Acute Medicine: Shock: Inadequate Tissue and Organ Perfusion
Diunggah oleh
myat252Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Acute Medicine: Shock: Inadequate Tissue and Organ Perfusion
Diunggah oleh
myat252Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
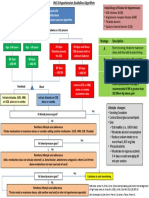
Acute Medicine: Shock Hypovolaemic Shock
Definition – inadequate tissue and organ perfusion leading to a hypoperfusion state & eventual Invxs FBC - Hct in acute alcoholic binge due to diuresis. Hct is an Inaccurate
cellular hypoxia and its attendant sequelae. marker of bld loss acutely.
GXM 6 units
S/S: Hypotension, urine output, tachycardia, diaphoresis, AMS U/E/Cr
Troponin T & Cardiac enzymes
Coagulation profile with DIVC screen (PT/PTT, pltlet, D-dimer)
Types of Shock ABG – metab acidosis, lactate, base deficits are poor Px factors
‘White’ shock ‘Red’ shock UPT - ?ectopic pregnancy? Ask for LMP
Types Hypovolaemic Cardiogenic Neurogenic Septic Anaphylactic Examine abdomen for pulsatile AAA
Causes Haemorrhage AMI Spinal injury Infxns Fluid Rx 1 L crystalloid fast infusion w/in 1 hr
Burns Dysrhythmia Assess response
Ruptured ectopic Subsequent colloid or whole blood infusion
pregnancy CVP line Used to guide fluid Rx, esp in CCF patients
Severe GE
Acute pancreatitis
S/S Pallor Pallor Warm skin Fever, rigors Fever, rigors Cardiogenic Shock
Cold clammy skin Cold clammy N/ heart Warm skin Warm skin ECG Manage accordingly – refer acute coronary syndrome &
peri vas skin rate Trop T & cardiac enzymes ACLS notes
peri vas Neuro deficit
Invxs Hct (late) Cardiac FBC
enzymes Bld C/S Neurogenic Shock
ECG Hx/PE Trauma – site, mechanism, force
Neuro exam, DRE – document initial neurological deficits
Also, Obstructive Shock due to tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade or pulmonary Immobilize Immobilize spine in neutral position
embolism Invxs C-spine X-ray (AP & lat) – ensure visualization up to C7/T1 junction
Swimmer’s view (visualize C7/T1 jn) & open mouth view (visualize C1/2
Management
injury)
Thoracic & lumbar spine X-ray (AP & lat)
General Mx
CT scan
Airway Maintain airway – consider intubation if necessary
MRI later
Breathing 100% O2 via non-rebreather mask
Fluid Rx Titrate fluid resus with urine output
Circulation 2 large bore (14-16G) cannulae
vasopressors if BP does not respond to fluid challenge
Inotropic support
IV methyl 30 mg/kg over 15mins, followed by 5.4mg/kg/h for nxt 23 hrs
o IV dopamine 5-10g/kg/min Indications – non-penetrating spinal cord injury & w/in 8 hrs of injury
prednisolone
o IV dobutamine 5-10g/kg/min (esp for cardiogenic shock) Contraindications
o IV norepinephrine 5-20g/kg/min (esp for septic shock) o <13YO
Monitoring Pulse oximetry o pregnancy
ECG o mild injury of the cauda equina / nerve root
BP o abdominal trauma present
Heart rate o major life-threatening morbidity
Urine output – catheterize patient
Disposition Refer Ortho / NeuroSx
DGIM – Last updated March 2005
o Complete IVC ligation or partial caval interruption
Obstructive Shock
Tension Decompression: insert 14G cannula over 2nd intercostals space in mid-
Pneumothorax clav. Line Septic Shock
Cardiac IV fluid bolus 500ml N/S Sepsis = 2 of the following present:
tamponade IV dopamine infusion 5g/kg/min o Temp >38 or <36oC
Prepare for pericardiocentesis o HR > 90bpm
Pul Embolism Invx o RR > 20 breaths/min OR PaCO2<32mmHg
