Introduction To Telecommunication Systems Theory: Stefanos Papadakis
Diunggah oleh
Yorgos0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
10 tayangan12 halamanDigital signal theroy
Judul Asli
HY330 Lecture 02
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniDigital signal theroy
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
10 tayangan12 halamanIntroduction To Telecommunication Systems Theory: Stefanos Papadakis
Diunggah oleh
YorgosDigital signal theroy
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 12
ΗΥ-330 Introduction to telecommunication
fall semester 2016 systems theory
University of Crete
Computer Science Department Stefanos Papadakis
Modulation
Why?
Time domain - Frequency domain
Analog - Continuous Wave (CW)
Digital…
<HY-330> Introduction to telecommunication systems theory
CSD.UoC Stefanos Papadakis fall 2016
Modulation Example
Ac cos (2⇡fc t)
(
Ac cos (2⇡fc t)
s(t) =
Ac cos (2⇡fc t)
<HY-330> Introduction to telecommunication systems theory
CSD.UoC Stefanos Papadakis fall 2016
Baseband Signal
“Low frequencies” - raw unmodulated signal
Typically:
nowadays up to few MHz
“audio” band 20 - 20000 Hz
Low pass filtered
<HY-330> Introduction to telecommunication systems theory
CSD.UoC Stefanos Papadakis fall 2016
Time vs. Frequency Domain
Analog signals are manipulated in time domain
Filters are used to restrict signals in frequency domain
We may go from one domain to the other using (Inverse) Fourier
Transform
The frequency domain representation reveals the bandwidth requirements
<HY-330> Introduction to telecommunication systems theory
CSD.UoC Stefanos Papadakis fall 2016
Spectrum Availability
<HY-330> Introduction to telecommunication systems theory
CSD.UoC Stefanos Papadakis fall 2016
Carrier
Cosine/Sine signal
fc >> fm c(t) = Ac cos (2⇡fc t)
Incorporates no info
<HY-330> Introduction to telecommunication systems theory
CSD.UoC Stefanos Papadakis fall 2016
Modulating Signal
Consisted by multiple cosines m(t) = M cos (2⇡fm t + )
Should make sure no over-modulation occurs
Follows the information source
<HY-330> Introduction to telecommunication systems theory
CSD.UoC Stefanos Papadakis fall 2016
Amplitude Modulation
M < 1 ) [1 + m(t)] > 0
s(t) = [1 + m(t)] · c(t)
= [1 + M cos (2⇡fm t + )] · Ac cos (2⇡fc t)
M Ac M Ac
s(t) = Ac cos (2⇡fc t) + cos (2⇡(fc + fm )t + ) + cos (2⇡(fc fm )t )
2 2
<HY-330> Introduction to telecommunication systems theory
CSD.UoC Stefanos Papadakis fall 2016
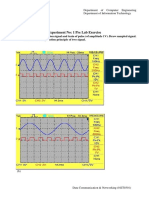
Amplitude Modulation
<HY-330> Introduction to telecommunication systems theory
CSD.UoC Stefanos Papadakis fall 2016
Frequency Modulation
f = kf M
⇣ f ⌘
s(t) = Ac cos 2⇡fc t cos(2⇡fm t)
fm
<HY-330> Introduction to telecommunication systems theory
CSD.UoC Stefanos Papadakis fall 2016
Frequency Modulation
<HY-330> Introduction to telecommunication systems theory
CSD.UoC Stefanos Papadakis fall 2016
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Dive Scubapro - Air2 3rd - Maintenance ProcedureDokumen5 halamanDive Scubapro - Air2 3rd - Maintenance Proceduremanonpom100% (1)
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignDari EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Terrorism and Political Violence PDFDokumen304 halamanUnderstanding Terrorism and Political Violence PDFmihaela buzatuBelum ada peringkat
- Wind Tunnel Technique Notes For Aeronautical Engineers TP 2Dokumen6 halamanWind Tunnel Technique Notes For Aeronautical Engineers TP 2Ramji VeerappanBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Signal and Power IntegrityDokumen100 halamanFundamentals of Signal and Power Integrityalantsd@hotmail.com100% (2)
