Classification of Matter PHYSICAL SCIENCE
Diunggah oleh
Yya Jalynna PenillaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Classification of Matter PHYSICAL SCIENCE
Diunggah oleh
Yya Jalynna PenillaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Rhoyet L.
Sola
Matter
Pure
Mixtures Substance
Heterogeneous Homogenous
Compounds Elements
Mixture Mixture
Colloids Suspension Neutral Bases Non-
Solutions Acids Metals Metalliods
Substance Metals
Classification of Matter
All matter can be classified as either a mixture or a pure substance. Mixtures can be homogeneous or heterogeneous. Pure substances can be either elements or
compounds.
Pure Substances cannot be separated into component parts by physical methods and follow the law of constant composition. The fundamental reason behind
these properties is that pure substances contain only a single type of molecule.
Pure Substances can be divided into two categories:
Elements � Contain only one type of atom. An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into different types of substances. There are
almost 120 known elements , each with its own personality. The chemical and physical properties of one element differ from any other. Elements are
arranged according to their properties in the Periodic Table.
o Example of Elements � Oxygen (O2), Gold (Au), Silicon (Si), Diamond (C)
TYPES OF ELEMENTS
PROPERTIES OF METALS PROPERTIES OF METALLOIDS OR PROPERTIES OF NONMETALS
SEMIMETALS
Most elements are metals. Metals exhibit the Nonmetals exhibit very different properties
following properties: Metalloids have some of the properties of from metals. Nonmetals display some or all of
metals and some nonmetallic characteristic. the following characteristics:
usually solid at room temperature
(mercury is an exception) dull or shiny dull appearance
high luster (shiny) usually conduct heat and electricity, usually brittle
metallic appearance though not as well as metals poor conductors of heat and electricity
good conductors of heat and electricity often make good semiconductors usually less dense, compared to metals
malleable (can be bent and pounded into often exist in several forms usually low melting point of solids,
thin sheets) often ductile compared with metals
ductile (can be drawn into wire) often malleable tend to gain electrons in chemical
corrode or oxidize in air and sea water may gain or lose electrons in reactions reactions
usually dense (exceptions include
lithium, potassium, and sodium)
may have a very high melting point
readily lose electrons
Rhoyet L. Sola
Compounds � Contain more than one type of atom
o Compounds � Water (H2O), Ethanol (C2H6O), Quartz (SiO2)
Acids Bases
the word 'acid' comes from the Neutral substance is a substance that shows feel slippery or soapy
Latin acere, which means 'sour' no acid or base properties, has an equal number bases don't change the color of litmus;
acids are corrosive of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions and does not they can turn red (acidified) litmus back
acids change litmus (a blue vegetable change the colour of litmus-paper. to blue
dye) from blue to red their aqueous (water) solutions conduct
their aqueous (water) solutions conduct and electric current (are electrolytes)
electric current (are electrolytes) react with acids to form salts and water
react with bases to form salts and water
Mixtures have variable composition and can be separated into component parts by physical methods. Mixtures contain more than one type of molecule.