FBC o WCC>12000/mm3, <4000/mm3,or >10% immature forms
GXM 6 units Hx / PE Identify site of infxn – UTI (indwelling cathether), gallbladder dz, peritonitis,
U/E/Cr pneumonia, appendicitis, immunocompromised state
DIVC screen (D-dimer) Invx FBC - TW
ABG U/E/Cr
o PaO2 & N/ PaCO2 DIVC screen – PT/PTT, pltlet, fibrinogen, D-dimer
o widened alveolo-arterial P02 gradient (AaPO2 >20mmHg) Bld C/S (2 different sites)
ECG (may be normal) Capillary bld glucose
o non-specific ST depression & T wave inversion ABG
o Sinus tachycardia CXR – pneumonia, ARDS
o Right heart strain ECG
Urine dipstick – UTI
Right axis deviation
Urine C/S
Transient RBBB
T wave inversion in V1-3 Fluid Rx Rapid infusion 1-2L crystalloids
P pulmonale CVP line insertion
S1Q3T3 Inotropic if no response to fluid Rx
o Exclude DDxes – MI, pericarditis support Noradrenaline (drug of choice) - 1g/kg/min OR
CXR (may be normal) Dopamin 5-20g/kg/min
o Westermark sign – oligaemic lung fields Empirical ABx Immunocompetent w/o obvious 3rd gen cephalosporin (IV ceftriaxone
o Pul infarcts – wedge shape opacities w apex pointing source 1g) OR
towards the hilum Quinolones (ciprofloxacin 200mg)
o Atelectasis Immunocompromised w/o Anti-pseudomonal ABx (IV ceftazidime
o Pleural effusions obvious source 1g) OR
o Raised diaphragm Quinolone
PLUS aminoglycoside (Gentamicin
o Consolidation
80mg)
o ‘Plump’ pul. arteries
Gram-positive (burns, FB / lines IV cefazolin 2g
o Exclude DDxes – pneumothorax, pneumonia, L heart present) IV vancomycin 1g if hx of IVDA,
failure, tumour, rib #, massive pleural effusion, lobar indwelling cath. Or penicillin allergy
collapse Anaerobic source (intra-abdo, IV metronidazole 500mg + ceftriazone
Spiral CT, Echo, MRI, lung scintigraphy, pulmonary angiogram (gold std) biliary, female genital tract, 1g + IV gentamicin 80mg
aspiration pneumonia)
Rx
Pain relieve – use Opioids with caution
Fluid Rx & inotropic support if haemodynamically unstable
Anticoagulation Rx:
o IV heparin 5000U bolus or SC fraxiparine (0.4ml if <50kg;
0.5ml if 50-65kg; 0.6ml if >65kg)
o Convert to Oral warfarin later
Thrombolysis
o Intra pul. arterial urokinase fro 12-24 hrs
Surgical
DGIM – Last updated March 2005
Anaphylactic Shock
Definitions
Urticaria – oedematous & pruritic plaques w pale centre & raised edges
Angioedema – oedema of deeper layers of the skin. Non-pruritic. May be a/w numbness & pain
Anaphylaxis – severe systemic allergic rxn to an Ag. Ppt by abrupt release of chemical
mediators in a previously sensitized patient
Anaphylactoid rxn – resembles anaphylactic rxn, but due to direct histamine release from mast
cells w/o need for prior sensitization
Common causes
Drugs – penicililns & NSAIDS commonest, aspirin, TCM, sulpha drugs
Food – shellfish, egg white, peanuts
Venoms – bees, wasps, hornets
Environment – dust, pollen
Infections – EBV, HBV, coxsackie virus, parasites
Stop Pptant Stop administration of suspected agent / flick out insect stinger with tongue
blade
Gastric lavage & activated charcoal if drug was ingested
Airway Prepare for intubation or cricothyroidectomy – ENT/Anaesthesia consult
Fluid Rx 2L Hartman’s or N/S bolus
Drug Rx Adrenaline Normotensive – 0.01ml/kg (max 0.5ml) 1:1000 dilution
SC/IM
Hypotensive – 0.1ml/kg (max 5ml) 1:10,000 dilution IV
over 5 mins
Glucagon Indications: failure of adrenaline Rx OR if adrenaline is
contraindicated eg IHD, severe HPT, pregnancy, -blocker
use
