Clinical AND ADVANCE Pathology: Topic
Diunggah oleh
Nestley TiongsonJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Clinical AND ADVANCE Pathology: Topic
Diunggah oleh
Nestley TiongsonHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Clinical AND ADVANCE pathology
TOPIC: DIAGNOSIS FOR INFECTIONS
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR FUNGAL INFECTIONS 5.01
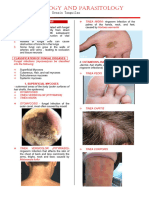
Tinea corporis- E.
floccosum/tricho
1. WHAT ARE THE BEST SPECIMEN FOR phyton,
MYCOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS? GIVE REPRESENTATIVE microsposrum
CONDITIONS. Tinea imbricate-
- Skin scrapings: candida, microsporum, tricophyton
trichophyton, epidermophyton, blastomyces, concentricum
dermatidis Tinea barbae,
- Nail clippings: aspergillus, epidermophyton, tinea cruris, tinea
trichophyton manuum
- Hair: microsporum, trichophyton (interdigital areas
- Scraping from mucous membrane – throat: and palmar
candida albicans, Geotrichum candidum, lungs: surfaces), tinea
candida albicans, aspergillus, rhizopus, pedis, tinea
penicillium, histoplasma capsilatum, unguium,
blastomyces dermatitidis, coccidiodes immitis
- Crust scraping
- Aspirated pus
Subcutan Involves Scrapin
- Tissue biopsy
eous dermis, g from
- Blood: Candida spp., blastomyces dermatidis, H.
mycoses subcutan mucous
capsulatum, C. neoformans
eous membr
- CSF: cyrptococcus neoformans, candida spp.,
tissue, ane,
histoplasma, coccisdioides immitis
muscles aspirate
- Urine: candida spp.
and fascia d pus,
- Genital tract: candida albicans
tissue
Fungal involeve specime fungi biopsy
infection ment n
Systemic Primarily Blood,
Superficia Outermos Skin Malassezia furfur mycoses lungs and CSF,
l mycoses t layers of scraping (Pityriasis spreading tissue
skin and s, hair versicolor), to other biopsy
hair Exophiala organs
wernekii (Tinea
Opportun Fungi of Mucous
nigra),
istic no secretio
Trichosporon
mycoses significan ns, CSF,
beigelii (white
ce or low
piedra), Piedraia
virulence
hortae (balck
infect
piedra)
humans
Cutaneou Extending Skin Dermatophytes: w/
s mycoses deeper scraping microsporum comprom
into the , nail (tinea capitis), ised
epidermis clipping Trichophyton immune
and its s, hair violaceum, system
integume epidermophyton
nts (dermatophytosis
/ ringworm) 2. WHAT ARE THE METHODS USED UN DIRECT
Candida albicans- EXAMINATION OF FUNGI? EXPLAIN EACH
candidiasis METHOD.
Transcribed by: Page 1 of 7
Patho 2 LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR
FUNGAL INFECTIONS
- 10-30% of KOH- dissolved non fungal materials - Bird seed/ caffeic acid agar- selective and
in skin, hair and nail samples, specimen is placed differential, Cryptococcus neoformans (black to
on a slide, drop of KOH is added and coverslip is brown colonies due to the activity of the phenol
placed left for 20 min in the incubator at 37C to oxidase), may contain chloramphenicol
degest keratin, then examined microscopically - Cornmeal Agar with Tween 80- used to
- Calcofluor white stain- fluorochrome stains differentiate candida species, blastoconida-
chitin, not absorbed by human tissue, UV light, budding yeast, chlamydoconidia- C. albicans,
fungi appear white to blue green, KOH used to Pseudohyphae, Blastoconidia germinate,
clear debris constricted at the septate, arthroconidia- begin
- Histological stains (H&E, PAS, grams stain, as true hyphae but break apart at cross walls
Methenamine Silver stain, Giemsa Stain)
- India ink- reveals capsules surrounding C.
neoformans in CSF, low sensitivity, replaced by 4. HOW ARE THE FOLLOWING DONE IN THE
direct antigen detection DIAGNOSIS OF FUNGAL INFECTIONS?
