Key Ideas
Diunggah oleh
api-2595665150 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
16 tayangan2 halamanJudul Asli
9
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
16 tayangan2 halamanKey Ideas
Diunggah oleh
api-259566515Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
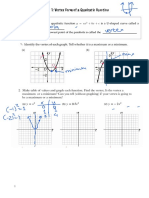
Key Ideas:
• Solving quadratic equations by graphing.
Instead of stating the x- intercepts as the solution,
the graph is used to identify intervals of x-values
where the y-values of the graph are above or below
the x-axis.
A quadratic inequality in one variable can be written in one of four forms.
Therefore, there are four possible scenarios when solving quadratic inequalities graphically.
Example 1: Given the graph of f (x) =(x – 1)(x + 7), solve the following.
a.) (x – 1)(x + 7) = 0
b.) (x – 1)(x + 7) < 0
c.) (x – 1)(x + 7) > 0
Example 2: For the graph of f (x) = -x2 – 5x – 6, determine each solution.
a.) -x2 – 5x – 6 = 0
b.) -x2 – 5x – 6 < 0
c.) -x2 – 5x – 6 > 0
Example 3: Is the value of x a solution to the given inequality? Show your work.
2
a.) x + 3x > -5, x=0
Example 4 and 5: Solve on Loose-leaf
x2 – 7x – 18 < 0
Method 1: Graphically
Method 2: Case Analysis
(Similar as sign analysis; only one number line)
Method 3: Sign Analysis
There are several methods however the one that
will be most useful for those going on to Pre-
calculus 30/Calculus is sign analysis.
Steps:
1. Factor (Finding roots/critical values)
2. Plot roots on number lines (making a sign
analysis chart)
3. Test each subset (positive/negative)
4. Analyze what happens to “y” (and therefore,
which section(s) satisfy the inequality)
5. Use interval notation to write the solution
Example 6. Solve each of the following using sign analysis. Show your work!!!
a.) x2 – 6x – 16 > 0
b.) -x (6x + 1) ≤ -12
c.) -2x(x + 5) ≥ 0
p. 484: 1, 2-3 (b, d), 4-7 (a,d), 9, 12
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Evaluating Algebraic ExpressionDokumen6 halamanEvaluating Algebraic ExpressionIbtsam YossefBelum ada peringkat
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDari EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (8)
- CE ENG HL660,660L, HL665,665L AUG2018 Rev.0 WebDokumen4 halamanCE ENG HL660,660L, HL665,665L AUG2018 Rev.0 WebJohn LeonneBelum ada peringkat
- IP BookDokumen96 halamanIP Booknew mediaBelum ada peringkat
- Fractal ForestsDokumen50 halamanFractal ForestsWell Fournier0% (1)
- Algebraic Curves: Analytic Geometry by Fuller and Tarwater Pages 161-170Dokumen15 halamanAlgebraic Curves: Analytic Geometry by Fuller and Tarwater Pages 161-170leepatrickbanezBelum ada peringkat
- MHF4U Unit 1 Polynomial Functions HomeworkDokumen31 halamanMHF4U Unit 1 Polynomial Functions HomeworkTony ParkBelum ada peringkat
- Stakeholder RegisterDokumen7 halamanStakeholder Registerrouzbehk6515Belum ada peringkat
- Sat Math Formula Practice - e Math AcademyDokumen6 halamanSat Math Formula Practice - e Math AcademytinlongBelum ada peringkat
- OHS Policies and Guidelines (TESDA CSS NC2 COC1)Dokumen1 halamanOHS Policies and Guidelines (TESDA CSS NC2 COC1)Anonymous fvY2BzPQVx100% (2)
- Grade 10 Math Performance Task 1Dokumen9 halamanGrade 10 Math Performance Task 1Dark ShadowBelum ada peringkat
- Section 2.3 Polynomial Functions and Their GraphsDokumen31 halamanSection 2.3 Polynomial Functions and Their GraphsAlexandria BakerBelum ada peringkat
- Quadratic Equation WeeblyDokumen3 halamanQuadratic Equation Weeblyapi-633813701Belum ada peringkat
- Exponentials PDFDokumen9 halamanExponentials PDFAhmad ELZohairyBelum ada peringkat
- Quadratic Function-1Dokumen8 halamanQuadratic Function-1Nabil MahdarBelum ada peringkat
- MHF4U Exam ReviewDokumen6 halamanMHF4U Exam ReviewBrooke McBride-GeenBelum ada peringkat
- 5 - Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing The SquareDokumen3 halaman5 - Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing The Squareed boBelum ada peringkat
