Blood Test Results: CMP Explained: Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
Diunggah oleh
giuzolinJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Blood Test Results: CMP Explained: Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
Diunggah oleh
giuzolinHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Blood Test Results: CMP Explained
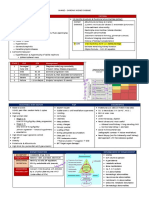
Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
Definition: Measures kidney and liver function, electrolyte levels
Substance What It Is Reference Ranges * What a Low Number May Mean What a High Number May Mean
USA UK/EU Australia/Canada
Glucose (fasting or non-fasting) Sugar in the blood 70-99 mg/dL (fasting) Hypoglycemia, liver disease, adrenal insufficiency, excess insulin Hyperglycemia, certain types of diabetes, prediabetes,
70-125 mg/dL (non-fasting) pancreatitis, hyperthyroidism
Sodium (Na) An electrolyte which keeps your body in balance 136-144 mEq/L Use of diuretics, diarrhea, adrenal insufficiency Kidney dysfunction, dehydration, Cushing's syndrome
Potassium (K) An electrolyte and mineral 3.7-5.2 mEq/L Use of diuretics or corticosteroids (such as prednisone or Acute or chronic kidney failure, Addison's disease, diabetes,
cortisone dehydration
Chloride (Cl) An electrolyte 96-106 mmol/L Emphysema, chronic lung disease Dehydration, Cushing's syndrome, kidney disease
Carbon dioxide (bicarbonate) (CO2) Gaseous waste product from metabolism 20-29 mmol/L Kidney disease, certain toxic exposures, severe infection Lung diseases, including COPD
BUN (blood urea nitrogen) A waste product formed in the liver and carried to the kidneys, filtered out 7-20 mg/dL Malnutrition Liver or kidney disease, heart failure
of blood, and excreted through urine
Creatinine A chemical waste produced by muscle metabolism 0.8-1.4 mg/dL Low muscle mass, malnutrition Chronic or temporary decrease in kidney function
BUN/creatinine ratio 10:1 to 20:1 Malnutrition Blood in bowels, kidney obstruction, dehydration
Calcium (Ca) A mineral stored in the hard part of bones 8.5-10.9 mg/dL Calcium, magnesium, or Vitamin D deficiency; malnutrition; Kidney disease, hyperparathyroidism, cancer, excess vitamin D
pancreatitis; neurological disorders intake
Magnesium (Mg) An electrolyte 1.8-2.6 mEq/L Diabetes, high blood calcium levels, kidney disease, pancreatitis, Dehydration, Addison's disease, hyperparathyroidism,
hypoparathyroidism hypothyroidism, kidney failure
Protein (total) Chains of amino acids essential for the growth and repair of cells 6.3-7.9 g/dL Malnutrition, liver disease, kidney disease Liver disease, kidney disease, dehydration, multiple myeloma,
WM
Albumin Protein that keeps fluid from leaking out of blood vessels and that 3.9-5.0 g/dL Malnutrition, liver disease, kidney disease Dehydration
nourishes tissues and transports nutrients through the body
Globulin Alpha, beta, and gamma proteins; some are produced by the liver and 2.0-3.5 g/dL Malnutrition, liver disease, kidney disease Multiple myeloma, WM, leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus,
others by the immune system and other autoimmune diseases
Albumin/globulin ratio 1.7-2.2 Multiple myeloma, WM, autoimmune diseases, liver disease, Certain genetic conditions, some leukemias, liver dysfunction,
kidney disease hypogammaglobulinemia
Bilirubin (direct or total) A pigment in the bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver 0-0.3 mg/dL (direct) Generally not a concern Liver disease, bile duct disorder, red cell destruction
0.3-1.9 mg/dL (total)
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) Enzyme found in the liver and bones 44-147 IU/L Malnutrition Paget's disease or certain cancers that spread to bone, bile duct
obstruction, liver cancer
Alanine amino-transferase (ALT) Enzyme found mostly in the liver 8-37 IU/L Generally not a concern Certain toxins such as excess acetaminophen or alcohol,
hepatitis
Aspartate amino-transferase (AST) Enzyme found in liver, muscle, and other tissues 10-34 IU/L Generally not a concern Excess acetaminophen, hepatitis muscle injury
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Checks how well the kidneys are working by estimating how much blood 90-120 mL/min/1.73 m2 Chronic kidney disease or kidney failure; GFR decreases Generally not a concern
passes through the glomeruli (filters) of the kidneys each minute progressively with age
* Reference ranges can vary by age, sex, methods of testing, and other factors. There are no KEY
nationally established reference ranges for CMP and CBC values; instead, each laboratory tests a mg: milligram g: gram mmol: millimole mEq: milliequivalent dL: deciliter
population and establishes its own reference ranges. Therefore, the reference ranges quoted are
IU: international unit L: liter mcL: microliter pg: picogram fL: femtoliter
only approximate.
