Culminatingtaskportwood
Diunggah oleh
api-3994618900 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
136 tayangan6 halamanJudul Asli
culminatingtaskportwood copy
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
136 tayangan6 halamanCulminatingtaskportwood
Diunggah oleh
api-399461890Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 6
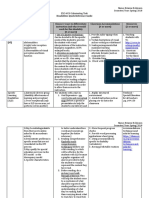
Name: Amber Portwood
Semester/Year: Fall 2016
EXC 4020 Culminating Task
Disabilities Quick Reference Guide
Disability Characteristics Choose 2 ways to differentiate Classroom Accommodations Resources
(4 or more) instruction and why it would (4 or more) (2 or more)
work for this disability
(2 or more)
Example: 1.Poor visual acuity 1. Use of Assistive technology: 1. Provide audio-taping when 1. Teaching
Visual 2.Visual field deficits Can be decided to fit the specific possible students with VI:
Impairments 3.Eye movement needs of the student to provide 2. Verbal descriptions of visual http://www.teac
(VI) abnormalities the student with visual aids or writing on whiteboard hingvisuallyimpai
4.Light/color reception interpretations of the 3. Seating arrangements that red.com
impairments instruction. Examples: maximize learning 2. American
5.Abnormalities of visual magnifiers, CCTV, enlarged 4. Provide materials/lessons in Foundation for
perception and brain books. alternate formats (such as the blind:
function 2. Alteration in material: Present enlarged font) http://www.afb.
the information in braille, large 5. Extended time org/default.aspx
print, or on CD. Also using 6. E-text with tracking devices
models that the student can
touch can also be helpful in
solidifying the content for
students with VI. Some students
with VI may need the
information presented in a
different way/format in order to
grasp the concept. If a
PowerPoint/or reading a
chapter is not an option, the
information will need to be
adjusted in order to allow them
access to the instruction.
Specific Deficits in: 1. Structured environment: by 1. Provide graphic organizers 1. http://www.par
Learning 1. short and long term providing students with a to visually represent content entcenterhub.or
Disabilities memory highly structured 2. Provide notes from books, g/repository/ld/
(SLD) 2. Auditory environment, they will be lectures, etc. 2. Learning
Name: Amber Portwood
Semester/Year: Fall 2016
discrimination able to develop routines to 3. Provide manipulatives for disabilities
3. Organization manage their behavior and counting (beads, etc) assosciation of
4. Social perception set expectations 4. Provide calculators or georgia:
5. Conceptualization/re 2. Frequent progress checks: number lines on the desk http://ldag.org/
asoning progress checks allow 5. Provide story starters to help
teachers to monitor student’s students generate ideas
progress and remind them of
what needs to be focused on
now as well as what they will
do next
Mild 1. Cognitive 1. Provide demonstration: by 1. Provide graphic organizers 1. http://www.edu
Intellectual development delays providing demonstration, with pictures cationcorner.co
Delays (MID) 2. Significant learning students can see a hands-on 2. Allow use of a calculator m/mild-
problems in many approach to how to solve a 3. Highlight important features intellectual-
areas problem with a highlighter disability.html
3. Inability to 2. Provide routines: by 4. Provide cue cards with visual 2. http://www.brig
discriminate relevant providing routines, students prompts hthubeducation.