- 3 3 Iterative Methods ME 310 Fall 2020Dokumen12 halaman3 3 Iterative Methods ME 310 Fall 2020Ege UygunturkBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 8 - System of Equations - InequalitiesDokumen29 halamanTutorial 8 - System of Equations - InequalitiesNguyễn Trọng HiếuBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Quarter 1st STDokumen3 halaman2nd Quarter 1st STLaurice BenalBelum ada peringkat
- Pre Cal-Q1 M2 PARABOLA FinDokumen17 halamanPre Cal-Q1 M2 PARABOLA FinDanny Lloyd Asan BuenafeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture-1 NMDokumen17 halamanLecture-1 NMSHASHWAT GUPTABelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 5 - Inverses of Functions & Polynomials ReviewDokumen9 halamanLesson 5 - Inverses of Functions & Polynomials ReviewdudoocandrawBelum ada peringkat
- ProportionDokumen2 halamanProportionRiddhi KhandelwalBelum ada peringkat
- Test-4 Maths SATDokumen21 halamanTest-4 Maths SATLobna El-HosseinyBelum ada peringkat
- SW 2.2 Sy 22-23Dokumen1 halamanSW 2.2 Sy 22-23Jed LambatinBelum ada peringkat
- Sec V TS Mathematics Term 2 - Unit 2 - Absolute Value FunctionDokumen16 halamanSec V TS Mathematics Term 2 - Unit 2 - Absolute Value FunctionDanyal PuglisiBelum ada peringkat
- 77Dokumen60 halaman77Jana AlqahtaniBelum ada peringkat
- Graphing Linear EquationDokumen6 halamanGraphing Linear EquationNursupriatna AmadBelum ada peringkat
- Cosido SemiDetailed-LessonPlan5Dokumen8 halamanCosido SemiDetailed-LessonPlan5Janin R. CosidoBelum ada peringkat
- Graphing Rational FunctionsDokumen2 halamanGraphing Rational FunctionsJosel JalonBelum ada peringkat
- Graphing Rational Functions PDFDokumen4 halamanGraphing Rational Functions PDFEljean Reana CabarlesBelum ada peringkat
- IM11 Semester Final Review - Spring 2020 PDFDokumen19 halamanIM11 Semester Final Review - Spring 2020 PDFAva SandersenBelum ada peringkat
- 4.2 - Binomial Probability DistributionsDokumen3 halaman4.2 - Binomial Probability DistributionsZeinab RamadanBelum ada peringkat
- 2Q-S4 Graphing Polynomial FunctionsDokumen25 halaman2Q-S4 Graphing Polynomial FunctionsAlice KrodeBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet 10c Common FactorsDokumen4 halamanWorksheet 10c Common Factorsapi-381868432Belum ada peringkat
- Quadratic EquationDokumen6 halamanQuadratic EquationJohn McCreaBelum ada peringkat
- A2 Semester 2 ReviewDokumen8 halamanA2 Semester 2 ReviewYb Andik Adi CahyonoBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment II PUCDokumen5 halamanAssignment II PUCBhargava S DBelum ada peringkat
- 2E Solving EquationsDokumen2 halaman2E Solving EquationsHoa VuBelum ada peringkat
- M1 Work Sheet PDFDokumen2 halamanM1 Work Sheet PDFMPS QUESTION PAPER SUBMISSIONBelum ada peringkat
- Graphing Quadratic Equations Using FactoringDokumen4 halamanGraphing Quadratic Equations Using FactoringJemeraldBelum ada peringkat
- Ee361 Mid2 Sp2021-3Dokumen6 halamanEe361 Mid2 Sp2021-3Seb SebBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 M 1Dokumen34 halamanChapter 2 M 1Isra WaheedBelum ada peringkat
- Mental Math Slide ShowDokumen22 halamanMental Math Slide Showapi-250788050Belum ada peringkat
- 1 Algebra and FunctionsDokumen50 halaman1 Algebra and FunctionsSri Devi NagarjunaBelum ada peringkat
- Training Deep Neural NetworksDokumen158 halamanTraining Deep Neural NetworksdawodyimerBelum ada peringkat
- Slope Fields For Apc 31625Dokumen9 halamanSlope Fields For Apc 31625karthikBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 3 - Graphs and FunctionsDokumen26 halamanChapter 3 3 - Graphs and Functionsapi-263209117Belum ada peringkat
- Vertex Form Lesson 1Dokumen2 halamanVertex Form Lesson 1neloBelum ada peringkat
- Quarter 2-Module-2-Graph-of-Polynomial-FunctionDokumen22 halamanQuarter 2-Module-2-Graph-of-Polynomial-FunctionDianne Dynah Bilaro DyBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3 Quadratic FunctionsDokumen13 halamanLesson 3 Quadratic FunctionsChet Jerry AckBelum ada peringkat
- Today in Pre-Calculus: - Go Over Homework - Notes: (NO Calculators) - HomeworkDokumen9 halamanToday in Pre-Calculus: - Go Over Homework - Notes: (NO Calculators) - HomeworkRejieBelum ada peringkat
