Modal Solution Method: ● Lanczos
Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors/
Number Desired: 1
OK
Problem ID: Plate Buckling
Sample Problem
OK
OK
OK
When asked if you wish to save the model, respond Yes.
Yes
File Name: plbuck
Save
When the MSC.Nastran manager is through running, MSC.Nastran
will be restored on your screen, and the Message Review form will
appear. To read the messages, you could select Show Details. Since
the analysis ran successfully, we will not bother with the details this
time.
Continue
10. Look at the results to find the first eigenvalue.
Answer the following question:
What is the first eigenvalue?
Eigenvalue 1 = _______
Since the applied pressure = 8/(8)(.01) = 100 psi,
MSC.Nastran for Windows 105 Exercise Workbook 5-9
scr = 1.722(100)
= 172.2 psi
11. Theory.
From: Formulas for Stress & Strain, Roark & Young, McGraw-Hill
E - --t- 2
σ cr = K --------------
2 b
1–υ
Here K depends on ratio a/b.
When a/b = 20/8 = 2.5, K = 3.373
Thus,
29e6 .01 2
σ cr = 3.373 --------------------- -------
1 – ( .3 ) 2 8
= 167.96 psi
This concludes the exercise.
1.722 Eigenvalue 1
5-10 MSC.Nastran for Windows 105 Exercise Workbook
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Understanding ANSYS Workbench Via Eccentric ColumnDokumen5 halamanUnderstanding ANSYS Workbench Via Eccentric ColumnKelvin ChungyBelum ada peringkat
- Bar - ACI 318-08 - Metric - SalamaDokumen6 halamanBar - ACI 318-08 - Metric - SalamaMourad BenaissaBelum ada peringkat
- The Next Generation of Codes For Seismic Isolation in The United States and Regulatory Barriers To Seismic Isolation DevelopmentDokumen12 halamanThe Next Generation of Codes For Seismic Isolation in The United States and Regulatory Barriers To Seismic Isolation DevelopmentfaisaladeBelum ada peringkat
- Programa Analisis de Armaduras en 2D Con Python - Edwin AlarconDokumen15 halamanPrograma Analisis de Armaduras en 2D Con Python - Edwin AlarconIng Edwin Alarcon MarquezBelum ada peringkat
- Elementos de Sistemas de Prefabricados de PuentesDokumen347 halamanElementos de Sistemas de Prefabricados de PuentesWaldo Enrique Quispe PalominoBelum ada peringkat
- 2005 Ibarra, Medina y Krawinkler PDFDokumen23 halaman2005 Ibarra, Medina y Krawinkler PDFLuis Gibran Urenda JimenezBelum ada peringkat
- 05-Mathcad Wall PilesDokumen17 halaman05-Mathcad Wall PilesIndika Jagath KumaraBelum ada peringkat
- Aws D1.4-98Dokumen54 halamanAws D1.4-98ArikBelum ada peringkat
- GTS Civil Safety RequerimentsDokumen14 halamanGTS Civil Safety RequerimentsMarco Antonio Roa Garces100% (1)
- Bracing of Steel Beams in Bridges - Joseph YuraDokumen96 halamanBracing of Steel Beams in Bridges - Joseph YuraMáryuri CriadoBelum ada peringkat
- Punching Shear Check in Reinforced Concrete SlabsDokumen7 halamanPunching Shear Check in Reinforced Concrete Slabscocococo1100% (1)
- Chapter 3: 2D & 3D Problems: Friday, February 05, 2010 12:22 PMDokumen59 halamanChapter 3: 2D & 3D Problems: Friday, February 05, 2010 12:22 PMroloheBelum ada peringkat
- ACI 318-19 Equivalencias de EcuacionesDokumen9 halamanACI 318-19 Equivalencias de EcuacionesLeonel SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- User-Defined Functions in Smath StudioDokumen21 halamanUser-Defined Functions in Smath StudiobricemikBelum ada peringkat
- Column Beam Fiber SectionDokumen3 halamanColumn Beam Fiber SectionJayanthan MadheswaranBelum ada peringkat
