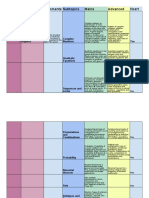
Science Syllabus Xi
Diunggah oleh
Nitin SharmaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Science Syllabus Xi
Diunggah oleh
Nitin SharmaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
CLASS XI - SYLLABUS DETAILS
ENGLISH SYLLABUS
MONTH TOPIC DETAILS
April THE PORTRAIT OF A LADY,. THE PORTRAIT OF A LADY
NOTICE
A PHOTOGRAPH
NOTE MAKING
A PHOTOGRAPH
May WE ARE NOT AFRAID TO DIE,NOTE WE ARE NOT AFRAID TO DIE,NOTE MAKING
MAKING
CANTERVILLE GHOST-INTRO,WRITING CANTERVILLE GHOST-INTRO,WRITING
SKILLS,NOVEL,COMPLAINT LETTER SKILLS,NOVEL,COMPLAINT LETTER
July DISCOVERING TUT DISCOVERING TUT
THE VOICE OF THE RAIN,RANGA'S THE VOICE OF THE RAIN,RANGA'S MARRIAGE
MARRIAGE
CANTERVILLE GHOST CANTERVILLE GHOST
WRITING SKILLS WRITING SKILLS
August TALE OF MELON CITY TALE OF MELON CITY
BROWNING VERSIONS BROWNING VERSIONS
August CANTERVILLE GHOSTS CANTERVILLE GHOSTS
THE SUMMER OF THE BEAUTIFUL THE SUMMER OF THE BEAUTIFUL WHITE
WHITE HOUSE HOUSE
GRAMMAR GRAMMAR
September GRAMMAR+WRITING SKILL GRAMMAR+WRITING SKILL
REVISION REVISION
October THE AILING PLANET THE AILING PLANET
GRAMMAR+WRITING SKILLS GRAMMAR+WRITING SKILLS
THE ADDRESS THE ADDRESS
October GRAMMAR+WRITING SKILLS GRAMMAR+WRITING SKILLS
GRAMMAR+WRITING SKILLS GRAMMAR+WRITING SKILLS
November THE MOTHER'S DAY THE MOTHER'S DAY
THE MOTHER'S DAY, ALBERT THE MOTHER'S DAY, ALBERT EINSTIEN,
EINSTIEN,
November ALBERT EINSTIEN, ALBERT EINSTIEN,
CHILDHOOD CHILDHOOD
NOTE MAKING,WRITING NOTE MAKING,WRITING
December FATHER TO SON FATHER TO SON
BIRTH BIRTH
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 1
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
December WRITING SKILLS WRITING SKILLS
January CANTERVILLE GHOST,GRAMMAR CANTERVILLE GHOST,GRAMMAR
GRAMMAR GRAMMAR
MOCK TEST MOCK TEST
February REVISION REVISION
MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS
MONTH TOPIC DETAILS
April Complex numbers and quadratic Brief description of algebraic properties of complex
equations numbers. Argand plane and polar representation of
complex numbers. Statement of Fundamental
Complex numbers and quadratic Theorem of Algebra, solution of quadratic
equations equations inthe complex number system.
Square root of a complex number, Cube roots of
unity and their properties
May Principle of mathematical Processes of the proof by induction, motivating the
induction application of the method by looking at natural
numbers as the least inductive subset of real
numbers. The principle of mathematical induction
and simple applications.
Trigonometry Positive and negative angles
July Trigonometry Measuring angles in radians & in degrees and
conversion from one measure to another.
Definition of trigonometric functions with the
help of unit circle. Truth of the identity, sin2x +
cos2x = 1, for all x.
Signs of trigonometric functions and sketch of
their graphs.
Expressing sin (x ± y) and cos (x ± y) in terms
of sinx, sin y, cos x & cos y. Deduction of
identities.
Trigonometry Identities related to sin 2x, cos2x, tan 2x, sin3x,
cos3x and tan3x. General solution of
trigonometric equations of the type sin θ = sin α
,
Trigonometry cos θ = cos α and tan θ = tan α. Proof and
simple application of sine and cosine rules only
Sets Sets and their representations. Empty set. Finite
& Infinite sets. Equal sets.Subsets. Subsets of
the set of real numbers especially intervals (with
notations). Power set. Universal set.
August Relations and functions Ordered pairs, Cartesian product of sets.
Number of elements in the cartesian product of
two finite sets. Cartesian product of the reals
with itself (upto R x R x R). Definition of
relation, pictorial diagrams, domain. codomain
and range of a relation. Function as a special
kind of relation from one set to another.
Pictorial representation of a function, domain,
co-domain & range of a function
Relations and functions Real valued function of the real variable,
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 2
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
domain and range of these functions, constant,
identity, polynomial, rational, modulus, signum
and greatest integer functions with their graphs.
Sum, difference, product and quotients of
Linear inequalities functions.
Linear inequalities. Algebraic solutions of linear
inequalities in one variable and their
representation on the number line. Graphical
solution of linear
August Linear inequalities inequalities in two variables. Solution of system
of linear inequalities in two variables-
graphically. Inequalities involving modulus
function
Permutations and combinations Fundamental principle of counting
Permutations and Factorial n. (n!)Permutations and
combinations
combinations, derivation of formulae and their
connections, simple applications.
