Effective Teaching of Mathematics PDF
Diunggah oleh
Maria Carmela Oriel MaligayaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Effective Teaching of Mathematics PDF
Diunggah oleh
Maria Carmela Oriel MaligayaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
What is effective teaching of mathematics?
The old paradigm of balanced instruction focused on enabling children and teachers to achieve
success at school. Today’s paradigm focuses on students achieving college and career readiness
in life, beyond school.
The old paradigm of balanced instruction
focused on enabling children and teachers Dimensions of Effective Mathematic Practice
to succeed at school. Today, the focus is
Effective Teachers:
for students to achieve college and career
readiness in life beyond school. This new • Know how students learn
paradigm expects that students:
• Know what students need to learn
• Construct their own understandings
• Apply prior knowledge and skills • Know what their students already know
• Are consistently challenged • Encourage risk taking
• Take risks
• Create purposeful learning experiences
• See purpose in what they learn
• Create challenge
The goal is for students to be literate
in mathematics so that we can prepare
them for a world where the subject is Effective teachers: Effective teachers know how students
rapidly growing and is extensively applied learn
to a diverse number of fields. • Know the pedagogy that determines
how their students successfully learn Effective teachers of mathematics know
Teaching mathematics can only be the pedagogy that determines how
• Know and understand the content
described as truly effective when it their students successfully learn. Such
and practices that students need
positively impacts student learning. We teachers recognize that in order for
to comprehend, as described in the
know that teaching practices can make students to effectively use mathematics
Standards framework
a major difference to student outcomes, they need to understand the concepts
as well as what makes a difference in the • Know the students they teach as presented as well as become fluent with
classroom. learners the skill taught. It is through the ongoing
• Challenge all students at their own and increasingly complex application of
Research and evidence from the field concepts and skills that students become
level
of mathematics lets us know, with a secure and competent in their use.
fair degree of certitude, how effective • Encourage risk taking
teachers of mathematics skillfully • Create purposeful learning Effective teachers of mathematics are
integrate a range of instructional experiences for students through knowledgeable in the theory of learning
approaches and resources to meet the the use of relevant and meaningful their subject.
diverse learning needs of their students. contexts
© Chris Coombes Generation Ready 2013 1
They recognize the importance of • Knowledge of where and how to
using concrete materials and visual apply and use mathematics skills and
representations to develop a deep concepts
understanding of the subject. They have Students need to use the above both in
a clear picture of the learning progression school, and in real world contexts.
that best develops the knowledge base
and skills of their students. They also have Effective teachers know their students
Allowing the subject to a broad palate of learning experiences as learners
be problematic means they can use in the classroom, to meet
allowing students to the different learning needs of each Knowing a student as a mathematics
student. learner is complex. An effective
wonder why things are,
mathematics teacher quickly builds a
to inquire, to search Effective teachers are able to look picture of their students by progressively
for solutions, and to at student misconceptions, either in providing opportunities to demonstrate
resolve incongruities. the classwork, through homework, or what he/she is learning. This way,
It means that both through assessments, and reteach the teachers update and deepen their
material using their understanding of the understanding of individual students.
the curriculum and developmental nature of what becomes
instruction should before or after the misconception. Deep The effective teacher continuously uses
begin with problems, understanding of the content enables this growing knowledge of students as
dilemmas, and teachers to directly address the specific learners to inform their instruction so
misunderstandings that students may they can better meet students’ needs.
questions for students.
have.
Assessment in mathematics is primarily
Hibert et al., 1996
Such teachers need to be continual formative. It involves collecting
learners. Effective pedagogy is the information from a range of sources, in a
subject of ongoing research and variety of ways. This includes information
development, and the way to teach and on students’ strategies, understandings,
learn mathematics is never static. attitudes, and prior knowledge and skills.
