Ibgzj 7 W 0 Mcib 1
Diunggah oleh
Yusuf HussenJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ibgzj 7 W 0 Mcib 1
Diunggah oleh
Yusuf HussenHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Rubrics for assessing academic language and literacies
The language and academic literacies rubrics are designed to assist RMIT teaching staff to give
practical advice to students on their language and academic skills. Teachers can use the language
and literacies rubrics to provide targeted feedback to students. This feedback aims to support
students in the development of their academic writing.
Why use the language and academic literacies rubric?
The rubric is based on the premise that academic literacies are best developed within contexts that
are meaningful and relevant to students. Given that assessment is a key focus for students, the
purpose of the rubric is to assist lecturers to support students to understand what is expected of them
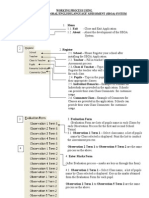
in their assessments. The rubric is based on the following academic writing ‘inverted triangle mode’
which demonstrates that there is hierarchy of academic literacies in assignment tasks.
The academic writing hierarchy triangle
Higher order skills:
can be supported
by the lecturer
using the rubric,
models, examples
and practice
activities
e.g. Learning Lab
Lower order skills:
mainly a student responsibility,
with general feedback from the
lecturer
Adapted from UniSA Learning Connection: a guide for staff
The academic writing triangle shows the importance of the higher order skills of understanding and
addressing the purpose (i.e. the assignment question), using an acceptable structure, and integrating
evidence from appropriate sources. Explicit feedback using the rubric can give students specific
advice on their academic writing skills. As feedback is highly valued by students it is anticipated that
use of the rubric could support positive GTS scores.
How to use the rubric to support your teaching
The writing skills rubric can be adapted to any assignment and is intended to be used as a template
only. In tutorials or lectures:
- Show students the academic writing triangle and explain the relative importance of each of the
academic writing skills areas.
- Show the rubric, how you have contextualised it to your assignment and explain the criteria. Most
of your criteria will fit into the first section (Purpose) of the rubric. You may want to add other
criteria categories here.
- Highlight to students the resources from the Learning Lab that have models of specific skills (far
right column). For example, if you are not sure how to structure an essay look at the essay
structure tutorial on the Learning Lab.
RMIT Study and Learning Centre 2 December 2012
Rubrics for assessing academic language and literacies
Academic writing skills rubric – generic
Task response Task questions Good response Links
Purpose Has the student understood the task and Appropriate, relevant Planning an assignment
Understanding and covered the key points? / Does the response Key points covered
addressing the task adequately address the topic and task?
Structure Is there a clear structure to the response? Clear argument Essay structure
argument Introduction, Easy to follow Quicktip
introduction body and conclusion? Context , topic and main ideas Essay structure
conclusion Do the paragraphs contain one main idea that Summing up Tutorial
+paragraphs is explored using relevant evidence? Paragraphs - 1 main idea (topic
sentence)
Linked to overall idea
Research Is there evidence of research? Information paraphrased and Paraphrasing
Integrating evidence - Is it properly referenced? synthesised in own words; quotes Paraphrasing tutorial
Paraphrasing/ synthesising Are source materials properly integrated and used sparingly Integrating references
Referencing, citing referenced in-text? Information is correctly referenced Referencing -
– in both in-text and in reference
list
Sentences Is there a range of vocabulary? Are sentences Range of sentences Sentence construction
Grammar grammatically correct? Are sentences accurate Few errors
Vocabulary and complete? Good use of appropriate words
Spelling Has a spell check been used? Correct spelling Spelling
Is spelling accurate?