0.5-1.0mg IV/IM. Can be repeated once after 30mins
Antihistamines Diphenhydramine 25mg IM/IV
Chlorpheniramine 10mg IM/IV
Promethazine 25mg IM/IV
Cimetidine For persistent symptoms unresponsive to above Rx
200-400mg IV bolus
Nebulised for persistent bronchospasm
bronchodilator Salbutamol 2:2 q20-30mins
Corticosteroids Hydrocortisone 200-300mg IV bolus, q 6hr
DGIM – Last updated March 2005
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Internal Medicine NBME Form 3 ExplanationsDokumen11 halamanInternal Medicine NBME Form 3 ExplanationssasghfdgBelum ada peringkat
- POPS PretestDokumen6 halamanPOPS Pretestkingjameson1Belum ada peringkat
- Assessment Cover Sheet: Student To Complete Please Read The Below CarefullyDokumen25 halamanAssessment Cover Sheet: Student To Complete Please Read The Below CarefullyNoreen Punjwani100% (1)
- Medical Triads, Tetrads, and PentadsDokumen10 halamanMedical Triads, Tetrads, and PentadsAyessa BandalBelum ada peringkat
- Main Dip Step 2ck Notes Info Doc - Read OnlyDokumen305 halamanMain Dip Step 2ck Notes Info Doc - Read Only[161]Shuaib AktherBelum ada peringkat
- Medicine 1 Final Practical Exam ReviewerDokumen10 halamanMedicine 1 Final Practical Exam ReviewerTP RMadBelum ada peringkat
- Ethicon Wound Closure Manual - (February 2004)Dokumen127 halamanEthicon Wound Closure Manual - (February 2004)7052XX100% (1)
- Picot Research Paper - MullenDokumen16 halamanPicot Research Paper - Mullenapi-596714348Belum ada peringkat
- Incentive SpirometerDokumen25 halamanIncentive SpirometerAnalyn Salvacion100% (2)
- JI Chart OrdersDokumen4 halamanJI Chart OrdersMel BillonesBelum ada peringkat
- EndoDokumen8 halamanEndoSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioBelum ada peringkat
- Medicine Review 2018 1Dokumen470 halamanMedicine Review 2018 1Norjetalexis Maningo CabreraBelum ada peringkat
- B - Embyrology HomologuesDokumen1 halamanB - Embyrology HomologuesS ParekhBelum ada peringkat
- Amazing Esqs With Answers Pediatrics-ShelfDokumen31 halamanAmazing Esqs With Answers Pediatrics-ShelfDrSajid BuzdarBelum ada peringkat
- History Physical FormatDokumen3 halamanHistory Physical FormatfilchibuffBelum ada peringkat
- DeVirglio NotesDokumen77 halamanDeVirglio NotesAlvand SehatBelum ada peringkat
- Simplified Diagnostic Approach in Acute HepatitisDokumen2 halamanSimplified Diagnostic Approach in Acute HepatitisJohn Christopher LucesBelum ada peringkat
- Internal MedicineDokumen83 halamanInternal MedicineSumbul PBelum ada peringkat
- MED2 5.02 Oncologic Emergencies - Dr. F. AdefuinDokumen5 halamanMED2 5.02 Oncologic Emergencies - Dr. F. AdefuinAra DiocosBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatal Case Presentation 2Dokumen6 halamanNeonatal Case Presentation 2Rabi SyedBelum ada peringkat
- New Intern Guide Quick NotesDokumen8 halamanNew Intern Guide Quick NotesTrisBelum ada peringkat
- Correlative AnatomyDokumen19 halamanCorrelative AnatomyLicensed to HealBelum ada peringkat
- OSCE Reviewer 2013Dokumen4 halamanOSCE Reviewer 2013rere choiBelum ada peringkat
- Part IIDokumen64 halamanPart IIhussainBelum ada peringkat
- West Notes-1 PDFDokumen17 halamanWest Notes-1 PDFSerious LeoBelum ada peringkat
- Medicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver2Dokumen4 halamanMedicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver2TrisBelum ada peringkat
- Mo Intern Handbook - FinalDokumen37 halamanMo Intern Handbook - FinalGideon K. MutaiBelum ada peringkat
