Lesson 28
Diunggah oleh
MarcTnnDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Lesson 28
Diunggah oleh
MarcTnnHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Lesson Plan
Lesson: Catalysis
Aim :
To study the effect of catalysts on the rate of reaction and how they work.
Learning Outcomes :
At the end of the lesson, students will be able to :
1. explain the effect of catalysts on the rate of a reaction.
2. explain how catalysts work.
3. describe homogenous and heterogenous catalysis.
4. explain the characteristics of biological enzymes.
Assumed prior knowledge :
Students should already :
1. be familiar with energy profiles of exothermic and endothermic reactions
and the concept of activation energy.
2. be familiar with the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of molecular energies.
Underlying Principles
Enabling students to know what to look for.
Time taken to complete the activities : 80 minutes
Differentiation
Questions in the student notes are designed to enable all students to complete the activity.
The pop-up answers are provided for the students to view when they have considered their
responses. Worksheet questions include questions that require recall, understanding and
application of the new concepts learned.
© 2003 Ministry Of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. Page 1 of 5
Development of Lesson :
No. Steps Strategy Resources
1 Set Induction. • Teacher to quiz students to ensure that
(Ascertaining prior they have the prior knowledge.
knowledge and
introducing lesson • Teacher to introduce lesson objectives for
topic for the day). the day.
2 Student Activity Teacher to go through Activities 1 - 4 • Courseware
with the students.
• Activity 1 : Catalysts
Students get to view the energy profiles of
both catalysed and uncatalysed reactions
and compare the difference in their
activation energies.
• Activity 2 : Homogeneous catalysis
Students are shown how catalysts are
categorised as homogeneous and
heterogeneous catalysts. They also get
to view an animation of how Fe2+
catalyses the oxidation of I− by S2O82− .
• Activity 3 : Heterogeneous catalysis
Students get to view an animation of how
nickel catalyses the hydrogenation of
ethene to ethane.
• Activity 4 : Enzymes
Students get to investigate the
characteristics of enzymes, how they are
affected by a change in temperature and
pH.
3 Evaluation • Students to answer questions in the • Worksheet
student worksheet on their own.
4 Extension activity • Students to go through the extension • Websites
activities on their own. • Reference
books.
© 2003 Ministry Of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. Page 2 of 5
Worksheet Answers
1. Catalysts
1.1 a. ii. Q+R
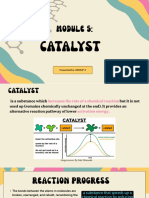
b. A catalyst increases the rate of a reaction.
Energy
R
M
P
P
Reaction coordinate
From the graph above, the activation energy Q for the catalysed
reaction is less than the activation energy Q + R for the uncatalysed reaction.
Hence, a catalyst works by providing an alternative reaction route which has a
lower activation energy.
1.2 i. No effect.
ii. Increases the rate constant.
iii. Increases the rate of the reaction.
iv. No effect.
© 2003 Ministry Of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. Page 3 of 5
1.3
Number of molecules
with energy, E
Ea2 Ea1
Ea1 = activation energy of uncatalysed reaction.
Ea 2 = activation energy of catalysed reaction.
number of molecules having energy
greater than or equal to E a1 .
number of molecules having energy
greater than or equal to Ea2 .
The activation energy of the uncatalysed reaction is taken as E a1 The activation
energy is lowered to E a2 in the presence of a catalyst. The number of molecules
having energy equal to or greater than E a2 is larger than that of E a1 Hence, the
frequency of effective collisions is increased and the rate of reaction is higher.
2. Homogeneous catalysis
2.1 Homogenous catalysts are of the same phase as the reactants while heterogeneous
catalysts are not.
3. Heterogeneous catalysis
3.1 a. Oxidation
b. Heterogeneous catalyst. It is a different phase from the reactants.
c. The adsorption of the reactant molecules on the surface of the catalyst
serves to bring these molecules closer together. The formation of weak bonds
with the catalyst during adsorption also results in the weakening of bonds in
the reactant molecules.
© 2003 Ministry Of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. Page 4 of 5
4. Enzymes
4.1 a. The rate of reaction increases with an increase in temperature up to
a certain temperature. Beyond this temperature, the rate decreases.
b. Enzyme is a protein molecule which can easily be denatured by high
temperature.