September Permutations and combinations, derivation of formulae and
combinations
their connections, simple applications.
REVISION REVISION
October Binomial theorem statement and proof of the binomial
theorem for positive integral indices.
Binomial theorem Pascal's triangle, General and middle term
in binomial expansion,
October Binomial theorem simple applications
Introduction to 3-d geometry Coordinate axes and coordinate planes in
three dimensions. Coordinates of a point.
Distance between two points and section
formula
November Straight lines Brief recall of 2D from earlier classes.
Slope of a line and angle between two
lines. Various forms of equations of a
line:
Straight lines parallel to axes, point-slope form, slope-
intercept form, two point form, intercepts
form and normal form. General equation of
a line. Distance of a point from a line
November Statistics Measure of dispersion; mean deviation,
variance and standard deviation of
ungrouped/grouped data. Analysis of
frequency distributions with equal
means but different variances.
Conic sections Sections of a cone: circle, ellipse, parabola,
hyperbola a straight line and pair of
intersecting lines as a degenerated case of a
conic section. Standard equation of a circle
Conic sections General equation of a circle; Standard
equations and simple properties of
parabola, ellipse and hyperbola.
Introduction of directrix of an ellipse
and hyperbola.
December Sequence and series Sequence and Series: Arithmetic progression
(A. P.). arithmetic mean (A.M.) Geometric
progression (G.P.), general term of a G.P., sum
of n terms of a G.P., geometric mean (G.M.),
relation between A.M. and G.M.
Arithmetic/Geometric series, infinite G.P.
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 3
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
Sequence and series AND its sum, Sum to n terms of the special
series Σn, Σn2 and Σn3
January Limits Concept of right hand limit and left hand
Derivatives
limit ,evaluation of Limits of algebraic
and trigonometric functions, limits of
exponential and logarithmic functions.
Derivative introduced as rate of change
both as that of distance function and
geometrically, intuitive idea of limit.
functions
Limits Definition of derivative, relate it to slope of
Derivatives tangent of the curve, derivative of sum,
difference, product and quotient of functions.
Derivatives of polynomial and trigonometric
MOCK TESTS
February MOCK TEST
Probability Random experiment ,use of permutations and
combinations ,venn diagrams
REVISION
PHYSICS SYLLABUS
Month Chapters Contents
April Chap1- 1.1What isPhysics
PhysicalWorld 1.2Scope andexcitementof physics
1.3Fundamentalforces innature
1.4Nature ofphysical laws
2.1Introduction
2.2Theinternational systemofunits
2.3MeasurementofLength
Chap2-Unitsand
2.4Measurementof mass
Measurement 2.5Measurementof time
2.6Accuracy,precisionofinstrumentsand
errorsinmeasurement
2.7Significantfigures
Chap2-Unitsand 2.8Dimensions in physical quantities
Measurement 2.9Dimensionalformulae and dimensional
equations
May Chap2-Unitsand 2.9Dimensionalformulae and dimensional
Measurement equations
Chap2-Unitsand Mathematical tools-Log, differential and integral
calculus
Measurement
July Chap 3-Motion 3.1Introduction
inastraight 3.2Position,path,lengthand displacement
line 3.3Average velocityand averagespeed
3.4Instantaneous velocityand speed
3.5Acceleration
3.6kinematic equations foruniformly
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 4
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
acceleratedmotion
3.7Relative velocity
Tomeasurediameterofa smallspherical body
usingVernierCallipers andhencefinditsvolume
Chap 4-Motion 4.1Introduction
ina plane 4.2Scalarsand vectors
4.3Multiplication ofvectorsbyrealnumbers
4.4Additionandsubtractionof vectors- graphical method
4.5Resolution ofvectors
4.6Vectoraddition-analytical method
4.7Motion ina plane
4.8Motion ina plane with constant acceleration
Tomeasurediameterofa smallcylindrical
bodyandtomeasureinternaldiameteranddepthof a
givenbeaker/calorimeterusingVernierCallipers
andhencefinditsvolume
July Chap 4-Motion 4.9Relative velocity in two dimensions
ina plane
4.10Projectile motion
4.11Uniform circularmotion
Todeterminevolumeofanirregularlaminausing
screwgauge.
Chap5- 5.1Introduction
Lawsofmotion 5.2Aristotle’sfallacy
5.3ThelawofInertia
5.4Newton’sFirst lawofmotion
5.5Newton’ssecondlaw ofmotion
5.6Newton’s thirdlawofmotion
5.7conservation of momentum
5.8Equilibriumofparticle
5.9commonforces inmechanics
5.10circular motion
5.11Solvingprobleminmechanics
T Tomeasurediameterofa givenwireandthicknessof a
givensheetusingscrewgauge.
August Chap6- 6.1Introduction
Work,energyand 6.2Notionsofworkandkineticenergy; the
power workenergytheorem
6.3Work
6.4kineticenergy
6.5Workdonebya variableforce
6.6Theworkenergytheoremforvariable force
6.7Theconceptofpotential energy
6.8Theconservation of mechanical energy
6.9Thepotential energy ofspring
6.10Variousform ofenergy: thelawof conservation
ofenergy
Tofindtheweightofa givenbodyusing parallelogramlaw
ofvectors.