- Dem Tickler NotesDokumen1 halamanDem Tickler NotesSeff CausapinBelum ada peringkat
- General Population (No Diabetes or CKD) Diabetes or CKD PresentDokumen1 halamanGeneral Population (No Diabetes or CKD) Diabetes or CKD PresentMuthia ArsilBelum ada peringkat
- 22 Disritmia 2018Dokumen60 halaman22 Disritmia 2018Nur akilaBelum ada peringkat
- MTB Cardiology NotesDokumen11 halamanMTB Cardiology Noteskabal321Belum ada peringkat
- Aquifer InternalMedicine11 - 45Dokumen8 halamanAquifer InternalMedicine11 - 45JulieBelum ada peringkat
- 2011-09 - Ob-GynDokumen24 halaman2011-09 - Ob-Gynsahilius100% (1)
- Basic ECG For Refresher Course 2014Dokumen116 halamanBasic ECG For Refresher Course 2014Winz DolleteBelum ada peringkat
- GI Signs and SymptomsDokumen40 halamanGI Signs and SymptomsJohnny BeeBelum ada peringkat
- CPG DyslipidemiaDokumen26 halamanCPG DyslipidemiaRenzy SalumbreBelum ada peringkat
- 24 HR History 2Dokumen2 halaman24 HR History 2Arjun KatariaBelum ada peringkat
- Junior Intern NotesDokumen3 halamanJunior Intern NotesTin SumangaBelum ada peringkat
- JI RevalidaDokumen61 halamanJI RevalidaAren LingadBelum ada peringkat
- Mark Tuttle Neurology Clerkship Study Guide PDFDokumen84 halamanMark Tuttle Neurology Clerkship Study Guide PDFDavid ChangBelum ada peringkat
- Ob GynDokumen4 halamanOb Gynroserem2000Belum ada peringkat
- أدوية الطوارىءDokumen162 halamanأدوية الطوارىءManar22Belum ada peringkat
- SketchyPath ChecklistDokumen1 halamanSketchyPath ChecklistFajar Raza100% (1)
- HY Mixed USMLE Review Part I 1Dokumen20 halamanHY Mixed USMLE Review Part I 1Jennifer Ross-ComptisBelum ada peringkat
- Shock PresentationDokumen20 halamanShock Presentationrosalyn sugayBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical ExaminationDokumen11 halamanClinical ExaminationMavra zBelum ada peringkat
- GYNECOLOGY Chief ComplaintsDokumen3 halamanGYNECOLOGY Chief ComplaintsJennifer HerediaBelum ada peringkat
- USMLE Step 3 ER PDFDokumen12 halamanUSMLE Step 3 ER PDFlalaBelum ada peringkat
- Obstetric FormDokumen4 halamanObstetric FormKhylamarie VillalunaBelum ada peringkat
- IMDokumen128 halamanIMShaz ChindhyBelum ada peringkat
- Cheat Sheet (Draft)Dokumen3 halamanCheat Sheet (Draft)bonziebuddyBelum ada peringkat
- OB Med Order KodigsDokumen1 halamanOB Med Order KodigsfloramaeyecyecBelum ada peringkat
- IM NotesDokumen79 halamanIM NotesInri Dumlao100% (1)
- A Case of C.SDokumen85 halamanA Case of C.Sนีล ไบรอันBelum ada peringkat
- Poliomyelitis Haemophilus Influenzae Type B VariecellaDokumen4 halamanPoliomyelitis Haemophilus Influenzae Type B VariecellaJeanna Chong100% (1)
- 2020 Apr Common Treatment OrdersDokumen32 halaman2020 Apr Common Treatment OrdersAlistair LauBelum ada peringkat
- Aquifer InternalMedicine09 - 55Dokumen7 halamanAquifer InternalMedicine09 - 55JulieBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatology I: Pediatrics 1.1Dokumen15 halamanNeonatology I: Pediatrics 1.1Kurt ZepedaBelum ada peringkat
- Fabella NotesDokumen96 halamanFabella NotesAndrassy Twinkle AlineaBelum ada peringkat
- Pedia HXDokumen3 halamanPedia HXeyakoyBelum ada peringkat
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyDari EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisBelum ada peringkat
- Catheterisation OSCE Mark SchemeDokumen2 halamanCatheterisation OSCE Mark Schememyat252Belum ada peringkat