© 2003 Ministry Of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. Page 5 of 5
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Detailed Demonstration Lesson Plan FinalDokumen8 halamanA Detailed Demonstration Lesson Plan FinalAriane Ignao Lagatic100% (7)
- Lesson PlanDokumen5 halamanLesson PlanSomasundariBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Standard Cell PotentialDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: Standard Cell PotentialMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Hermes-Pjt Training Manual: RSJ1/RSH1Dokumen152 halamanHermes-Pjt Training Manual: RSJ1/RSH1Cesar Calderon Gr100% (2)
- D7GDokumen8 halamanD7Gfirman manaluBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 27Dokumen4 halamanLesson 27MarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Enzyme Worksheet Answer KeyDokumen3 halamanEnzyme Worksheet Answer KeyEnessa Yurkin100% (1)
- Lesson 29Dokumen3 halamanLesson 29MarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (II)Dokumen4 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (II)MarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations (JNV)Dokumen3 halamanScience Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations (JNV)KEVEN LIAM WILLIAMBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Sem Q3 Module 5 Chemical KineticsDokumen18 halaman2nd Sem Q3 Module 5 Chemical KineticsLia SantillanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 4Dokumen13 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 4ridwan100% (1)
- ANACHEM WEEK 3 TransDokumen4 halamanANACHEM WEEK 3 TransAnn Frencis Louise PalaoBelum ada peringkat
- Aqa Chem New Both Yr's ChecklistDokumen48 halamanAqa Chem New Both Yr's Checklisttbcrqjp7psBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 and 5Dokumen51 halamanChapter 4 and 5Kyla Gabrielle TutoBelum ada peringkat
- Term 2 Reate of Reaction G 12Dokumen41 halamanTerm 2 Reate of Reaction G 12Lesedi TsoaiBelum ada peringkat
- 21 Chemical Kinetics Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDokumen8 halaman21 Chemical Kinetics Formula Sheets Getmarks AppRockstarBelum ada peringkat
- Gen Chem 2 Q2 Module 19Dokumen14 halamanGen Chem 2 Q2 Module 19Beverly JoyBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical KineticsDokumen6 halamanChemical KineticsAjay PawarBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry 2 - Introduction of The SubjectDokumen35 halamanGeneral Chemistry 2 - Introduction of The SubjectNina Grace FamosoBelum ada peringkat
- Aqa Chem New Both Yr's ChecklistDokumen48 halamanAqa Chem New Both Yr's Checklistsumanzaib10Belum ada peringkat
- Bahria College Karachi Chapter # 8: Introduction To Chemical KineticsDokumen15 halamanBahria College Karachi Chapter # 8: Introduction To Chemical KineticsNayan RoyBelum ada peringkat
- Bscpe Sci1 SLM 6Dokumen36 halamanBscpe Sci1 SLM 6April Joy GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Topic Exploration Pack: Instructions and Answers For TeachersDokumen27 halamanTopic Exploration Pack: Instructions and Answers For TeachersTinke WinkeBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Sciences Grade 12 Term 2 Week 5 - 2020Dokumen4 halamanPhysical Sciences Grade 12 Term 2 Week 5 - 2020thabotomoledi1Belum ada peringkat
- Rate of Reaction and Various Factors That Influence ItDokumen28 halamanRate of Reaction and Various Factors That Influence Itjulie cadungonBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Science DLP Q1W5Dokumen8 halamanPhysical Science DLP Q1W5junar asentistaBelum ada peringkat
- Test 10 ChemistryDokumen21 halamanTest 10 Chemistry030929Belum ada peringkat
- Physci Catalyst 101Dokumen34 halamanPhysci Catalyst 101Kyuptonite KimBelum ada peringkat
- KHAMANGA-Pharmaceutics 3 - Stability 2021-AUGUST 2021Dokumen83 halamanKHAMANGA-Pharmaceutics 3 - Stability 2021-AUGUST 2021AkshayKumarSinghBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Science SHS 10.2 Mole-To-Mole StoichiometryDokumen36 halamanPhysical Science SHS 10.2 Mole-To-Mole StoichiometryqueennieBelum ada peringkat
- Phy Sci Week 9Dokumen10 halamanPhy Sci Week 9Queency Panaglima PadidaBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Collision TheoryDokumen30 halamanSimple Collision TheoryJona FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Collision Theory States That For A Reaction To OccurDokumen9 halamanCollision Theory States That For A Reaction To OccurSupia NazmaBelum ada peringkat
- CHem InalsDokumen3 halamanCHem InalsAbigail OconBelum ada peringkat
- Bscpe Sci1 SLM 5Dokumen25 halamanBscpe Sci1 SLM 5April Joy GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 - Q4 - SLM2Dokumen15 halamanGENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 - Q4 - SLM2basisterjohnlorenzBelum ada peringkat
- Dec 4,5,6, 2019 DLPDokumen2 halamanDec 4,5,6, 2019 DLPJedidiah Jara Quidet100% (1)
