CE00398-4 Security Technologies
Diunggah oleh
yoges_0695Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CE00398-4 Security Technologies
Diunggah oleh
yoges_0695Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Asia Pacific Institute of Information Technology
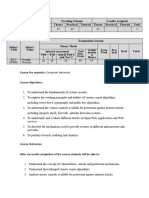
1. Name of Course/Module Security Technologies
2. Course Code: CE00398-4
3. Name(s) of academic staff: Yogeswaran Nathan
4. Rationale for the inclusion of the course/module in the programme:
Refer to Programme Specification
5. Semester and Year offered: Refer to Programme Specification
6. Total Student Face to Face Total Guided and Independent Learning
Learning Time
(SLT)
L = Lecture L T P O
T = Tutorial 32 16 160
P = Practical
O= Others
7. Credit Value: 4
8. Prerequisite (if any): Nil
9. Objectives
The objectives of this module is to:
1. Contribute to the achievement of the Learning Outcomes specified for the student’s award
at Level 4.
2. Develop knowledge and skills in relation to Computer Security.
3. Develop an understanding of the history of security technologies, system intrusion
techniques, system vulnerability assessment, methods of system exploitation, system
intrusion detection and prevention.
4. Develop lifelong learning skills of independent learning and study in relation to Computer
Security.
10. Learning outcomes:
On successful completion of this module, you should be able to:
1. Identify and describe aspects of historical and current systems associated with
security. (MQF1, MQF7)
2. Relate typical security techniques to typical scenarios. (MQF1,MQF6,MQF7)
3. Identify and describe current technology trends relating to security techniques and
technology.(MQF1, MQF7)
MQF Learning Outcome Area
MQF1 - Knowledge
MQF2 - Practical skills
MQF3 - Social skills & responsibilities
MQF4 - Values, attitudes, professionalism and ethics
MQF5 - Communications, leadership and team skills
MQF6 - Problem solving & scientific skills
MQF7 - Information management and lifelong learning skills
MQF8 - Managerial & entrepreneurial skills
Security Technologies– CE00398-4 Page 1of 4
Asia Pacific Institute of Information Technology
11. Transferable Skills:
The following employability skills are introduced (I), developed (D) and/or assessed (A):
Time Management(I,D)
Problem solving(I,D,A)
Knowledge & Understanding (I)
Application (I,D,A)
Analytical Skills (I,D, A)
12. Teaching-learning and assessment strategy:
2 hours lecture and 1 hour practical per week
In addition the student will be required to undertake an amount of independent learning for
the production of the module assignment together with other background reading to support
lecture and tutorial material.
13. Synopsis:
An introduction to a range of techniques associated with computer security. The module will
consider the different aspects separately and combined to aid with the reduction of
unauthorised access and usage together with techniques to detect intrusions.
14. Mode of Delivery:
Lecture and Practical
15. Assessment Methods and Types
A COURSEWORK weighted at 70%. A CLASS TEST weighted at 30%.
