Biol 2420 Lecture 12
Diunggah oleh
mike huntJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Biol 2420 Lecture 12
Diunggah oleh
mike huntHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Biol 2420 Lecture 12
Respiratory System
Primary Functions:
1. Respiration
a. External Respiration
O2 and CO2 exchange
between lungs and atmosphere, between alveoli and blood, blood transport,
between blood and cells
b. Internal Respiration
O2 utilization by mitochondria to regenerate ATP forming CO2
2. Homeostatic regulation of body pH
excretory organ
selectively retains and releases CO2
3. Defends against microbes
traps and destroys harmful pathogens
4. Modifies concentration of chemical messengers
removes and inactiates others e.g. angiotensin 1 to 2
5. Vocalization
6. Sense of smell
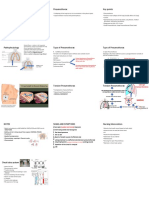
Anatomy
located in thoracic cavity
each lung divided into loves right 3, left 2
Air enters each lugs by upper airways and the respiratory tract.
each lung is covered by a two layered serous membrane - pleural sac
visceral pleura attached to lung by CT
parietal pleura attached to thoracic wall and diaphragm
filled with a very thin layer of fluid that holds the layers close together and lubricates them
during breathing
this reduces friction and transfers forces directly unto lungs
if the sac is punctured, there is a pneumothorax (collapsed lung)
respiratory tract has 23 generations of branches
each becomes narrower, shorter and more numerous than the last
2 functioning zones
1. conducting zone
a. total volume - 150mL
anatomical dead space
b. gases transported by bulk flow
down pressure gradients
air warmed and humidified as it enters lungs
c. walls have SM, elastic tissue and cartilage
less cartilage as progress down
lined by goblet cells
ciliated epithelium
mucus traps stuff cilia moves them upward
2. Respiratory zone
a. post-inspiration air volume
3000mL at rest
huge thin surface area for gas exchange
richly supplied with capillaries
b. gases move internally by bulk flow and diffusion
exchange between adjacent alveoli facilitated by pores of kohn
c. no cartilage, little SM
SM has no role in breathing
elastin fibres between alveolar cells provide tensile strength and stretch/recoil
properties
d. foreign matter eliminated by phagocytotic macrophages
Alveolar structure
individual ones are .25mm in diameter - polyhedral in shape
composed of
i. single layer of type 1 cells and basement membrane
respiratory membrane is 2 cells thick
ii type 2 cells
secrete surfactant
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Nexus Magazine, Vol 6, N°5 (Aug 1999) - The Buteyko Method - An Effective Treatment For AsthmaDokumen15 halamanNexus Magazine, Vol 6, N°5 (Aug 1999) - The Buteyko Method - An Effective Treatment For AsthmaJavier Giraldo ArangoBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Physiology Handout 2 Slides Per Page PDFDokumen37 halamanRenal Physiology Handout 2 Slides Per Page PDFmike hunt100% (1)
- Breathing Exercise Effective CoughDokumen52 halamanBreathing Exercise Effective CoughDesy Suryani Pais100% (1)
- Respi Demo Lesson PlanDokumen6 halamanRespi Demo Lesson PlanBunny BansBelum ada peringkat
- CH 8 Study GuideDokumen4 halamanCH 8 Study Guideapi-3423342160% (1)
- Modes of Mechanical Ventilation For The Operating Room BestPracResAnest 2015 PDFDokumen15 halamanModes of Mechanical Ventilation For The Operating Room BestPracResAnest 2015 PDFRicardoBelum ada peringkat
- Breathing TechniquesDokumen15 halamanBreathing Techniquesapi-338095748Belum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 22Dokumen3 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 22mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Gastro 2014 Handout Wo Images PDFDokumen188 halamanGastro 2014 Handout Wo Images PDFmike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 27Dokumen5 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 27mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 1Dokumen2 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 1mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1Dokumen2 halamanLecture 1mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- BIol 2420 Lecture 34Dokumen3 halamanBIol 2420 Lecture 34mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 25Dokumen4 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 25mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 35Dokumen2 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 35mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 26Dokumen4 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 26mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 24Dokumen3 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 24mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 32Dokumen3 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 32mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 22Dokumen3 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 22mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 21Dokumen3 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 21mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 29Dokumen3 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 29mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 