- General Chemistry 2: 2 Semester - Module 7Dokumen16 halamanGeneral Chemistry 2: 2 Semester - Module 7Juan JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Learner GuidesDokumen106 halamanLearner Guidesmephiboshethmavundla249Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson 2Dokumen2 halamanLesson 2Roderick DacaoBelum ada peringkat
- Cohesive DeviceDokumen10 halamanCohesive Devicemoralesmarkfrancis9Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: and 3 Periods in Terms of Variation in Melting Points, Boiling Points and Ionisation EnergiesDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan: and 3 Periods in Terms of Variation in Melting Points, Boiling Points and Ionisation EnergiesMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Ideal Gas EquationDokumen5 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: Ideal Gas EquationMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Gen - Chem 2 VELASCO ENCARNACION Part 2Dokumen12 halamanGen - Chem 2 VELASCO ENCARNACION Part 2Edreyan Adong Cortez LimbagaBelum ada peringkat
- 5 2024 245 CH 5 ReactionsAlkenesAlkynes Lecture V3 STUDENTDokumen38 halaman5 2024 245 CH 5 ReactionsAlkenesAlkynes Lecture V3 STUDENTdingdong19690Belum ada peringkat
- Chemical KineticsDokumen80 halamanChemical KineticsCristyn BMBelum ada peringkat
- Lubao, Aaron Charles L. (Reflection Paper 4)Dokumen3 halamanLubao, Aaron Charles L. (Reflection Paper 4)Icy MakerBelum ada peringkat
- Stem Gc11tc III G I 122Dokumen2 halamanStem Gc11tc III G I 122chemistoliverBelum ada peringkat
- Biochem Lec Transes (Week 4)Dokumen6 halamanBiochem Lec Transes (Week 4)Juren LasagaBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Lesson LOG: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDokumen4 halamanDaily Lesson LOG: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayJeffrey YumangBelum ada peringkat
- 2025 Chemistry SyllabusDokumen82 halaman2025 Chemistry SyllabusNubar MammadovaBelum ada peringkat
- June 6 - Collision TheoryDokumen4 halamanJune 6 - Collision TheoryDare QuimadaBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Science DLP Q1W5Dokumen8 halamanPhysical Science DLP Q1W5JennyMaeAguilarMeruBelum ada peringkat
- Science 10 Learning Guide Q4 Week 4Dokumen8 halamanScience 10 Learning Guide Q4 Week 4Smb05 PlaylistBelum ada peringkat
- Gr.11, Unit 3, Mod 15, L1, Reaction RatesDokumen35 halamanGr.11, Unit 3, Mod 15, L1, Reaction Ratesaminbigman15Belum ada peringkat
- Topic 4 - Chemical Kinetics - Intro To Theories and Boltzmann CurveDokumen37 halamanTopic 4 - Chemical Kinetics - Intro To Theories and Boltzmann CurveJoshua LaBordeBelum ada peringkat
- Rate of Reactions 18 April 2024Dokumen46 halamanRate of Reactions 18 April 2024Amahle KudaBelum ada peringkat
- Bioseparation MESD Part1-3Dokumen97 halamanBioseparation MESD Part1-3fjasfBelum ada peringkat
- The Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) Explains The Properties of Gases and Describes The Behavior of GasesDokumen3 halamanThe Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) Explains The Properties of Gases and Describes The Behavior of GasesLørd Ken M. DilaoBelum ada peringkat
- June 13 - Nature and Chemical ReactionDokumen4 halamanJune 13 - Nature and Chemical ReactionDare QuimadaBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersDari EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Heat Energy ChangeDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: Heat Energy ChangeMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson PlanDokumen4 halamanLesson PlanMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson PlanDokumen4 halamanLesson PlanMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Dun DownloadDokumen1 halamanDun DownloadMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Uses of ElectrolysisDokumen3 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: Uses of ElectrolysisMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 50Dokumen3 halamanLesson 50MarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: The Base Dissociation ConstantDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: The Base Dissociation ConstantMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson PlanDokumen4 halamanLesson PlanMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 49Dokumen3 halamanLesson 49MarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 48Dokumen3 halamanLesson 48MarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 45Dokumen4 halamanLesson 45MarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Colligative Properties of SolutionsDokumen3 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: Colligative Properties of SolutionsMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 41Dokumen4 halamanLesson 41MarcTnn100% (1)