- Wet mount- used to view fungal elements such A. SELECTION OF MEDIA
as hyphae, conidia and budding yeast. It has - Type of media for fungal culture in important. It
limited use and is most commonly applicable for is recommended that this culture media need to
vaginal secretions to diagnose vaginosis have special substance that will help support in
- Gram stain can be used to view budding yeast the growth of the organism and inhibit the
- Lactophenol cotton blue wet mount- used to growth of other fungi for identification or inhibit
stain and preserve fungal elements in culture bacterial decontamination
isolates, phenol- kill any live oragnisms, lactic - The media with or without cyclohexamide:
acid- preserves fungal structures, cotton blue- inhibits the growth of rapidly growing
stains chitin in fungal cell walls contaminating molds
- Saline wet mount- used to view hyphae, conidia, - The media with or without antimicrobial agent
budding yeast, mostly used forvaginal secretions such as chloramphenicol, gentamicin and
to diagnose vaginitis ciprofloxacin are commonly used.
Culture media description
3. WHAT ARE THE COMMONLY USED CULTURE Brain heart infusion Non selective, permits
MEDIA IN FUNGAL ISOLATION? growth of all clinically
- (SDA) sabouraud dextrose agar- general relevant fungi, primary
purpose, nutritionally poor, mildly selective for recovery of saprophytic
fungi, acidic pH 5.6 to inhibit bacterial growth, and dimorphic fungi
- SABHI- Sabouraud brain heart infusion- non- Czapek’s agar Used in subculture of
selective for all fungi, contains dextrose, aspergillus spp. For
peptone and brain heart infusion, can be made differential diagnosis
selective for dimorphic fungi with addition of Inhibitory Mold Primary recovery of
cyclohexamide, chloramphenicol and Agar dimorphic pathogenic
gentamicin fungi. However
- BHIB- brain heart infusion agar with blood- used saprophytic and
to grow most fungi from sterile sites, contains dermatophytes will not
brain and heart infusion and sheep blood, can be be recovered
made selective for dimorphic fungi with addition Mycosel/mycobiotic Used to recovery
of cyclohexmaide, chloramphenicol and agar (SDA with dermatophytes
gentamicin cycloheximide +
- Potato dextrose agar- used to enhance conidia chloramphenicol)
development, enhances pigment development Niger seed agar Used to identify C.
of Trichophyton rubrum neoformans
Transcribed by: John Velasco #makingEAC-SMGreatAgain Page 2 of 7
Patho 2 LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR
FUNGAL INFECTIONS
Potato dextrose Rich medium for 6.
agar growing wide range of A. SEROLOGIC IDENTIFICATION
fungi
Sabourad’s heart Primary recovery of - Serological methods utilizes the reaction and
infusion agar saprophytic and properties of serum, it is a non-cultured based
dimorphic fungi- technique in identifying fungal infection
fastidious strains - Antigen and antibodies are easier to detect via
Sabourad’s dextrose Sufficient for the the blood , CSF, urine and Brochoalveolar lavage
agar recovery of samples
dermatophytes from - Generally, Sensitivity 80%, Specificity 80% this
cutaneous samples and may vary depending on the test.
yeasts from vaginal - Immunoblot analysis of the serological response
culture is a useful tool for the identification of
Potato flake agar Recovery of saprophytic immunogenic fungal components that elicit a
and dimorphic fungi, specific antibody response in invasive disease.
particulary fastifious This method, and others, have been successfully
and slow growing applied to the study of the immune response to
strains several fungi, including Candida, Aspergillus and
Rhizopus.