m: meter mL: milliliter
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Bloodcharts CMP PDFDokumen1 halamanBloodcharts CMP PDFSujay DhumalBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Test Results: CMP Explained: Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)Dokumen1 halamanBlood Test Results: CMP Explained: Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)Kimberly Joy GregorioBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Lab Values GuideDokumen6 halamanNormal Lab Values Guidejetri0905Belum ada peringkat
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen47 halamanChronic Kidney DiseaseSaowda HussainBelum ada peringkat
- Blood and urine tests guideDokumen3 halamanBlood and urine tests guidemayrzaBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with DiabetesDokumen47 halamanManaging Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with DiabetesTamzid Rabby TanmoyBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Values Chart GuideDokumen5 halamanLab Values Chart GuideVanessaMUeller100% (3)
- Interpretation of Common Lab ResultsDokumen3 halamanInterpretation of Common Lab ResultsSivasangkari AnbalaganBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Normal Value Comments: AlbuminDokumen4 halamanLab Normal Value Comments: AlbumindelantarzBelum ada peringkat
- ValuesDokumen19 halamanValuescabrerahazel100% (1)
- Laboratory Values Reference RangesDokumen2 halamanLaboratory Values Reference RangesJenna DantBelum ada peringkat
- LP CKD AnemiaDokumen12 halamanLP CKD AnemiaNanan SaputraBelum ada peringkat
- Interpreting Common Lab TestsDokumen2 halamanInterpreting Common Lab Testsali jasimBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding ElectrolytesDokumen2 halamanUnderstanding Electrolytessurviving nursing schoolBelum ada peringkat
- Interpreting Common Lab ValuesDokumen7 halamanInterpreting Common Lab ValuesGabriel PatalodBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal CKD FaizDokumen12 halamanJurnal CKD FaizToxic idBelum ada peringkat
- Farmakoterapi GinjalDokumen13 halamanFarmakoterapi GinjaldameriaBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Case Aki Presentation EportfolioDokumen32 halamanClinical Case Aki Presentation Eportfolioapi-463444835Belum ada peringkat
- Biomedical Diagnosis: Department of Clinical Laboratory Fujian Medical University Union HospitalDokumen30 halamanBiomedical Diagnosis: Department of Clinical Laboratory Fujian Medical University Union HospitalIbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Diagnosis and TherapyDokumen21 halamanChronic Kidney Disease: Diagnosis and TherapyLindsBelum ada peringkat
- CKD EsrdDokumen83 halamanCKD EsrdRita Lakhani100% (1)
- Care of Patients With Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen23 halamanCare of Patients With Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Diseasesho bartBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanDokumen3 halamanLab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanGiacen100% (3)
- Managing nutrition for chronic kidney disease patientsDokumen29 halamanManaging nutrition for chronic kidney disease patientsPinny Rilenda L NgaraBelum ada peringkat
- 23 Triyani - Asuhan Gizi Ginjal KronisDokumen30 halaman23 Triyani - Asuhan Gizi Ginjal KronisFanda RubakBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen47 halamanManaging Chronic Kidney DiseaseAnn Michelle TarrobagoBelum ada peringkat
- DKA: A Life-Threatening Complication of DiabetesDokumen26 halamanDKA: A Life-Threatening Complication of DiabetesJennifer BryantBelum ada peringkat
- Alternative NamesDokumen67 halamanAlternative NamespashaBelum ada peringkat
- Patofisiologi Penyakit Ginjal KronikDokumen35 halamanPatofisiologi Penyakit Ginjal KronikEgy Sunanda Putra Direktorat Poltekkes JambiBelum ada peringkat
- 3D-Dominno, Donna Mae LDokumen3 halaman3D-Dominno, Donna Mae Ldonna dominnoBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Normal Values Appendix Medical Surgical Nursing Lewis Copyrighted 2014Dokumen8 halamanLaboratory Normal Values Appendix Medical Surgical Nursing Lewis Copyrighted 2014Kierzteen Brianna TaromaBelum ada peringkat