... our best evidence... Assessing a student involves making
is that what happens Effective teachers know what students informed judgments about what the
in classrooms through need to know student knows. Hence, effective teachers
quality teaching and Effective teachers know and understand
not only monitor the performance of a
through the quality student, but also their ability to show
the content and practices of the their understanding of the content that
of the learning mathematics Standards framework that has been taught. Effective teachers:
environment generated students need to know. Such teachers
by the teacher and the have deep understanding of concepts • Integrate assessment into
and utilize multiple ways to represent instructional practice
students, is the key and explain them. They are also fluent
variable in explaining with the procedures and practices their
• Acknowledge students’ prior learning
and help them make connections
up to 59%, or even students will need in order to succeed in
between what they already know and
more, of the variance in mathematics.
what they are currently learning
student scores. The Common Core focus on career and • Gather information from a range of
college readiness requires that students formal and informal sources using
Ministry of Education, 2003
be able to apply mathematics to complex a variety of means, in particular
problems in multiple contexts, both real written and verbal, and analyze the
and mathematical. As a consequence, this information presented
is also true for their teachers.
• Use ongoing assessments to identify
Effective teachers augment fluency the learning needs of each student.
procedure with: This allows them to teach pro-
actively, assisting students to meet
• Deep conceptual understanding articulated goals
© Chris Coombes Generation Ready 2013 2
Effective teachers create challenge The social setting that teachers provide
is equally as important as the physical
Each student learns best within their environment. Research tells us that
‘Zone of Proximal Development.’ The the quality of the instruction makes
effective teacher: the difference, and it is the interaction
between the teacher and student, most
• Is able to identify and keep track of … Learning
especially the feedback the student gets,
a student’s ‘Zone’ through ongoing
formative assessment
which is essential (Hattie, 2003). mathematics with
Learning mathematics involves taking
understanding is
• Designs instruction that enables
each student to learn within their risks. This is more likely to happen if essential. Mathematics
‘Zone’ students feel that their attempts will be today requires not only
• Provides each student with
valued. Teachers need to help students computational skills
see that mistakes are a natural part of but also the ability
challenges that meet their own
the learning process. By accepting their
level through the careful use of
approximations and providing informed,
to think and reason
investigative tasks
genuine, and encouraging responses, mathematically in
When referring to “challenges,” it is meant teachers are letting students know that order to solve the new
that a student will need to experience they believe in them. While teachers can problems and learn the
some degree of struggle to achieve a create the conditions that foster learning, new ideas that students
learning goal. An effective teacher will and demonstrate strategies for learning
challenge every student to consistently to occur, the students have to actively
will face in the future.
operate at the upper end of their ‘Zone of be engaged. The program needs to be
Proximal Development.’ interesting enough so that students will … Learning is enhanced
want to engage in the learning. in classrooms where
Many strategies introduce challenges into
a lesson, including the use of a rigorous Effective teachers create purposeful
students are required
open task, the use of questioning learning experiences to evaluate their own
strategies (such as turn and talk) that ideas and those of
involve all students, asking exploratory Effective teachers of mathematics create
others, are encouraged
and generative questions, and purposeful learning experiences for
students through solving problems in
to make mathematical
consistently requiring students to pose,
reflect on, and justify arguments. relevant and meaningful contexts. conjectures and test
them, and are helped to
Along with providing a challenge is the There is ample evidence showing the
develop their reasoning
need to provide differing degrees of need for problem-solving to be an integral
support for students. The greater the part of all mathematics learning. Teaching skills.
challenge, the greater the need for through problem solving, however, means
John Van De Walle
teacher support in a gradual release of that students learn mathematics through
responsibility from the teacher to the real contexts, problems, situations,
student. and models. The contexts and models
allow students to build meaning for the
Effective teachers encourage risk taking concepts. This way, they can move on to
increasingly more abstract concepts.
