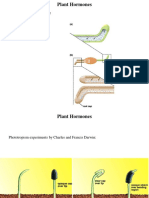
Plant Hormones Location Specific Function
Diunggah oleh
MC Aberca0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
9 tayangan1 halamanBiology
Judul Asli
BIO2
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniBiology
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
9 tayangan1 halamanPlant Hormones Location Specific Function
Diunggah oleh
MC AbercaBiology
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
Al Jhun M.
Aberca 3/2/18
G12 – Campos
Plant Hormones Location Specific Function
AUXIN stem, buds, and root tips promote stem elongation, inhibit growth of
lateral buds (maintains apical dominance).
Auxin also plays a role in maintaining apical
dominance.
GIBBERELLIN plant cell's plastids, or the regulate growth and influence various
double membrane-bound developmental processes, including stem
organelles responsible for elongation, germination, dormancy, flowering,
making food, sex expression, enzyme induction, and leaf and
fruit senescence.
CYTOKININ meristems at tip of the shoot. promote cell division in plant roots by
stimulating the process of mitosis and shoots
and the growth of buds.
ETYLENE Ripe fruits serves as a hormone in plants. It acts at trace
levels throughout the life of the plant by
stimulating or regulating the ripening of fruit,
the opening of flowers, and the abscission (or
shedding) of leaves.
ABSCISIC ACID Stomata promotes seed dormancy by inhibiting cell
growth. It is also involved in opening and
closing of stomata as leaves wilt.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Letter To PredecessorDokumen2 halamanLetter To PredecessorMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Name of Endocrine Gland Hormones Specific Function: Al Jhun M. Aberca ' 3/2/18 G12 - CamposDokumen1 halamanName of Endocrine Gland Hormones Specific Function: Al Jhun M. Aberca ' 3/2/18 G12 - CamposMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Letter To PredecessorDokumen2 halamanLetter To PredecessorMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Topic: Plant Growth Regulators: Subject: Pharmacognosy Prepared By: Urooj UmerDokumen4 halamanTopic: Plant Growth Regulators: Subject: Pharmacognosy Prepared By: Urooj UmerUrooj UmerBelum ada peringkat
- Cogollodo - Plant Hormones AssignmentDokumen5 halamanCogollodo - Plant Hormones AssignmentShaira CogollodoBelum ada peringkat
- Plant HormonesDokumen2 halamanPlant HormonesNikko Gabriel AquinoBelum ada peringkat
- Plant HormonesDokumen3 halamanPlant Hormonesministore kmcBelum ada peringkat
- Bio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Dokumen12 halamanBio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Amar SafwanBelum ada peringkat
- BIO109P Module 4. Plant HormonesDokumen48 halamanBIO109P Module 4. Plant HormonesJet DelimaBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Materials Growth and DevelopmentDokumen6 halamanTeaching Materials Growth and DevelopmentAndi NurhidayahBelum ada peringkat
- Plant HormonesDokumen2 halamanPlant HormonesKhylene Zhen MARQUEZBelum ada peringkat
- The Plant Cell Wall: Growth and DevelopmentDokumen29 halamanThe Plant Cell Wall: Growth and DevelopmentbeneBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 6 FITOHORMONEDokumen23 halamanBab 6 FITOHORMONEnormaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 3Dokumen3 halamanAssignment 3abdullamalek339Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture-9 Growth HormonesDokumen14 halamanLecture-9 Growth HormonesFaith MasalilaBelum ada peringkat
- S.No Plant Hormones Composition: FunctionsDokumen1 halamanS.No Plant Hormones Composition: FunctionsAngelin JacobBelum ada peringkat
- Folio 1 Biology STPM Sem 2Dokumen5 halamanFolio 1 Biology STPM Sem 2陈凯雯Belum ada peringkat
- Control and Coordination Control and Coordination Control and CoordinationDokumen3 halamanControl and Coordination Control and Coordination Control and CoordinationaaaBelum ada peringkat
- Plant GrowthDokumen33 halamanPlant GrowthDave SmtBelum ada peringkat
- Fistum2 HormonDokumen7 halamanFistum2 HormondorynemoBelum ada peringkat