- MVFOSMDokumen5 halamanMVFOSMNabil MuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- Criteria For Ductile Fracture and Their ApplicationsDokumen17 halamanCriteria For Ductile Fracture and Their ApplicationsSaeed GhaffariBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding CUFSM: An Introduction to the SoftwareDokumen14 halamanUnderstanding CUFSM: An Introduction to the Softwarechristos032100% (1)
- Finite Element Methods1 PDFDokumen12 halamanFinite Element Methods1 PDFAnil KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Introducing RS: A New 3D Program For Geotechnical AnalysisDokumen4 halamanIntroducing RS: A New 3D Program For Geotechnical AnalysisAriel BustamanteBelum ada peringkat
- Stability Analysis of Concrete Structures: EM 1110-2-2100 1 December 2005Dokumen20 halamanStability Analysis of Concrete Structures: EM 1110-2-2100 1 December 2005Edson HuertaBelum ada peringkat
- Compression Theory AISC PDFDokumen99 halamanCompression Theory AISC PDFMJPBelum ada peringkat
- RF Tendon DesignDokumen66 halamanRF Tendon DesignJoaquin Galeano AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- Newmark&Hall Earthquake Spectrum MakingDokumen6 halamanNewmark&Hall Earthquake Spectrum MakingLobsang MatosBelum ada peringkat
- Oregon DOT Pushover Analysis Training MaterialDokumen37 halamanOregon DOT Pushover Analysis Training MaterialHisham MohiuddinBelum ada peringkat
- STI0802 Drucker PragerDokumen4 halamanSTI0802 Drucker Pragertinchofran100% (1)
- Evaluation of Earthquake Damaged Concrete and Masonry BuildingsDokumen270 halamanEvaluation of Earthquake Damaged Concrete and Masonry BuildingsSuhas MangaloreBelum ada peringkat
- Characteristics of Strong-Motion EarthquakesDokumen13 halamanCharacteristics of Strong-Motion EarthquakeselimosyBelum ada peringkat
- Nonlinear Analysis of Concrete StructuresDokumen28 halamanNonlinear Analysis of Concrete StructuresMarko ŠimićBelum ada peringkat
- Fema 357Dokumen107 halamanFema 357Daniel Suares FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Norma Astm A1007Dokumen9 halamanNorma Astm A1007Alfredo RangelBelum ada peringkat
- Designing Reinforced Concrete WallsDokumen8 halamanDesigning Reinforced Concrete WallsAndrea SalcedoBelum ada peringkat
- Simpson Strong Tie Strong Rod Systems 1464426Dokumen68 halamanSimpson Strong Tie Strong Rod Systems 1464426Alexis Carlos Rodriguez SalamancaBelum ada peringkat
- Sudden Collapse of The 27-Story Space Building in Medellin, Colombia, Yamin Et Al 2018Dokumen13 halamanSudden Collapse of The 27-Story Space Building in Medellin, Colombia, Yamin Et Al 2018Tránsito SUDEN SASBelum ada peringkat
- Matlab Sap20Dokumen9 halamanMatlab Sap2083357796Belum ada peringkat
- Diseño de VigasDokumen12 halamanDiseño de VigasRussel CapchaBelum ada peringkat
- Ruaumoko-2D Examples: 1 Earthquake ResponseDokumen30 halamanRuaumoko-2D Examples: 1 Earthquake ResponseCARLOS DANIEL TERAN QUINTEROBelum ada peringkat
- CSI Shell Forces Stresses FormDokumen5 halamanCSI Shell Forces Stresses FormVladimir Sánchez CalderónBelum ada peringkat
- Non Linearity in Structural DynamicsDokumen679 halamanNon Linearity in Structural Dynamicsashkantorabi100% (1)
- SOILPROP, A Program For Estimating Unsaturated Soil Hydraulic Properties and Their Uncertainty From Particle Size Distribution DataDokumen48 halamanSOILPROP, A Program For Estimating Unsaturated Soil Hydraulic Properties and Their Uncertainty From Particle Size Distribution DataScary CreaturesBelum ada peringkat