from irrelevant info are able to better manage 5. Allow for breaks com/special-ed-
4. Significant deficits in self-care tasks such as learning-
two or more adaptive washing hands after using disorders/9689
behavior categories the bathroom 6-what-is-a-
such as: 3. Co-teaching: having a co- mild-
communication, self- teacher under the one intellectual-
care, home living, teach/one support model disability/
social skills, etc. allows students to have one
on one support when needed
Emotional 1. outbursts 1. behavior management plan: 1. provide counseling services 1. http://www.par
Disturbance 2. defiance clearly outlining expected 2. provide reinforcement for entcenterhub.or
(ED) 3. verbal assault behaviors and rules good behavior g/repository/em
Choose one: 4. restlessness minimizes potential 3. provide outlines and otionaldisturban
*Internalizing 5. withdrawal disruptive behaviors organizers ce/
*Externalizing 1. structured environment: this 4. small group instruction 2. http://cherokee
allows the student to adhere k12.net/wp-
to their expectations and content/uploads
avoid frustration that can /2016/07/Emoti
lead to outbursts onal-and-
Name: Amber Portwood
Semester/Year: Fall 2016
Behavioral-
Disability-
Eligibility.pdf
Attention 1. inability to focus for 2. structured environment: this 1. Breaks 1. https://www.ni
Deficit appropriate amounts allows the student to have 2. Provide outlines to maintain mh.nih.gov/healt
Hyperactivity of time minimized distractions and focus and guidance h/topics/attenti
Disorder 2. careless mistakes on stay on task 3. Rewards for staying on on-deficit-
(ADHD) schoolwork 3. Frequent progress checks: task/completing hyperactivity-
3. not following progress checks allow assignments disorder-
directions teachers to monitor student’s 4. Provide behavior contract adhd/index.sht
4. inability to control progress and remind them of 5. Concrete list of rules and ml
behaviors what needs to be focused on expectations along with 2. http://www.cha
5. excessive fidgeting now as well as what they will consequences dd.org/
and squirming in seat do next 3.
Traumatic 1. physical disability 1. Assistive technology: 1. Extra time on assignments 1. http://www.trau
Brain Injury 2. cognitive processing depending on the degree of 2. Graphic organizers maticbraininjury
(TBI) deficits impairment, technology can 3. Color coding .com/
3. language skill deficits be used to assist in 4. Mnemonic devices 2. http://www.bia
4. behavioral/emotiona movement, mobility, oregon.org/doce
l conduct deficits communication, etc. tc/Resources/ch
(severity of all 2. Peer assistance: the use of a ildren/teaching.s
dependent on injury) peer to help assist in trategies.for.stud
activities that would ents.with.brain.i
otherwise be difficult to njuries.pdf
complete due to impairments
Autism 1. difficulty relating to 1. provide predictable routines: 1. visual cues 1. https://www.au
Spectrum others routines help students with 2. graphic organizers tismspeaks.org/r
Disorder (ASD) 2. unusual reactions to ASD better understand 3. minimize sensory stimuli esource/aspire-
events expectations for behavior 4. guided notes autism-
3. abnormal responses within routines spectrum-
to sensations 2. implementing a first/then instructional-
4. self-stimulation schedule: this allows the resources
5. self-injurious student to do a preferred 2. http://www.lear
behaviors task after first completing nnc.org/lp/editi
the non-preferred task ons/every-
learner/6692
Name: Amber Portwood
Semester/Year: Fall 2016
Hearing 1. loss of hearing 1. assistive technology: the use 1. Repeat questions and 1. http://www.ferr
Impairment 2. decreased hearing of amplification devices answers from other students is.edu/htmls/col
3. difficulty discerning during lecture allows the 2. Provide handouts leges/university
words (misinterpret) student to hear the teacher 3. Provide all instructions in /disability/facult
4. difficulty with speech and classmates written format y-
5. delays in language 2. Alter Materials: presenting 4. Do not speak with back to staff/classroom-
skills information in a visual student issues/hearing/
format such as powerpoint hearing-
presentations and captions strategy.htm
on videos allows the student 2. http://www.proj
to succeed ectidealonline.or
g/v/hearing-
impairments/
Communicatio 1. stuttering 1. assistive technology: the use 1. give longer time for student 1. http://do2learn.