- PATOFISIOLOGI & PENATALAKSANAAN GAGAL GINJAL KRONIKDokumen40 halamanPATOFISIOLOGI & PENATALAKSANAAN GAGAL GINJAL KRONIKRavinder SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Farmakoterapi Ginjal Dan HDDokumen42 halamanFarmakoterapi Ginjal Dan HDDenniWahyuniSafitriBelum ada peringkat
- GGK PKMRS PugerDokumen12 halamanGGK PKMRS Pugersyamsul arifinBelum ada peringkat
- AMLS Mobile Reference GuideDokumen6 halamanAMLS Mobile Reference GuideLim Jun BinBelum ada peringkat
- CKD Du 22Dokumen76 halamanCKD Du 22PUTROSM DARSONOBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory ValuesDokumen12 halamanLaboratory ValuesJaney Co100% (2)
- Week 7 Kidney Disease: Sierra Parker, RD, LDN, CNSC, MBADokumen38 halamanWeek 7 Kidney Disease: Sierra Parker, RD, LDN, CNSC, MBASierra ParkerBelum ada peringkat
- Noel A. Villanueva, MD, FPCP, FPSNDokumen62 halamanNoel A. Villanueva, MD, FPCP, FPSNagilBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetic NephropathyDokumen38 halamanDiabetic NephropathySwapnaBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Renal Failure: PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanChronic Renal Failure: PathophysiologyCindy Mae Dela Torre100% (2)
- CKD 2016Dokumen39 halamanCKD 2016husnaBelum ada peringkat
- MagnesiumDokumen2 halamanMagnesiumtuffie85Belum ada peringkat
- Diabetes MelitusDokumen65 halamanDiabetes MelitusDiaBelum ada peringkat
- Penyakit Ginjal Kronik Dan Indikasi DialisisDokumen56 halamanPenyakit Ginjal Kronik Dan Indikasi DialisisantoajaBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen22 halamanChronic Kidney DiseaseMathan KarthikBelum ada peringkat
- Anemia in Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen37 halamanAnemia in Chronic Kidney DiseaseRendyBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Kidney Disease - Genitourinary Disorders - MSD Manual Professional EditionDokumen11 halamanChronic Kidney Disease - Genitourinary Disorders - MSD Manual Professional EditionAdi PomeranzBelum ada peringkat
- Penyakit Ginjal Kronik Dan Indikasi Dialisis DR Ratih Tri KD MAJUDokumen56 halamanPenyakit Ginjal Kronik Dan Indikasi Dialisis DR Ratih Tri KD MAJUFitriana WijayatiBelum ada peringkat
- Renal FailureDokumen5 halamanRenal FailureAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.Belum ada peringkat
- 2 CKDDokumen69 halaman2 CKDDammaqsaa W BiyyanaaBelum ada peringkat
- DR Aida Lombok 3 Mei 2017 - HisfarsiDokumen39 halamanDR Aida Lombok 3 Mei 2017 - HisfarsiBasri BaslamBelum ada peringkat
- Case Presentation CKDDokumen17 halamanCase Presentation CKDPrabal bhuniaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Evaluation Dogs Cats CKIDokumen5 halamanLab Evaluation Dogs Cats CKIDarija LausBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis, Stages, and ManagementDokumen3 halamanChronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis, Stages, and ManagementPetrina XuBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Function Tests GuideDokumen4 halamanRenal Function Tests GuideAhmed ImranBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen29 halamanChronic Kidney DiseaseEsayas KebedeBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Renal FailureDokumen54 halamanChronic Renal FailureAkia Cayasan BayaBelum ada peringkat
- ATI Lab ValuesDokumen4 halamanATI Lab ValuesWhite BoiBelum ada peringkat
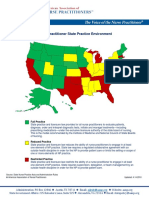
- Map Nurse Practitioner StatesDokumen1 halamanMap Nurse Practitioner StatesgiuzolinBelum ada peringkat
- 2.15 Interpretasi Darah 3 Sudah Di Stabilo PDFDokumen1 halaman2.15 Interpretasi Darah 3 Sudah Di Stabilo PDFalodiaBelum ada peringkat
- NP Facts: The Voice of The Nurse Practitioner®Dokumen1 halamanNP Facts: The Voice of The Nurse Practitioner®giuzolinBelum ada peringkat
- PMHN 2nd EditionDokumen5 halamanPMHN 2nd EditiongiuzolinBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Assessment FormatDokumen20 halamanCardiac Assessment FormatSalman Habeeb75% (4)
- Process Recording - ExampleDokumen7 halamanProcess Recording - ExamplegiuzolinBelum ada peringkat
