Math 202-102 Sec: 21 Solution Quiz 2
Diunggah oleh
AndreaMunozDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Math 202-102 Sec: 21 Solution Quiz 2
Diunggah oleh
AndreaMunozHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1
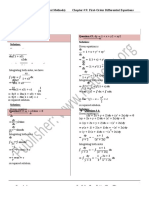
Math 202-102 Sec: 21 Solution Quiz 2 (B)
—————————————————————————————————————————–
dy
Q.1: Solve the initial value problem (x + 2) + y = 2 ln(x), y(1) = 1.
dx
d
Sol. We can write the given equation as [(x + 2)y] = 2 ln (x)
dx
∫ 2x ln (x) − 2x + c
Which ⇒ (x+2)y = 2 ln (x)dx+c, ⇒ (x+1)y = 2x ln (x)−2x+c or y =
x+2
0 − 21 + c 2x ln (x) − 2x + 5
y(1) = 1 ⇒ 1 = ⇒ c = 5 and the solution is y = .
3 x+2
Q.2: Solve the differential equation 6xydx + (4y + 9x2 )dy = 0 by making it exact.
∂M ∂N
Sol. M (x, y) = 6xy and N (x, y) = 4y + 9x2 . = 6x and = 18x. So the equation is not
∂y ∂x
exact.
Nx − My 18x − 6x 2
= = is a function of y alone.
M 6xy y
∫ 2
dy
µ(x) = e y = e2 ln y = y 2 is the integrating factor.
Multiplying by integration factor, we get 6xy 3 dx + (4y 3 + 9x2 y 2 )dy = 0
∂M ∂N
M (x, y) = 6xy 3 and N (x, y) = 4y 3 + 9x2 y 2 . = 184xy 2 and = 18xy 2 . So the
∂y ∂x
equation is exact.
∂f ∂f
There exists a function f (x, y) such that = M and =N
∂x ∂y
∂f
= M = 6xy 3 , ⇒ f (x, y) = 3x2 y 3 + g(y)
∂x
∂f
= 9x2 y 2 + g ′ (y) = N = 4y 3 + 9x2 y 2 ⇒ g ′ (y) = 4y 3 ⇒ g(y) = y 4
∂y
So f (x, y) = 3x2 y 3 + y 4 + c
Q.3: (a.) Use appropriate substitution to transform (y 2 + xy)dx + x2 dy = 0 into a
separable equation. Do not solve the new equation.
Sol. Given equation is a homogeneous equation of degree 2. Let y = ux, then dy = udx + xdu
(y 2 + xy)dx + x2 dy = 0 ⇒ (u2 x2 + ux2 )dx + (x2 )(udx + xdu) = 0
u2 x2 dx + ux2 dx + x2 udx + x3 du = 0 ⇒ x2 (u2 + 2u)dx + x3 du = 0
1 −1
⇒ x2 (u2 + 2u)dx = −x3 du ⇒ dx = 2 du
x u + 2u
Which is a separable equation.
2
dy
(b.) Use appropriate substitution to transform − y = ex y 2 into a linear equation. Do not
dx
solve the new equation.
dy
Sol. − y = ex y 2 is a Bernoulli equation with n = 2.
dx
dy du
Let u = y 1−2 = y −1 or y = u−1 and = −u−2
dx dx
dy du
So − y = ex y 2 ⇒ −u−2 − u−1 = ex u−2
dx dx
du
Multiplying by −u2 we get + u = −ex which is a linear equation.