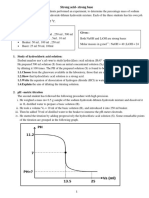
Solutions Colloids Suspensions
Homogeneous Heterogeneous Heterogeneous
Particle size: 0.01-1 nm; atoms, ions, or Particle size: 1-1000 nm, dispersed; large molecules or Particle size: over 1000 nm, suspended; large particles
molecules aggregates or aggregates
Do not separate on standing Do not separate on standing Particles settle out
Cannot be separated by filtration Cannot be separated by filtration Can be separated by filtration
Do not scatter light Scatter light (Tyndall effect) May either scatter light or be opaque
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Lesson 1.2 Writing and Naming of Compounds-Group UploadDokumen60 halamanLesson 1.2 Writing and Naming of Compounds-Group UploadMike MarquisBelum ada peringkat
- NaCN Process Description PDFDokumen9 halamanNaCN Process Description PDFEncepMuhammadIlyasBelum ada peringkat
- Reaksi PA Dan ButanolDokumen5 halamanReaksi PA Dan ButanolUnlucky 2019Belum ada peringkat
- Gen Chem Chapt.1Dokumen45 halamanGen Chem Chapt.1Dave Cercado BugadorBelum ada peringkat
- General Physics 1module1 Week1 CLEAN COPY3Dokumen30 halamanGeneral Physics 1module1 Week1 CLEAN COPY3garryBelum ada peringkat
- GeneralChemistry1 - Quarter1 - Week 1-4Dokumen81 halamanGeneralChemistry1 - Quarter1 - Week 1-4Aze Mamalayan100% (1)
- Module 7 GAS STOICHIOMETRYDokumen4 halamanModule 7 GAS STOICHIOMETRYAnn DayritBelum ada peringkat
- Chem SolutionsDokumen28 halamanChem SolutionsAileen I ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- ELS 2Q Periodical TestDokumen2 halamanELS 2Q Periodical TestJosaphat M. AnteBelum ada peringkat
- STEM - Gen Chem 1 and 2 CG - With Tagged Sci EquipmentDokumen23 halamanSTEM - Gen Chem 1 and 2 CG - With Tagged Sci EquipmentWichel Ann0% (1)
- Physicalproperties of SolutionsDokumen25 halamanPhysicalproperties of SolutionsJan AmoresBelum ada peringkat
- Gen Chem 1 Q1 M 5-6Dokumen12 halamanGen Chem 1 Q1 M 5-6Joselito UbaldoBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry 1 Week 3: Prepared By: Ma'am KimDokumen39 halamanGeneral Chemistry 1 Week 3: Prepared By: Ma'am KimRichelle San AntonioBelum ada peringkat
- Characteristics of LifeDokumen32 halamanCharacteristics of Lifekaren bokierBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry 1 Reviewer Cpe4Dokumen13 halamanGeneral Chemistry 1 Reviewer Cpe4Fiona MarieBelum ada peringkat
- Eals Q1 SLMDokumen24 halamanEals Q1 SLMJanice DagamacBelum ada peringkat
- Gen Chem 1Dokumen16 halamanGen Chem 1Carl Lawrence R. CarpioBelum ada peringkat
- Reviewer in Physical ScienceDokumen5 halamanReviewer in Physical ScienceCalvin Carl D. Delos ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Elsq2 W1&2 - Fabrigas-11abmcharityDokumen4 halamanElsq2 W1&2 - Fabrigas-11abmcharityFabrigasBennetBelum ada peringkat
- Gen. Chem II Week 3 Group 3 QUARTZDokumen36 halamanGen. Chem II Week 3 Group 3 QUARTZAgatha Sigrid GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Cell TheoryDokumen10 halamanCell TheoryLuigi Miguel G. TiranaBelum ada peringkat
- LAP 11 Separating Mixtures GR 6Dokumen3 halamanLAP 11 Separating Mixtures GR 6Hannah Mariel CabañeroBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry 1: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Components of Consumer ProductsDokumen12 halamanGeneral Chemistry 1: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Components of Consumer ProductsHannah PascualBelum ada peringkat
- Gen Chem 1 Q1 M4Dokumen9 halamanGen Chem 1 Q1 M4Joselito UbaldoBelum ada peringkat
- CABAL GenChem1Q1 DescartesDokumen35 halamanCABAL GenChem1Q1 DescartesRhodel CabalBelum ada peringkat
- Physical-Science11 Q1 MODULE-2 08082020Dokumen26 halamanPhysical-Science11 Q1 MODULE-2 08082020Sarah Mae TulodBelum ada peringkat
- Limiting ReagentDokumen6 halamanLimiting ReagentdsaafaBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry 2Dokumen10 halamanGeneral Chemistry 2Aubrey GuilaranBelum ada peringkat