- Lesson 42Dokumen4 halamanLesson 42MarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Acid-Base TitrationDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: Acid-Base TitrationMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 40Dokumen5 halamanLesson 40MarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Introduction To Ionic EquilibriumDokumen3 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: Introduction To Ionic EquilibriumMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: K and K For Heterogeneous SystemDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: K and K For Heterogeneous SystemMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: PH and pOHDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: PH and pOHMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 21Dokumen5 halamanLesson 21MarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemsDokumen7 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemsMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (I)Dokumen4 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (I)MarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Zero Order ReactionDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: Zero Order ReactionMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: First and Second Order ReactionDokumen6 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: First and Second Order ReactionMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemDokumen5 halamanLesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemMarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 20Dokumen4 halamanLesson 20MarcTnnBelum ada peringkat
- Project GuitarDokumen11 halamanProject GuitarMns100% (2)
- Science and Empricism in Pile Foundation Design (Randolph 2003)Dokumen34 halamanScience and Empricism in Pile Foundation Design (Randolph 2003)Abdul Mozid ShikderBelum ada peringkat
- 01-08-2023 Quality Assurance certificate-RERADokumen3 halaman01-08-2023 Quality Assurance certificate-RERAMohsin ShaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Maryland Metrics - Thread Data ChartsDokumen4 halamanMaryland Metrics - Thread Data ChartsAnonymous VC68Xndnu9Belum ada peringkat
- Vice Cosmetics Duo Finish FoundationDokumen14 halamanVice Cosmetics Duo Finish FoundationChunne LinqueBelum ada peringkat
- 1963, Cakebread Robey & Co, London, UKDokumen176 halaman1963, Cakebread Robey & Co, London, UKHouse HistoriesBelum ada peringkat
- Dalamatic Insertable: Replacement Parts ListDokumen20 halamanDalamatic Insertable: Replacement Parts ListWaldomiroCanoBelum ada peringkat
- SVN Process Capability Strength ListDokumen1 halamanSVN Process Capability Strength ListrutujaBelum ada peringkat
- Skoda Kodiaq - Brief Instructions EnglishDokumen36 halamanSkoda Kodiaq - Brief Instructions EnglishMario Redsocial100% (1)
- 计量泵metering pump PDFDokumen43 halaman计量泵metering pump PDFAnonymous Tj3ApePIrBelum ada peringkat
- 2160654Dokumen53 halaman2160654MemoPalacioBelum ada peringkat
- Polymers PPT PDFDokumen47 halamanPolymers PPT PDFShivani RajeevBelum ada peringkat
- API NotesDokumen4 halamanAPI NotesMohammad RizwanBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg524 - Term PaperDokumen11 halamanEcg524 - Term PaperamierulBelum ada peringkat
- Iso 9624Dokumen12 halamanIso 9624Ayman S. AshourBelum ada peringkat
- Processing of MAX Phases From Synthesis To ApplicationsDokumen32 halamanProcessing of MAX Phases From Synthesis To ApplicationsVikram JainBelum ada peringkat
- Tesla High Freq CoilDokumen168 halamanTesla High Freq Coilto_netiks100% (1)
- Energy Balance With ReactionsDokumen26 halamanEnergy Balance With ReactionsLuthfianiAddina100% (1)
- Transmission Electrical Testing On 096Dokumen45 halamanTransmission Electrical Testing On 096Michelle KerriganBelum ada peringkat
- Ir CompDokumen94 halamanIr CompmahaveenBelum ada peringkat
- ATLAS OF ISOTHERMAL TRANSFORMATION AND COOLING TRANSFORMATION DIAGRAMS - CompressedDokumen430 halamanATLAS OF ISOTHERMAL TRANSFORMATION AND COOLING TRANSFORMATION DIAGRAMS - CompressedYENIFER PLATA LOPEZBelum ada peringkat
- Grafen 2Dokumen94 halamanGrafen 2murat TorenBelum ada peringkat
- Idealarc DC-600: Rugged Multi-Process Power For Industrial ManufacturingDokumen4 halamanIdealarc DC-600: Rugged Multi-Process Power For Industrial ManufacturingmoorthysanmukamBelum ada peringkat
- Surface PreparationDokumen31 halamanSurface PreparationT aljuBelum ada peringkat
- Vap Premium: Rapid Steam GeneratorDokumen2 halamanVap Premium: Rapid Steam GeneratorMahmoud AliBelum ada peringkat
- Kenmore 253.16342101 Chest FreezerDokumen14 halamanKenmore 253.16342101 Chest FreezerJVH1978Belum ada peringkat
- Example Planning Experiment Form 4 and 5 Updated 2018Dokumen37 halamanExample Planning Experiment Form 4 and 5 Updated 2018Melor DihatiBelum ada peringkat
- Buckling and Postbuckling of Beams, Plates, and ShellsDokumen8 halamanBuckling and Postbuckling of Beams, Plates, and Shellslalo198Belum ada peringkat