An optimal learning environment is one
that generates an atmosphere of trust, A problem can be defined as
where it is understood that making
mistakes is acceptable, because mistakes ‘…. any task or activity for which the
are the essence of learning. A learning students have no prescribed or memorized
environment that promotes student rules or methods, nor is there a perception
mathematics learning is one where by students that there is a specific “correct”
multiple strategies are encouraged. solution method’ - Hiebert et al.,1997
Understanding and recognizing
connections within mathematics comes
by finding different ways to achieve the
same result.
© Chris Coombes Generation Ready 2013 3
Effective teachers will use such problems
as starting points and an ongoing Gradual Release of Responsibility
means for students to investigate and Students Teachers
understand conceptual ideas so they
can develop skills and procedures. Introduce and provide
Observe, listen
Through such problems, all students are models of strategies and
and respond
texts
provided with appropriate entry points to
Student Independence
progressively develop the understanding Demonstrate how the
Teacher Support
of concepts and increasingly more Participate and respond strategy works in a shared
complex skills that facilitate efficient setting
problem solving.
Support students as they
Attempt with support
practice in small groups
Practice and Observe students as they
problem solve practice independently
References
Alton-Lee, A. (2004). Using best evidence Hattie, J. (2003, October). Teachers Teachers Matter: Attracting, Developing
syntheses to assist in making a bigger make a difference: What is the research and Retaining Effective Teachers. (2005).
difference for diverse learners. Wellington: evidence? Paper presented at the OECD: Paris
Ministry of Education. Australian Council for Educational
Research Annual Conference on Building Steel, C.F. (2009). The inspired teacher:
Au, R., Watkins, D.W., Hattie, J.A.C., Teacher Quality, Melbourne. How to know one, grow one, or to be one.
& Alexander, P. (2009). Reforming Alexandria, VA: ASCD
the depression model of learned Hattie, J.A,C. (2009). Visible Learning:
hopelessness for academic outcomes. A synthesis of 800+ meta-analysis on Weinstein, R. (2002). Reaching higher: the
Educational Research Review. 4, 103-17 achievement. London: Routledge. power of expectations in schooling. MA:
Harvard University Press.
Ausubel, D.P. (1968). Educational Hiebert, J., Carpenter, T., Fennema,
Psychology: A cognitive view. New York: K., Fuson, D., Wearne, D., Murray,
Holt, Rinehart and Winston Hanle., Olivier, A., and Human, P. (1997).
Making Sense: teaching and learning
Boykin, A. W. & Noguera P. (2011) mathematics with understanding.
Creating the opportunity to learn: moving Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann.
form research to practice to close the
achievement gap. Alexandria, VA: ASCD
© Chris Coombes Generation Ready 2013 4
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Effective Teaching of LiteracyDokumen4 halamanEffective Teaching of LiteracyNasser AmmarBelum ada peringkat
- Georgia Teacher Keys Effectiveness System guide to Professional Knowledge standardDokumen1 halamanGeorgia Teacher Keys Effectiveness System guide to Professional Knowledge standarderica de castroBelum ada peringkat
- Resecrhbaseffectivtchgprinc 11 27 18wbaDokumen2 halamanResecrhbaseffectivtchgprinc 11 27 18wbaMorente Hazel F.Belum ada peringkat
- Assessment of Trainee Teachers - Grading DescriptorsDokumen18 halamanAssessment of Trainee Teachers - Grading DescriptorsLKjfuiewfb Efhkbnvsb DhudiouhwBelum ada peringkat
- Student Teach Tws FinalDokumen36 halamanStudent Teach Tws Finalapi-332044132Belum ada peringkat