- Directional: 12 1/4in Sdi519 PDCDokumen1 halamanDirectional: 12 1/4in Sdi519 PDCKhairatul Nada BurhanuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Synchronous Motor AC DrivesDokumen40 halamanSynchronous Motor AC DrivesHarshal Thakur100% (1)
- Sonet/sdh PDFDokumen80 halamanSonet/sdh PDFRyanXuBelum ada peringkat
- World Is Flat Thomas FriedmanDokumen10 halamanWorld Is Flat Thomas FriedmanGilean DalidaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Telecommunication Systems Theory: Stefanos PapadakisDokumen12 halamanIntroduction To Telecommunication Systems Theory: Stefanos PapadakisYorgosBelum ada peringkat
- Gaussian and White Random Processes: y X Xy XX Yy XXDokumen4 halamanGaussian and White Random Processes: y X Xy XX Yy XXArin KudlacekBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 201 2Dokumen59 halamanChapter 201 2Mulugeta AlewaBelum ada peringkat
- Advance Communication System Lectures Part 1Dokumen36 halamanAdvance Communication System Lectures Part 1Shahzad Khalid ChBelum ada peringkat
- S-72.1140 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (5 CR)Dokumen46 halamanS-72.1140 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (5 CR)chinguetas_82600Belum ada peringkat
- Phase-Locked Techniques-A Survey: (Invited Paper)Dokumen7 halamanPhase-Locked Techniques-A Survey: (Invited Paper)KoldodeRostovBelum ada peringkat
- Miniproject Communicationlinksimulation Digitalmodulationtechniqueslecture 100215034826 Phpapp01Dokumen33 halamanMiniproject Communicationlinksimulation Digitalmodulationtechniqueslecture 100215034826 Phpapp01Surya Mundamala0% (2)
- UtyuoiuouiouioDokumen6 halamanUtyuoiuouiouioG Reddy GangadharBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter6 Modulation Techniques For Mobile Radio Imp PDFDokumen57 halamanChapter6 Modulation Techniques For Mobile Radio Imp PDFAnita Shrinivas100% (2)
- 2010 15396Dokumen8 halaman2010 15396Rose MansouriBelum ada peringkat
- A New Algorithm For A High-Modulation Frequency and High-Speed Digital Lock-In AmplifierDokumen7 halamanA New Algorithm For A High-Modulation Frequency and High-Speed Digital Lock-In AmplifierVicBelum ada peringkat
- ESS101-Modeling and Simulation: Paolo FalconeDokumen28 halamanESS101-Modeling and Simulation: Paolo FalconeElvir PecoBelum ada peringkat
- Modulation and Multiplexing: How To Send Data Fast and Far?Dokumen22 halamanModulation and Multiplexing: How To Send Data Fast and Far?Saifuddin Mohammed TarekBelum ada peringkat
- Analog Communication Systems: Amplitude ModulationDokumen36 halamanAnalog Communication Systems: Amplitude ModulationRanz KopaczBelum ada peringkat
- LightDokumen17 halamanLightShridhar MathadBelum ada peringkat
- Techniques of Modulation: Pulse Amplitude Modulation, Pulse Width Modulation, Pulse Position ModulationDokumen9 halamanTechniques of Modulation: Pulse Amplitude Modulation, Pulse Width Modulation, Pulse Position ModulationNeel SarkarBelum ada peringkat
- An Efficient Fast-Fading Channel Estimation and Equalization Method With Self Ici CancellationDokumen4 halamanAn Efficient Fast-Fading Channel Estimation and Equalization Method With Self Ici CancellationSandeep KhandavalliBelum ada peringkat
- Transmission Channels: September 2011 Lectured by Assoc Prof. Thuong Le-TienDokumen27 halamanTransmission Channels: September 2011 Lectured by Assoc Prof. Thuong Le-TienVu Phan NhatBelum ada peringkat
- Document PDFDokumen5 halamanDocument PDFAnusha PenchalaBelum ada peringkat
- Ep 2061162 A1 20090520 (En)Dokumen2 halamanEp 2061162 A1 20090520 (En)SamerFouadZakharyBelum ada peringkat
- S-72.245 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (4 CR)Dokumen28 halamanS-72.245 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (4 CR)Sandra JaramilloBelum ada peringkat