- LoraineDokumen29 halamanLoraineR I R IBelum ada peringkat
- Genchem ModuleDokumen68 halamanGenchem ModuleThessa Vee Capuno RioBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet For Examining Household ProductsDokumen5 halamanWorksheet For Examining Household ProductsMary JuntillaBelum ada peringkat
- What Is AtomDokumen7 halamanWhat Is AtomLawrence Abella PendiBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial QuestionsDokumen3 halamanTutorial QuestionsIbrahim Ali0% (2)
- George Blaire Ras - Week-5-WorksheetDokumen3 halamanGeorge Blaire Ras - Week-5-WorksheetGeorge Blaire RasBelum ada peringkat
- Q4 Week 3 - ELSDokumen7 halamanQ4 Week 3 - ELSAgatha KimBelum ada peringkat
- LC 4Dokumen4 halamanLC 4JT SaguinBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 12 General Biology I Quarter 2 Module 2 For StudentsDokumen12 halamanGrade 12 General Biology I Quarter 2 Module 2 For StudentsStar DustBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Cal Limits 1Dokumen11 halamanBasic Cal Limits 1Lust SINBelum ada peringkat
- Precalculus11 q1 Mod7 Sequencesandseries v6Dokumen21 halamanPrecalculus11 q1 Mod7 Sequencesandseries v6Erlinda CabanlitBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Science Week 2Dokumen18 halamanPhysical Science Week 2BbGrace OrilloBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry Module 4Dokumen15 halamanGeneral Chemistry Module 4Junelle Ramos AquinoBelum ada peringkat
- Gen Bio 2 Module 6Dokumen4 halamanGen Bio 2 Module 6Kimberly MercadoBelum ada peringkat
- Activity Sheet 1 & 2 GenBio1Dokumen12 halamanActivity Sheet 1 & 2 GenBio1Marlou GayaneloBelum ada peringkat
- HES1610 Lecture 1-Unifying Themes in BiologyDokumen60 halamanHES1610 Lecture 1-Unifying Themes in BiologyWong Kiong NguongBelum ada peringkat
- Gen Chem 1 Module 4 2nd Edition 2021Dokumen20 halamanGen Chem 1 Module 4 2nd Edition 2021jonzebedeeBelum ada peringkat
- ELECTRONEGATIVITYDokumen7 halamanELECTRONEGATIVITYRohini SelvarajahBelum ada peringkat
- Q1 M8 SHS - General-Chemistry-1 - Limiting-ReagentDokumen18 halamanQ1 M8 SHS - General-Chemistry-1 - Limiting-ReagentElysha Mae RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- What I Know: Practical Research 1Dokumen3 halamanWhat I Know: Practical Research 1Johnrey BaldozaBelum ada peringkat
- Asexual Vs Sexual ReproductionDokumen9 halamanAsexual Vs Sexual ReproductionEdenBelum ada peringkat
- Taxonomic Concept and PrinciplesDokumen14 halamanTaxonomic Concept and Principlespotatoo frieeesBelum ada peringkat
- Empirical and Molecular Formula ActivityDokumen5 halamanEmpirical and Molecular Formula ActivityChristian Geordel de GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Calculate The Amount of Substances Used or ProducedDokumen10 halamanCalculate The Amount of Substances Used or ProducedJonessa HeartifiliaBelum ada peringkat
- Eapp Module 3 Week 5-6Dokumen5 halamanEapp Module 3 Week 5-6Marichelle Idmilao PurosBelum ada peringkat
- Bio ActivitiesDokumen10 halamanBio ActivitiesErrol Chester Salvador CabadingBelum ada peringkat
- Plant CellDokumen19 halamanPlant CellIdasari DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Questions by Coming Up With Answers About Real Things and Asking "Why?"Dokumen5 halamanQuestions by Coming Up With Answers About Real Things and Asking "Why?"Kinect Nueva EcijaBelum ada peringkat
- Week 1 - Modules 1-3: Earth As The Only Habitable PlanetDokumen25 halamanWeek 1 - Modules 1-3: Earth As The Only Habitable PlanetDon't mind meBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Science: Submitted By: Criestefiel Ann S. Lolo Grade 12 - GatesDokumen13 halamanPhysical Science: Submitted By: Criestefiel Ann S. Lolo Grade 12 - GatesCriestefiel LoloBelum ada peringkat