- CulusDokumen20 halamanCulusgaBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics Worksheet For Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate MSC: 1 Curve SketchingDokumen8 halamanMathematics Worksheet For Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate MSC: 1 Curve Sketchingharshbardhan singhBelum ada peringkat
- Determining Roots Using The Methods of Soving Quadratic EquationDokumen6 halamanDetermining Roots Using The Methods of Soving Quadratic EquationBaems Ambor0% (1)
- EECE 5639 Computer Vision I: Coordinate Systems Transformations, ColorDokumen50 halamanEECE 5639 Computer Vision I: Coordinate Systems Transformations, ColorSourabh Sisodia SrßBelum ada peringkat
- MATLABDokumen14 halamanMATLABKritikaBelum ada peringkat
- 2d - Linear and Quadratic EquationsDokumen11 halaman2d - Linear and Quadratic EquationsNihad MehmedovićBelum ada peringkat
- 1.3 Algebraic ExpressionsDokumen10 halaman1.3 Algebraic ExpressionsJong FrancoBelum ada peringkat
- Calculus of Variation Assignment-1 (J-2023)Dokumen2 halamanCalculus of Variation Assignment-1 (J-2023)Sameer BhattaBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge Mathematics AS Level Course: Second EditionDari EverandCambridge Mathematics AS Level Course: Second EditionBelum ada peringkat
- When Two Binomials Contain Only Positive Terms, Here Are Strategies To Determine The Product of The BinomialsDokumen5 halamanWhen Two Binomials Contain Only Positive Terms, Here Are Strategies To Determine The Product of The Binomialsapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Law of Sines:: Part 1 (ASA)Dokumen2 halamanLaw of Sines:: Part 1 (ASA)api-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- 7Dokumen2 halaman7api-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Unesco and Mwa10 ConnectionsDokumen4 halamanUnesco and Mwa10 Connectionsapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- 6Dokumen2 halaman6api-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- 6-2 Multiplying Dividing Rational Expressions MarkersDokumen1 halaman6-2 Multiplying Dividing Rational Expressions Markersapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Resume 2018 SummerDokumen4 halamanResume 2018 Summerapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Professional Project - Final 3Dokumen31 halamanProfessional Project - Final 3api-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- CFR Jot NotesDokumen6 halamanCFR Jot Notesapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 Lesson PlansDokumen35 halamanUnit 2 Lesson Plansapi-259566515100% (1)
- 01 4 Sa and Volume of A Sphere PravdaDokumen4 halaman01 4 Sa and Volume of A Sphere Pravdaapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Plan - Unit S OverviewDokumen3 halamanPlan - Unit S Overviewapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Asgn 2 Doc 1Dokumen51 halamanAsgn 2 Doc 1api-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- 1 Lesson Plan TemplateDokumen1 halaman1 Lesson Plan Templateapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Eal b10l VocabularyDokumen2 halamanEal b10l Vocabularyapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 BDokumen10 halamanAssignment 1 Bapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Plan - Year Long 2015-2016Dokumen3 halamanPlan - Year Long 2015-2016api-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Differentiated Instruction NotesDokumen3 halamanDifferentiated Instruction Notesapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Tesl 36 Ass 1 AlipDokumen11 halamanTesl 36 Ass 1 Alipapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Professional Project ProposalDokumen4 halamanProfessional Project Proposalapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Asignment 3 Part 2 2Dokumen33 halamanAsignment 3 Part 2 2api-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2bDokumen5 halamanAssignment 2bapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Tesl 363 Assignment 1Dokumen8 halamanTesl 363 Assignment 1api-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Tesl 34 Assignment 2-1Dokumen10 halamanTesl 34 Assignment 2-1api-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 