A class test weighted at 30% (learning outcomes 1-3)
A coursework weighted at 70% (learning outcomes 1-3)
16. Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims :
Refer to the Programme Specification
17. Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes:
Refer to the Programme Specification
18. Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic:
Week Topics L T P O Ind
Introduction
Overview of the Module
General Guidelines & Learning Approach
Assessments Briefing
1 Introduction to the Subject Area 2 1 7
o History and Overview of Security
o Users, Systems and Data
o The Information Security Cycle
o Security Threats
Security Technologies– CE00398-4 Page 2of 4
Asia Pacific Institute of Information Technology
Security Concepts, Models and Protocols
CIA – Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability
AAA – Authentication, Authorization and
2 2 1 7
Accounting
Security Operations: Essential Functions
Physical Security: Structural, Electronic and
Human Protection Systems
Personnel Security: Management, Leadership
and Ethics
3 Information Security: Information Protection 2 1 7
Strategies, Communications Security, Computer
Security
Network Security
Manage Data Security
Network Security Threats
Terminology and Background
2 1 7
Understand network attack techniques
4
Identify network attack detection problems
Use network scanning tools
Risk Management
Risk Analysis
Implement Vulnerability Assessment Tools and 2 1 7
5
Techniques
Scan for Vulnerabilities
Mitigate and Deterrent Techniques
Managing Certificates
Install a CA Hierarchy
Enroll Certificates 2 1 7
6
Secure Network Traffic by Using Certificates
Renew,Backup,Restore and Revokes
Certificates
Fundamental of Firewall
Types of Firewall
Pros and Cons of Firewalls 4 2 14
7-8 Rules and packet filters
Proxy
Honey pot
Wireless Network Security
Understand the components of a wireless
network
4 2 14
Understand wireless technologies
9-10
Detect wireless network
Secure wireless communication
Developing a wireless policy
Implement Compliance and Operational Security
Physical Security
4 2 14
11-12 Legal Compliance
Security Awareness and Training
Integrate System and Data with Third Parties
Security Technologies– CE00398-4 Page 3of 4
Asia Pacific Institute of Information Technology
Troubleshooting and Managing Security Incidents
13 Respond to Security Incidents
Recover from a Security Incident 2 1 7
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Planning
14-15 Business Continuity 4 2 14
Plan for Disaster Recovery
Execute DRPs and Procedure
Summary
Summary of Module
Revision of Major Topic Areas
16 2 1 7
Assessment Discussion
Presentation
TOTAL 32 16 112
19.
Essential Reading
Darril Gibson (2017) Comptia Security + (4th edition), YCDA LLC Press, ISBN 978-
1939136053
Charles J. Brooks, Philip Craig (2018), Cybersecurity Essentials 1st Edition, Sybex
ISBN 978-1119362395
20. Other additional information:
None
Security Technologies– CE00398-4 Page 4of 4
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Course Description - ACADEMIC YEAR 2022/2023: Software and Systems SecurityDokumen3 halamanCourse Description - ACADEMIC YEAR 2022/2023: Software and Systems SecurityazfaryaqubBelum ada peringkat
- IT 513 Course OutlineDokumen4 halamanIT 513 Course OutlineWaleed HussainBelum ada peringkat
- Bca Ds Sem-5 Information Security FundamentalsDokumen4 halamanBca Ds Sem-5 Information Security FundamentalsVikas SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Course Plan Information SecurityDokumen7 halamanCourse Plan Information SecurityMalik KashifBelum ada peringkat
- CT037 3.5 2 Network SecurityDokumen6 halamanCT037 3.5 2 Network SecurityYogeswaran NathanBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Cybersecurity: Nanodegree Program SyllabusDokumen15 halamanIntroduction To Cybersecurity: Nanodegree Program SyllabusaamirBelum ada peringkat
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional - CISSPDokumen3 halamanCertified Information Systems Security Professional - CISSPirfantrvlBelum ada peringkat
- Information and Network SecurityDokumen4 halamanInformation and Network SecurityMananBelum ada peringkat