dx
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsDari EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Dari EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Belum ada peringkat
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsDari EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsBelum ada peringkat
- Differential Equations - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Dokumen38 halamanDifferential Equations - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Muhammad UmairBelum ada peringkat
- Bitcoin Encryption Decryption DSADokumen16 halamanBitcoin Encryption Decryption DSASrinivas Mahankali100% (1)
- Linear Inequality DLPDokumen7 halamanLinear Inequality DLPHarley Laus75% (4)
- 2 Elimination of Arbitrary ConstantsDokumen9 halaman2 Elimination of Arbitrary ConstantsChristine SalamatBelum ada peringkat
- On Determinat of Non Square MatricesDokumen115 halamanOn Determinat of Non Square MatricesRaymond Carreon DomingoBelum ada peringkat
- ENGR 213 Midterm 1 Sol 2010Dokumen3 halamanENGR 213 Midterm 1 Sol 2010akabaka123Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter-2 First Order and First Degree Ordinary Differential EquationsDokumen7 halamanChapter-2 First Order and First Degree Ordinary Differential EquationsSatish BarotBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes 2 - Differential Equations 2020Dokumen41 halamanLecture Notes 2 - Differential Equations 2020Alucard FighterBelum ada peringkat
- Ncert Exemplar Math Class 12 Chapter 09 Differential EquationsDokumen49 halamanNcert Exemplar Math Class 12 Chapter 09 Differential EquationsAnitaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-2-Separation-of-Variables-ModuleDokumen6 halamanChapter-2-Separation-of-Variables-ModuleMARK JAMES PUTOLANBelum ada peringkat
- ODE Notes Lecture 2-4Dokumen49 halamanODE Notes Lecture 2-4manam unguBelum ada peringkat
- Exact Differential EquationsDokumen7 halamanExact Differential Equationsفاطمة الرويليBelum ada peringkat
- TYPE V - Intergrating Factor by FormulasDokumen3 halamanTYPE V - Intergrating Factor by FormulasKimberly BorjaBelum ada peringkat
- First Order Differential EquationDokumen15 halamanFirst Order Differential Equationdether acopiadoBelum ada peringkat
- MATH1500 Notes PDFDokumen7 halamanMATH1500 Notes PDFruiyu liuBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 7 EDEDokumen2 halamanChap 7 EDEsuhel ahmedBelum ada peringkat
- TYPE VI - Linear Differential EquationDokumen5 halamanTYPE VI - Linear Differential EquationKimberly BorjaBelum ada peringkat
- Differential Equations URPDokumen26 halamanDifferential Equations URPabcd xyzBelum ada peringkat
- Differential Equations - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2006Dokumen46 halamanDifferential Equations - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2006Muhammad UmairBelum ada peringkat
- Review Questions For Final Exam - Solutions: Ucsc AMS 211 FALL 2014Dokumen21 halamanReview Questions For Final Exam - Solutions: Ucsc AMS 211 FALL 2014mriboostBelum ada peringkat
- DE Lecture 3 New HandoutDokumen36 halamanDE Lecture 3 New HandoutBarrett M82Belum ada peringkat
- MAT060 13 Implicit-DifferentiationDokumen42 halamanMAT060 13 Implicit-DifferentiationShine Ibarra AlabaBelum ada peringkat
- Ordinary Differential BP106RMTDokumen87 halamanOrdinary Differential BP106RMTdhurvchavda4Belum ada peringkat
- Maths I CompiledDokumen193 halamanMaths I CompiledmasihakhanBelum ada peringkat
- Implicit Differentiation: 2nd Semester, 2022-2023Dokumen42 halamanImplicit Differentiation: 2nd Semester, 2022-2023Ammar TagoranaoBelum ada peringkat
- PDE Solving TechniquesDokumen4 halamanPDE Solving TechniquesTusharbhutadBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise # 9.2: B.Sc. Mathematics (Mathematical Methods) Chapter # 9: First-Order Differential EquationsDokumen12 halamanExercise # 9.2: B.Sc. Mathematics (Mathematical Methods) Chapter # 9: First-Order Differential EquationsMuhammad Haseeb RazaBelum ada peringkat