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 5
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
Chap6- 6.11Power
Work,energyand 6.12Collisions
Power Todetermineradiusofcurvatureofagiven spherical
surfacebya spherometer.
August Chap8- 8.1Introduction
Gravitation 8.2Keplers law
8.3Universal lawof gravitation
8.4Thegravitational constant
8.5Accelerationduetogravityofearth
8.6acceleration duetogravitybelowand above
thesurfaceofearth
Usinga simplependulum,plotitsL-T2graphand useit
tofindtheeffectivelengthof second's pendulum.
Chap8- 8.7Gravitational potential energy
Gravitation
8.8Escapespeed
8.9Earthsatellite
8.10Energyofanorbiting satellite
8.11Geostationaryandorbitingsatellite
8.12Weightlessness
To studytherelationshipbetweenforceoflimiting
frictionandnormalreactionandtofindtheco-
efficientoffrictionbetweena blockanda horizontal surface.
October Chap7- 7.1Introduction
Systemofparticles 7.2centreof mass
and 7.3Motion ofcentre of mass
Rotationalmotion 7.4Linearmomentumof systemofparticles
7.5Vectorproductof two vectors
Tofindtheforceconstantofa helicalspringby plottinga
graphbetweenloadandextension.
Chap7- 7.5Vectorproductof two vectors
Systemofparticles 7.6Angularvelocityand itsrelationwith
and linearvelocity
Rotationalmotion 7.7Torqueandangular momentum
7.8Equilibriumof rigidbody
Todeterminethecoefficientofviscosityofagiven
viscousliquidbymeasuringterminalvelocityofa
givensphericalbody.
October Chap7- 7.13Angularmomentum in caseofrotationabout
Systemofparticles fixedaxis
and 7.14Rolling motion
Rotationalmotion To studytherelationshipbetweenthetemperatureof a
hotbodyandtimebyplottinga coolingcurve.
November Chap-9 9.1introduction
Mechanical 9.2elasticbehaviorofsolids
properties ofsolid 9.3Stressand Strain
9.4Hooke’sLaw
9.5Stress-Strain curve
9.6Elasticmoduli
9.7Applications ofelasticbehaviorof materials
To studytherelationbetweenfrequencyandlength
ofagivenwireunderconstanttensionusing
sonometer.
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 6
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
Chap 10- 10.1Introduction
Mechanical 10.2 Pressure
properties of 10.3Streamlineflow
fluids 10.4 Bernoulli’sPrinciple
10.5 Viscosity
10.6 Reynolds number
10.7 SurfaceTension
To studytherelationbetweenthelengthofa given
wireandtensionforconstantfrequencyusing sonometer.
November Chap 11-Thermal 11.1Introduction
properties 11.2Temperatureand heat
ofmatter 11.3 Measurementof Temperature
11.4Idealgasequationand absolute
Temperature
11.5thermal expansion
11.6 Specific Heat capacity
11.7 Calorimetry
Tofindthespeedof soundinairatroom
temperatureusinga resonancetubebytwo
resonancepositions.
Chap 11-Thermal 11.8 Changeofstate
properties 11.9 HeatTransfer
ofmatter 11.10Newton’slawofcooling
Tofind the downward force along an inclined plane acting
on a roller due to gravitational pull and study its
relationship with the angle of inclination by plotting graph
between force and sin .
December Chap 12- 12.1Introduction
Thermodynamics 12.2Thermal Equilibrium
12.3 Zeroth lawofthermodynamics
12.4 Heat, internal energyand work
12.5 Firstlawofthermodynamics
12.6 Specificheat capacity
Chap 12- 12.7Thermodynamicstate variables and
Thermodynamics equationofstate
12.8Thermodynamicprocesses
12.9 Heat engine
12.10Refrigeratorsand Heatpumps
12.11Secondlawofthermodynamics
12.12reversible and irreversible processes
12.13Carnot engine
December Chap 13- 13.1Introduction
Kinetictheory 13.2molecularnatureof matter
13.3 Behaviourof gases
13.4 Kinetictheoryofideal gas
13.5 Lawofequipartionofenergy
13.6 Specificheat capacity
13.7 Meanfreepath
January Chap 14- 14.1Introduction
Oscillations 14.2 Periodicandoscillatorymotions
14.3 Simple harmonicmotion
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 7
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
14.4 Simple harmonicmotion and uniform circular
motion
14.5 Velocityand accelerationinsimple
harmonicmotion
14.6 Force lawforsimple harmonicmotion
14.7 Energy insimple harmonicmotion
14.8 somesystemexecutingsimple harmonic motion
14.10Forcedoscillations andresonance
Chap15-Waves 15.1Introduction
15.2Transverseandlongitudinal waves
15.3 Displacement relationin progressive waves
15.4Thespeedof atravellingwave
15.5Theprinciple ofsuperpositionofwaves
15.6 Reflectionofwaves
February Chap15-Waves 15.7 Beats
15.8Doppler’s effect
CHEMISTRY SYLLABUS
Month Chapters Contents
April Chap1-Some 1.1 What is chemistry
Basic Concepts of 1.2 Importance of chemistry
Chemistry 1.3 properties of matter and their measurements
1.4 uncertainty in measurement
1.5 Laws of chemical combination
1.6 Daltons Atomic Theory
Chap1-Some 1.7 Atomic and Molecular Masses
Basic Concepts of 1.8 Mole Concept and Molar Masses
Chemistry LAB
To prepare crystals of pure copper sulphate from a given
sample of the blue vitriol
May
1.9 Percentage Composition
1.10 Stoichiometry and stoichiometric calculation
Chapter 14- 14.1 Environmental pollution
14.2 Atmospheric pollution
Environmental 14.3 Water Pollution
Chemistry 14.4 Soil Pollution
14.5 Industrial waste
14.6 Strategies to control environmental pollution
14.7 Green chemistry
LAB
