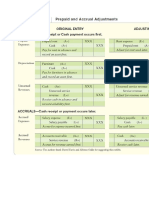
4.0 Presentation of Financial Statements
Diunggah oleh
andrea lasagnaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
4.0 Presentation of Financial Statements
Diunggah oleh
andrea lasagnaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
4.
0 Presentation of Financial Statements
IAS 1 – Presentation of Financial Statements
IAS 8 – Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors
IAS 10 – Events after the Reporting Period
IAS 7 – Statement of Cash Flows
IAS 18 – Revenues
IFRS 15 – Revenue from contracts with Customers
IAS 24 – Related Party Disclosures
4.1 Statement of Financial Position
4.2 Statement of Comprehensive Income
4.3 Statement of Cash Flows
Definition
Integral part of financial statements
Summarizes operating, investing, and financing activities
Provides information about cash receipts and cash payments
Classification of cash flows
- Operating activities
Derived primarily from principal revenue producing activities. Those that
enter into the determination of net income or loss.
- Investing activities
Derived from acquisition and disposal of long-term assets and other
investments not included in cash equivalent.
Cash flows from transaction involving non-operating assets
- Financing activities
Derived from equity capital and borrowings of the entity
Transactions involving entity & owners and entity & creditors Commented [r1]: Entity financing
Involving nontrade liabilities and equity Commented [r2]: Debt financing
Noncash activities – investing and financing transactions that do not require
use of C / CE shall be excluded from statement of cash flows. Shall be disclosed
in notes or separate schedule.
Interest – SHALL be classified as operating cash flows because they enter into
the determination of net income or loss. ALTERNATIVELY interest paid may be
classified as financing cash flow and interest received may be classified as
investing cash flow.
Dividends – SHALL be classified as operating cash flows. ALTERNATIVELY
dividend received may be classified as investing cash flows and dividend paid
may be classified as financing cash flows.
Income taxes – SHALL be separately disclosed as cash flows arising from
operating activities unless they can be specifically identified with investing and
financing.
Direct and indirect method
IAS 7 provides entity shall report cash flows from operating activities using either
direct or indirect method. Provides that entities are encouraged to report cash
flow from operating activities using the direct method
- Direct method shows in detail or itemizes major classes of gross receipts
and payments. Considered as ’cash basis’ income statement.
Computation of collections
Trade AR and NR, beg xx
Add: sales (accrual basis) xx
Total xx
Less: trade AR and NR, end (xx)
Collection of AR and NR xx
Computation of payment to merchandise creditors
Trade AP and NP, beg xx
Add: purchases (accrual basis) xx
Total xx
Less: trade AP and NP, end (xx)
Payment to merchandise creditors xx
Computation of payments for expenses
Expenses (Accrual) xx
Add: Prepaid expenses, end xx
Accrues expenses, beg xx
Total xx
Less: Prepaid expenses, beg (xx)
Accrued expenses, end (xx)
Expenses paid xx
Computation of collection of other income
Income other than sale (Accrual) xx
Add: Deferred income, end xx
Accrued income, beg xx
Total xx
Less: Deferred income, beg (xx)
Accrued income, end (xx)
Collection of other income xx
- Indirect method
4.4 Statement of Changes in Equity
4.5 Notes to the Financial Statements
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Reviewer SentDokumen44 halamanReviewer Sentandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Audit SamplingDokumen1 halamanAudit Samplingandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Bonds PayableDokumen8 halamanBonds Payableandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- Sw2 Budgeting Bsa 4 1Dokumen3 halamanSw2 Budgeting Bsa 4 1andrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Payroll LiabilitiesDokumen11 halamanPayroll Liabilitiesandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Ch01 Test Bank Jeter Advanced Accounting 3rd EditionDokumen14 halamanCh01 Test Bank Jeter Advanced Accounting 3rd EditionJohn Marenco0% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- BREAKING DOWN 'Economy': Supply and Demand SectorDokumen2 halamanBREAKING DOWN 'Economy': Supply and Demand Sectorandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis: Sign in - Sign UpDokumen11 halamanCost-Volume-Profit Analysis: Sign in - Sign Upandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Partnership AccountingDokumen3 halamanPartnership Accountingandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- Accounts PayableDokumen7 halamanAccounts Payableandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- Volume 1 - Copy TheoryDokumen34 halamanVolume 1 - Copy Theoryandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- BREAKING DOWN 'Economy': Supply and Demand SectorDokumen2 halamanBREAKING DOWN 'Economy': Supply and Demand Sectorandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Sales by Spouses With Third Parties Shall Be Governed by EitherDokumen3 halamanSales by Spouses With Third Parties Shall Be Governed by Eitherandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Practical Accounting II (Corporate Liquidation)Dokumen5 halamanPractical Accounting II (Corporate Liquidation)andrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- 10 Accountancy Facts For International Accounting DayDokumen5 halaman10 Accountancy Facts For International Accounting Dayandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Advanced EconomiesDokumen6 halamanAdvanced Economiesandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- AfarDokumen30 halamanAfarandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- Six Step Audit ProcessDokumen19 halamanSix Step Audit Processandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- CHAPTER13 Home Office and Branch - Special ProblemsDokumen21 halamanCHAPTER13 Home Office and Branch - Special ProblemsAlgifariAdityaBelum ada peringkat