B. INOCULATION AND INCUBATION Serological techniques for diagnosis of fungal
Each sample is cultured in two set of culture infection | Request PDF. Available from:
media and is incubated at two https://www.researchgate.net/publication/206
59157_Serological_techniques_for_diagnosis_o
different temperatures at 30oC (Room
f_fungal_infection [accessed Jan 18 2018].
temperature) and at 35oC
All fungal cultures are incubated for a
minimum of 30 days before discarding - This techiniques includes the detection of
as negative. specific host immune responses to fungal
The choice between the use of culture tubes antigens using immunologic reagents.
or plate is optional. For tube, the
media is poured in thick slants to prevent - Amplification and detection of specific fungal
nucleic acid sequences
dehydration during prolonged
incubation period. After the medium is - Detection of and quantification of specific fungal
inoculated, do not screw down the cap metabolite products
too tightly because fungi require breathing.
- Targets of serological test: antigen. Antibody.
Metabolites
C. BLOOD CULTURES
- Blood is with draw from both arms right and left
- Decision of fungal serologic test is based on the
1 ml each side and will be place in BHI in sterile
clinical presentation, exposure history and risk
technique and be incubated. If it should turbidity
factor of infection
in the sample, it will be cultured with the
appropriate media to isolate the organism.
Examples:
Culture media are highly sensitive and specific.
Once it shows growth in this media plates, direct 1. agglutination
examination/ microscopy is done for evaluation. - principle: antigen antibody interaction
- will from agglutinates, positive reaction
5. EXPLAIN THE FOLLOWING TECHNIQUES IN - advantage: long shelf life 4-6 mos, rapid
RELATION TO FUNGAL IDENTIFICATION:
Transcribed by: John Velasco #makingEAC-SMGreatAgain Page 3 of 7
Patho 2 LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR
FUNGAL INFECTIONS
- disadvantage: false positive, - Can detect fungi which cannot be
exoantigens with sodium cultured such us aspergillus in the blood
metaperioidate / pretrating serum with
2 B mercaptoethanol C. MORPHOLOGIC IDENTIFICATION
- Morphology may be distinct to the fungi
2. immunodiffusion, - Fungal structure:
Principle: patient samples are placed in wells in a. Hyphae- long brancing filaments
an agar plate surrounded by a larger well that come tohether to form
containing purified antigen, Ab and Ag will mycelium
diffuse out of their respective wells and a - It could be septated – cellular separation
complex will form a visible precipitation band in or cross walls from 3-6 um
between the wells (positive test) - Pseudohyphae- chain cells formed from
Advantage: 80-90%$ sensitivity, >90% specific budding that resemble a true hyphae.
Disadvantage: costly, difficult to standardize, b. Vegetative hyphae- food absorbtion
long TAT and are portion which extends
below the agar
3. complement fixation test, c. Aerial hyphae- extends above the
- principle: ability of the Ag-Ab complex to agar function is to support
fix complement, antibody + fungal reproductive structures – conidia
antien = complex inactivates d. Conidia formation of imperfect
exogenouly added complement fungi: asexual reproduction
- results: - Important in fungal identification
o specific ab + = complement - Microconidia: single celled, small
fixed, RBC pellet - Macroconidia: multicellular, large
o specific ab - = complement lyse - Athroconidia: fragmentation of hyphae
RBCs - Blastoconidia: conidia in budding
- Chlamydoconidia: terminal cells in the
4. ezyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), hyphae that enlarge and have thick walls