- Concrete Detailing 1127-3f 289Dokumen1 halamanConcrete Detailing 1127-3f 289bagmassBelum ada peringkat
- 2011-10-05 Section Analysis Program Response 2000Dokumen5 halaman2011-10-05 Section Analysis Program Response 2000adc26Belum ada peringkat
- Descripción Norma RmiDokumen31 halamanDescripción Norma RmiJuan Mauricio Palacios AnzolaBelum ada peringkat
- STKODokumen198 halamanSTKOAwais Kiani0% (1)
- Earthquake Textbook Site GuideDokumen2 halamanEarthquake Textbook Site GuideBobby WskBelum ada peringkat
- Seismic Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Buildings - SozenDokumen41 halamanSeismic Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Buildings - SozentrabajosicBelum ada peringkat
- Concise Beam Demo PDFDokumen33 halamanConcise Beam Demo PDFluciafmBelum ada peringkat
- 05 FiniteElementMethodDokumen83 halaman05 FiniteElementMethodmileBelum ada peringkat
- 721u0201sp Rev 06 - Micromate Operator ManualDokumen152 halaman721u0201sp Rev 06 - Micromate Operator ManualCarla OrdóñezBelum ada peringkat
- Shell Element Internal ForcesDokumen15 halamanShell Element Internal ForcesengsalamBelum ada peringkat
- Use of Shear Lugs For Anchorage To Concrete: January 2009Dokumen9 halamanUse of Shear Lugs For Anchorage To Concrete: January 2009Sandeep BhatiaBelum ada peringkat
- Descargar Reglamento de Construccion Del D F IlustradoDokumen3 halamanDescargar Reglamento de Construccion Del D F IlustradoMisa JCBelum ada peringkat
- M17 - CHOPRA - Dinamica - Systems With Distributed Mass and ElasticityDokumen32 halamanM17 - CHOPRA - Dinamica - Systems With Distributed Mass and ElasticityRocío Alvarez Jiménez100% (1)
- Asic Steel and Wrought Iron Columns)Dokumen145 halamanAsic Steel and Wrought Iron Columns)Bj Cody50% (2)
- 5100 PDFDokumen20 halaman5100 PDFcarangoretrepoBelum ada peringkat
- Elastic Stability of Plates (Plate Buckling Analysis) : WorkshopDokumen10 halamanElastic Stability of Plates (Plate Buckling Analysis) : WorkshopscribdigiBelum ada peringkat
- Exer 03 Radiate EnclosDokumen18 halamanExer 03 Radiate EnclosSaadelnour AdamBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of A Tension Coupon: Workshop 14Dokumen16 halamanAnalysis of A Tension Coupon: Workshop 14CarlosDeLaMataBelum ada peringkat
- Load Deflection of 3-Rod StructureDokumen28 halamanLoad Deflection of 3-Rod StructureMarija ZaharBelum ada peringkat
- Workshop 8 Lateral Buckling: Cross SectionDokumen11 halamanWorkshop 8 Lateral Buckling: Cross SectionSia Ping Chong100% (1)
- Steel Development LengthDokumen9 halamanSteel Development Lengthsheraz1212Belum ada peringkat
- IS Code 13920Dokumen21 halamanIS Code 13920ruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Bitucel Bitumen Impregnated FibreboardDokumen2 halamanBitucel Bitumen Impregnated Fibreboardruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Common Shape CodesDokumen1 halamanCommon Shape CodesIrfanBelum ada peringkat
- UTM Zone Map for the WorldDokumen1 halamanUTM Zone Map for the WorldAgustinus Nugroho KarangBelum ada peringkat
- Dreamland Waterfront Camping-26!10!2010Dokumen6 halamanDreamland Waterfront Camping-26!10!2010ruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- ConcreteDokumen2 halamanConcreteruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Behaviour of High Strength GradeDokumen6 halamanBehaviour of High Strength GradeUğur DündarBelum ada peringkat
- Marshall Stability and Flow Test for Asphalt Concrete Mix DesignDokumen2 halamanMarshall Stability and Flow Test for Asphalt Concrete Mix Designruhul720% (1)