- Transmission Fundamentals: Wireless CommunicationsDokumen54 halamanTransmission Fundamentals: Wireless Communicationschriskorir2447Belum ada peringkat
- Radio FrequeciesDokumen42 halamanRadio FrequeciesRafia ShoukatBelum ada peringkat
- Modulation and Multiplexing: How To Send Data Fast and Far?Dokumen16 halamanModulation and Multiplexing: How To Send Data Fast and Far?Hacralo100% (1)
- Exercise Ofdm Ieee 802 11a PDFDokumen13 halamanExercise Ofdm Ieee 802 11a PDFmhaabBelum ada peringkat
- Fibra 3.4Dokumen43 halamanFibra 3.4francisco llledoBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Loss Due To Atmospheric Noise and Noisy Carrier Reference Signal in QPSK Communication SystemsDokumen5 halamanPerformance Loss Due To Atmospheric Noise and Noisy Carrier Reference Signal in QPSK Communication SystemsBryam kevin Perez VasquezBelum ada peringkat
- 1 What Is OFDM?: X (T) C eDokumen15 halaman1 What Is OFDM?: X (T) C eRajib MukherjeeBelum ada peringkat
- 01 1330682265 93458 PDFDokumen32 halaman01 1330682265 93458 PDFSanjay Kumar SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Communication System DesignDokumen39 halamanCommunication System Designsriblue7Belum ada peringkat
- The Physical LayerDokumen116 halamanThe Physical Layer13521145Belum ada peringkat
- The Basic Principles of OFDMDokumen30 halamanThe Basic Principles of OFDMsureshya22Belum ada peringkat
- Fahad Poc Assignment03Dokumen6 halamanFahad Poc Assignment03FAHAD KHAN NIAZIBelum ada peringkat
- Active Noise Control Systems With The TMS320 Family: January 1998Dokumen10 halamanActive Noise Control Systems With The TMS320 Family: January 1998Vasanth RajaBelum ada peringkat
- Study Material 1Dokumen14 halamanStudy Material 1Ananyo Banerjee 16BEE0148Belum ada peringkat
- Presented at The American Mathematical Society Short Course On Computer Communications, Denver, CO, January 3-4, 1983Dokumen10 halamanPresented at The American Mathematical Society Short Course On Computer Communications, Denver, CO, January 3-4, 1983duncanndegwaBelum ada peringkat
- Name:-Rahul Vora: Enroll No: - 92000103089Dokumen12 halamanName:-Rahul Vora: Enroll No: - 92000103089RAHUL VORABelum ada peringkat
- Elec3505 Exp1 2018-2Dokumen6 halamanElec3505 Exp1 2018-2Sharmaine FernandoBelum ada peringkat
- EE235 - CH 1-2 PDFDokumen35 halamanEE235 - CH 1-2 PDFPhan Phuong NgocBelum ada peringkat
- AFC TrackingDokumen13 halamanAFC TrackingGasser Alaa EldienBelum ada peringkat
- 2MB Mux PDFDokumen114 halaman2MB Mux PDFRohit Sharma100% (1)
- Txu 30Dokumen4 halamanTxu 30Poliana PolyBelum ada peringkat
- Voelcker 1960Dokumen8 halamanVoelcker 1960FAKHRI AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Essence and Advantages of FM-DCSK Versus ConventioDokumen18 halamanEssence and Advantages of FM-DCSK Versus ConventioBasma Nazar AlraweBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Analysis of Error Control Coding and DDokumen8 halamanPerformance Analysis of Error Control Coding and DNegese TeklearegayBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 6Dokumen8 halamanLecture 6ArYanChoudhAryBelum ada peringkat
- Noise Cancellation Using Anc (Active Noise Control) System: Bana Handaga, Fajar SuryawanDokumen8 halamanNoise Cancellation Using Anc (Active Noise Control) System: Bana Handaga, Fajar Suryawanvedant shahBelum ada peringkat
- 02 channels-VP PDFDokumen27 halaman02 channels-VP PDFSilicon DaltonBelum ada peringkat
- Ec8394 Analog and Digital Communication: Handled by Arun Chakravarthy RDokumen27 halamanEc8394 Analog and Digital Communication: Handled by Arun Chakravarthy RSandeep RavikumarBelum ada peringkat
- Fiber Optics ToolkitDokumen20 halamanFiber Optics ToolkitAbdirihmanBelum ada peringkat