- 1plant Growth and DevelopmentDokumen8 halaman1plant Growth and Developmentadityaaggarwal821Belum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDokumen5 halamanPlant Growth RegulatorsNishamolKSBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth Regulators (2014)Dokumen34 halamanPlant Growth Regulators (2014)matthewBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 PLANTDokumen3 halamanChapter 4 PLANTSedsed QuematonBelum ada peringkat
- Crop - Lecture - Growth HormonesDokumen9 halamanCrop - Lecture - Growth HormonesCynel DelaBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDokumen28 halamanPlant Growth RegulatorsFaishol MuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- 65322aa09c03ac0018698fa9 ## Plant Growth and Development Short NotesDokumen2 halaman65322aa09c03ac0018698fa9 ## Plant Growth and Development Short Notesgohilsumit5050Belum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth, Development and Life CycleDokumen19 halamanPlant Growth, Development and Life CycleCeazar Ian PesimoBelum ada peringkat
- FaizDokumen2 halamanFaizFaiz ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDokumen29 halamanPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionJodd Ardee TorresBelum ada peringkat
- Group 6 Plant HormonesDokumen13 halamanGroup 6 Plant HormonesJv Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Plants: Growth and DevelopmentDokumen17 halamanPlants: Growth and Developmentmiss uBelum ada peringkat
- MidtemDokumen6 halamanMidtemkhahoaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Coordination in Plants Class 10 ICSE NotesDokumen6 halamanChemical Coordination in Plants Class 10 ICSE NotesSamarth BandodkarBelum ada peringkat
- Plant StimulatorsDokumen19 halamanPlant Stimulatorskane likBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth Hormonesbotany 2.4Dokumen7 halamanPlant Growth Hormonesbotany 2.4nitesh.th15005Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 - Plant HormonesDokumen49 halamanChapter 8 - Plant Hormonessayidah nafisah100% (2)
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDokumen30 halamanPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionTeguh SaputraBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Hormones - NotesDokumen8 halamanPlant Hormones - Notesspotter178195Belum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth Regulators (PGRS) : Gibberella Fujikuroi Gibberellic Acid Was Later Isolated From The FungusDokumen4 halamanPlant Growth Regulators (PGRS) : Gibberella Fujikuroi Gibberellic Acid Was Later Isolated From The FungusvertebratesBelum ada peringkat
- Control and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTDokumen19 halamanControl and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTArpithaBelum ada peringkat
- CRSC 5 - Guerrero Macy G.Dokumen7 halamanCRSC 5 - Guerrero Macy G.RanielJohn CollantesBelum ada peringkat
- Plant HormoneDokumen31 halamanPlant HormoneChristine De GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Outline The Application of Plant Growth Regulators (Synthetic Auxin, Synthetic Gibberellins, Synthetic Ethylene) in AgricultureDokumen3 halamanOutline The Application of Plant Growth Regulators (Synthetic Auxin, Synthetic Gibberellins, Synthetic Ethylene) in AgricultureArichandranMuniandyBelum ada peringkat
- Plant HormonesDokumen9 halamanPlant Hormonesbravohr98100% (1)
- Plant Hormones SummaryDokumen11 halamanPlant Hormones SummaryRamesh Kumar MuniandyBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 4Dokumen10 halamanActivity 4Kalea Kassandra MatthewsBelum ada peringkat
- Plant HormonesDokumen40 halamanPlant HormonesAhmed ImranBelum ada peringkat
- Ass in Gen BioDokumen4 halamanAss in Gen BioDivine PadillaBelum ada peringkat
- Peran Hormon Pada Pertumbuhan Dan Perkembangan TumbuhanDokumen39 halamanPeran Hormon Pada Pertumbuhan Dan Perkembangan TumbuhanMuhammad Naufal IndriatmokoBelum ada peringkat
- Phyto HormonesDokumen15 halamanPhyto HormonesrithanBelum ada peringkat
- PHYTOHORMONESDokumen39 halamanPHYTOHORMONESshiyas100% (7)