- Fa17 Tws For SteDokumen26 halamanFa17 Tws For Steapi-295303640Belum ada peringkat
- Summary of Recommendations: Metacognition and Self-Regulated LearningDokumen1 halamanSummary of Recommendations: Metacognition and Self-Regulated LearningjayBelum ada peringkat
- RDG 323 Philosophy of Disciplinary Literacy Final ReflectionDokumen3 halamanRDG 323 Philosophy of Disciplinary Literacy Final Reflectionapi-523679344Belum ada peringkat
- SPEC 116 Activity 6Dokumen4 halamanSPEC 116 Activity 6Mean MirafuentesBelum ada peringkat
- Fa17 Tws For Ste 1Dokumen39 halamanFa17 Tws For Ste 1api-329368543Belum ada peringkat
- Northern State University Student Teaching Experience Teacher Work Sample Spring 2017Dokumen77 halamanNorthern State University Student Teaching Experience Teacher Work Sample Spring 2017api-298084991Belum ada peringkat
- Learner-Centered Teacher TraitsDokumen15 halamanLearner-Centered Teacher TraitsElla ZambraBelum ada peringkat
- Ed 35 Learning Journey 2 Activity 1Dokumen3 halamanEd 35 Learning Journey 2 Activity 1Kiara TrozziBelum ada peringkat
- Overview TPIDokumen5 halamanOverview TPIMehran MousaviBelum ada peringkat
- Pangasinan State University: School of Advanced Studies Urdaneta City, Pangasinan 2 Semester, Academic Year 2021-2022Dokumen4 halamanPangasinan State University: School of Advanced Studies Urdaneta City, Pangasinan 2 Semester, Academic Year 2021-2022avy mariel alcantaraBelum ada peringkat
- Comparison of 20th and 21st Century EducationDokumen9 halamanComparison of 20th and 21st Century EducationHermie RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Effective Pedagogies in PersonDokumen24 halamanEffective Pedagogies in PersonKiwinKoreaBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Process792Dokumen4 halamanTeaching Process792AhlemBelum ada peringkat
- Northern State University Student Teaching Experience Teacher Work Sample Spring 2018Dokumen43 halamanNorthern State University Student Teaching Experience Teacher Work Sample Spring 2018api-331892318Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment No. 01 Autumn, 2020: Teaching Education in Pakistan (829) M.A/M.EDDokumen24 halamanAssignment No. 01 Autumn, 2020: Teaching Education in Pakistan (829) M.A/M.EDSana BashirBelum ada peringkat
- Tws Spring 2021Dokumen26 halamanTws Spring 2021api-489134454Belum ada peringkat
- L3 Constructivism and Direct InstructionDokumen31 halamanL3 Constructivism and Direct Instructionasmahmahadi92_620656Belum ada peringkat
- Intellectual Rigour Challenges All Students: Professional Practice Note 7Dokumen4 halamanIntellectual Rigour Challenges All Students: Professional Practice Note 7nanaBelum ada peringkat
- Pedagogy: Ensuring Trainee UnderstandingDokumen1 halamanPedagogy: Ensuring Trainee UnderstandingMuhammad AkramBelum ada peringkat
- Activity No. 1 Finals 2EDFIL4ADokumen5 halamanActivity No. 1 Finals 2EDFIL4AMichaella DometitaBelum ada peringkat
- Things to Consider in Planning Instructions copy copyDokumen2 halamanThings to Consider in Planning Instructions copy copylydinemercado5Belum ada peringkat
- InductionplanDokumen10 halamanInductionplanapi-286077564Belum ada peringkat
- Cadaa_Module 4_EDUC 126Dokumen6 halamanCadaa_Module 4_EDUC 126Elfe Grace L. CadaaBelum ada peringkat
- E5 A1PosterTable4Dokumen1 halamanE5 A1PosterTable4steffb23Belum ada peringkat
- Casandra ADokumen3 halamanCasandra ACasandra CalacatBelum ada peringkat
- Field Study Overview JournalDokumen7 halamanField Study Overview JournalJohn VibarBelum ada peringkat
- Activity Sheet No. 1.6Dokumen5 halamanActivity Sheet No. 1.6jab villBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment in Student Learning 2Dokumen12 halamanAssessment in Student Learning 2Maribel Nitor Lopez100% (1)