- DCSK F Checked 2014 03 12Dokumen7 halamanDCSK F Checked 2014 03 12Leo SimpleBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Digital and Analog Modulation To Undergradute Information Technology Students Using Matlab and SimulinkDokumen7 halamanTeaching Digital and Analog Modulation To Undergradute Information Technology Students Using Matlab and Simulinkmyo htetBelum ada peringkat
- Nasa Seminar Lecture 3Dokumen37 halamanNasa Seminar Lecture 3Nguyen Duc TaiBelum ada peringkat
- Noise in Nanoscale Semiconductor DevicesDari EverandNoise in Nanoscale Semiconductor DevicesTibor GrasserBelum ada peringkat
- Innovations in Telecommunications Part ADari EverandInnovations in Telecommunications Part AJamal ManassahBelum ada peringkat
- The Fourth Terminal: Benefits of Body-Biasing Techniques for FDSOI Circuits and SystemsDari EverandThe Fourth Terminal: Benefits of Body-Biasing Techniques for FDSOI Circuits and SystemsSylvain ClercBelum ada peringkat
- Megger-Mjolner-600 Ds enDokumen5 halamanMegger-Mjolner-600 Ds enAmit Kumar KandiBelum ada peringkat
- 14 ComputoDokumen549 halaman14 ComputoEver Henry FloresBelum ada peringkat
- A Practical Guide To HL7 Interface DevelopmentDokumen5 halamanA Practical Guide To HL7 Interface DevelopmentmjohnstnBelum ada peringkat
- IN804 UV-VIS Nomenclature and UnitsDokumen5 halamanIN804 UV-VIS Nomenclature and UnitsAnurak OnnnoomBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4 - Community Health AssessmentDokumen8 halamanModule 4 - Community Health AssessmentSteffi100% (1)
- Unit B: What Is Customer-Based Brand Equity?Dokumen3 halamanUnit B: What Is Customer-Based Brand Equity?So-Nam Dorji Dr-UKpaBelum ada peringkat
- Pilot Implementation of The Limited Face-to-Face Class Program at Librada Avelino Elementary SchoolDokumen10 halamanPilot Implementation of The Limited Face-to-Face Class Program at Librada Avelino Elementary SchoolCher GeriBelum ada peringkat
- The Man Who Named The CloudsDokumen7 halamanThe Man Who Named The Cloudsapi-302345936Belum ada peringkat
- TGA Interpretation of Data, Sources of ErrorDokumen28 halamanTGA Interpretation of Data, Sources of ErrorUsman GhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Post Covid StrategyDokumen12 halamanPost Covid Strategyadei667062Belum ada peringkat
- 5 Levels of Leadership AnswersDokumen4 halaman5 Levels of Leadership Answersk98hk8wnnbBelum ada peringkat
- EKONET CPRS Importer 26062014Dokumen6 halamanEKONET CPRS Importer 26062014anthony0216Belum ada peringkat
- P16mba7 1Dokumen4 halamanP16mba7 1Vishalatchi MBelum ada peringkat
- Stelma & Cameron PDFDokumen35 halamanStelma & Cameron PDFCatarinaBelum ada peringkat
- Overcoming Obstacles To Ethical BehaviourDokumen4 halamanOvercoming Obstacles To Ethical BehaviourSimran SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Erp Case StudyDokumen19 halamanErp Case StudyMøÑïkå Shàrmå100% (1)
- BSBPMG632 Manage Program RiskDokumen221 halamanBSBPMG632 Manage Program RiskgurpreetBelum ada peringkat
- Intermed Products: International CatalogueDokumen12 halamanIntermed Products: International CatalogueRicardo Bonetti TadenBelum ada peringkat
- FWD Week 47 Learning Material For Alaric YeoDokumen7 halamanFWD Week 47 Learning Material For Alaric YeoarielBelum ada peringkat
- ISMR B-School BrochureDokumen28 halamanISMR B-School Brochurerahul kantBelum ada peringkat
- FOCGB5 Rtest 1-6BDokumen3 halamanFOCGB5 Rtest 1-6BM-DBelum ada peringkat
- BS9266 2013 Adaptable HousingDokumen46 halamanBS9266 2013 Adaptable HousingGrant MastersonBelum ada peringkat
- Fame and FortuneDokumen8 halamanFame and FortuneNguyễn Đình Tuấn ĐạtBelum ada peringkat
- The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDokumen8 halamanThe Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesAragon KhailBelum ada peringkat