- Plant HormonesDokumen61 halamanPlant HormonesKarylle Chloe MarceloBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment - Plant PhyDokumen7 halamanAssignment - Plant PhyTrucBelum ada peringkat
- Sevilla - Activity 2 - Cassci 1BDokumen3 halamanSevilla - Activity 2 - Cassci 1BJoyce SevillaBelum ada peringkat
- Phytohormones: Presented By:-ShiyasDokumen39 halamanPhytohormones: Presented By:-ShiyaserikabeltranBelum ada peringkat
- c12 BioDokumen3 halamanc12 BioNur Anisha Binti Mohd AzmyBelum ada peringkat
- Two Faces of One Seed: Hormonal Regulation of Dormancy and GerminationDokumen12 halamanTwo Faces of One Seed: Hormonal Regulation of Dormancy and Germinationsalma sabilaBelum ada peringkat
- Bio270 Tutorial Week 12Dokumen1 halamanBio270 Tutorial Week 12Mirza KarmilaBelum ada peringkat
- 9.plant HarmonesDokumen6 halaman9.plant HarmonesRAVINDRA PRASADBelum ada peringkat
- P3 OrganogenesisDokumen13 halamanP3 OrganogenesisPanca Ayu VirgirlBelum ada peringkat
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3Dari EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3Belum ada peringkat
- Volcano HazardsDokumen1 halamanVolcano HazardsMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- IAS12Dokumen2 halamanIAS12JCPAJOBelum ada peringkat
- The Mystery of MathematicsDokumen2 halamanThe Mystery of MathematicsMC Aberca100% (2)
- PSA-620 Using The Work of An Auditor's ExpertDokumen19 halamanPSA-620 Using The Work of An Auditor's ExpertcolleenyuBelum ada peringkat
- Al Jhun M. Aberca 8/ 7 /17 G12 - Campos: Iii. Discussion / EvaluationDokumen2 halamanAl Jhun M. Aberca 8/ 7 /17 G12 - Campos: Iii. Discussion / EvaluationMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- PSA-620 Using The Work of An Auditor's ExpertDokumen19 halamanPSA-620 Using The Work of An Auditor's ExpertcolleenyuBelum ada peringkat
- Balance Sheet Dec FinalDokumen2 halamanBalance Sheet Dec FinalMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Income Statement Dec FinalDokumen2 halamanIncome Statement Dec FinalMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Group GryffindorDokumen5 halamanGroup GryffindorMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- General Ledger Dec FinalDokumen8 halamanGeneral Ledger Dec FinalMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Date Last Price Change %change Open Low Hig H Net ForeignDokumen3 halamanDate Last Price Change %change Open Low Hig H Net ForeignMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- SPACE MatrixDokumen1 halamanSPACE MatrixMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Limit Properties: Calculus Analysis Function InputDokumen5 halamanLimit Properties: Calculus Analysis Function InputMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Psa 120 PDFDokumen9 halamanPsa 120 PDFMichael Vincent Buan SuicoBelum ada peringkat
- AnnouncementDokumen2 halamanAnnouncementMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Engagement Partner: Phase 1 - Preliminary Planning A. Identify Issue or ConcernDokumen8 halamanEngagement Partner: Phase 1 - Preliminary Planning A. Identify Issue or ConcernMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Mcdonald'S Corporation: A Brief HistoryDokumen15 halamanMcdonald'S Corporation: A Brief HistoryMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Reviewer Comp-OODBMSDokumen5 halamanReviewer Comp-OODBMSMC Aberca100% (1)
- Preformatted Data Entry Screens: Prenumbered DocumentsDokumen4 halamanPreformatted Data Entry Screens: Prenumbered DocumentsMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Harer & Jones Standard Audit Team StructureDokumen2 halamanHarer & Jones Standard Audit Team StructureMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Plain EnglishDokumen7 halamanPlain EnglishMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Malcolm BaldrigeDokumen7 halamanMalcolm BaldrigeMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Date Last Price Change %change Open Low Hig H Net ForeignDokumen3 halamanDate Last Price Change %change Open Low Hig H Net ForeignMC AbercaBelum ada peringkat
- Daedalus and IcarusDokumen5 halamanDaedalus and IcarusAnneNosa0% (1)