- … - Poroconidia: conidia pushed through a
small pore in the parent cell
5. lateral flow assay, - Phialoconidia: tube shape
- principle: analyte + Ab conjugated to - Annelloconida: vase shape , saw toothe
gold nanoparticles = test line band pos, appearance
immune chromatography
6. counter immune electrophoresis,
7. radio immunosorbent assay
B. MOLECULAR INDENTIFICATION
- Polymerase chain reaction based
techniques and other molecular
methods have been proven, in several
cases, to be fast, cheap and reliable
- May provide faster and more sensitive
diagnostics
- Can detect fungi which grew slowly such
as dermatophytes
Transcribed by: John Velasco #makingEAC-SMGreatAgain Page 4 of 7
Patho 2 LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR
FUNGAL INFECTIONS
D. SUSCEPTIBILITY
Transcribed by: John Velasco #makingEAC-SMGreatAgain Page 5 of 7
Clinical AND ADVANCE pathology
TOPIC: DIAGNOSIS FOR INFECTIONS
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR FUNGAL INFECTIONS 5.01
Transcribed by: Page 6 of 7
Patho 2 LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR
FUNGAL INFECTIONS
Transcribed by: John Velasco #makingEAC-SMGreatAgain Page 7 of 7
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Aoun, Lucas (2021) BOOST YOUR BRAIN - A Beginner's Guide To Leverage The Power of Nootropics For Ultimate Brain EnhancementDokumen49 halamanAoun, Lucas (2021) BOOST YOUR BRAIN - A Beginner's Guide To Leverage The Power of Nootropics For Ultimate Brain EnhancementJordan67% (3)
- Video Recap of Alleles and Genes by Amoeba SistersDokumen3 halamanVideo Recap of Alleles and Genes by Amoeba Sistersur100% (2)
- Immunohematology PDFDokumen126 halamanImmunohematology PDFNicole Tan Calayca100% (1)
- Gastric Cancer Liver Metastasis Case ReportDokumen24 halamanGastric Cancer Liver Metastasis Case ReportNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Detox For Covid VaccinesDokumen4 halamanDetox For Covid VaccinessunitaranpiseBelum ada peringkat
- Derma Notes 22pages. DR - Vishwa Medical CoachingDokumen23 halamanDerma Notes 22pages. DR - Vishwa Medical CoachingΝίκος ΣυρίγοςBelum ada peringkat
- Dermatology RevisionDokumen7 halamanDermatology RevisionAbdelrahman MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- TinnitusDokumen34 halamanTinnitusHnia UsmanBelum ada peringkat
- Mycology TransDokumen11 halamanMycology TransKita kitaBelum ada peringkat
- Mycology SOM CJBDokumen91 halamanMycology SOM CJBYlia MastarsBelum ada peringkat
- SKDI-Jamur, Parasit, VesikobulosaDokumen71 halamanSKDI-Jamur, Parasit, Vesikobulosasoraya olyfia100% (1)
- CompilationDokumen3 halamanCompilationBelle Cherlette FelipeBelum ada peringkat
- ICD 10 Codes For Neurology-MI4957Dokumen6 halamanICD 10 Codes For Neurology-MI4957fkuii2009Belum ada peringkat
- DERMATOPHYTOSES: LAB DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATIONDokumen34 halamanDERMATOPHYTOSES: LAB DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATIONKana FajarBelum ada peringkat
- The Truth Behind The Polio VaccineDokumen28 halamanThe Truth Behind The Polio VaccineFreedomFighter32100% (2)
- Facts and Myths of AgingDokumen50 halamanFacts and Myths of AgingangayarkanniBelum ada peringkat
- Lab DiagnosisDokumen42 halamanLab DiagnosisNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Power Passages and Passenger PDFDokumen13 halamanPower Passages and Passenger PDFNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- ENT Scholar Volume 1Dokumen93 halamanENT Scholar Volume 1Dr. T. BalasubramanianBelum ada peringkat
- Scaling and Root Planing Presentation - DR - Naaz GillDokumen37 halamanScaling and Root Planing Presentation - DR - Naaz GillNaazGill100% (1)