Feedback Writing communicates meaning Editing writing
clearly and achieves purpose of
the task
RMIT Study and Learning Centre 3 December 2012
Rubrics for assessing academic language and literacies
Essay writing rubric
Task response Good response Satisfactory response Unsatisfactory response Links
Purpose Appropriate, relevant Understands the task and the Not demonstrated an understanding Planning and
Understanding and Key points covered information but not all key points of the topic assignment
addressing the are included or fully developed Information often inaccurate or
task irrelevant
Structure Easy to follow Not always easy to follow Difficult to follow Essay structure
- argument - Clear argument - Evidence of an overall - argument attempted but Quicktip
- introduction - Context, topic and main argument, - does not fully address the Essay structure
- conclusion ideas - does not address the three context, topic and main ideas Tutorial
- paragraphs - Summing up main areas adequately - no clear conclusion
- One main idea (in a topic - Conclusion attempted but - lacks a main idea
sentence); linked to does not appropriately sum up
overall idea the argument presented; main
idea not always clear
Research Paraphrases and synthesises Some ability to express ideas in Relies heavily on words and Paraphrasing
Integrating information in own words; own words passages copied from texts Paraphrasing
evidence Quotes used sparingly Aware of required system and how Referencing requirements not tutorial
Paraphrasing/ Information is correctly it should be used followed Integrating
synthesising referenced –in-text and in references
Referencing reference list Referencing -
citing
Sentences Range of sentences Some errors but do not interfere Errors are frequent, making Sentence
Grammar Few errors with meaning understanding difficult construction
Vocabulary Good use of appropriate Vocabulary adequate for the task Limited vocabulary, words often Spelling
Spelling words occasional errors. Some difficulty incorrect or incorrectly used
Correct with subject-specific words, terms Numerous errors, spell check not
Generally correct, some errors used
Feedback Writing communicates Writing generally communicates Logic and meaning not clear
meaning clearly and achieves effectively but logic and meaning
purpose of the task not always clear
RMIT Study and Learning Centre 4 December 2012
Rubrics for assessing academic language and literacies
Report rubric
Task response Good response Satisfactory response Unsatisfactory response Links
Purpose Appropriate, relevant Understands the task and the Not demonstrated Learning Lab
Understanding and Key points covered information but not all key points understanding of the topic reports
addressing the task are included or fully developed Information often inaccurate Sample report
or irrelevant
Structure Uses appropriate report Uses report structure but not all Does not use appropriate
Uses appropriate structure appropriate report structure
report structure
Format Appropriate sections with Sections generally appropriate but Does not address all
Sections headings some gaps sections adequately
Executive summary Format generally consistent Format generally consistent but Format inconsistent Executive
Summarises whole Summarises whole report gaps does not summarise whole summary and
report attempts to summarise whole report introduction
-all main sections report with some gaps does not cover all main
sections
Introduction Context, topic and purpose Does not address the three main Does not address the
outlines context, areas (context, topic and purpose) context, topic and purpose
introduces topic, adequately
states purpose
The main section/s: Clear sections in paragraphs Information in sections with some Insufficient structure and Results/discussion-
findings, discussion, with appropriate subheadings lack of clarity or accuracy in clarity in sections and paragraphs,
etc. paragraphs and subheadings subheadings analysing and
integrating
evidence
Conclusion Sums up report Conclusion attempted but does not No clear conclusion Conclusion and
appropriately sum up findings recommendations
Recommendations Clearly outlines further actions Outlines further action but needs Does not clearly outline
clarity and/or not linked to the appropriate further actions
conclusion
Paragraphs One main idea in each Main idea of paragraph not always Lacks a main idea in most Results/discussion-
paragraph (in a topic clear; paragraphs; sections with paragraphs,
sentence); linked to overall wrong information analysing and
idea integrating
evidence
RMIT Study and Learning Centre 5 December 2012
Rubrics for assessing academic language and literacies
Task response Good response Satisfactory response Unsatisfactory response Links
Research Paraphrases, synthesises Some ability to express ideas in Relies heavily on words and
Integrating evidence: information in own words; own words passages copied from texts
paraphrasing/ quotes used sparingly
synthesising
Referencing, citing Information is correctly Aware of required system and how Referencing requirements
referenced – both in-text and it should be used; some not followed Integrating
in reference list inaccuracies references
Sentences, grammar Range of sentences Grammar generally appropriate to Errors are frequent, making