- List of Concrete SourceDokumen1 halamanList of Concrete Sourceruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Julien Boutoille CVDokumen1 halamanJulien Boutoille CVHayat AfridiBelum ada peringkat
- P 1Dokumen1 halamanP 1ruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Subgrade Modulus EffectDokumen13 halamanSubgrade Modulus EffectGie SiegeBelum ada peringkat
- Majestic International ToursDokumen1 halamanMajestic International Toursruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Essential Tips For Independent Contractors and ConsultantsDokumen14 halamanEssential Tips For Independent Contractors and ConsultantsAna Rusu100% (1)
- Finite Element Analysis CapabilitiesDokumen8 halamanFinite Element Analysis Capabilitiesruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Thermal ComfortDokumen6 halamanThermal ComfortHoucem Eddine MechriBelum ada peringkat
- LNGValueOfStd 2005Dokumen14 halamanLNGValueOfStd 2005ruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Estimated Quantity of Reinforcement (Kg/m3) : Building Elements:-Description QuantityDokumen2 halamanEstimated Quantity of Reinforcement (Kg/m3) : Building Elements:-Description Quantityruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Calculation of Effective Length Factor for ColumnsDokumen49 halamanCalculation of Effective Length Factor for Columnsruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Checkered Plates & GratingsDokumen1 halamanCheckered Plates & Gratingsruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Foundation DepthDokumen2 halamanFoundation Depthruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Lifting AnalysisDokumen14 halamanLifting Analysisruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Pod 9232748755Dokumen1 halamanPod 9232748755ruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Torque - Chart For BoltsDokumen2 halamanTorque - Chart For Boltsruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- Design of Equipment FoundationsDokumen28 halamanDesign of Equipment Foundationsapi-379773793% (42)
- Guide To Design Criteria For Bolts and Riveted JointsDokumen352 halamanGuide To Design Criteria For Bolts and Riveted JointsHomero Silva96% (24)
- Eczema HomeopathyDokumen4 halamanEczema Homeopathyruhul72Belum ada peringkat
- List of BS CodesDokumen33 halamanList of BS Codesnavaneethsparkwest100% (8)
- Unit 8 (SERVICEABILITY LIMIT STATE (SLS) )Dokumen26 halamanUnit 8 (SERVICEABILITY LIMIT STATE (SLS) )Zara Nabilah100% (2)
- Peek Optima Natural Typical Material PropertiesDokumen2 halamanPeek Optima Natural Typical Material PropertiesDrummerationBelum ada peringkat
- Crane Girder Design Sheet - ASD 2005Dokumen36 halamanCrane Girder Design Sheet - ASD 2005Panha Menh100% (3)
- A03 Material PropertiesDokumen31 halamanA03 Material PropertiesNiraj BhaktwartiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter C15 Design Requirements For Structures With Supplemental Energy DissipationDokumen6 halamanChapter C15 Design Requirements For Structures With Supplemental Energy DissipationEDWIN CHAUCA MEJÍABelum ada peringkat
- StrainGage PDFDokumen422 halamanStrainGage PDFEmilio GalindoBelum ada peringkat
- The Development of A New Design Procedure For Conventional Single-Plate Shear ConnectionsDokumen12 halamanThe Development of A New Design Procedure For Conventional Single-Plate Shear ConnectionsMiguelBelum ada peringkat