Qualitative Analysis (anion So4-2Co3-2)
July Chap2-Structure 2.1 Sub atomic particles
of Atom 2.2 Atomic models
Chap2-Structure 2.3 Developments and leading to the Bohr’s model of atom
of Atom 2.4 Bohr’s model for hydrogen atom
July
Chap2-Structure 2 .5 Towards quantum mechanical model of the atom
of Atom
Chap 3 -
3.1 -3.3 Modern periodic law and the present form of
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 8
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
Classification of the periodic table
elements and
periodicity in 3.4-3.6 Nomenclature and Electronic configuration
properties. 3. 3.7 Periodic trends in the properties of elements
LAB
Qualitative Analysis Al2(SO4)3
August 4.1 Kossel- Lewis approach to chemical bonding
Chapter 4-
Chemical bonding 4.2 Ionic or electrovalent bond
4.3 Bond Parameters
4.8 Bonding in homonuclear diatomic molecules
4.9 Hydrogen bonding
Chapter 4- 4.4 VSEPR Theory
Chemical bonding
4.5 Valence bond theory
4. 4.6 Hybridisation
4.7 Molecular orbital theory
August Chapter 4- 4.8 Bonding in homonuclear diatomic molecules
Chemical bonding
4.9 Hydrogen bonding
Chapter 5 -States
of matter 5.1 Inter nuclear forces
5.2 Thermal energy
5.3 Intermolecular forces VS thermal energy
Chapter 5 -States 5.4 The gaseous state
of matter
5.5 The gas laws
5.6 Ideal gas equation
Chapter 5 -States 5.7 Kinetic molecular theory
of matter
5.8 Deviation from ideal behavior
5.9 Liquification of gases
LAB
1 Volumetric Analysis (Na2CO3) with HCl
2 Qualitative Analysis BaCl2, ZnCO3
September Chapter7- 7.1 Equilibrium in physical process
Equilibrium
7.2 Equilibrium in chemical process
7.3 Law of chemical Equilibrium
Chapter7- 7.4 -7.5 Homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibria
Equilibrium
7.6 Application of equilibrium
7.7 Relation between equilibrium constants
LAB
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 9
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
Qualitative Analysis Pb(CH3COOH)2
October 7.8 Factors affecting equilibrium
7.9 Ionic equilibrium
Chapter7- 7.10 Arrhenius concept of acid and bases
Equilibrium
7.11 The Bronsted -Lowry acid bases and ionization of acid
and bases
7.12 Buffer solution
7.13 Solubility equilibria of sparingly soluble salts
Chapter6- 6.1 Thermodynamic terms
Thermodynamics 6.2 Application
6.3 Measurement of H and U
November 12.1General Introduction
Chapter12-
Organic 12.2 Tetravalency of carbon
chemistry-some
basic principal and
techniques
12.3 Structural representations of organic
Chapter12-
Organic compounds
chemistry-some 12.4 Classification of organic compounds
basic principal and
techniques 12.5 Nomenclature of organic compounds
12.6 Isomerism
Chapter12- 12.6 Isomerism
Organic
chemistry-some 12.7 Fundamental concepts in organic reaction
basic principal and mechanism
techniques
12.8 Methods of purification of organic compound
Chapter12- 12.9 Qualitative analysis of organic compounds
Organic
chemistry-some 12.10 Quantitative analysis
basic principal and
techniques
Chapter12- 12.10 Quantitative analysis
Organic
chemistry-some LAB
basic principal and Qualitative Analysis MgSO4, Sr(NO3)2
techniques
December Chapter13- 13.1 Classification
Hydrocarbon 13.2 Alkanes
13.3 Alkenes
13.4 Alkynes
13.5 Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Chapter13- 13.6 Carcinogenicity and toxicity
Hydrocarbon
Chapter9- 9.1 Position of hydrogen in the periodic table
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 10
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
Hydrogen 9.2 Dihydrogen, Preparation, and properties
9.5 Hydrides
9.6 Water
9.7 Hydrogen peroxide
9.8 Heavy water
December Chapter13- 13.1 Classification
Hydrocarbon 13.2 Alkanes
13.3 Alkenes
13.4 Alkynes
13.5 Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Chapter13- 13.6 Carcinogenicity and toxicity
Hydrocarbon
Chapter9- 9.1 Position of hydrogen in the periodic table
Hydrogen
9.2 Dihydrogen, Preparation, and properties
9.5 Hydrides
9.6 Water
9.7 Hydrogen peroxide
9.8 Heavy water
December Chapter8-Redox 8.1 Classification
Reaction 8.2 Redox reaction in terms of electron transfer reaction
8.3 Oxidation number
LAB
Detection of elements in organic compounds
January Chapter10-S- 10.1 Group1 Elements
Block Elements
10.2 General characters of Alkali metals
10.3 Anomalous properties of Lithium
10.4 Some important compounds of sodium
10.5 Biological Importance of Sodium and potassium
10.6 Group 2 elements, General characters
10.8 Anomalous properties of Beryllium
10.9 Some important compounds of sodium
Chapter11-The p- 11.1 Group 13 elements
Block elements 11.2 Anomalous properties of Boron
11.3 Some important compounds of Boron and uses
11.5 Group14 elements
11.6 Anomalous properties of Carbon
Chapter11-The p- 11.8 Some important compounds of Carbon and
Block elements
Silicon
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 11
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
February Revision
COMPUTER SCIENCE SYLLABUS
Month Chapter Details
April COMPUTER Evolution of computers; Basics of computer and its
FUNDAMENTALS operation
Software Concepts:
Types of Software - System Software, Utility,Device
Drivers.