- GEM - 111 - Module 1 (Chapter 1)Dokumen21 halamanGEM - 111 - Module 1 (Chapter 1)Aberin Andoyo AlimbonBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry ActivitiesDokumen5 halamanGeneral Chemistry ActivitiesTots TitsBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of MatterDokumen5 halamanClassification of Mattercherry shane abanesBelum ada peringkat
- AnshumanDokumen18 halamanAnshumanARK GAMINGBelum ada peringkat
- HUG y LEUPIN 2003Dokumen9 halamanHUG y LEUPIN 2003Juan Ignacio Gonzalez CabreraBelum ada peringkat
- Sachin Rana (Iitb) : Answer The FollowingDokumen32 halamanSachin Rana (Iitb) : Answer The FollowingAkshat SoniBelum ada peringkat
- Woodward Fisher RulesDokumen19 halamanWoodward Fisher RulesDavidBelum ada peringkat
- The Eighteen-Electron RuleDokumen4 halamanThe Eighteen-Electron RuleCarlos AlarconBelum ada peringkat
- The Complete Aqueous Hydrochloric Acid Solutions Density-Concentration CalculatorDokumen2 halamanThe Complete Aqueous Hydrochloric Acid Solutions Density-Concentration CalculatorEngr. Md. Tipu SultanBelum ada peringkat
- CH 17-Solubility Equilibria - Chem163 Outline - S2016-6Dokumen21 halamanCH 17-Solubility Equilibria - Chem163 Outline - S2016-6Bailey FongBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1Dokumen3 halamanTutorial 1sylvieBelum ada peringkat
- Balancing Equations: Practice Problems: Equation Balancing Chemistry Assignment: No 1Dokumen4 halamanBalancing Equations: Practice Problems: Equation Balancing Chemistry Assignment: No 1Sher KhanBelum ada peringkat
- English 1000 Word EssayDokumen4 halamanEnglish 1000 Word Essayapi-320830647Belum ada peringkat
- Exercise - III: (Only One Option Is Correct)Dokumen5 halamanExercise - III: (Only One Option Is Correct)Ihtisham Ul HaqBelum ada peringkat
- Chelating AgentsDokumen5 halamanChelating AgentsSalil MukundanBelum ada peringkat
- Neccesity of Auxiliaries in DyeingDokumen3 halamanNeccesity of Auxiliaries in DyeingMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryBelum ada peringkat
- Shrinkage Values of PolymersDokumen4 halamanShrinkage Values of PolymersVijaya SimhaBelum ada peringkat
- PRELAB For 2,4 - Dinitrophenylhydrazine SynthesusDokumen2 halamanPRELAB For 2,4 - Dinitrophenylhydrazine SynthesusSollen LataquinBelum ada peringkat
- Aluminium Bromide Salt AnalysisDokumen3 halamanAluminium Bromide Salt AnalysisShanmuganathan100% (1)
- Alkyl Halides and Ary HalidesDokumen27 halamanAlkyl Halides and Ary HalidesShubham ChandwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Gravity of MaterialsDokumen1 halamanGravity of Materialsck19654840Belum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen As A Reducing Agent State-Of-The-Art Science and TechnologyDokumen7 halamanHydrogen As A Reducing Agent State-Of-The-Art Science and TechnologyGus AcevedoBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan Ulangkaji Chapter 3: Chemical Formula and EquationDokumen15 halamanLatihan Ulangkaji Chapter 3: Chemical Formula and EquationIzz KhawarizmiBelum ada peringkat
- Table of ContentsDokumen34 halamanTable of ContentslaraBelum ada peringkat
- Extra Ex1 Strong Acid and Strong BaseDokumen2 halamanExtra Ex1 Strong Acid and Strong BaseSara KhalifehBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5th Edition Gunstream Solution ManualDokumen7 halamanAnatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5th Edition Gunstream Solution Manualelizabeth100% (26)
- 541 TitrimetryDokumen5 halaman541 TitrimetryCristian GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Equations and ReactionsDokumen4 halamanChemical Equations and ReactionsGauravBelum ada peringkat
- Astm D 2036-98 CianuroDokumen20 halamanAstm D 2036-98 CianuroGianinaRoncalChávezBelum ada peringkat
- Economics of ABS Production ProcessesDokumen4 halamanEconomics of ABS Production ProcessesfdfBelum ada peringkat
- Imp Questions 12-Chemistry 2022 (EM) - WingofeducationDokumen17 halamanImp Questions 12-Chemistry 2022 (EM) - WingofeducationVickyBelum ada peringkat