Grammar appropriate to communicate meaning clearly; understanding difficult
communicate meaning clearly; some errors Sentences
few errors - do not detract from
meaning
Vocabulary, Uses appropriate vocabulary Vocabulary adequate; occasional Limited vocabulary, words
spelling and Spelling and punctuation errors using subject-specific often incorrect or incorrectly
Academic word list
punctuation accurate; carefully checked words/terms used
tool
Spelling and punctuation generally Numerous errors, spell
Spelling
accurate; some errors requiring check not used
more careful checking
Feedback Writing communicates Writing generally communicates Logic and meaning not clear
meaning clearly and achieves effectively but logic and meaning
purpose of the task not always clear
RMIT Study and Learning Centre 6 December 2012
Rubrics for assessing academic language and literacies
Oral presentation rubric – Structure
Task response Good response Satisfactory response Unsatisfactory response Links
Structure and Appropriate structure and Generally appropriate structure and Structure and organisation not Oral
content organisation organisation some parts difficult to appropriate –difficult to follow presentations
follow
Introduction Outlines context, topic and Outlines context, topic and content Does not outline context, topic Oral
content but not all clear and content presentation
structure
Body Main ideas logical & clear Main ideas generally clear Does not clearly address main
Some lack of clarity ideas
Conclusion Sums up topic well Generally sums up topic well Does not sum up – no clear
conclusion
Evidence Appropriately paraphrases & Generally appropriately paraphrases Relies on information copied
references & references from texts; not appropriately
referenced
Oral presentation rubric – Delivery
Task response Good response Satisfactory response Unsatisfactory response Links
Use of notes / Notes used well Notes / slides used more than Overuse of notes Oral
slides necessary Read rather than talked presentations-
presenting
Volume and clarity Clear, easy to hear and Mainly clear ; appropriate Difficult to understand;
of expression understand; appropriate expression – errors do not detract inappropriate words and
expression for oral presentation from meaning expression for oral presentation
Timing Timing enhances meaning, Mostly well timed; could pause Too fast/slow; timing detracts
suitable pauses from meaning
Eye contact & body Eye contact consistent Eye contact but not necessarily Little eye contact with audience
language inclusive
Audience Confident and enthusiastic Lack of confidence affects audience Audience not engaged Engaging the
engagement presentation engagement audience
Use of visual aids Enhance the presentation Enhance the presentation; Not relevant – distract rather than
occasionally distracting add to the presentation
RMIT Study and Learning Centre 7 December 2012
Rubrics for assessing academic language and literacies
Reflective journal rubric
Task response Good response Satisfactory response Unsatisfactory response Links
Purpose
Understood and addressed task Has understood the task but points Has not understood the nature of Reflective
Understanding and
Information is appropriate and selected are not always relevant or the task. Relies on information journal
addressing the task
relevant fully discussed copied from texts
Key points organised to illustrate
points being made
Structure and Well structured, easy to follow Some structure but information not Information randomly presented Reflective
content Addressed the task always presented in a logical order No sense of structure journal .pdf
Introduction Context and purpose – identified Context and purpose introduced but Context and purpose – not clear
and clearly described need further clarification
Paragraphs Main ideas expressed in clear Main ideas not always clear or fully Main ideas not clearly defined Paragraphs
topic sentences supported Relevant research - not used to Integrating
Theory integrated to Evidence of research but its inform analysis references
demonstrate how it informed applicability and value flawed
practice
Conclusion Learning and the benefit of Basic summary of the benefits of the Reflection lacks evidence of Conclusion
reflection well summarised reflection personal growth
Reflection Theory well integrated to Evidence of research and thinking Evaluation of experience lacking Reflective
indicate how it has and will journal
inform behaviour and thinking
Sentences Range of sentences Errors do not interfere with meaning Errors are frequent, often making Sentence
Grammar Few errors understanding difficult construction
Vocabulary Demonstrated knowledge of key Vocabulary adequate for the task Limited vocabulary, no use made Academic
vocabulary Subject specific vocabulary not fully of specialised course vocabulary word list tool
utilised
Spelling Correct Occasional errors Numerous errors Spelling
Spellcheck not used
Feedback Reflection structured and clearly Has benefitted from the experience Writing does not show evidence
written but not adequately used learning of personal learning
Has reflected on the experience and research Ideas not clearly expressed
and indicated its implications for Shown some insight into future Structure lacking
the future relevance
RMIT Study and Learning Centre 8 December 2012