- Pste 496-Teacher Work SampleDokumen20 halamanPste 496-Teacher Work Sampleapi-497960091Belum ada peringkat
- ROJO - Teachers and Students in The Digital AgeDokumen2 halamanROJO - Teachers and Students in The Digital AgeESTHER ROSE ROJOBelum ada peringkat
- a. Hallmarks of Effective TeachingDokumen23 halamana. Hallmarks of Effective TeachingchristianarcigaixBelum ada peringkat
- Spec 16 Activity 6Dokumen6 halamanSpec 16 Activity 6Bia LamayoBelum ada peringkat
- 102-Midterm-ExamTSCI SabanDokumen3 halaman102-Midterm-ExamTSCI SabanpresonalstffBelum ada peringkat
- 21st Century LearningDokumen2 halaman21st Century LearningGerald Mallillin BeranBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1 and 2 - Facilitating Learner - Centered Teaching - Nicko Jay Y. Gabayno - Gen. Science IIIDokumen2 halamanLesson 1 and 2 - Facilitating Learner - Centered Teaching - Nicko Jay Y. Gabayno - Gen. Science IIIRoland GanBelum ada peringkat
- Developing The Cambridge LearnerDokumen122 halamanDeveloping The Cambridge LearnerNonjabuloBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Teaching ReviewerDokumen3 halamanPrinciples of Teaching ReviewerKaitlyn Rayter100% (1)
- Northern State University Pre-Student Teaching Experience Eled/Sped/Seed 496 Teacher Work Sample Fall 2017Dokumen16 halamanNorthern State University Pre-Student Teaching Experience Eled/Sped/Seed 496 Teacher Work Sample Fall 2017api-332013451Belum ada peringkat
- Educ 290 Presentation PortfolioDokumen21 halamanEduc 290 Presentation Portfolioapi-576700084Belum ada peringkat
- Ste Teacher Work Sample-SommersDokumen27 halamanSte Teacher Work Sample-Sommersapi-497960091Belum ada peringkat
- Learner Centered TeachingDokumen10 halamanLearner Centered TeachingPintash BastinoBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Perspectives Inventory (TPI) SummariesDokumen5 halamanTeaching Perspectives Inventory (TPI) SummariesDavid WooBelum ada peringkat
- Sbutterfield - Idaho Core Teacher Standards and Danielson Framework For Teaching 1Dokumen35 halamanSbutterfield - Idaho Core Teacher Standards and Danielson Framework For Teaching 1api-665452212Belum ada peringkat
- Final Weebly TwsDokumen34 halamanFinal Weebly Twsapi-332331761Belum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen3 halamanUntitledjaneBelum ada peringkat
- Observation and Participation: Is Personal. There Must Be A Focus For What The Teacher Is Viewing. ItDokumen7 halamanObservation and Participation: Is Personal. There Must Be A Focus For What The Teacher Is Viewing. ItKylie MayʚɞBelum ada peringkat
- Planning instruction factors to considerDokumen2 halamanPlanning instruction factors to considerJezza PastorizaBelum ada peringkat
- Eled Sped Seed496tws FinalDokumen28 halamanEled Sped Seed496tws Finalapi-295655000Belum ada peringkat
- Mod42 Prof LearnDokumen16 halamanMod42 Prof LearnRoginee Del SolBelum ada peringkat
- Tws No InfoDokumen39 halamanTws No Infoapi-427123455Belum ada peringkat
- High Leverage Instructinal PracticesDokumen3 halamanHigh Leverage Instructinal Practicesapi-557677748Belum ada peringkat
- Designing InstructionDokumen2 halamanDesigning InstructionJarra RuddyBelum ada peringkat
- EDUC-109-NOTESDokumen20 halamanEDUC-109-NOTESHannahBelum ada peringkat
- Qualities of Excellent Classrooms - 2020-2021Dokumen5 halamanQualities of Excellent Classrooms - 2020-2021Mary Kate McGetrickBelum ada peringkat
- Professional Development and the Mathematics EducatorDari EverandProfessional Development and the Mathematics EducatorBelum ada peringkat
- Health Declaration Form: (Buong Pangalan) (Petsa) (Oras) (Kasa/ukuyang Tirahan) : (Numero NG Telepono)Dokumen1 halamanHealth Declaration Form: (Buong Pangalan) (Petsa) (Oras) (Kasa/ukuyang Tirahan) : (Numero NG Telepono)Reichmond LegaspiBelum ada peringkat