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDokumen1 halamanMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturdayandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Article 1767Dokumen1 halamanArticle 1767andrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- ReviewerDokumen8 halamanReviewerandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- PartnershipDokumen4 halamanPartnershipandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- PartnershipDokumen4 halamanPartnershipandrea lasagnaBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- IAS 1 Classification AmendmentsDokumen10 halamanIAS 1 Classification Amendmentscynthia karylle natividadBelum ada peringkat
- Prelim Departmental Exam Reviewer With Answer Key PDFDokumen11 halamanPrelim Departmental Exam Reviewer With Answer Key PDFAndrea Marie CalmaBelum ada peringkat
- Partnership: Q#1. Record The Following in The Necessary Journals and Show The Relevant ProprietorshipDokumen7 halamanPartnership: Q#1. Record The Following in The Necessary Journals and Show The Relevant ProprietorshipUnais AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Notes Fa1Dokumen20 halamanNotes Fa1som_tiwariBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- FUNAC TheoriesDokumen5 halamanFUNAC TheoriesAlvin QuizonBelum ada peringkat
- Framework of AccountingDokumen11 halamanFramework of AccountingAngelica ManaoisBelum ada peringkat
- Eskimo Limited financial statements and notes summaryDokumen6 halamanEskimo Limited financial statements and notes summaryMuhammad ArmaghanBelum ada peringkat
- CEVA Logistics Cote d’Ivoire SEA FCL Job ProfitDokumen2 halamanCEVA Logistics Cote d’Ivoire SEA FCL Job ProfitZamurradBelum ada peringkat
- DipIFR+Study+Text+D17 J18+ (1) +Dokumen1.563 halamanDipIFR+Study+Text+D17 J18+ (1) +mahi_kunkuBelum ada peringkat
- Accounting For Business CombinationsDokumen29 halamanAccounting For Business CombinationsAmie Jane MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Adjusting Process PDFDokumen47 halamanAdjusting Process PDFJohn Oliver D. OcampoBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Finance Interview Prep - Course ManualDokumen273 halamanTechnical Finance Interview Prep - Course ManualChandan Khanna100% (1)
- Chapter 6-Liquidity of Short-Term Assets Related Debt-Paying AbilityDokumen25 halamanChapter 6-Liquidity of Short-Term Assets Related Debt-Paying AbilityAriel ZamoraBelum ada peringkat
- MTN FinancialsDokumen200 halamanMTN FinancialsIshaan SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Accounting and Reporting Iii Financial Accounting and Reporting Iii (Reviewer) (Reviewer)Dokumen18 halamanFinancial Accounting and Reporting Iii Financial Accounting and Reporting Iii (Reviewer) (Reviewer)Jhaan Key Losita�oBelum ada peringkat
- Decision on Loan Based on Income StatementDokumen3 halamanDecision on Loan Based on Income StatementLorelyn TriciaBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- ch04.ppt - Income Statement and Related InformationDokumen68 halamanch04.ppt - Income Statement and Related InformationAmir ContrerasBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis Ias 16Dokumen4 halamanThesis Ias 16aflobjhcbakaiu100% (2)
- Financial Statement AnalysisDokumen20 halamanFinancial Statement AnalysisPowerPoint GoBelum ada peringkat
- (C) San Antonio Home Furnishings Company-1Dokumen3 halaman(C) San Antonio Home Furnishings Company-1Mark OteroBelum ada peringkat
- Module 17 - ReceivablesDokumen8 halamanModule 17 - ReceivablesLuiBelum ada peringkat
- Advacc2 MQ2Dokumen2 halamanAdvacc2 MQ2Karina Barretto Agnes0% (1)
- Class Activity, Adjustments & WORK SHEETDokumen18 halamanClass Activity, Adjustments & WORK SHEETkhanBelum ada peringkat
- PT Sam Putra Inti: Balance SheetDokumen21 halamanPT Sam Putra Inti: Balance SheetIkhsan Al IzyraBelum ada peringkat
- WIKADokumen246 halamanWIKACuan 3Belum ada peringkat
- Ifrs Guide BdoDokumen94 halamanIfrs Guide Bdoanilnair1966Belum ada peringkat
- Tools of Financial Analysis & PlanningDokumen68 halamanTools of Financial Analysis & Planninganon_672065362100% (1)
- TUGAS DOSEN Chapter 5Dokumen15 halamanTUGAS DOSEN Chapter 5novita sariBelum ada peringkat
- ACC124 Receivables Quizzer W/ SolutionsDokumen43 halamanACC124 Receivables Quizzer W/ Solutionsジェロスミ プエブラスBelum ada peringkat
- Future of International Accounting Standards in the American Business EnvironmentDokumen12 halamanFuture of International Accounting Standards in the American Business EnvironmentNoureddine MezianiBelum ada peringkat
- Value: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceDari EverandValue: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinancePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (18)
- 7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelDari Everand7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelBelum ada peringkat
- Joy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerDari EverandJoy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Angel: How to Invest in Technology Startups-Timeless Advice from an Angel Investor Who Turned $100,000 into $100,000,000Dari EverandAngel: How to Invest in Technology Startups-Timeless Advice from an Angel Investor Who Turned $100,000 into $100,000,000Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (86)