Software and Application Software;
System Software: Operating System, Compilers,
Interpreters and Assembler,Types of Operating
System,open source Concepts
COMPUTER Generations of Computers,Architecture of Central
FUNDAMENTALS Processing unit,Memory,Types of
memory,Microprocessor.
May COMPUTER Classification of Computers,RISC,CISC architecture,
FUNDAMENTALS Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer,
NUMBER SYSTEM Types of Number System,Binary Number System,Decimal
Number System,HexaDecimal Number SystemConversion
Of Decimal Number System to Binary, Octal, Hexadecimal
and VICE-Versa
July ALGORITHMS Introduction to Algorithms,Developing
AND Algoritms,Flowcharts,Control Structures of Flowcharts.
FLOWCHARTS
Getting Started Character set, C++ Tokens (Identifiers, Keywords,
with C++ Constants, Operators,),
Structure of a C++ Program (include files,
Main function(),Input/Output in C++
Functions.Input/Output Operator,Concept of
variable,Cascading of Input/output operator,Compilation
and Linking,Errors in C++program
Data Concept of Data types; Built-in Data types: char, int, float
Types,Variables and double; Constants,Operators,Comments in C++,Access
and Constants Modifiers,Data type Modifiers,Programs using cin and
cout.
Constants: Integer Constants, Character Constants,
Floating Point Constants, String Constants.
Declaration/Initialization of variables,
Assignment statement; Type modifier: signed, unsigned,
long.
Operator and Operators: Arithmetic operators (-,+,*,/,%), Unary
Expressions: operator (-), Increment
(++) and Decrement (--) Operators, Relation operator
(>,>=,<=,=,!=), Logical operators (!,&&,II), Conditional
operator: <condition>?<if false>; Precedence of Operators;
Automatic type conversion
in expressions, Type casting; C++ shorthands (+=,-
=,*=,/=,%=)
Operator and Operators: Arithmetic operators (-,+,*,/,%), Unary
Expressions: operator (-), Increment
(++) and Decrement (--) Operators, Relation operator
(>,>=,<=,=,!=), Logical operators (!,&&,II), Conditional
operator: <condition>?<if false>; Precedence of Operators;
Automatic type conversion
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 12
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
in expressions, Type casting; C++ shorthands (+=,-
=,*=,/=,%=)
August Flow of Control Sequence , Selection, Iteration
Conditional statements:
if-else, Nested if,
Programs based on if else condition.
Flow of Control Switch..case..default,
Nested switch..case,
break statement (to be used in switch..case only);
Difference between if-else and switch case.
Flow of Control Practice programs on switch case and if
Loops: while ,
do - while , for
Flow of Control Loops Program Practice
Flow of Control Nested while loops
September Nested for loops
Jump statements
Revision
October Structured Data Derived Data Type,Need and Advantages of array.
Type: Array Declaratrion/initialisation of One dimensional array and
manipulation.
Programs based on one dimensional array.
Array Indices
Manipualtion of Array elements.
Sum of Array elements,product of Array
elements,Searching element in array,
Maximum and minimum in array.
String Manipulation-Declaration ,counting
vowels,digits,Special characters,reversing a
string,reversing each word
Multi Dimensional Array- Adding of two
arrays,manipulation of two dimensional arrays.
Multi Dimensional Array-Array of strings,Initialization
of array of strings,passing array to functions,passing
string to functions
November Programs on Matrices
Row total and Average
Column Total and Average
Diagonls(both)
Above and below Diagonal
Transpose
Marix multipication
November Mathematical and String and Character related Library functions: isalnum(),
Other Functions: isalpha(), isdigit(), islower(), isupper(),tolower(), toupper(),
strcpy(), strcat(), strlen(), strcmp(), strcmpi();
Header Files-math.h, stdlib.h;Functions: fabs(), log(),
log10(), pow(), sqrt(), sin(), cos(), abs(),
randomize(),random() ;
Programs based on standard functions
User Defined Defining a function; function prototype,
Functions
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 13
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
Invoking/calling a function, passing arguments to
function, specifying argument data types,
Default argument, constant argument, call by value,
call by reference, returning values from a function
Programs involving functions and arguments
December Functions and Calling functions with arrays, scope rules of
arrays functions and variables local and global variables;
Programs on Passing Arrays as arguments to functions
Programs on Passing Arrays as arguments to functions
December Structures What is astructure,Why structures,Defining and declaring
a structure,Referencing a structure elements,Nested
structures
January Structures Passing structures to functions,
Call by value,call by reference
Typedef,#define preprocessor Directive.