- ASME VIII-1 Low Temperature Operation Impact Test ExemptionsDokumen10 halamanASME VIII-1 Low Temperature Operation Impact Test Exemptionschuckhsu1248Belum ada peringkat
- PSC 35m - 4 Girders - 14.5m Width - M50 (As Per Shuttering) (Ch-109+700) PDFDokumen315 halamanPSC 35m - 4 Girders - 14.5m Width - M50 (As Per Shuttering) (Ch-109+700) PDFKhirai HelpBelum ada peringkat
- EN 13445-2 +A2 (2012) Unfired Pressure Vessels, Part 2 MaterialsDokumen86 halamanEN 13445-2 +A2 (2012) Unfired Pressure Vessels, Part 2 Materials김창배Belum ada peringkat
- Ethane Pressure Enthalpy Diagram PDFDokumen1 halamanEthane Pressure Enthalpy Diagram PDFNatalia Rosa SimanjuntakBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Plate GirdersDokumen30 halamanDesign of Plate GirdersTHULASI MBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Properties of PolymersDokumen25 halamanMechanical Properties of PolymersPreet Kamal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Materials Properties Uses GuideDokumen16 halamanMaterials Properties Uses GuideMallesh KaruparthyBelum ada peringkat
- MOL-5906 Elastomers: TUT Plastics and Elastomer Technology (Autumn 2008)Dokumen63 halamanMOL-5906 Elastomers: TUT Plastics and Elastomer Technology (Autumn 2008)arfu~Belum ada peringkat
- Uniaxial TestDokumen6 halamanUniaxial Testanil chejaraBelum ada peringkat
- A Review of Self Compacting ConcreteDokumen23 halamanA Review of Self Compacting Concretedhwani100% (1)
- Polymers: Modeling of Flexible Polyurethane Foam Shrinkage For Bra Cup Moulding Process ControlDokumen13 halamanPolymers: Modeling of Flexible Polyurethane Foam Shrinkage For Bra Cup Moulding Process ControlMansi ChaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Properties of Lattice Structured MaterialsDokumen13 halamanMechanical Properties of Lattice Structured MaterialsHadiBelum ada peringkat
- Performance of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete - Comparability of Tests According To Dafstb-Guideline "Stahlfaserbeton" and en 14651Dokumen3 halamanPerformance of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete - Comparability of Tests According To Dafstb-Guideline "Stahlfaserbeton" and en 14651Oscar NietoBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd LawDokumen3 halaman2nd LawTotok PrasetyoBelum ada peringkat
- Engin Analysis of A Diesel Generator Crankshaft FailureDokumen9 halamanEngin Analysis of A Diesel Generator Crankshaft FailureDarel DalmassoBelum ada peringkat
- Shell Stress and ForcesDokumen57 halamanShell Stress and ForcesFiras DiknashBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Channel With Flexible LiningDokumen21 halamanDesign of Channel With Flexible Liningmamay papayBelum ada peringkat
- Calibrating Pressure Dependent and Independent Multi Yield Surface Soil ModelsDokumen49 halamanCalibrating Pressure Dependent and Independent Multi Yield Surface Soil ModelsmohanBelum ada peringkat
- SDSS 2019Dokumen1.373 halamanSDSS 2019Fangxin HU100% (1)
- Viscoelastic ModellingDokumen18 halamanViscoelastic ModellingNimisha VedantiBelum ada peringkat
- Design of reinforced concrete columns: Short column vs long columnDokumen25 halamanDesign of reinforced concrete columns: Short column vs long columndashne134100% (4)
- Introduction to Non-Destructive Testing MethodsDokumen13 halamanIntroduction to Non-Destructive Testing MethodsNurjihan Binti Aimi100% (1)
- Materials Engineering MIDTERM EXAM 1Dokumen13 halamanMaterials Engineering MIDTERM EXAM 1ahber yenaaBelum ada peringkat