- Instructions Process RecordingDokumen4 halamanInstructions Process RecordinggiuzolinBelum ada peringkat
- Process Recording 1: Nurse's Behavior, Patient's Behavior, and ConceptsDokumen3 halamanProcess Recording 1: Nurse's Behavior, Patient's Behavior, and ConceptsgiuzolinBelum ada peringkat
- Final CommunityDokumen1 halamanFinal CommunitygiuzolinBelum ada peringkat
- % Chapter 1: Regulation of Water ContentDokumen39 halaman% Chapter 1: Regulation of Water ContentK CBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology of Urinary SystemDokumen384 halamanPathology of Urinary SystemNzau MuangeBelum ada peringkat
- SocLeg Cases (2nd)Dokumen304 halamanSocLeg Cases (2nd)jade123_129Belum ada peringkat
- Congenital Kidney Anomalies and Cystic DiseasesDokumen4 halamanCongenital Kidney Anomalies and Cystic DiseasesEMILY N CRUZ-VARGASBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Block Lecture Four & Five Key Points on Nephrotic and Nephritic SyndromesDokumen27 halamanRenal Block Lecture Four & Five Key Points on Nephrotic and Nephritic Syndromesafaq alismailiBelum ada peringkat
- NSAT 2020 Class X Maths and Science TestDokumen13 halamanNSAT 2020 Class X Maths and Science TestSujal Kumar Jaiswal71% (7)
- Anatomy and Physiology Final ReviewDokumen4 halamanAnatomy and Physiology Final ReviewPaige PattersonBelum ada peringkat
- AKI definition and use in practiceDokumen12 halamanAKI definition and use in practicewelinBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Assignment Class-XDokumen3 halamanBiology Assignment Class-XCoolCJ 1410Belum ada peringkat
- Term 2 P7 Science WorkDokumen61 halamanTerm 2 P7 Science WorkSamson KisenseBelum ada peringkat
- HBT 108 Minggu 05 TutorialDokumen1 halamanHBT 108 Minggu 05 TutorialErin PnehBelum ada peringkat
- Hemodialysis PDFDokumen80 halamanHemodialysis PDFJenie FeloniaBelum ada peringkat
- Leaves of Cat's Whiskers Plant (Orthosiphon Aristatus)Dokumen20 halamanLeaves of Cat's Whiskers Plant (Orthosiphon Aristatus)issa pinkBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To PolyuriaDokumen15 halamanApproach To PolyuriaPucca' Jerny100% (1)
- The Urinary System: Paired Kidneys A Ureter For Each Kidney Urinary Bladder UrethraDokumen28 halamanThe Urinary System: Paired Kidneys A Ureter For Each Kidney Urinary Bladder UrethraWorknesh AmlakuBelum ada peringkat
- Manejo Hta Unidad Cuidados Criticos PediátricoDokumen9 halamanManejo Hta Unidad Cuidados Criticos PediátricoCatalina Cruz NunjaBelum ada peringkat
- Hemodialysis Thesis - Analytical EssayDokumen4 halamanHemodialysis Thesis - Analytical EssayDianne LopezBelum ada peringkat
- ASTRO Contouring-Table - 1supplementDokumen5 halamanASTRO Contouring-Table - 1supplementEskadmas BelayBelum ada peringkat
- NCP HypomagnesemiaDokumen2 halamanNCP HypomagnesemiaMark Zedrix MediarioBelum ada peringkat
- Elimination Needs 04Dokumen52 halamanElimination Needs 04Kishore RathoreBelum ada peringkat
- Aqa Byb4 W QP Jan08 PDFDokumen20 halamanAqa Byb4 W QP Jan08 PDFCindyVortexBelum ada peringkat
- Renal System Physiology Lab ReportDokumen4 halamanRenal System Physiology Lab ReportDominiqueLovesAmaurionnaSmith33% (9)
- Drug Prescribing in Renal Impairment Information. Patient PatientDokumen13 halamanDrug Prescribing in Renal Impairment Information. Patient PatientEffy AngeLi LomocsoBelum ada peringkat
- Good Thesis Topics On NutritionDokumen6 halamanGood Thesis Topics On NutritionScott Donald100% (2)
- Human Excretory System: Kidneys, Ureters, Urinary Bladder and UrethraDokumen6 halamanHuman Excretory System: Kidneys, Ureters, Urinary Bladder and UrethraRahul SinghBelum ada peringkat
- All Conditions Data NCTDokumen506 halamanAll Conditions Data NCTMuneer Ashraf0% (1)
- Urine FormationDokumen14 halamanUrine FormationWaziri MbarukuBelum ada peringkat
- CKD - Grade and TreatmentDokumen2 halamanCKD - Grade and TreatmentIwan SetiawanBelum ada peringkat
- Osmo PrepDokumen5 halamanOsmo PrepStephanie FisherBelum ada peringkat
- EDEXCEL A2 BIOLOGY UNIT 5 OSMOREGULATION IN MAMMALSDokumen24 halamanEDEXCEL A2 BIOLOGY UNIT 5 OSMOREGULATION IN MAMMALSMithun ParanitharanBelum ada peringkat