- AnovaDokumen80 halamanAnovamyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Ampullary CADokumen11 halamanAmpullary CAmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Gallbladdercancer: Diagnosis, Surgical Management, and Adjuvant TherapiesDokumen19 halamanGallbladdercancer: Diagnosis, Surgical Management, and Adjuvant Therapiesmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Asa Physical Status Classification SystemDokumen1 halamanAsa Physical Status Classification Systemmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- NG InsertionDokumen3 halamanNG Insertionmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Example of Bad Answer: Press The Number of The Question To Get The AnswerDokumen12 halamanExample of Bad Answer: Press The Number of The Question To Get The Answermyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Anaemia - B12 and Folate Deficiency: SummaryDokumen16 halamanAnaemia - B12 and Folate Deficiency: Summarymyat252100% (1)
- Benko Gambit Move by MoveDokumen189 halamanBenko Gambit Move by Movemyat25290% (10)
- Samsung Galaxy Tab s4 MANUALDokumen159 halamanSamsung Galaxy Tab s4 MANUALmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Ent Notes Moammed AteegDokumen39 halamanEnt Notes Moammed Ateegmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- CAPD PeritonitisDokumen1 halamanCAPD Peritonitismyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen62 halamanNervous Systemmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Duplex Scan Kidneys: Abdo USSDokumen1 halamanDuplex Scan Kidneys: Abdo USSmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- NICE SummariesDokumen21 halamanNICE Summariesmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Acinetobacter PDFDokumen1 halamanAcinetobacter PDFmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Bone Marrow Transplant - Pulmonary ComplicationsDokumen1 halamanBone Marrow Transplant - Pulmonary Complicationsmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Adjunctive Respiratory TherapiesDokumen1 halamanAdjunctive Respiratory Therapiesmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Chronic Disease MXDokumen263 halamanChronic Disease MXmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Opthamology AKT Study This Set Online atDokumen6 halamanOpthamology AKT Study This Set Online atmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Surgery FinalADokumen102 halamanSurgery FinalAvaegmundig100% (1)
- Surgery Shock PDFDokumen9 halamanSurgery Shock PDFmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- CSA ABC 50 Top Tips To Pass The CSADokumen25 halamanCSA ABC 50 Top Tips To Pass The CSAmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- SurgeryDokumen48 halamanSurgerymyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Oncology AKT Study This Set Online atDokumen1 halamanOncology AKT Study This Set Online atmyat252Belum ada peringkat
- MeningitisDokumen2 halamanMeningitismyat252Belum ada peringkat
- Complete MRCGP Revision GuideDokumen45 halamanComplete MRCGP Revision Guidemyat2520% (3)
- Fauci Dossier Valentine S Day Document 2022 (1) SummaryDokumen5 halamanFauci Dossier Valentine S Day Document 2022 (1) SummarySherri StreightBelum ada peringkat
- Beta 2 AgonistsDokumen198 halamanBeta 2 AgonistsLeonardo FerreiraBelum ada peringkat