- Secure Software DevelopmenttDokumen3 halamanSecure Software DevelopmenttRama ElhouniBelum ada peringkat
- IT202 DCCY2103 Internetworking SecurityDokumen4 halamanIT202 DCCY2103 Internetworking SecuritylillyBelum ada peringkat
- SYLLABUSDokumen3 halamanSYLLABUSLaugh For FunBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Information SecurityDokumen5 halamanIntroduction To Information SecurityjamesBelum ada peringkat
- Cyber SecurityDokumen11 halamanCyber SecurityGM RajputBelum ada peringkat
- Course Outcomes Course Title: IF5966 IT Security Course Code Semester Name of The Course Course Outcomes StatementsDokumen12 halamanCourse Outcomes Course Title: IF5966 IT Security Course Code Semester Name of The Course Course Outcomes StatementsSwapnil KaleBelum ada peringkat
- fundametal of secueity courseoutlineDokumen2 halamanfundametal of secueity courseoutlinehaileBelum ada peringkat
- TOC CRS IDAM SailPointDokumen17 halamanTOC CRS IDAM SailPointAl-Ameen Engineering College ErodeBelum ada peringkat
- Penetration Testing and Ethical Hacking Syllabus 2023 2.2024 UpdateDokumen9 halamanPenetration Testing and Ethical Hacking Syllabus 2023 2.2024 UpdateSanjay DilipBelum ada peringkat
- Infrastructure TracksDokumen8 halamanInfrastructure Tracksabdlwhapahmed12Belum ada peringkat
- Cyber Expert - Masters V3Dokumen23 halamanCyber Expert - Masters V3John JosephBelum ada peringkat
- CybersecurityDokumen3 halamanCybersecurityjnwahangidjolBelum ada peringkat
- Module 3 - IASDokumen14 halamanModule 3 - IASKirito ZachariasBelum ada peringkat
- Cyber Security: Master's ProgramDokumen25 halamanCyber Security: Master's ProgramKishore.v Kishore.VBelum ada peringkat
- Network & Cyber Security AcademyDokumen10 halamanNetwork & Cyber Security AcademyKYAW SHWE WINBelum ada peringkat
- Claned ZharBiz Cyber Security For Leaders CourseDokumen4 halamanClaned ZharBiz Cyber Security For Leaders CourseRobert RainmanBelum ada peringkat
- IT502 - Information SecurityDokumen3 halamanIT502 - Information SecurityNader AzalBelum ada peringkat
- Cyber Security Expert - Masters - SimplilearnDokumen23 halamanCyber Security Expert - Masters - SimplilearnKopparapu MukeshBelum ada peringkat
- CyberEssentials v1.1 - Scope and Sequence PDFDokumen4 halamanCyberEssentials v1.1 - Scope and Sequence PDFAlionEminiBelum ada peringkat
- Network Management and Security CIT4035 - August 2018Dokumen7 halamanNetwork Management and Security CIT4035 - August 2018Jordane RandallBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Bonus ClassesDokumen7 halaman7 Bonus ClassesDev ZakBelum ada peringkat
- Network CsDokumen5 halamanNetwork Csnotsubhash2000Belum ada peringkat
- SYLLABUSDokumen3 halamanSYLLABUSOpanyin GabbiBelum ada peringkat
- Information Security Analysis and Audit CourseDokumen3 halamanInformation Security Analysis and Audit CourseSukriti Jaitly100% (1)
- Cyber Network Security Syllabus and OutlineDokumen5 halamanCyber Network Security Syllabus and Outlines.hakimBelum ada peringkat
- CT702-N Cyber SecurityDokumen4 halamanCT702-N Cyber SecurityDevanshBelum ada peringkat
- Simplilearn Cyber Security Expert MastersDokumen23 halamanSimplilearn Cyber Security Expert MastersNadeem MsBelum ada peringkat
- CySA SyllabusDokumen4 halamanCySA Syllabussmm azadBelum ada peringkat
- Lead Security Operations ManagementDokumen1 halamanLead Security Operations Managementgyan.9999Belum ada peringkat
- Course Overview: This Course Provides In-Depth Coverage of The Eight Domains Required To Pass The CISSP ExamDokumen30 halamanCourse Overview: This Course Provides In-Depth Coverage of The Eight Domains Required To Pass The CISSP ExamAbdul GhaffarBelum ada peringkat
- Cyber Security Project ProposalDokumen8 halamanCyber Security Project Proposalsiwachchinmay272004Belum ada peringkat
- Intro To Cybersecurity Nanodegree Program SyllabusDokumen15 halamanIntro To Cybersecurity Nanodegree Program SyllabusvictorBelum ada peringkat
- Ethical Hacking CourseDokumen17 halamanEthical Hacking CoursegiansantosmendoncaBelum ada peringkat
- Pecb Iso 27002 Manager Exam Preparation GuideDokumen8 halamanPecb Iso 27002 Manager Exam Preparation GuideMike StudLabBelum ada peringkat