n Impairments 2. speech impairment of gestures, manual signs, to answer questions out loud com/disabilities
(CI) 3. language impairment objects, picture notebooks, 2. allow use of pictures to /Characteristics
4. improper and communication devices communicate needs AndStrategies/S
pronunciation of allow students to 3. small group activities peechLanguageI
words communicate when unable to 4. promotion of positive mpairment_Strat
2. peer assistance: small groups environment egies.html
and one-on-one teaming 5. allow use of written 2. http://www.ses
allows the student’s peers to communication to answer d.info/inclusion
model appropriate speech questions %20site/disabili
and may be less intimidating ties%20teaching
to self-conscious students %20strategies/C
ommunication%
20Disorders/co
mmunication%2
0disorders%20s
trategies.htm
Physical 1. mild to severe 1. Assistive technology: 1. Position students to 1. http://cerebralp
Impairments uncoordinated assistance with posture, maximize range of motion alsyresource.we
(PI) movement hand and arm use, mobility, 2. Arrange classroom to allow ebly.com/teachi
Choose one: 2. inability to complete motor coordination, etc. for mobility ng-
*Cerebral daily activities in 2. Peer Assistance: the use of a 3. Shorten assignments to avoid strategies.html
Palsy severe cases peer or teacher to aid in fatigue 2. http://www.cer
Name: Amber Portwood
Semester/Year: Fall 2016
3. poor balance activities that require 4. Alter physical activities to be ebralpalsyworld.
4. one or more limbs movement that the student is performed on the computer com/cp_educatio
affected unable to perform (manually n.aspx
sharpening a pencil)
Other Health 1. recurrent seizures 1. Use of a person: teachers 1. Have emergency procedure 1. https://www.epi
Impairments 2. loss of consciousness should be well informed on ready for incidents lepsy.com/sites/
(OHI) or altered the student’s condition to 2. Have students remain calm core/files/atoms
Choose one: consciousness properly take care of them in 3. Allow student to rest after /files/IDEA%20
*Epilepsy 3. absent stares case of an incident, peers, incidence 6-24-14.pdf
4. rhythmic jerking nurses, etc may also assist 4. Know referral information if 2. http://edmedkid
motion 2. Alter materials: avoid any necessary s.arizona.edu/co
materials or presentations ntent/education
that could trigger a seizure al-implications-1
Intellectual 1. developmental delay 1. Teaching a functional 1. Hands on activities 1. https://us.corwi
Delays (MOID 2. comorbidities such curriculum: students with 2. Small group work n.com/en-
& SID) as sensory, physical, MOID and SID require a 3. Visual cues us/nam/academ
and health functional curriculum to 4. Material modifications ic-instruction-
impairments benefit them the most in for-students-
3. deficits in daily life with-moderate-
generalization, 2. Person assistance: the use of and-severe-
memory ability, co-teaching, or a teachers aid intellectual-
attention to work solely with the disabilities-in-
4. inability to student to focus on their inclusive
communicate functional tasks 2. http://ceedar.ed
effectively ucation.ufl.edu/
wp-
content/uploads
/2014/09/IC-
3_FINAL_03-03-
15.pdf
Gifted and 1. unusual capacity for 1. Curriculum compacting: by 1. Provide opportunities for 1. https://www.na
Talented memory curriculum compacting, discussion gc.org/resources
2. extensive vocabulary teachers allow students to 2. Challenge students to think -
3. argumentativeness move at a faster pace and deeper publications/gift
4. an awareness for avoid doing what they have 3. Provide stimulating content ed-education-
detail already mastered 4. Diversity of material practices/what-
Name: Amber Portwood