- Nurs 3020 - Erin Final EvaluationDokumen14 halamanNurs 3020 - Erin Final Evaluationapi-505854426Belum ada peringkat
- MED-ORG-TOPIC-234Dokumen9 halamanMED-ORG-TOPIC-234barbadillojames419Belum ada peringkat
- Medfools Fungus Chart for the USMLE IDokumen4 halamanMedfools Fungus Chart for the USMLE IPrashant MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 8 MycologyDokumen3 halamanActivity 8 MycologyBrent Lee100% (1)
- Introduction To Fungi: Ex - Aspergillus, DermatophytesDokumen4 halamanIntroduction To Fungi: Ex - Aspergillus, DermatophytesBanana CakeBelum ada peringkat
- FUNGAL and PARASITIC INFECTIONSDokumen3 halamanFUNGAL and PARASITIC INFECTIONSKathleen Hazel AndresBelum ada peringkat
- (Internal) The Epidermis That Grow On The Keratin Present On TheseDokumen8 halaman(Internal) The Epidermis That Grow On The Keratin Present On TheseAthena Irish LastimosaBelum ada peringkat
- Fungal InfectionsDokumen76 halamanFungal InfectionsHrishikesh NachinolkarBelum ada peringkat
- Subcutaneous MycosesDokumen1 halamanSubcutaneous MycosesJulia IshakBelum ada peringkat
- Micro Chart Test 3Dokumen8 halamanMicro Chart Test 3api-26938624Belum ada peringkat
- Myco Myco OwnDokumen4 halamanMyco Myco OwnMarielle Anne TuazonBelum ada peringkat
- Fungal InfectionDokumen3 halamanFungal InfectionNicole TorralbaBelum ada peringkat
- Birao Sas 14 Microbiology and ParasitologyDokumen6 halamanBirao Sas 14 Microbiology and ParasitologyFrancis Jacob Dejecacion GarcesBelum ada peringkat
- Skin PathogensDokumen4 halamanSkin PathogensEhi EdialeBelum ada peringkat
- Fungal Classifications and DiseasesDokumen11 halamanFungal Classifications and DiseasesRusselBelum ada peringkat
- Fungi Table Short MemorizeDokumen4 halamanFungi Table Short MemorizeTrisBelum ada peringkat
- General Pathology Lecture Eyes and Skin Part IDokumen5 halamanGeneral Pathology Lecture Eyes and Skin Part IMae GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Mycology 170328040158Dokumen84 halamanMycology 170328040158Zainab KhadharBelum ada peringkat
- dermatophytes_20240314_214707_0000Dokumen18 halamandermatophytes_20240314_214707_0000khushi.gupta2122Belum ada peringkat
- Superficial Mycoses IdentificationDokumen7 halamanSuperficial Mycoses IdentificationjwanaBelum ada peringkat
- Mycology MycosesDokumen7 halamanMycology MycosesSarah Grace KamlaniBelum ada peringkat
- Fungal Pneumonia Causes and Risk FactorsDokumen3 halamanFungal Pneumonia Causes and Risk FactorsskBelum ada peringkat
- Table of Sytemic MycosesDokumen1 halamanTable of Sytemic MycosesLexie BulanBelum ada peringkat
- AntifungalagentsDokumen57 halamanAntifungalagentsRafia Rayana btbcBelum ada peringkat
- Wuolah Free Bacteria TableDokumen11 halamanWuolah Free Bacteria TableELENA FERNANDEZBelum ada peringkat
- Cutaneous Mycoses Guide: Classification, Agents and Clinical ManifestationsDokumen56 halamanCutaneous Mycoses Guide: Classification, Agents and Clinical ManifestationsHafsa ImranBelum ada peringkat
- ED Na STR FUNGIDokumen46 halamanED Na STR FUNGIdw21541Belum ada peringkat
- Dimorphic Fungi Systemic Mycoses DiagnosisDokumen3 halamanDimorphic Fungi Systemic Mycoses DiagnosisThea MallariBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To MycologyDokumen35 halamanIntroduction To MycologyTheBoss 20Belum ada peringkat
- Micro Chart #3 - Italics OnlyDokumen27 halamanMicro Chart #3 - Italics Onlyapi-26938624100% (1)
- Systemic Mycoses: A. BlastomycosisDokumen3 halamanSystemic Mycoses: A. Blastomycosisbaihern24Belum ada peringkat
- Superficial Fungal Infections ExplainedDokumen69 halamanSuperficial Fungal Infections Explainedputri.SpABelum ada peringkat
- InfectionsDokumen7 halamanInfectionsMaliha Zaman KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology Lecture 10 - Subcutaneous Mycoses (Palindrome)Dokumen3 halamanMicrobiology Lecture 10 - Subcutaneous Mycoses (Palindrome)miguel cuevasBelum ada peringkat