- ModdelDokumen14 halamanModdelArif ShaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Wireless Network Makes Information Access Much EasierDokumen3 halamanWireless Network Makes Information Access Much Easierapi-6929342Belum ada peringkat
- Program:B.Tech (BA+BD) Course Code:CSBD4070 Course Name:Big Data SecurityDokumen23 halamanProgram:B.Tech (BA+BD) Course Code:CSBD4070 Course Name:Big Data SecurityVairavel ChenniyappanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1-Overview & Course ProjectsDokumen74 halamanLecture 1-Overview & Course ProjectsHasham AkramBelum ada peringkat
- Bcse354e Information-Security-Management Eth 1.0 77 Bcse354eDokumen2 halamanBcse354e Information-Security-Management Eth 1.0 77 Bcse354eRajvardhan PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Brochure ECSADokumen4 halamanBrochure ECSAjuniBelum ada peringkat
- CSCD 418 Computer Systems Security Course Outline - 2021Dokumen3 halamanCSCD 418 Computer Systems Security Course Outline - 2021TrialBelum ada peringkat
- Cyber Security: Professional Diploma inDokumen5 halamanCyber Security: Professional Diploma inAnshpreet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- FULL Download Ebook PDF Information Security Principles and Practices 2nd Edition PDF EbookDokumen41 halamanFULL Download Ebook PDF Information Security Principles and Practices 2nd Edition PDF Ebookjorge.goldwyn787100% (27)
- Computer Security Spec 1617Dokumen1 halamanComputer Security Spec 1617maxventoBelum ada peringkat
- Obls 6it2Dokumen11 halamanObls 6it2eigertechnoBelum ada peringkat
- Cyber Security Fundamentals and PracticesDokumen6 halamanCyber Security Fundamentals and PracticesAravind VbkBelum ada peringkat
- ITE Network Security SyllabusDokumen3 halamanITE Network Security SyllabusJojo CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Information Technology and Cyber SecurityDokumen250 halamanInformation Technology and Cyber Securitycn8q8nvnd5Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Cybersecurity Nanodegree Program SyllabusDokumen15 halamanIntroduction to Cybersecurity Nanodegree Program SyllabusLuiz Henrique Oliveira de SouzaBelum ada peringkat
- IT Risk Management & Cyber Security Course OverviewDokumen7 halamanIT Risk Management & Cyber Security Course Overviewskkk kkkBelum ada peringkat
- System SecurityDokumen4 halamanSystem SecurityTanishka MayekarBelum ada peringkat
- Wi CFG VlansDokumen16 halamanWi CFG Vlansyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- Netw 05A: Applied Wireless Security: 802.11i & Wi-Fi Protected AccessDokumen10 halamanNetw 05A: Applied Wireless Security: 802.11i & Wi-Fi Protected Accessyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- (A) Given Values As Below:: TutorialDokumen3 halaman(A) Given Values As Below:: Tutorialyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- VLAN ID-Based Forwarding: DateDokumen9 halamanVLAN ID-Based Forwarding: Dateyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- Networks and Networking AICT003-3-2 Local Area Network TechnologiesDokumen41 halamanNetworks and Networking AICT003-3-2 Local Area Network Technologiesyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- 006 - Security ManagementDokumen15 halaman006 - Security Managementyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- ConfigGuide VLAN 1Dokumen44 halamanConfigGuide VLAN 1अमित सिंहBelum ada peringkat
- RedPort WXa Admin Guide VLAN AddendumDokumen10 halamanRedPort WXa Admin Guide VLAN Addendumyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- VlanDokumen35 halamanVlanAmjad KhanBelum ada peringkat