Semester/Year: Fall 2016
5. extraordinary degree 2. Independent study projects: presented it-means-teach-
of intellectual students are allowed to gifted-learners-
curiosity develop a project, gifted well
students being encouraged to 2. https://www.ed
dive deeper into content they utopia.org/blog/
wouldn’t otherwise learn in gifted-students-
general education general-ed-
classrooms-
elissa-brown
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Culminating Task FinalDokumen13 halamanCulminating Task Finalapi-403386868100% (2)
- ldm2 Rose Gee Final 2 4Dokumen14 halamanldm2 Rose Gee Final 2 4Aienna Lacaya MatabalanBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Philosophy of The Human Person-Week-1-4Dokumen4 halamanIntroduction To Philosophy of The Human Person-Week-1-4Raymond DizonBelum ada peringkat
- List of Targeted Learner InterventionsDokumen8 halamanList of Targeted Learner InterventionsAlvin CastanedaBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Education: Learning Tasks For Distance Learning (DL)Dokumen2 halamanDepartment of Education: Learning Tasks For Distance Learning (DL)Angela QuintoBelum ada peringkat
- Module 0 - Community OrganizingDokumen21 halamanModule 0 - Community OrganizingPaul Niño S. TabigneBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Task For Distance Learning: Learning Delivery Modality Course 2Dokumen2 halamanLearning Task For Distance Learning: Learning Delivery Modality Course 2Ai Leen Anaz Nam100% (1)
- Title: Logical Fallacies: PlanningDokumen7 halamanTitle: Logical Fallacies: Planningapi-354144566Belum ada peringkat
- ASSCAT Vision, Mission & Quality PolicyDokumen16 halamanASSCAT Vision, Mission & Quality PolicyRuby Jane DuradoBelum ada peringkat
- MIL DLL Feb 24-28Dokumen3 halamanMIL DLL Feb 24-28Joel Morales MalongBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2: Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) : Department of Education El Pardo National High SchoolDokumen6 halamanModule 2: Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) : Department of Education El Pardo National High SchoolZypher BlakeBelum ada peringkat
- Espayos, Jackyline C. - LDMDokumen8 halamanEspayos, Jackyline C. - LDMZypher BlakeBelum ada peringkat
- SHS Mil Q2 Module2 WK4-9Dokumen63 halamanSHS Mil Q2 Module2 WK4-9Annie LouBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Delivery Modalities Course 2: PortfolioDokumen14 halamanLearning Delivery Modalities Course 2: PortfolioMarie Grace SuarezBelum ada peringkat
- AitechresourceguideDokumen6 halamanAitechresourceguideapi-358302290Belum ada peringkat
- 2.1. BASIC Observing Gender SensitivityDokumen3 halaman2.1. BASIC Observing Gender SensitivityOrlando NajeraBelum ada peringkat
- GED0104 STS Module 2 Facilitation GuideDokumen8 halamanGED0104 STS Module 2 Facilitation GuideFaith CastroBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 2 Activity 4: Learning Tasks: Learning Delivery Modality (Select One) : ODLDokumen2 halamanLesson 2 Activity 4: Learning Tasks: Learning Delivery Modality (Select One) : ODLSun Shine OalnacarasBelum ada peringkat
- ZFacilitator Handbook 5 (2018)Dokumen198 halamanZFacilitator Handbook 5 (2018)mohdaqil595Belum ada peringkat
- Barrios, Ronald L. - LDMDokumen8 halamanBarrios, Ronald L. - LDMZypher BlakeBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Delivery Modalities Course: For TeachersDokumen17 halamanLearning Delivery Modalities Course: For TeachersJoel BrionesBelum ada peringkat
- Puti-An National High SchoolDokumen2 halamanPuti-An National High SchoolNoli FriasBelum ada peringkat