Programs based on structures
Mock Test starts
February
Mock Test
PROGRAMMING General Concepts; Modular approach; Clarity and
METHODOLOGY Simplicity of Expressions, Use of proper Names for
identifiers, Comments, Indentation; Documentation and
Program Maintenance; Running and Debugging programs,
Syntax Errors, Run-Time Errors, Logical Errors;
Problem Solving Methodology and Techniques
REVISION
BIOLOGY SYLLABUS
Month Unit CHAPTERS
I TERM
April & May I-Diversity of living organism 1.The Living World
2.Biological classification
July I-Diversity of living organism 3.Plant kingdom
4.Animal kingdom
August II-Structural organisation in 5. Morphology of flowering plants
plants and animals 6.Anatomy of flowering plants
7.Structural organisation in animals
September III- Cell:Structure and functions 8. Cell: The unit of life
Revision of 1st term syllabus
II TERM
October III cont. 9.Biomolecules
10.Cell cycle and cell division
IV- Plant physiology 11. Transport in plants
November IV cont. 12.Mineral nutrition
13.Photosynthesis in higher plants
14.Respiration in plants
15.Plant Growth and Development
December V- Human physiology 16.Digestion and absorption
17.Breathing and exchange of gases
18.Body fluid and circulation
19.Excretory products and their elimination
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 14
LANCER'S CONVENT
SESSION(2017-2018)
20.Locomotion and movement
Jan V - cont. 21.Neural control and coordinaton
22.Chemical coordination and integration
Feb Revision
CLASS XI SCIENCE SYLLABUS 15
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Class 11 MATHSDokumen2 halamanClass 11 MATHSAbhimanyu AbhirajBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Syl Lab UsDokumen8 halamanPhysics Syl Lab UsABHINAV KUMAR SHUKLABelum ada peringkat
- SYLLABUS DIVISION For CLASS XII MATHEMATICS BY SUDHANSU JALI SIRDokumen6 halamanSYLLABUS DIVISION For CLASS XII MATHEMATICS BY SUDHANSU JALI SIRsekharsudhansuBelum ada peringkat
- X + Cos X 1, For All X. Signs of Trigonometric Functions. Domain andDokumen3 halamanX + Cos X 1, For All X. Signs of Trigonometric Functions. Domain andPriya SatheeshBelum ada peringkat
- Math - 11-Split Up SyllabusDokumen3 halamanMath - 11-Split Up SyllabusAryan singhBelum ada peringkat
- D.A.V Public Schools, Jharkhand Zone-B Month-Wise Distribution of Syllabus Subject - English Class - XI Session - 2018-19Dokumen23 halamanD.A.V Public Schools, Jharkhand Zone-B Month-Wise Distribution of Syllabus Subject - English Class - XI Session - 2018-19kkBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Old New Class 11 Mathematics Revised Syllabus For Term - 1Dokumen2 halamanLesson Old New Class 11 Mathematics Revised Syllabus For Term - 1Suneeti AroraBelum ada peringkat
- On The Behavior of Multiple Zeta-Functions With Identical Arguments On The Real Line I Kohji Matsumoto, Ilija Tanackov - Kristian Seip-AistleitnerDokumen16 halamanOn The Behavior of Multiple Zeta-Functions With Identical Arguments On The Real Line I Kohji Matsumoto, Ilija Tanackov - Kristian Seip-AistleitnerSam TaylorBelum ada peringkat
- Math Group 3 55491Dokumen21 halamanMath Group 3 55491Trazona CabzBelum ada peringkat
- Logic ReportDokumen19 halamanLogic ReportEllen VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus 10 Mathematics Session 2023-24Dokumen10 halamanSyllabus 10 Mathematics Session 2023-24Geeta KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSDokumen1 halamanEdexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSMohammed Aayan PathanBelum ada peringkat
- SyllabusDokumen15 halamanSyllabusvedantacharya1829Belum ada peringkat
- Mathematics (860) : Class XiiDokumen8 halamanMathematics (860) : Class XiiUTKARSH TIWARIBelum ada peringkat
- The Riemann Hypothesis - Arithmetic and Geometry - Jeffrey C. LagariasDokumen16 halamanThe Riemann Hypothesis - Arithmetic and Geometry - Jeffrey C. Lagariasantonio.mm.neves5467Belum ada peringkat
- April17 2120178thgradeadvDokumen2 halamanApril17 2120178thgradeadvapi-327299670Belum ada peringkat
- Riemann Hypothesis - WikipediaDokumen15 halamanRiemann Hypothesis - Wikipediarapo73100% (3)
- Problems ITYM 2016Dokumen9 halamanProblems ITYM 2016Iustin SurubaruBelum ada peringkat