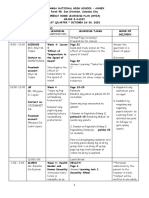
- WHLP Grade 8 Daisy Week 4Dokumen8 halamanWHLP Grade 8 Daisy Week 4Maria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Calamba National High School Annex Weekly Home Learning PlanDokumen8 halamanCalamba National High School Annex Weekly Home Learning PlanMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Theorems on Rectangles, Rhombus, Trapezoids and KitesDokumen7 halamanTheorems on Rectangles, Rhombus, Trapezoids and KitesMaria Carmela Oriel Maligaya100% (1)
- Exam in g8Dokumen2 halamanExam in g8Maria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring and Baking Bread and PastryDokumen3 halamanMeasuring and Baking Bread and PastryMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- TOS Pre Final2Dokumen3 halamanTOS Pre Final2Maria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Theorems on Rectangles, Rhombus, Trapezoids and KitesDokumen7 halamanTheorems on Rectangles, Rhombus, Trapezoids and KitesMaria Carmela Oriel Maligaya100% (1)
- Summative 8 4THDokumen2 halamanSummative 8 4THMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Math Absolute Value Number Line Stations Travelled DistancesDokumen10 halamanMath Absolute Value Number Line Stations Travelled DistancesMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Math Absolute Value Number Line Stations Travelled DistancesDokumen10 halamanMath Absolute Value Number Line Stations Travelled DistancesMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- TOS Pre FinalDokumen3 halamanTOS Pre FinalMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Perfect AttendanceDokumen59 halamanPerfect AttendanceMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Cot Rpms Demo TeachingDokumen11 halamanCot Rpms Demo TeachingMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Exam in g8Dokumen2 halamanExam in g8Maria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Mps ComputationDokumen34 halaman2 Mps ComputationMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Math Pre/Post Test ReferencesDokumen4 halamanMath Pre/Post Test ReferencesMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Long QuizDokumen5 halamanLong QuizMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Personal lifelong learning plan for mathematics teacherDokumen9 halamanPersonal lifelong learning plan for mathematics teacherMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz No2Dokumen2 halamanQuiz No2Maria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Paul Bryan R. Arabos: "With Honors" (1)Dokumen3 halamanPaul Bryan R. Arabos: "With Honors" (1)Maria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Long QuizDokumen5 halamanLong QuizMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Liham Paanyaya Sa Mga MagulangDokumen3 halamanLiham Paanyaya Sa Mga MagulangMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Year Plan Template Math SampleDokumen2 halaman3 Year Plan Template Math SampleMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Methods of Plant PropagationDokumen7 halamanMethods of Plant PropagationMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- In A Group of StudentsDokumen3 halamanIn A Group of StudentsMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Certificate - Perfect Attendance20Dokumen1 halamanCertificate - Perfect Attendance20Maria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Complement and Set DifferenceDokumen2 halamanComplement and Set DifferenceMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Hypothesis: Science Reviewer Lesson: 1 HypothesisDokumen7 halamanHypothesis: Science Reviewer Lesson: 1 HypothesisMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Teachers Performance Review RevisedDokumen8 halamanTeachers Performance Review RevisedMaria Carmela Oriel MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Why Use Eportfolios and Web 2.0 ToolsDokumen21 halamanWhy Use Eportfolios and Web 2.0 ToolsHazel Owen100% (1)