- LEARNING TASKS FOR DL and ASSESSMENT METHODS IN DL (DISTANCE LEARNING)Dokumen3 halamanLEARNING TASKS FOR DL and ASSESSMENT METHODS IN DL (DISTANCE LEARNING)Joseph Arnold AlmonteBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Task For DLDokumen2 halamanLearning Task For DLrowielahmercy.piosangBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan MILDokumen82 halamanLesson Plan MILMitch Diamola100% (1)
- UDL Lesson PlanDokumen4 halamanUDL Lesson Planharshali7850% (2)
- CTE Toolkit Lesson Plans and HandoutsDokumen16 halamanCTE Toolkit Lesson Plans and Handoutsrobertsbunch100% (1)
- Output No. 2 Learning Tasks Lesson 2 Activity 4: Learning TasksDokumen2 halamanOutput No. 2 Learning Tasks Lesson 2 Activity 4: Learning TasksMariepet Acantilado Cristuta-AgustinesBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Delivery Modality PDFDokumen2 halamanLearning Delivery Modality PDFSionet AlangilanBelum ada peringkat
- Disablity HandbookDokumen31 halamanDisablity Handbookapi-529069420Belum ada peringkat
- Udl Lesson PlanDokumen16 halamanUdl Lesson Planapi-276907530Belum ada peringkat
- Outputs in LDM Module 2-Melcs: Individual/Lac Group Presentation On Unpacking of A Sample MelcDokumen10 halamanOutputs in LDM Module 2-Melcs: Individual/Lac Group Presentation On Unpacking of A Sample MelcZypher BlakeBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Lesson Plan - DifferentiatedDokumen6 halamanEnvironmental Lesson Plan - Differentiatedapi-352851812Belum ada peringkat
- 2 Semester, A.Y. 2021-2022 Vision: Course Syllabus in MAT051Dokumen9 halaman2 Semester, A.Y. 2021-2022 Vision: Course Syllabus in MAT051Nestor AcalaBelum ada peringkat
- FS 2 Episode 12Dokumen7 halamanFS 2 Episode 12Pontejos Princess Dianne G.67% (3)
- Field STUDY 3-Marichu Bolocon-JerusalemDokumen25 halamanField STUDY 3-Marichu Bolocon-JerusalemJoana B. SolatorreBelum ada peringkat
- Eduu 512 Direct Instruction Lesson Plan Template2Dokumen2 halamanEduu 512 Direct Instruction Lesson Plan Template2api-468416466Belum ada peringkat
- Module 3 - MILDokumen12 halamanModule 3 - MILMary Rose DomingoBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 2 Activity 4: Learning Tasks: MDL Tv/Rbi BLDokumen2 halamanLesson 2 Activity 4: Learning Tasks: MDL Tv/Rbi BLShiela Marie Galo Sanico-DespoyBelum ada peringkat
- P Alexander Vaneaton Rank and Order Technology Tools v2Dokumen2 halamanP Alexander Vaneaton Rank and Order Technology Tools v2api-356979259Belum ada peringkat
- Activity Prof Ed Building New Literacies 2022 2023Dokumen1 halamanActivity Prof Ed Building New Literacies 2022 2023Vaniza OrayBelum ada peringkat
- Quality Capsules For IInd Cycle of NAACDokumen18 halamanQuality Capsules For IInd Cycle of NAACmonika.yogaBelum ada peringkat
- 3 MIL-11-12EMIL-IIIc-8 - 9 - Group 1Dokumen7 halaman3 MIL-11-12EMIL-IIIc-8 - 9 - Group 1Chel MaglanqueBelum ada peringkat
- Module 3A:: Designing Instruction in The Different Learning Delivery ModalitiesDokumen9 halamanModule 3A:: Designing Instruction in The Different Learning Delivery ModalitiesMariel Lopez - MadrideoBelum ada peringkat
- With Learning Disabilities: Teaching StudentsDokumen2 halamanWith Learning Disabilities: Teaching StudentsKaylaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1: Understanding The Different LDMS: Activity 1Dokumen12 halamanLesson 1: Understanding The Different LDMS: Activity 1JENEVIE SALIOTBelum ada peringkat
- Cot 2Dokumen5 halamanCot 2Rochelle LimetBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Plan La9 - Short FictionDokumen9 halamanUnit Plan La9 - Short Fictionapi-287503702Belum ada peringkat
- Module 2: Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) : Lesson 1: Background, Rationale, and Development of MelcsDokumen4 halamanModule 2: Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) : Lesson 1: Background, Rationale, and Development of Melcskikoy20Belum ada peringkat
