Lab 2 Refrigerator
Diunggah oleh
Muhammad Fasih0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
39 tayangan3 halamanlab2
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inilab2
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
39 tayangan3 halamanLab 2 Refrigerator
Diunggah oleh
Muhammad Fasihlab2
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 3
Lab Report HV & AC
WAH ENGINEERING COLLEGE
HEAT VENTILLATION & AIR CONDITIONING
Lab Engr. Afsar Zaidi Course Instructor: M. Umer Sohail
EXPERIMENT No 02
Objective:
Familiarization with various components and working of Refrigerator in the HV & AC Lab
& draw the lay-out
Introduction:
The Refrigerator is a cooling appliance comprising of thermally insulated compartments
to transfer heat from it to external environment, thus removing the heat thereby providing
cooling effect to the contents below the ambient temperature.
Hardware Used:
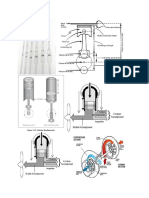
Model of simple Home Refrigerator (Kelvinator)
Basic Refrigerator Working:
In air refrigeration, the air is used as a refrigerant
Since air does not change its phase i.e , remains gaseous throughout the cycle,
therefore the heat carrying capacity per kg of air is very small as compared to vapour absorbing
systems.
Refrigeration essentially means continued abstraction of heat from a substance
(perishable foods, drinks and medicines etc.) at low temperature level and then transfers this
heat to another system at high potential of temperature.
• The basic elements of an air cycle refrigeration system are as follows:
1) Fluid Refrigerant
2) Compressor
3) Condenser
4) Evaporator
5) Expansion device
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
Lab Report HV & AC
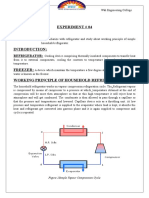
Refrigerator CYCLE :
1. Starting at the compressor;
2. Low pressure vapor refrigerant is compressed and discharged out of the compressor.
3. The refrigerant at this point is a high temperature, high pressure, superheated vapor.
4. The high pressure refrigerant flows to the condenser by way of the "Discharge Line".
5. The condenser changes the high pressure refrigerant from a high temperature vapor to
a low temperature liquid and leaves through the "Liquid Line".
6. The high pressure refrigerant then flows through a filter dryer to the Thermal
Expansion valve or TXV.
7. The TXV meters the correct amount of liquid refrigerant into the evaporator. As the TXV
meters the refrigerant, the high pressure liquid changes to a low pressure, low
temperature, saturated vapor.
9. This saturated vapor enters the evaporator and is changed to a low pressure dry vapor.
10. The low pressure dry vapor is then returned to the compressor in the "Suction line".
11. The cycle then starts over.
Tasks :
To open the refrigerator & freezer portion.
Identification of various Mechanical Components.
Functions of various components
Demonstration of working principal Refrigerator
Deliverables:
Draw the Schematic /Flow Diagram of the Refrigerator Cycle
Draw the Electric Circuit of the Home model Refrigerator
Questionnaires /Assignments:
What is refrigerator normal run time?
What are the factors that contribute refrigerator run time?