- Mycology and Virology MYCV311: Bsmls TermDokumen6 halamanMycology and Virology MYCV311: Bsmls TermIgnacias //Belum ada peringkat
- Mycology and VirologyDokumen14 halamanMycology and VirologysherwinbuluranBelum ada peringkat
- SubcutaneousDokumen2 halamanSubcutaneousMary ChristelleBelum ada peringkat
- Cutaneous and Subcutaneous mycoses-FMS2-2558Dokumen68 halamanCutaneous and Subcutaneous mycoses-FMS2-2558Marl EstradaBelum ada peringkat
- Enterococci: S. AureusDokumen2 halamanEnterococci: S. AureusShift UallBelum ada peringkat
- GEJALA KLINIK MIKOSIS DAN PENEGAKAN DIAGNOSA LABORATORIUMDokumen36 halamanGEJALA KLINIK MIKOSIS DAN PENEGAKAN DIAGNOSA LABORATORIUMH PBelum ada peringkat
- 07LongChap70 Cellulitis PDFDokumen11 halaman07LongChap70 Cellulitis PDFRatih KimBelum ada peringkat
- Opportunistic MycosesDokumen6 halamanOpportunistic MycosesJullana Rondina EscondeBelum ada peringkat
- Fungal Infections-SubcutaneousDokumen24 halamanFungal Infections-SubcutaneousKato CalebBelum ada peringkat
- BRANCHING, AEROBIC ACTINOMYCETES AND RELATED GRAM-POSITIVE BACILLIDokumen2 halamanBRANCHING, AEROBIC ACTINOMYCETES AND RELATED GRAM-POSITIVE BACILLIJustine Marie RevillaBelum ada peringkat
- Bacterial Infection 2Dokumen3 halamanBacterial Infection 2jihanBelum ada peringkat
- MATA MERAH VISUS NORMAL & TURUN: PENGOBATAN KONJUNKTIVITIS DAN KERATITISDokumen56 halamanMATA MERAH VISUS NORMAL & TURUN: PENGOBATAN KONJUNKTIVITIS DAN KERATITISMuhammad HasanBelum ada peringkat
- Microscopic Examination of Fungal SmearDokumen73 halamanMicroscopic Examination of Fungal SmearAmeliaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 MycoDokumen11 halamanUnit 2 MycoElyssa VergaraBelum ada peringkat
- DNA VIRUSES-handout PDFDokumen11 halamanDNA VIRUSES-handout PDFROTHESSA MARY CARINGALBelum ada peringkat
- Case Presentation Group 5: Patron Rayo Reyes Salazar Sandhu Sandoval Sangalang SasakiDokumen28 halamanCase Presentation Group 5: Patron Rayo Reyes Salazar Sandhu Sandoval Sangalang SasakiNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology of Parturition PDFDokumen17 halamanPhysiology of Parturition PDFNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology of Parturition PDFDokumen17 halamanPhysiology of Parturition PDFNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDokumen4 halamanSexually Transmitted InfectionsNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- BioethicsDokumen86 halamanBioethicsNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Respi DisordersDokumen8 halamanRespi DisordersNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Cervical BiopsyDokumen17 halamanCervical BiopsyNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Benign Tumor Vulva Epidemiol OGY Etiology Clinical Manifestation Pathogenesis MorphologyDokumen3 halamanBenign Tumor Vulva Epidemiol OGY Etiology Clinical Manifestation Pathogenesis MorphologyNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal TraumaDokumen4 halamanAbdominal TraumaNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Psych Ward HistoryDokumen6 halamanPsych Ward HistoryNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- N. Meningitidis (MENINGOCOCCUS) : Meningococcemia/MeningitisDokumen5 halamanN. Meningitidis (MENINGOCOCCUS) : Meningococcemia/MeningitisNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Case 2b TuberculosisDokumen37 halamanCase 2b TuberculosisNestley Tiongson100% (1)