- Ldm2module3outputs-Marina RacazaDokumen22 halamanLdm2module3outputs-Marina RacazaJames racazaBelum ada peringkat
- List of Targeted Learner InterventionsDokumen10 halamanList of Targeted Learner InterventionsRandolf CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan MIL COR11Dokumen81 halamanLesson Plan MIL COR11NANCITA O. PERLASBelum ada peringkat
- Ldm2output - Day3 - Learning Modalities - AmaslogDokumen16 halamanLdm2output - Day3 - Learning Modalities - AmaslogChester Austin Reese Maslog Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- Information Reports Unit PlanDokumen4 halamanInformation Reports Unit Planapi-526103844Belum ada peringkat
- Learning Task For DL-ROSE ANNDokumen2 halamanLearning Task For DL-ROSE ANNrose annBelum ada peringkat
- Week 1Dokumen4 halamanWeek 1Alvin CatubigBelum ada peringkat
- Aries Jude P.fasfdDokumen3 halamanAries Jude P.fasfdARIES JUDE S. PALEYANBelum ada peringkat
- Mailyn C. LaidanDokumen15 halamanMailyn C. LaidanJenny polancosBelum ada peringkat
- What if everything you knew about education was wrong?Dari EverandWhat if everything you knew about education was wrong?Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Teacher Guide for A Girl Called Echo: Learning About the History and Culture of the Métis Nation in Grades 6–8Dari EverandTeacher Guide for A Girl Called Echo: Learning About the History and Culture of the Métis Nation in Grades 6–8Belum ada peringkat
- PortwoodaffectivelabDokumen3 halamanPortwoodaffectivelabapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- VB Written TestDokumen3 halamanVB Written Testapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- Volleyball QuizDokumen1 halamanVolleyball Quizapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- Forearm Pass Teacher ChecklistDokumen1 halamanForearm Pass Teacher Checklistapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- Teaching Reflection #2: Due: Wednesday, September 21 8:00 Am D2L/icollege Only (Emailed or Hard Copies NotDokumen2 halamanTeaching Reflection #2: Due: Wednesday, September 21 8:00 Am D2L/icollege Only (Emailed or Hard Copies Notapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- 4 DDokumen3 halaman4 Dapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 Stages of Learning Application QuestionsDokumen1 halamanUnit 2 Stages of Learning Application Questionsapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- Focus Student 1 Skill AssessmentDokumen1 halamanFocus Student 1 Skill Assessmentapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- 4 BDokumen1 halaman4 Bapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- PortwoodDokumen5 halamanPortwoodapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- ObjectivesDokumen1 halamanObjectivesapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- Portwoodpositionpaper 2Dokumen3 halamanPortwoodpositionpaper 2api-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- Student Survey On Physical Education ClassDokumen3 halamanStudent Survey On Physical Education Classapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- Conley Hills Elementary Skipping DataDokumen4 halamanConley Hills Elementary Skipping Dataapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- Amber Portwood Unit: Tennis Grade: 7 Model: Peer Teaching Length: 2 WeeksDokumen82 halamanAmber Portwood Unit: Tennis Grade: 7 Model: Peer Teaching Length: 2 Weeksapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- Curriculumprojectpart 5Dokumen9 halamanCurriculumprojectpart 5api-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- PortwoodfitnessplanDokumen5 halamanPortwoodfitnessplanapi-399461890Belum ada peringkat