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
Lab Report HV & AC
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialDari EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialBelum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration, Air Conditioning and Heat PumpsDari EverandRefrigeration, Air Conditioning and Heat PumpsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (21)
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning (7.2.22)Dokumen148 halamanRefrigeration and Air Conditioning (7.2.22)Edwin Abregú Leandro100% (1)
- PermeabilityDokumen66 halamanPermeabilityValSal Boris100% (1)
- Functioning of ChillersDokumen22 halamanFunctioning of ChillersAnonymous b9fcR5Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 4-Simple Vapour Compression Refrigeration SystemDokumen141 halamanChapter - 4-Simple Vapour Compression Refrigeration SystemMohamed Al-Odat0% (1)
- Vapor Compression Refrigeration SystemDokumen6 halamanVapor Compression Refrigeration SystemGerson Paul BangoyBelum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration Test RigDokumen28 halamanRefrigeration Test RigOxmere SalesBelum ada peringkat
- Building Assignment - Ii: ServicesDokumen53 halamanBuilding Assignment - Ii: ServicesVivek SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Framo Service ManualDokumen82 halamanFramo Service ManualednsmnBelum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration PlantDokumen130 halamanRefrigeration PlantMarvin ArnaizBelum ada peringkat
- Wrokover ManualDokumen14 halamanWrokover ManualCARLOSELSOARESBelum ada peringkat
- HAZOPDokumen30 halamanHAZOPgandalalake2002Belum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Dokumen33 halamanRefrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Christina OhBelum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Lab ManualDokumen25 halamanRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Lab ManualShalini Manchikatla100% (4)
- RAC Lab ManualDokumen27 halamanRAC Lab ManualKewal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Waste Heat RecoveryDokumen20 halamanWaste Heat RecoveryAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4-Simple Vapour Compression Refrigeration SystemDokumen40 halamanChapter 4-Simple Vapour Compression Refrigeration Systemm_alodat614450% (2)
- Insulated Pipe - Temperature Loss CalculationDokumen5 halamanInsulated Pipe - Temperature Loss CalculationnopBelum ada peringkat
- Adsorption RefrigerationDokumen22 halamanAdsorption RefrigerationVijay Krishnan100% (1)
- Transport Phenomena Mass Transfer PDFDokumen150 halamanTransport Phenomena Mass Transfer PDFKhuram MaqsoodBelum ada peringkat
- Wah Engineering College: Heat Ventillation & Air ConditioningDokumen3 halamanWah Engineering College: Heat Ventillation & Air ConditioningMuhammad FasihBelum ada peringkat
- BATCH 8 Domestic RefrigeratorDokumen22 halamanBATCH 8 Domestic RefrigeratorSai RamBelum ada peringkat
- Rac 7th Sem ManualDokumen26 halamanRac 7th Sem Manualmanishsingla88Belum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Heat PumpDokumen8 halamanMechanical Heat PumpClara SariBelum ada peringkat
- HVAC Practical Journal PDFDokumen43 halamanHVAC Practical Journal PDFMujjo SahbBelum ada peringkat
- Ec & Us Manual PDFDokumen111 halamanEc & Us Manual PDFRamnarayan MeenaBelum ada peringkat
- Air Conditioning Systems Experiment: ProposalDokumen16 halamanAir Conditioning Systems Experiment: ProposalShaktivell Letchumanan100% (1)
- Refrigeration and Air Conditiong Lab MannualDokumen24 halamanRefrigeration and Air Conditiong Lab MannualCreative 360Belum ada peringkat
- Rac Lab MannualDokumen24 halamanRac Lab MannualRAZA ULLAHBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4RACDokumen32 halamanChapter 4RACSameer AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Evaporators and The Refrigeration System Unit 21 GroupDokumen27 halamanEvaporators and The Refrigeration System Unit 21 Groupnyein chanBelum ada peringkat