- Using A Dense PTFE Membrane Without Primary Closure To Achieve Bone and Tissue RegenerationDokumen5 halamanUsing A Dense PTFE Membrane Without Primary Closure To Achieve Bone and Tissue RegenerationDiego SiqueiraBelum ada peringkat
- Biosafety and Bioethics of Biotechnology ABS-832: DR Attya Bhatti Assistant Professor Head of Department Asab-NustDokumen25 halamanBiosafety and Bioethics of Biotechnology ABS-832: DR Attya Bhatti Assistant Professor Head of Department Asab-NustAviation MedicineBelum ada peringkat
- Mikrobiologi DiagramDokumen2 halamanMikrobiologi Diagrampuguh89Belum ada peringkat
- Tipos de SuturasDokumen5 halamanTipos de SuturasLeandro PeraltaBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Vector Control ProgramDokumen35 halamanIntegrated Vector Control ProgramKeerthi VasanBelum ada peringkat
- Local AnestheticDokumen4 halamanLocal AnestheticAndrea TrescotBelum ada peringkat
- HR Policy ManualDokumen34 halamanHR Policy Manualshamna AbdullaBelum ada peringkat
- Oxygen Therapy For NurseDokumen46 halamanOxygen Therapy For NurseselviiBelum ada peringkat
- Fracture of The Upper HumerusDokumen22 halamanFracture of The Upper HumerusOlasinde AnthonyBelum ada peringkat
- Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Atan Baas Sinuhaji, Spa (K)Dokumen35 halamanSupervisor: Prof. Dr. Atan Baas Sinuhaji, Spa (K)Ranap HadiyantoBelum ada peringkat
- Five"EFFICACY OF GANDHARVAHASTADI KASHAYAM IN THE MANAGEMENT OF ESSENTIAL HYPERTENSION (UCCHA - RAKTHACHAAPA)Dokumen12 halamanFive"EFFICACY OF GANDHARVAHASTADI KASHAYAM IN THE MANAGEMENT OF ESSENTIAL HYPERTENSION (UCCHA - RAKTHACHAAPA)Pradeep SambandamBelum ada peringkat
- Tosoh Series 2147Dokumen3 halamanTosoh Series 2147ShahinBelum ada peringkat
- Tanda, Ciri-Ciri Dan Perbedaan Versi B InggrisDokumen2 halamanTanda, Ciri-Ciri Dan Perbedaan Versi B Inggriselama natilaBelum ada peringkat
- Radioembolization of Hepatic Malignancies - Background, Quality Improvement Guidelines, and Future DirectionsDokumen15 halamanRadioembolization of Hepatic Malignancies - Background, Quality Improvement Guidelines, and Future DirectionsVeronica AlexanderBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan BrochodilatorsDokumen14 halamanLesson Plan BrochodilatorsVaishali SinghBelum ada peringkat
- ELISIO Clinical StudiesDokumen12 halamanELISIO Clinical StudiesIndra NugrohoBelum ada peringkat
- Chylothorax OriginalDokumen4 halamanChylothorax OriginalMaria CostandachiBelum ada peringkat
- Franco, Danica A. (Cardio)Dokumen5 halamanFranco, Danica A. (Cardio)Danica FrancoBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine DisordersDokumen106 halamanEndocrine DisordersMansur MuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- Silicone - MSDS - PT. Lemindo IndonesiaDokumen6 halamanSilicone - MSDS - PT. Lemindo IndonesialiemsaputrarendiBelum ada peringkat
- 2 AleDokumen10 halaman2 AleAna María ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- The Bidirectional Relationship Between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Metabolic DiseaseDokumen14 halamanThe Bidirectional Relationship Between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Metabolic DiseaseVenny SarumpaetBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes On AphDokumen41 halamanLecture Notes On AphEyob MizanBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular Examination: Preparation of The PatientDokumen4 halamanCardiovascular Examination: Preparation of The PatientLolla SinwarBelum ada peringkat