- AvazuDokumen1 halamanAvazuyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- 005 - Security Concepts Models and ProtocolsDokumen22 halaman005 - Security Concepts Models and Protocolsyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction to VDM-SL Specification of Incubator Monitoring SystemDokumen36 halamanIntroduction to VDM-SL Specification of Incubator Monitoring Systemyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorial NWTDokumen12 halamanTutorial NWTyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- L1 NWT - IP Addressing-RevisionDokumen32 halamanL1 NWT - IP Addressing-Revisionyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- Networks and Networking AICT003-3-2 RoutingDokumen58 halamanNetworks and Networking AICT003-3-2 Routingyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Networking CT043-3-1 Wireless NetworksDokumen46 halamanIntroduction To Networking CT043-3-1 Wireless Networksyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- Aravindh's: This Version Made Exclusively For: SubscribersDokumen69 halamanAravindh's: This Version Made Exclusively For: Subscribersyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- Instagram LectureDokumen3 halamanInstagram Lectureyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- Downloading ErrorDokumen1 halamanDownloading Erroryoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- Aravindh's: This Version Made Exclusively For: SubscribersDokumen69 halamanAravindh's: This Version Made Exclusively For: Subscribersyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- AvazuDokumen1 halamanAvazuyoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- Recommendation for Salah Uddin Khan from LecturerDokumen1 halamanRecommendation for Salah Uddin Khan from Lectureryoges_0695Belum ada peringkat
- C# Multithreaded and Parallel Programming Sample ChapterDokumen36 halamanC# Multithreaded and Parallel Programming Sample ChapterPackt PublishingBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamic PricingDokumen9 halamanDynamic PricingkoolboyankitBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To Supply Chain Management Commerce EssayDokumen9 halamanAn Introduction To Supply Chain Management Commerce EssayarakeelBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrotrac Ii User Manual 0.9 PDFDokumen43 halamanHydrotrac Ii User Manual 0.9 PDFViliame D RoqicaBelum ada peringkat
- Excel ResearchDokumen11 halamanExcel Researchjanjan eresoBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Behind Cost Differences in Similar Software ProductsDokumen5 halamanFactors Behind Cost Differences in Similar Software ProductsMary Joy Paclibar BustamanteBelum ada peringkat
- Moldova Ict Summit Agenda enDokumen5 halamanMoldova Ict Summit Agenda enGlyukvaBelum ada peringkat
- Case StudyDokumen11 halamanCase StudyAbinaya Sathya0% (1)
- Game InfoDokumen2 halamanGame InfoNatt BookerBelum ada peringkat
- Blockchain Application On Financial Sector in The FutureDokumen12 halamanBlockchain Application On Financial Sector in The FutureVincent RinaldyBelum ada peringkat
- Matlab R2010a LinkDokumen8 halamanMatlab R2010a LinktariBelum ada peringkat
- Anna University:: Chennai - 600 025. May, 2019 - Semester ExaminationsDokumen4 halamanAnna University:: Chennai - 600 025. May, 2019 - Semester ExaminationsdkBelum ada peringkat
- Equipment and Controls for Automatic Transfer Systems (ATSDokumen7 halamanEquipment and Controls for Automatic Transfer Systems (ATSrajneesh jainBelum ada peringkat
- Processing of Satellite Image Using Digital Image ProcessingDokumen21 halamanProcessing of Satellite Image Using Digital Image ProcessingSana UllahBelum ada peringkat
- 02 6Dokumen13 halaman02 6chaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis Final Document Tall BuildingsDokumen194 halamanThesis Final Document Tall BuildingsPab Fer Man100% (3)
- Python TutorDokumen116 halamanPython TutorRajkumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Vxworks Installing 6.5 1.1.2.0Dokumen16 halamanVxworks Installing 6.5 1.1.2.0premathiraviamBelum ada peringkat
- Assembly LanguageDokumen21 halamanAssembly LanguageAbdul MateenBelum ada peringkat
- Group Output Scoring RubricDokumen1 halamanGroup Output Scoring RubricsheilaBelum ada peringkat
- DragonWave Horizon COMPACT Plus User Manual PDFDokumen200 halamanDragonWave Horizon COMPACT Plus User Manual PDFpankajengBelum ada peringkat
- Parts Manual - Carro de Limpeza TennantDokumen184 halamanParts Manual - Carro de Limpeza TennantMarcelo LopesBelum ada peringkat
- Whitepaper Supplier CollaborationDokumen20 halamanWhitepaper Supplier Collaborationghosh_souvikBelum ada peringkat