- Air Refrigerant 2015Dokumen18 halamanAir Refrigerant 2015Aman RedhaBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment # 04: ObjectiveDokumen3 halamanExperiment # 04: ObjectiveAhsen NasimBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Sheet 2 PDFDokumen13 halamanLab Sheet 2 PDFmalaBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Analysis of A Domestic Refrigerator Using Various Alternative ReffrigerantDokumen12 halamanPerformance Analysis of A Domestic Refrigerator Using Various Alternative ReffrigerantGulshan SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning: Lab ManualDokumen48 halamanRefrigeration and Air Conditioning: Lab ManualcaxxvadgvadgfsBelum ada peringkat
- Rac PPT-1Dokumen108 halamanRac PPT-1Moges AsefaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Experiment # 03: ObjectiveDokumen4 halamanLab Experiment # 03: ObjectiveSayam AliBelum ada peringkat
- ARCHABArch65021rBUIrAP - Basic Thermodynamics-1Dokumen23 halamanARCHABArch65021rBUIrAP - Basic Thermodynamics-1AditiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter OneDokumen135 halamanChapter OneTaytoBelum ada peringkat
- Report (Refrigeration)Dokumen9 halamanReport (Refrigeration)TITU NATHBelum ada peringkat
- Application of 1 Law 1Dokumen31 halamanApplication of 1 Law 1Melak TsehayeBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Manual: RGPV University (Bhopal)Dokumen6 halamanLab Manual: RGPV University (Bhopal)Pushpendra KushwahaBelum ada peringkat
- EME Notes RefrigerationDokumen7 halamanEME Notes RefrigerationedhanaaBelum ada peringkat
- Vapour Compreession Refrigeration System: Bugade Ghanshyam K. Osekar Prasad M. Pashte Dinesh V. Rane Rohit VDokumen18 halamanVapour Compreession Refrigeration System: Bugade Ghanshyam K. Osekar Prasad M. Pashte Dinesh V. Rane Rohit VGhanshyam BugadeBelum ada peringkat
- R & AC NotesDokumen16 halamanR & AC NotesÄkshày Khâñgrë AKBelum ada peringkat
- Rac Lab ManualDokumen69 halamanRac Lab ManualHrshita SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration & Air ConditioningDokumen11 halamanRefrigeration & Air ConditioningMADHU MITHA0% (1)
- Hvac Chiller Basics: Working Principle of Vapor Compression ChillerDokumen2 halamanHvac Chiller Basics: Working Principle of Vapor Compression ChillersamsungloverBelum ada peringkat
- Vapor Compression CycleDokumen14 halamanVapor Compression CycleMir HaziqBelum ada peringkat
- DesuperheaterDokumen15 halamanDesuperheaterAVI_ROHINI100% (5)
- Table of ContentDokumen29 halamanTable of ContentMuhammad Nasif100% (1)
- Lab Sheet: Title: Refrigeration SystemDokumen6 halamanLab Sheet: Title: Refrigeration SystemShan aliBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 1 Testing of A Vapor Compression Refrigeration System 1Dokumen12 halamanExperiment 1 Testing of A Vapor Compression Refrigeration System 1Ashley Justine RowanBelum ada peringkat
- Prelab Exp1 Refrigeration CycleDokumen7 halamanPrelab Exp1 Refrigeration CycleDean Joyce AlborotoBelum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration CycleDokumen12 halamanRefrigeration CycleVishalVaishBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment #1 - Testing of A Vapor-Compression Refrigeration SystemDokumen8 halamanExperiment #1 - Testing of A Vapor-Compression Refrigeration SystemIvanBelum ada peringkat
- HVAC Source Equipment For Cooling I TranscriptDokumen30 halamanHVAC Source Equipment For Cooling I Transcriptfernanda boldtBelum ada peringkat
- Exp. No. 02 Domestic Refrigerator Test Rig: Pimpri Chinchwad College of Engineering & Research, RavetDokumen34 halamanExp. No. 02 Domestic Refrigerator Test Rig: Pimpri Chinchwad College of Engineering & Research, RavetAbcd EfgBelum ada peringkat
- CH 1Dokumen32 halamanCH 1beila.amu.22Belum ada peringkat
- HVAC Interview Questions - Interview Q & A - Industrial Automation, PLC Programming, Scada & Pid Control System PDFDokumen1 halamanHVAC Interview Questions - Interview Q & A - Industrial Automation, PLC Programming, Scada & Pid Control System PDFprabhanshu241991Belum ada peringkat
- Calculating The Various Moisture Loads - Bry AirDokumen1 halamanCalculating The Various Moisture Loads - Bry Airprabhanshu241991Belum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration & Air ConditioningDokumen11 halamanRefrigeration & Air ConditioningMADHU MITHABelum ada peringkat