- MA 102 (Ordinary Differential Equations)Dokumen3 halamanMA 102 (Ordinary Differential Equations)Lynx101Belum ada peringkat
- 110.302 Differential Equations Professor Richard BrownDokumen2 halaman110.302 Differential Equations Professor Richard BrownLuis BaldassariBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1 SolutionsDokumen4 halamanTutorial 1 SolutionsAkshay NarasimhaBelum ada peringkat
- Equations of Order One: Differential Equations Module 2ADokumen5 halamanEquations of Order One: Differential Equations Module 2AJuvilee RicoBelum ada peringkat
- Exact PDFDokumen5 halamanExact PDFAnupati Bhanu PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Solutions: MATH 214-2 - Fall 2000 - First Midterm (Solutions)Dokumen6 halamanSolutions: MATH 214-2 - Fall 2000 - First Midterm (Solutions)LopitalsBelum ada peringkat
- First Order Differential Equations: BCCC Tutoring CenterDokumen4 halamanFirst Order Differential Equations: BCCC Tutoring CenterCarloBelum ada peringkat
- LatexDokumen5 halamanLatexbbiplab023Belum ada peringkat
- Sol 1Dokumen4 halamanSol 1Adeyasa RPBelum ada peringkat
- Integrating Factor by InspectionDokumen8 halamanIntegrating Factor by InspectionAileen Joyce EscasinasBelum ada peringkat
- 2Z03 Final SolDokumen24 halaman2Z03 Final SolAbha Hameed100% (1)
- Degree and Order of ODEDokumen7 halamanDegree and Order of ODEadiba adibBelum ada peringkat
- Degree and Order of ODEDokumen7 halamanDegree and Order of ODEadiba adibBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter1 SolutionDokumen35 halamanChapter1 SolutionHải Anh ĐặngBelum ada peringkat
- Defslt Lec # 05 18-01-21Dokumen3 halamanDefslt Lec # 05 18-01-21AkashBelum ada peringkat
- EXAM 1 - MATH 212 - 2017 - SolutionDokumen3 halamanEXAM 1 - MATH 212 - 2017 - SolutionTaleb AbboudBelum ada peringkat
- Instructor: Dr. Yuli B. Rudyak MAP 2302, Differential Equations Sample Final ExamDokumen4 halamanInstructor: Dr. Yuli B. Rudyak MAP 2302, Differential Equations Sample Final ExamConnie PacisBelum ada peringkat
- Differential Equations - Additional Topics First Order ODE PDFDokumen31 halamanDifferential Equations - Additional Topics First Order ODE PDFRicky Perez100% (1)
- Department of Mathematics Manipal Institute of Technology, ManipalDokumen5 halamanDepartment of Mathematics Manipal Institute of Technology, ManipalDpt HtegnBelum ada peringkat
- Math 334 (A1) Spring 2009 Introduction To Differential Equations Solutions To Midterm ExaminationDokumen5 halamanMath 334 (A1) Spring 2009 Introduction To Differential Equations Solutions To Midterm ExaminationZakky Maftukhil WafaBelum ada peringkat
- Separable Equations & Linear Equations: This Report Is Submitted To Fulfill The Requirements of The Numerical AnalysisDokumen9 halamanSeparable Equations & Linear Equations: This Report Is Submitted To Fulfill The Requirements of The Numerical Analysistareq omarBelum ada peringkat
- Test 1 SolutionsDokumen3 halamanTest 1 SolutionsFrantz ClermontBelum ada peringkat
- Ordinary Differential Equations Segment Wise Questions From 1983 To 2011 Civil ServiceDokumen6 halamanOrdinary Differential Equations Segment Wise Questions From 1983 To 2011 Civil ServiceNagendran KrishnamoorthiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Exact and Linear Differential EquationsDokumen8 halamanChapter 2 Exact and Linear Differential EquationsMehmet Akif KözBelum ada peringkat
- Week 7.1E Differential EquationsDokumen10 halamanWeek 7.1E Differential Equationschumafasi2004Belum ada peringkat
- Practice Final Exam - SolutionsDokumen8 halamanPractice Final Exam - SolutionsNALUGOODHA MUSABelum ada peringkat