- eQUEST v3 65 Update SummaryDokumen8 halamaneQUEST v3 65 Update SummaryJames YoungBelum ada peringkat
- Tws Inst Pull Info v3 8 READMEDokumen3 halamanTws Inst Pull Info v3 8 READMENavaneetha KrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- 7+ Years SAP ABAP ExpertiseDokumen6 halaman7+ Years SAP ABAP ExpertisemysrulesBelum ada peringkat
- Mumtaz CV 2.doc1Dokumen2 halamanMumtaz CV 2.doc1100-235100% (4)
- Question Bank for Python ProgrammingDokumen5 halamanQuestion Bank for Python ProgrammingJyoti SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Emu 4Dokumen16 halamanEmu 4Adhithya SrinivasanBelum ada peringkat
- CEH Certified Ethical Hacker Practice Exams, Third EditionDari EverandCEH Certified Ethical Hacker Practice Exams, Third EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityDari EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Cybersecurity For Beginners: Learn How To Defend Against Online ThreatsDari EverandCybersecurity For Beginners: Learn How To Defend Against Online ThreatsBelum ada peringkat
- An Ultimate Guide to Kali Linux for BeginnersDari EverandAn Ultimate Guide to Kali Linux for BeginnersPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (4)
- IAPP CIPM Certified Information Privacy Manager Study GuideDari EverandIAPP CIPM Certified Information Privacy Manager Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- HACKING: Hacking Firewalls & Bypassing HoneypotsDari EverandHACKING: Hacking Firewalls & Bypassing HoneypotsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationDari EverandThe Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (6)
- OSCP Offensive Security Certified Professional Practice Tests With Answers To Pass the OSCP Ethical Hacking Certification ExamDari EverandOSCP Offensive Security Certified Professional Practice Tests With Answers To Pass the OSCP Ethical Hacking Certification ExamBelum ada peringkat
- (ISC)2 CCSP Certified Cloud Security Professional Official Study GuideDari Everand(ISC)2 CCSP Certified Cloud Security Professional Official Study GuidePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Facing Cyber Threats Head On: Protecting Yourself and Your BusinessDari EverandFacing Cyber Threats Head On: Protecting Yourself and Your BusinessPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (27)
- Social Engineering: The Science of Human Hacking 2nd EditionDari EverandSocial Engineering: The Science of Human Hacking 2nd EditionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (38)
- No Place to Hide: Edward Snowden, the NSA, and the U.S. Surveillance StateDari EverandNo Place to Hide: Edward Snowden, the NSA, and the U.S. Surveillance StatePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (250)
- Hacking With Kali Linux : A Comprehensive, Step-By-Step Beginner's Guide to Learn Ethical Hacking With Practical Examples to Computer Hacking, Wireless Network, Cybersecurity and Penetration TestingDari EverandHacking With Kali Linux : A Comprehensive, Step-By-Step Beginner's Guide to Learn Ethical Hacking With Practical Examples to Computer Hacking, Wireless Network, Cybersecurity and Penetration TestingPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (9)
- Social Engineering: The Science of Human HackingDari EverandSocial Engineering: The Science of Human HackingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (44)
- Apple Card and Apple Pay: A Ridiculously Simple Guide to Mobile PaymentsDari EverandApple Card and Apple Pay: A Ridiculously Simple Guide to Mobile PaymentsBelum ada peringkat
- Cybersecurity: The Hacker Proof Guide To Cybersecurity, Internet Safety, Cybercrime, & Preventing AttacksDari EverandCybersecurity: The Hacker Proof Guide To Cybersecurity, Internet Safety, Cybercrime, & Preventing AttacksBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Resilience: Is Your Company Ready for the Next Cyber Threat?Dari EverandDigital Resilience: Is Your Company Ready for the Next Cyber Threat?Belum ada peringkat
- Hackers & Painters: Big Ideas from the Computer AgeDari EverandHackers & Painters: Big Ideas from the Computer AgePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (5)