- Trauma-Informed Care For Behavioral Health Service ProvidersDokumen159 halamanTrauma-Informed Care For Behavioral Health Service ProvidersAlguémBelum ada peringkat
- Stages of Psychosexual Development and Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentDokumen7 halamanStages of Psychosexual Development and Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentjosedenniolimBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheets - Coping Skills For AnxietyDokumen4 halamanWorksheets - Coping Skills For AnxietyLansing Cai100% (1)
- SSCT OverviewDokumen5 halamanSSCT OverviewNicko Espineda VargasBelum ada peringkat
- Natalie Brickner-Slp ResumeDokumen1 halamanNatalie Brickner-Slp Resumeapi-238387904Belum ada peringkat
- Beautiful Child ReportDokumen6 halamanBeautiful Child Reportapi-361697104Belum ada peringkat
- The Role of Dietary Restriction in Binge EatingDokumen11 halamanThe Role of Dietary Restriction in Binge EatingSofie WiddershovenBelum ada peringkat
- Stephen W. PorgesDokumen15 halamanStephen W. Porges2rightBelum ada peringkat
- Fregoli Syndrome - Psych ReportingDokumen15 halamanFregoli Syndrome - Psych ReportingAngela AbañoBelum ada peringkat
- Module 16-17 - Goal-Setting TheoryDokumen25 halamanModule 16-17 - Goal-Setting TheoryLowela Mae BenlotBelum ada peringkat
- Leader'S Manual For Adolescent Groups: Adolescent Coping With Depression CourseDokumen321 halamanLeader'S Manual For Adolescent Groups: Adolescent Coping With Depression CourseHéctorMartínez100% (1)
- Stress and Academic PerformanceDokumen29 halamanStress and Academic PerformanceReem NurBelum ada peringkat
- Autism PhysiotherapyDokumen4 halamanAutism PhysiotherapyPooja ChhabraBelum ada peringkat
- Price Jones (1998) .PDF-PQS and AllianceDokumen13 halamanPrice Jones (1998) .PDF-PQS and AllianceGianluca AddamianoBelum ada peringkat
- Depression and Islam - Iblal Rakha and DR Menaz AkhtarDokumen11 halamanDepression and Islam - Iblal Rakha and DR Menaz AkhtarIblal Rakha100% (3)
- Crossword NSTP1Dokumen2 halamanCrossword NSTP1Atienza Sheryl100% (1)
- WEIKERT, ACP Masculinity - and - ViolenceDokumen8 halamanWEIKERT, ACP Masculinity - and - ViolenceIVYS DE ALCANTARA SILVABelum ada peringkat
- Letter To MacCharlesDokumen5 halamanLetter To MacCharlesjkobopoliBelum ada peringkat
- Acceptance-Commitment - Steven C. Hayes PDFDokumen27 halamanAcceptance-Commitment - Steven C. Hayes PDFEspíritu CiudadanoBelum ada peringkat
- App2Dokumen3 halamanApp2Johnykutty JosephBelum ada peringkat
- Hayes Et Al. (1999)Dokumen3 halamanHayes Et Al. (1999)GABRIELBelum ada peringkat
- Mercedes D. Hernandez, Ph.D. - 9.21.10Dokumen6 halamanMercedes D. Hernandez, Ph.D. - 9.21.10deyanira1112Belum ada peringkat
- Disturbances in Thought KJW 161Dokumen23 halamanDisturbances in Thought KJW 161zulfantri1983Belum ada peringkat
- Freud's Structural and Topographical Models of PersonalityDokumen3 halamanFreud's Structural and Topographical Models of PersonalityHarjeet Kaur100% (1)
- The Unified Protocol For Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders in Children (UP-C) in Portugal: Feasibility Study ResultsDokumen24 halamanThe Unified Protocol For Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders in Children (UP-C) in Portugal: Feasibility Study ResultsAndrade GuiBelum ada peringkat
- Obe Syllabus - Personal DevelopmentDokumen13 halamanObe Syllabus - Personal DevelopmentChello Ann Pelaez Asuncion100% (3)
- NCP For Parent and Child PDFDokumen3 halamanNCP For Parent and Child PDFMariana Mikaela AlagarBelum ada peringkat
- Social Connectedness, Compassion, Gratitude and ForgivenessDokumen12 halamanSocial Connectedness, Compassion, Gratitude and ForgivenessShaira ManiegoBelum ada peringkat
- BellDokumen8 halamanBellZu MieBelum ada peringkat