- Performance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration Sysytem: (Mel Lab 3 Report)Dokumen14 halamanPerformance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration Sysytem: (Mel Lab 3 Report)Yhan SombilonBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesDari EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesBelum ada peringkat
- ICDokumen3 halamanICMuhammad FasihBelum ada peringkat
- Pin Bush Coupling DesignDokumen15 halamanPin Bush Coupling Designyogwani79Belum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing Processes-Ll Laboratory Practical Hand Out Number: 03Dokumen4 halamanManufacturing Processes-Ll Laboratory Practical Hand Out Number: 03Muhammad FasihBelum ada peringkat
- New Microsoft Excel WorksheetDokumen3 halamanNew Microsoft Excel WorksheetMuhammad FasihBelum ada peringkat
- New Microsoft Excel WorksheetDokumen2 halamanNew Microsoft Excel WorksheetMuhammad FasihBelum ada peringkat
- HeatDokumen1 halamanHeatMuhammad FasihBelum ada peringkat
- Keys and Coupling (Design For A Simple Rigid Flanged CouplingDokumen1 halamanKeys and Coupling (Design For A Simple Rigid Flanged CouplingMuhammad FasihBelum ada peringkat
- Keys and Coupling (Design For A Simple Rigid Flanged CouplingDokumen1 halamanKeys and Coupling (Design For A Simple Rigid Flanged CouplingMuhammad FasihBelum ada peringkat
- Activity No. 2 3 and 4 M.E. 323Dokumen9 halamanActivity No. 2 3 and 4 M.E. 323Cyra AndayaBelum ada peringkat
- TCVN 4513-1988 Internal Water Supply - Design Standard PDFDokumen37 halamanTCVN 4513-1988 Internal Water Supply - Design Standard PDFDoThanhTungBelum ada peringkat
- Operator Installation & Instruction Manual: Auto-Purger Plus, App Non-Condensible Gas (Air) & Water Purger For AmmoniaDokumen20 halamanOperator Installation & Instruction Manual: Auto-Purger Plus, App Non-Condensible Gas (Air) & Water Purger For AmmoniaRASHEED YUSUFBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 6 Conduction Through A Cylindrical Wall, Composite CylindricalDokumen27 halamanLesson 6 Conduction Through A Cylindrical Wall, Composite Cylindricalsurya kiranBelum ada peringkat
- Chap5 Open SystemDokumen19 halamanChap5 Open SystemRoberto Pu100% (4)
- Coalescence of Surfactant-Laden Drops by A Phase Field MethodDokumen20 halamanCoalescence of Surfactant-Laden Drops by A Phase Field MethodAlfredo SoldatiBelum ada peringkat
- ERTAA213 Trane ChillerDokumen20 halamanERTAA213 Trane Chillernomi1873Belum ada peringkat
- Parabolic EquationsDokumen8 halamanParabolic EquationsPuneeth G PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Conduction Heat Transfer in Food ProcessingDokumen20 halamanConduction Heat Transfer in Food Processingmarco_doniseteBelum ada peringkat
- CDL/CDLF Vertical Multistage PumpDokumen12 halamanCDL/CDLF Vertical Multistage PumpSams AnderBelum ada peringkat
- PermeabilityDokumen6 halamanPermeabilitytwinklecawas099Belum ada peringkat
- CGE653 Chapter2 Part2Dokumen61 halamanCGE653 Chapter2 Part2Muhammad NursalamBelum ada peringkat
- Mepl CPCLCBR Eil DWG 001 2022 2023Dokumen5 halamanMepl CPCLCBR Eil DWG 001 2022 2023Mathi Vinoth PillaiBelum ada peringkat
- Real Gas JT4Dokumen78 halamanReal Gas JT4otis-a2013Belum ada peringkat
- Tute 1Dokumen2 halamanTute 1Fearless HeroBelum ada peringkat
- Hot Water Generation and StorageDokumen10 halamanHot Water Generation and StorageAhamed Manazir HazzaanBelum ada peringkat
- Topic Selection: Thermal Performance of Heat Sink With Modified Plate Fins Subjected To Natural ConvectionDokumen11 halamanTopic Selection: Thermal Performance of Heat Sink With Modified Plate Fins Subjected To Natural ConvectionAsmBelum ada peringkat
- Price ListDokumen12 halamanPrice ListAgung Pramu AjiBelum ada peringkat
- Study of RefrigiratorDokumen14 halamanStudy of RefrigiratorRobo RajaBelum ada peringkat
- Parker-SVLA1006P07 Cartridge ValveDokumen12 halamanParker-SVLA1006P07 Cartridge Valvemhmd.bilal1Belum ada peringkat
- Cooling Water Sump Model Studies Through CFD AnalysisDokumen6 halamanCooling Water Sump Model Studies Through CFD AnalysisvijayasarathiBelum ada peringkat
- IbrDokumen5 halamanIbrSuresh Ram RBelum ada peringkat