- Cardboard Arcade Rubric-Timeline 301-1Dokumen3 halamanCardboard Arcade Rubric-Timeline 301-1api-300424365Belum ada peringkat
- GRE Vocabulary ListDokumen15 halamanGRE Vocabulary ListMadhavi Kandadai100% (2)
- Naeyc Statement of Commitment 123Dokumen3 halamanNaeyc Statement of Commitment 123api-311435461Belum ada peringkat
- Mark Nunes - Error. Glitch, Noise, and Jam in New Media CulturesDokumen283 halamanMark Nunes - Error. Glitch, Noise, and Jam in New Media Culturesbig_julie100% (3)
- Writing The College EssayDokumen18 halamanWriting The College Essayapi-255229633Belum ada peringkat
- Description: Tags: WWC Wilson Reading 070207Dokumen5 halamanDescription: Tags: WWC Wilson Reading 070207anon-697598Belum ada peringkat
- Charterhouse School, The Heritage TourDokumen9 halamanCharterhouse School, The Heritage TourFuzzy_Wood_PersonBelum ada peringkat
- Visible ThinkingDokumen2 halamanVisible Thinkingorellnairma88Belum ada peringkat
- ITAL 1001 Introduction To Italian IDokumen12 halamanITAL 1001 Introduction To Italian IMikaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2 Cordova VidalDokumen5 halamanAssignment 2 Cordova Vidalapi-257908691Belum ada peringkat
- General Knowledge Test Information GuideDokumen42 halamanGeneral Knowledge Test Information Guideapi-321973122Belum ada peringkat
- Aqa - Applied Bs - Ex of Long Answers - T.guideDokumen43 halamanAqa - Applied Bs - Ex of Long Answers - T.guideMissesMatthewsBelum ada peringkat
- Childselfdescription - SDQ I MarshDokumen7 halamanChildselfdescription - SDQ I MarshwinazhonniwaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan Template: Essential QuestionsDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan Template: Essential Questionsapi-352684188Belum ada peringkat
- Sri Lanka Institute of Information Technology: Student: Supervised byDokumen62 halamanSri Lanka Institute of Information Technology: Student: Supervised bySamsudeen Sabraz NawazBelum ada peringkat
- MAE 377 SyllabusDokumen3 halamanMAE 377 Syllabusgreeneggsandspam6Belum ada peringkat
- 1st Grade Synonyms Crossword 2Dokumen2 halaman1st Grade Synonyms Crossword 2srinathanklBelum ada peringkat
- Teacher Education ObjectivesDokumen24 halamanTeacher Education ObjectivesFaryal AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Aini Fang Resume Assistant TeacherDokumen1 halamanAini Fang Resume Assistant Teacherapi-253826149Belum ada peringkat
- Critical Pedagogy, Ecoliteracy, and Planetary CrisisDokumen210 halamanCritical Pedagogy, Ecoliteracy, and Planetary CrisisRichard Kahn100% (2)
- Web Catalog 2010Dokumen309 halamanWeb Catalog 2010wwjdusaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3 - Sociological Research MethodsDokumen31 halamanLesson 3 - Sociological Research MethodsRajesh DharamsothBelum ada peringkat
- DLL - Tle 6 - Q2 - W4Dokumen5 halamanDLL - Tle 6 - Q2 - W4Nota Belz100% (11)
- INFJ CareerDokumen2 halamanINFJ Careervaruntyagi100% (1)
- Testing and Assessing Final Presentation PDFDokumen46 halamanTesting and Assessing Final Presentation PDFRahhal Ajbilou0% (1)
- Evaluation in Curriculum DevelopmentDokumen12 halamanEvaluation in Curriculum DevelopmentPax GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- John Marshall-Descartes's Moral Theory (1999)Dokumen141 halamanJohn Marshall-Descartes's Moral Theory (1999)José PalmaSantyagoBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Question Paper Generator for Autonomous InstitutesDokumen6 halamanAutomatic Question Paper Generator for Autonomous InstitutesPrajwal sBelum ada peringkat
- Murphy MadisonDokumen1 halamanMurphy Madisonapi-315700369Belum ada peringkat