20Dokumen3 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 20mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 31Dokumen3 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 31mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 33Dokumen3 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 33mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 10Dokumen3 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 10mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 30Dokumen4 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 30mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 23Dokumen4 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 23mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 36Dokumen3 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 36mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 28Dokumen4 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 28mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 9Dokumen2 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 9mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 15Dokumen3 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 15mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 18-19Dokumen3 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 18-19mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 8Dokumen2 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 8mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 16Dokumen2 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 16mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- Biol 2420 Lecture 13Dokumen4 halamanBiol 2420 Lecture 13mike huntBelum ada peringkat
- A&P Chapter 15 Respiratory SystemDokumen21 halamanA&P Chapter 15 Respiratory SystemKarl RobleBelum ada peringkat
- Intraoperative Recruitment Manoeuvres: Protective Ventilation in The ORDokumen7 halamanIntraoperative Recruitment Manoeuvres: Protective Ventilation in The ORGede Eka Putra NugrahaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment On Chest PhysiotherapyDokumen15 halamanAssignment On Chest PhysiotherapyAxsa AlexBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding The WOB Bar PAVDokumen2 halamanUnderstanding The WOB Bar PAVCarlos Julián Ortiz DallosBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Function TestDokumen19 halamanPulmonary Function TestAshenafi BerhanuBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 24 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASEDokumen10 halamanChapter 24 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASEZahra Margrette SchuckBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment of The Respiratory SystemDokumen49 halamanAssessment of The Respiratory SystemMariana Mikaela AlagarBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory Failure (Aan) PDFDokumen19 halamanRespiratory Failure (Aan) PDFYudionoBelum ada peringkat
- CRT Exam Review Guide Chapter 6Dokumen28 halamanCRT Exam Review Guide Chapter 6Dharlyn MungcalBelum ada peringkat
- Cellular RespirationDokumen59 halamanCellular RespirationApirak SantiweerawongBelum ada peringkat
- The Respiratory System 2019 dk-20191118110326Dokumen26 halamanThe Respiratory System 2019 dk-20191118110326Jackson JastariBelum ada peringkat
- Bio Lab#3 - Aerobic RespirationDokumen2 halamanBio Lab#3 - Aerobic RespirationtahjsalmonBelum ada peringkat
- B5132300T01 GebrauchsanweisungDokumen156 halamanB5132300T01 GebrauchsanweisungCami 10Belum ada peringkat
- MTV1000 - Pneuma PDFDokumen2 halamanMTV1000 - Pneuma PDFNhật LongBelum ada peringkat
- 4th Summative Mapeh 8Dokumen4 halaman4th Summative Mapeh 8rappidoBelum ada peringkat
- Post operative physiotherapy management for flail chest or Multiple ribs fracture or Cardio-pulmonary rehabilitation or physiotherapy or physical therapy or flail chest or BPT or MPT or PT or project report or case study or medical field or MGR medical university or Senthil Kumar BPTDokumen67 halamanPost operative physiotherapy management for flail chest or Multiple ribs fracture or Cardio-pulmonary rehabilitation or physiotherapy or physical therapy or flail chest or BPT or MPT or PT or project report or case study or medical field or MGR medical university or Senthil Kumar BPTdskmpt88% (8)
- NIV and HFNCDokumen16 halamanNIV and HFNCMarceline GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- WORKSHEET 7.1 The Respiratory Structures and Breathing Mechanisms in Humans and AnimalsDokumen9 halamanWORKSHEET 7.1 The Respiratory Structures and Breathing Mechanisms in Humans and AnimalsGhanapathi RamanathanBelum ada peringkat
- Buble Cpap DataDokumen1 halamanBuble Cpap DataTubagus JulianBelum ada peringkat
- Label Trolley Emergency EditDokumen4 halamanLabel Trolley Emergency EditAnggi Wijayanti KBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDokumen3 halamanPneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYElle RosalesBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumothorax Key PointsDokumen2 halamanPneumothorax Key PointsJose UringBelum ada peringkat
- Office Spirometry - UpToDateDokumen17 halamanOffice Spirometry - UpToDateCamilo HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Trach TubesDokumen8 halamanTrach TubesDinesh SuryanarayananBelum ada peringkat