- Confident/Not Confident Checklist: Radian MeasureDokumen4 halamanConfident/Not Confident Checklist: Radian MeasurehdawgBelum ada peringkat
- The Class Schedule Clasa A VIII ADokumen5 halamanThe Class Schedule Clasa A VIII AJack BulletsBelum ada peringkat
- ISC Class 12 Mathematics Syllabus 2023 24Dokumen10 halamanISC Class 12 Mathematics Syllabus 2023 24Gowtham JayavarapuBelum ada peringkat
- Year PlansDokumen2 halamanYear Plansapi-571898884Belum ada peringkat
- ISC Mathematics XI RevisedDokumen8 halamanISC Mathematics XI RevisedDev KhariBelum ada peringkat
- STPM Maths T Sem 1 Chapter 2 Past Year QuestionsDokumen5 halamanSTPM Maths T Sem 1 Chapter 2 Past Year QuestionsKangJiaJiaBelum ada peringkat
- Jee Main 2024 Maths SyllabusDokumen8 halamanJee Main 2024 Maths Syllabusbholu803201Belum ada peringkat
- 11 Math Eng 2018Dokumen231 halaman11 Math Eng 2018Karuna SuriBelum ada peringkat
- Y9 Math WorksheetDokumen111 halamanY9 Math Worksheetanita_83Belum ada peringkat
- Second Semester Projects ExpandedDokumen2 halamanSecond Semester Projects Expandedsobre1982Belum ada peringkat
- GEC 04 Module 2 BeamerDokumen60 halamanGEC 04 Module 2 BeamerJonwille Mark CastroBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 7: Classification and Definition of Common Solid ShapesDokumen2 halamanUnit 7: Classification and Definition of Common Solid ShapesyitagesBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematic GemsDokumen1 halamanMathematic GemsGREEN BOXBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus Comparison - XII MathsDokumen4 halamanSyllabus Comparison - XII MathsSparsh SinghalBelum ada peringkat
- Negative FactorialDokumen9 halamanNegative FactorialWallace MonibidorBelum ada peringkat
- Jee Advance MathematicsDokumen2 halamanJee Advance MathematicssaravaBelum ada peringkat
- Linear AlgebraDokumen205 halamanLinear AlgebratebaaanBelum ada peringkat
- XII Syllabus With Deleted PartDokumen5 halamanXII Syllabus With Deleted PartlalithBelum ada peringkat
- Prermo Rmo SyllabusDokumen4 halamanPrermo Rmo Syllabus0926PlayerBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus 9 T0 12 Mathematics Session 2022-23Dokumen30 halamanSyllabus 9 T0 12 Mathematics Session 2022-23ARCHITA DHARBelum ada peringkat
- Test Schedule Maths-1Dokumen8 halamanTest Schedule Maths-1strategicsuryaBelum ada peringkat
- OCT 2 Syllabus - 5 SeptDokumen1 halamanOCT 2 Syllabus - 5 SeptrichaBelum ada peringkat
- 01 ArithmeticDokumen6 halaman01 ArithmetichongnhBelum ada peringkat
- Discovering Mathematics - Philipp LegnerDokumen29 halamanDiscovering Mathematics - Philipp Legnersj6pmc7zghBelum ada peringkat
- 11 SM 2017 Math Eng-1Dokumen222 halaman11 SM 2017 Math Eng-1nehabehlBelum ada peringkat
- Term - Wise Syllabus Session-2019-20 Class-VIII Subject: MathematicsDokumen53 halamanTerm - Wise Syllabus Session-2019-20 Class-VIII Subject: MathematicsDebayan MitraBelum ada peringkat
- Math FinalDokumen11 halamanMath Finalabirholmes2000Belum ada peringkat
- Random Matrices and L-FunctionsDokumen26 halamanRandom Matrices and L-FunctionsOliver TanBelum ada peringkat
- 2024 인천영재학교 미적분학 중간직보 3회 - 2024 - 04 - 06 - 09 - 58 - 37Dokumen55 halaman2024 인천영재학교 미적분학 중간직보 3회 - 2024 - 04 - 06 - 09 - 58 - 37khs0723skBelum ada peringkat
- AP AB ManualDokumen53 halamanAP AB ManualStanleyBelum ada peringkat
- Math 4 - 3RDQDokumen23 halamanMath 4 - 3RDQMark Anthony EspañolaBelum ada peringkat
- Isc Class12 Maths SyllabusDokumen9 halamanIsc Class12 Maths Syllabusviveksahu47156Belum ada peringkat
- Unpacking of Most Essential Learning Competencies Mathematics 8 First QuarterDokumen3 halamanUnpacking of Most Essential Learning Competencies Mathematics 8 First Quartergarry casipitBelum ada peringkat
- Screenshot 2021-12-03 at 8.16.46 PMDokumen192 halamanScreenshot 2021-12-03 at 8.16.46 PMLavalina PatraBelum ada peringkat
- ISC 12 Mathematics SyllabusDokumen8 halamanISC 12 Mathematics Syllabussupercell.mail.helpshift.sharingBelum ada peringkat
- MMW Modules 1 and 2Dokumen4 halamanMMW Modules 1 and 2GraceGolimlimBelum ada peringkat
- Afda Vocab Cards 2016Dokumen143 halamanAfda Vocab Cards 2016Hatice A. GürhanoğluBelum ada peringkat
- Stage 1-Desired Results: Established GoalsDokumen35 halamanStage 1-Desired Results: Established GoalsMark Anthony EspañolaBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To Real Analysis - (3 Real Numbers)Dokumen10 halamanAn Introduction To Real Analysis - (3 Real Numbers)FaisBelum ada peringkat