- Neuromuscular Junction DsoDokumen9 halamanNeuromuscular Junction DsoNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Lung Tumour Types and CausesDokumen7 halamanLung Tumour Types and CausesNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Adrenal Gland - Surgical PathologyDokumen3 halamanAdrenal Gland - Surgical PathologyNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Cis 2018 PDFDokumen3 halamanCis 2018 PDFTara Oliveros Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Clinicopharmacological ConferenceDokumen7 halamanClinicopharmacological ConferenceNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Comfort Care for Terminally Ill Patient with Multiple ComorbiditiesDokumen14 halamanComfort Care for Terminally Ill Patient with Multiple ComorbiditiesNestley TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Endometrial Study by TVS and It's Correlation With Histopathology in Abnormal Uterine BleedingDokumen12 halamanEndometrial Study by TVS and It's Correlation With Histopathology in Abnormal Uterine BleedingIOSRjournalBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetes Mellitus (D9)Dokumen92 halamanDiabetes Mellitus (D9)Alishba MushtaqBelum ada peringkat
- Incisions For Open Abdominal Surgery - UpToDate2020 PDFDokumen36 halamanIncisions For Open Abdominal Surgery - UpToDate2020 PDFGerii Pucllas VillarBelum ada peringkat
- Ayurveda Medicine of the GodsDokumen20 halamanAyurveda Medicine of the Godsramdas2430Belum ada peringkat
- Ok 466962500 Ok 7 Yds Nisan 2017Dokumen22 halamanOk 466962500 Ok 7 Yds Nisan 2017gizemcetinBelum ada peringkat
- Hypoxia: Deficiency in Oxygen Delivery or Utilization at Tissue LevelDokumen37 halamanHypoxia: Deficiency in Oxygen Delivery or Utilization at Tissue LevelandrenicholastobingBelum ada peringkat
- Nanda Hematemesis MelenaDokumen13 halamanNanda Hematemesis MelenaLiya AnjelinaBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Myiasis PublicationDokumen6 halamanOral Myiasis PublicationAnkita GoklaniBelum ada peringkat
- Formulation of Mosquito Repellent Lotion by Using Oregano (, Neem Tree and Lemongrass Extracted OilDokumen9 halamanFormulation of Mosquito Repellent Lotion by Using Oregano (, Neem Tree and Lemongrass Extracted OilSimi- Simi0% (1)
- The Impact of Childhood Cancer On Family FunctioningDokumen13 halamanThe Impact of Childhood Cancer On Family Functioningapi-585969205Belum ada peringkat
- Potassium: Enzymatic MethodDokumen2 halamanPotassium: Enzymatic MethodFariz KasyidiBelum ada peringkat
- VERVE DYNAMICS - African Dream and Other Gels - 2017Dokumen4 halamanVERVE DYNAMICS - African Dream and Other Gels - 2017Lesley HollardBelum ada peringkat
- Jipmer 2010 Rapid Review: Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & ResearchDokumen15 halamanJipmer 2010 Rapid Review: Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & ResearchgokunambiarBelum ada peringkat
- Pembagian PPK Elektif OrthoDokumen4 halamanPembagian PPK Elektif OrthoIbnu ImadudinBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Necrotizing PancreatitisDokumen37 halamanAcute Necrotizing PancreatitisVania SuSanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Rice Bran Oil - Natures Gift To MankindDokumen2 halamanRice Bran Oil - Natures Gift To Mankindlehmanwolf100% (1)
- 3rd Ed General Cheat Sheet PDFDokumen9 halaman3rd Ed General Cheat Sheet PDFAlan RideoutBelum ada peringkat
- Investigation of Blood Culture Using BACTEC SystemsDokumen36 halamanInvestigation of Blood Culture Using BACTEC SystemsGregorio De Las CasasBelum ada peringkat
- Karyotype WorksheetDokumen4 halamanKaryotype WorksheetKellieM.8406Belum ada peringkat
- Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & ReviewsDokumen5 halamanDiabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & ReviewsPetra Diansari ZegaBelum ada peringkat
- Biosimilars JapanDokumen2 halamanBiosimilars JapanVijay Nag ThotaBelum ada peringkat