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Civil Code (Amharic) - REdDokumen742 halamanCivil Code (Amharic) - REdErmiyas TarikuBelum ada peringkat
- Ms JESBS 46300Dokumen21 halamanMs JESBS 46300Yusuf HussenBelum ada peringkat
- 01 WholeDokumen186 halaman01 WholeYusuf HussenBelum ada peringkat
- We Dance Around in A Ring and Suppose - Academic Engagement With Traditional KnowledgeDokumen5 halamanWe Dance Around in A Ring and Suppose - Academic Engagement With Traditional KnowledgeYusuf HussenBelum ada peringkat
- Biopiracy - The Struggle For Traditional Knowledge RightsDokumen23 halamanBiopiracy - The Struggle For Traditional Knowledge RightsYusuf HussenBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Culture: Perspectives in PracticeDokumen4 halamanTeaching Culture: Perspectives in PracticeYusuf HussenBelum ada peringkat
- Nigeria - Conservation, 'Traditional' Knowledge & The CommonsDokumen9 halamanNigeria - Conservation, 'Traditional' Knowledge & The CommonsYusuf HussenBelum ada peringkat
- ExerciseDokumen1 halamanExerciseYusuf HussenBelum ada peringkat
- Learning From The Past - Traditional Knowledge and Sustainable DevelopmentDokumen22 halamanLearning From The Past - Traditional Knowledge and Sustainable DevelopmentYusuf Hussen100% (1)
- Wabiilee FaxeeeeeDokumen3 halamanWabiilee FaxeeeeeYusuf Hussen0% (1)
- Du/doll/575/2010 14/03/2010 . 2011 PHDDokumen1 halamanDu/doll/575/2010 14/03/2010 . 2011 PHDYusuf HussenBelum ada peringkat
- Poetry NotesDokumen26 halamanPoetry NotesYusuf Hussen75% (8)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- AISSEE 2021 Information BulletinDokumen72 halamanAISSEE 2021 Information BulletinCGM RO HYDBelum ada peringkat
- WIPO Academy Advanced Distance Learning Course On Basics of Patent Drafting (DL320E15S1)Dokumen7 halamanWIPO Academy Advanced Distance Learning Course On Basics of Patent Drafting (DL320E15S1)cresjohnBelum ada peringkat
- MRCP (UK) Regulations October 2023 UpdateDokumen18 halamanMRCP (UK) Regulations October 2023 Updateniamul islamBelum ada peringkat
- Resume-Mayur Kasar Jan 16Dokumen3 halamanResume-Mayur Kasar Jan 16Mayur KasarBelum ada peringkat
- Working Process SBOADokumen2 halamanWorking Process SBOAalehanieBelum ada peringkat
- Expert Advanced TRB 9781447973768 UNIT 1Dokumen11 halamanExpert Advanced TRB 9781447973768 UNIT 1Natalia Kozlowska0% (2)
- Dissertation Module Guide OnlyDokumen20 halamanDissertation Module Guide OnlyAKSHIT SHUKLABelum ada peringkat
- QA SyllabusDokumen9 halamanQA SyllabusSophiaBelum ada peringkat
- Hogar Dulce Hogar - QuizDokumen2 halamanHogar Dulce Hogar - QuizLiam JosephBelum ada peringkat
- Course SpecificationDokumen8 halamanCourse Specificationللل اتتBelum ada peringkat
- GKDokumen101 halamanGKAastha MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Reflective Learning Journal (Teacher Guide) PDFDokumen21 halamanReflective Learning Journal (Teacher Guide) PDFGary ZhaiBelum ada peringkat
- Dedication 5. Table of Contents: Research Form and StyleDokumen7 halamanDedication 5. Table of Contents: Research Form and StyleKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isBelum ada peringkat
- 02 Olympiads PhysicsDokumen4 halaman02 Olympiads PhysicsHarsh Tiwari33% (6)
- Common Abbreviations & Acronyms Used in Education Acronym Definition AADokumen8 halamanCommon Abbreviations & Acronyms Used in Education Acronym Definition AASarigta Ku KadnantanoBelum ada peringkat
- Official Notification For TSNPDCL RecruitmentDokumen16 halamanOfficial Notification For TSNPDCL RecruitmentSupriya SantreBelum ada peringkat
- Root Cause Analysis For Drugmakers-ExecSeriesDokumen57 halamanRoot Cause Analysis For Drugmakers-ExecSeriesDholakiaBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Specialist 3C3D Calc Assumed Exam 2014Dokumen28 halamanMaths Specialist 3C3D Calc Assumed Exam 2014gragon.07Belum ada peringkat
- MSC PhysicsDokumen1 halamanMSC PhysicssampannkumarBelum ada peringkat
- UP Admission RequirementsDokumen1 halamanUP Admission RequirementsCamille GrefaldiaBelum ada peringkat
- Year Ten Feature Article StructureDokumen3 halamanYear Ten Feature Article Structureapi-253030443100% (1)
- Action Plan 2022 2023Dokumen6 halamanAction Plan 2022 2023Devie Anne BiscarraBelum ada peringkat
- Bahasa Inggeris Upsr: Prepared By: Norhafizah Binti Hamidi SK Seri Bintang SelatanDokumen23 halamanBahasa Inggeris Upsr: Prepared By: Norhafizah Binti Hamidi SK Seri Bintang SelatankienleongBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Planning PDFDokumen19 halamanEnvironmental Planning PDFYeng M. De Vera100% (1)
- Action Research Proposal ROLDAN PR2Dokumen11 halamanAction Research Proposal ROLDAN PR2Alehxis Gglc Fonts RnlptBelum ada peringkat
- MD RadiodiagnosisDokumen12 halamanMD RadiodiagnosisPravin TamminanaBelum ada peringkat
- Georgia Studies Syllabus 2020-2021 1Dokumen2 halamanGeorgia Studies Syllabus 2020-2021 1api-551964423Belum ada peringkat
- The Civil Engineering Professional Licensure Examination - docx-CLAVERIADokumen3 halamanThe Civil Engineering Professional Licensure Examination - docx-CLAVERIArose ann claveriaBelum ada peringkat
- MTS 2016 Final NoticeDokumen38 halamanMTS 2016 Final NoticeManprita BasumataryBelum ada peringkat
- Research About Divisoria PartialDokumen4 halamanResearch About Divisoria PartialSean M. InocencioBelum ada peringkat