- Differentiation: Dy DX Dy DZ × DZ DXDokumen2 halamanDifferentiation: Dy DX Dy DZ × DZ DXPatro GoodfridayBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 5 SolutionsDokumen3 halamanTutorial 5 SolutionsAkshay NarasimhaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-2 First Order and First Degree Ordinary Differential EquationsDokumen12 halamanChapter-2 First Order and First Degree Ordinary Differential EquationsSatish BarotBelum ada peringkat
- HW3 SolDokumen3 halamanHW3 Sol劉德信Belum ada peringkat
- Math 2dDokumen98 halamanMath 2dhashoBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Order ODE and Its ApplicationsDokumen76 halaman1st Order ODE and Its ApplicationsMuhammad EhsanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture - 1 - June - 18 - 2020 5Dokumen18 halamanLecture - 1 - June - 18 - 2020 5Sanjeev khatriBelum ada peringkat
- Transformation of FunctionsDokumen38 halamanTransformation of FunctionsEddy R. VélezBelum ada peringkat
- 5116 NotesDokumen7 halaman5116 NotesKoh JZBelum ada peringkat
- SPB AddMaths Answer SPM 2009Dokumen19 halamanSPB AddMaths Answer SPM 2009murulikrishanBelum ada peringkat
- Orthogonality: Orthogonality of The Four Subspaces 4.1Dokumen10 halamanOrthogonality: Orthogonality of The Four Subspaces 4.1jhhidalgorBelum ada peringkat
- Trigonometric Equation: Solved ExampleDokumen32 halamanTrigonometric Equation: Solved Example10x RiderBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 4 Application of Matrix Operations-1Dokumen7 halamanActivity 4 Application of Matrix Operations-1Georji kairuBelum ada peringkat
- Note On Vector AnalysisDokumen37 halamanNote On Vector AnalysisNabil MunshiBelum ada peringkat
- Wavelets and Subband Coding Solutions ManualDokumen90 halamanWavelets and Subband Coding Solutions Manualwilliam_windsor100% (8)
- Quantitative Aptitude Test 6: (ERPV, Numbers)Dokumen6 halamanQuantitative Aptitude Test 6: (ERPV, Numbers)chaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- HW 9Dokumen2 halamanHW 9Vaibhav GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematical DiagramDokumen5 halamanMathematical Diagramwoodword99Belum ada peringkat
- Process Dynamics and Control - Ch05Dokumen20 halamanProcess Dynamics and Control - Ch05etayhailuBelum ada peringkat
- How To Do Cube Roots of 9 Digit Numbers in Your HeadDokumen5 halamanHow To Do Cube Roots of 9 Digit Numbers in Your HeadAnonymous vcdqCTtS9Belum ada peringkat
- Machine ProblemDokumen15 halamanMachine ProblemLuisa PerniaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 6 Higher Derivatives and Implicit DifferentiationDokumen17 halamanLesson 6 Higher Derivatives and Implicit DifferentiationANABEL EGOCBelum ada peringkat
- Chaper 9 NotesDokumen22 halamanChaper 9 NotesEamon BarkhordarianBelum ada peringkat
- Math g9 q1 Las Book 1Dokumen94 halamanMath g9 q1 Las Book 1Veronica LlagasBelum ada peringkat
- Division of PolynomialsDokumen112 halamanDivision of Polynomialsbangtan loverBelum ada peringkat
- Muldowney PDFDokumen189 halamanMuldowney PDFnutchai2538Belum ada peringkat
- Finite Dimensional Vector Spaces Paul HalmosDokumen204 halamanFinite Dimensional Vector Spaces Paul HalmosFede del CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- MATH 3rd Grading Summative 2 Grade 6Dokumen3 halamanMATH 3rd Grading Summative 2 Grade 6Aubrey Gay SarabosquezBelum ada peringkat
- Fast ConvolutionDokumen2 halamanFast ConvolutiongulanitoyoBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Maths Exemplar Ch01 LongDokumen13 halaman12 Maths Exemplar Ch01 LongDeepakBelum ada peringkat
- AIS Theory of Groups Lectures 2010 SlidesDokumen145 halamanAIS Theory of Groups Lectures 2010 SlidessonicaBelum ada peringkat
- 03 - Partial Derivatives of Functions PDFDokumen13 halaman03 - Partial Derivatives of Functions PDFzul hilmiBelum ada peringkat
- Notes Lower Form 2023Dokumen93 halamanNotes Lower Form 2023NORIDAH BINTI RAHMAT MoeBelum ada peringkat