3 Final DocumentDokumen25 halamanAssignment 3 Final Documentapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Tesl 363 Assignment 2 1Dokumen10 halamanTesl 363 Assignment 2 1api-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 3: Materials Development and Unit Assessment PlanDokumen39 halamanAssignment 3: Materials Development and Unit Assessment Planapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1b - Final DraftDokumen13 halamanAssignment 1b - Final Draftapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 3 - Final DraftDokumen57 halamanAssignment 3 - Final Draftapi-259566515Belum ada peringkat
- eManmanualNo15623hark 599 Brochure - Eca PDFDokumen2 halamaneManmanualNo15623hark 599 Brochure - Eca PDFKimberly VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Engineering & Site DataDokumen13 halamanBasic Engineering & Site DataBalasubramanianBelum ada peringkat
- Airtel Case Study Channel StrategyDokumen2 halamanAirtel Case Study Channel StrategyTushar GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- PVG 32 BobinasDokumen64 halamanPVG 32 BobinasSaul CastañedaBelum ada peringkat
- Bursting and Collapsing Pressures of ASTM A312 Stainless Steel PipesDokumen1 halamanBursting and Collapsing Pressures of ASTM A312 Stainless Steel PipesManuKumarMittalBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Thinking Handout PDFDokumen1 halamanCritical Thinking Handout PDFAnoosh IqraBelum ada peringkat
- Kadvani Forge Limitennnd3Dokumen133 halamanKadvani Forge Limitennnd3Kristen RollinsBelum ada peringkat
- Updated Official All Campuses ON CAMPUS Final Exams Schedule Spring 2021-22 Plan BDokumen11 halamanUpdated Official All Campuses ON CAMPUS Final Exams Schedule Spring 2021-22 Plan BMohammad SafadiehBelum ada peringkat
- Pulungmasle High School: Boy Scouts of The Philippines - Pulungmasle High School Chapter Work Plan For S.Y 2018-2019Dokumen3 halamanPulungmasle High School: Boy Scouts of The Philippines - Pulungmasle High School Chapter Work Plan For S.Y 2018-2019Rd DavidBelum ada peringkat
- ChuzaChen Hydroelectric Power ProjectDokumen13 halamanChuzaChen Hydroelectric Power ProjectkanabaramitBelum ada peringkat
- Brochure GM IM Roller Mill Antares MDDR MDDT en LowDokumen8 halamanBrochure GM IM Roller Mill Antares MDDR MDDT en Lowahmed shomanBelum ada peringkat
- Systems ClassDokumen53 halamanSystems ClassBhetariya PareshBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Six: Capital Allocation To Risky AssetsDokumen26 halamanChapter Six: Capital Allocation To Risky AssetsjimmmmBelum ada peringkat
- ECO Report 03Dokumen96 halamanECO Report 03ahmedshah512Belum ada peringkat
- ADokumen3 halamanAcristinandreeamBelum ada peringkat
- Viking Tech ARG03FTC2551 - C217943Dokumen8 halamanViking Tech ARG03FTC2551 - C217943ALIRIO SOLANOBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4 Language Summary: VocabularyDokumen1 halamanUnit 4 Language Summary: VocabularyStephania GalindezBelum ada peringkat
- Certified Lead-Base White Metal AnalysisDokumen2 halamanCertified Lead-Base White Metal AnalysisIshmael WoolooBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulic Accumulator - Test and Charge: Cerrar SIS Pantalla AnteriorDokumen9 halamanHydraulic Accumulator - Test and Charge: Cerrar SIS Pantalla AnteriorHomer Yoel Nieto Mendoza100% (1)
- Alenar R.J (Stem 11 - Heliotrope)Dokumen3 halamanAlenar R.J (Stem 11 - Heliotrope)REN ALEÑARBelum ada peringkat
- TMJC - H2 - 2021 - Prelim P2Dokumen9 halamanTMJC - H2 - 2021 - Prelim P2猪猪侠Belum ada peringkat
- UN 9252-06 Part 1-UD-AU-000-EB-00020 PDFDokumen7 halamanUN 9252-06 Part 1-UD-AU-000-EB-00020 PDFManjeet SainiBelum ada peringkat
- Spiros Styliaras: Devops EngineerDokumen2 halamanSpiros Styliaras: Devops EngineerΣπύρος ΣτυλιαράςBelum ada peringkat
- MTBF and MTTR For Metal-Enclosed Capacitor Banks and Harmonic Filter SystemsDokumen4 halamanMTBF and MTTR For Metal-Enclosed Capacitor Banks and Harmonic Filter SystemsbansalrBelum ada peringkat
- C 6 Slings SafetyDokumen29 halamanC 6 Slings SafetyAshraf BeramBelum ada peringkat