- Annexure 1. A. 1 Cbse - GR 10 Prelim Exam Portion 23 24Dokumen27 halamanAnnexure 1. A. 1 Cbse - GR 10 Prelim Exam Portion 23 24deeptiBelum ada peringkat
- Hadamard Matrix Analysis and Synthesis With Applications To Communications and Signal Image ProcessingDokumen119 halamanHadamard Matrix Analysis and Synthesis With Applications To Communications and Signal Image ProcessingEmerson MaucaBelum ada peringkat
- Paul Smitson Riddle of The Distorted BTODokumen56 halamanPaul Smitson Riddle of The Distorted BTOU862Belum ada peringkat
- Khayyam & His Solutions of The CubicDokumen4 halamanKhayyam & His Solutions of The Cubicfelipe_cruz_6Belum ada peringkat
- 01 GeoStrucAnal Cylinder Elastic PDFDokumen12 halaman01 GeoStrucAnal Cylinder Elastic PDFSiddhant KaushikBelum ada peringkat
- Class - VI Mathematics (Ex. 11.1) QuestionsDokumen2 halamanClass - VI Mathematics (Ex. 11.1) Questionse625796Belum ada peringkat
- Combur 10 M 100 STR - EsDokumen2 halamanCombur 10 M 100 STR - EsVictor Manuel Parra Torres50% (4)
- Module 9 - RoboticsDokumen20 halamanModule 9 - RoboticsdharshanirymondBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Mod 3Dokumen15 halamanLecture Mod 3amlan sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Deleuze and The Genesis of Form PDFDokumen6 halamanDeleuze and The Genesis of Form PDFRoman RuizBelum ada peringkat
- Backward EulerDokumen2 halamanBackward EulerCherry JyotshnaBelum ada peringkat
- M.Tech Geotechnical Engineering Syllabus PDFDokumen13 halamanM.Tech Geotechnical Engineering Syllabus PDFernestnsabimana74Belum ada peringkat
- INDÍSE LosssssssssssssssDokumen4 halamanINDÍSE LosssssssssssssssDarioBelum ada peringkat
- Facts: High-Speed Research - The Tu-144LL: A Supersonic Flying LaboratoryDokumen4 halamanFacts: High-Speed Research - The Tu-144LL: A Supersonic Flying LaboratoryNASAdocumentsBelum ada peringkat
- Report Lab 109: One Dimensional MotionDokumen3 halamanReport Lab 109: One Dimensional MotionBalthazar Torres0% (1)
- Lect 1Dokumen19 halamanLect 1Kong DuiDuiBelum ada peringkat
- (1967) How Safe Are Our Large Reinforced Concrete Beams PDFDokumen14 halaman(1967) How Safe Are Our Large Reinforced Concrete Beams PDFMohammad AshrafyBelum ada peringkat
- Parachute Lab ReportDokumen4 halamanParachute Lab ReportNathan T. Cheung100% (2)
- Heat Conduction Composite WallDokumen22 halamanHeat Conduction Composite WallMoosa NaseerBelum ada peringkat
- GR From LI 2Dokumen14 halamanGR From LI 2Shreya ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Jan7 & Jan12Dokumen53 halamanLecture Jan7 & Jan12armon_domingoBelum ada peringkat
- Low Voltage Distribution Transformers - Single Phase - EE25S3H PDFDokumen4 halamanLow Voltage Distribution Transformers - Single Phase - EE25S3H PDFGalih TrisnanugrahaBelum ada peringkat
- IWCF Mark PDFDokumen175 halamanIWCF Mark PDFDanish Khan100% (2)
- Power Amplifier Application NoteDokumen3 halamanPower Amplifier Application NoteSanthos KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Fiziks: Institute For NET/JRF, GATE, IIT JAM, M.Sc. Entrance, JEST, TIFR and GRE in Physics Optics JEST 2013Dokumen4 halamanFiziks: Institute For NET/JRF, GATE, IIT JAM, M.Sc. Entrance, JEST, TIFR and GRE in Physics Optics JEST 2013shubham varudkarBelum ada peringkat
- Manual D12RDokumen179 halamanManual D12RHennis Alfonzo100% (1)
- European Adhesives HandbookDokumen70 halamanEuropean Adhesives Handbooksam071122701Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Process Engineering SkillsDokumen9 halamanIntroduction To Process Engineering SkillsJia Kai LowBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Solar Tracker With Dust Wiper Using PID ControllerDokumen6 halamanAutomatic Solar Tracker With Dust Wiper Using PID ControllerEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- Medina 2018 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1065 082002Dokumen5 halamanMedina 2018 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1065 082002boborg8792Belum ada peringkat
- COMSOL ApplicationLibraryManualDokumen390 halamanCOMSOL ApplicationLibraryManualJessicaTorresRedondoBelum ada peringkat