Cardiovascular System
Diunggah oleh
Elena Arvaniti0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
25 tayangan4 halamanheart vessels
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Iniheart vessels
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
25 tayangan4 halamanCardiovascular System
Diunggah oleh
Elena Arvanitiheart vessels
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 4
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
1. Organs: Heart, blood vessels, blood)
A. Functions:
1. Transportation of substances: Nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide,
hormones, minerals, etc.
2. Second defense against microbial invasion. WBC = phagocytosis,
antibody formation
2. Vessels of the Circulatory System
A. Vascular Tissue = Three layered structure
1. Tunica Intima
a. Endothelium (processes that extend into the muscle layer)
b. Loose Connective Tissue with occasional smooth muscle cell
c. Internal elastic membrane (Arteries only)
2. Tunica Media
a. Variable amounts of Collagen, Proteoglycans, and elastic fibers
b. Circular Smooth Muscle cells
c. thickness, number of layers and type of tissue varies
with the diameter of the vessel and its distance from the heart.
d. External elastic membrane, thiner than Internal, found in some
(Arteries only)
3. Tunica Adventitia
a. Connective tissure support, fuses with CT of organ
b. Vasa vasorum (small vessels for nutrient supply of vessel walls),
c. Nerves, myelinated, sensory fibers reach to intima
Nonmyelinated vasomotor, network in adventitia. end amonug
muscle cells
B. Arterial system
1. Elastic (Conducting)
a. Major arteries leaving the heart
b. Elastic recoil = diastolic pressure
c. Tunica Intima - [A in photo] post
mortum changes, folded
endothelium
highly active endothelial cells, microvilli, pinocytotic vessicles
constant turnover by mitosis
Subendothelium - thick, ;ongitudinally arranged CT fibers.
Internal elastic usually not seen
due to elastic tissue of Media.
d. Tunica Media - 40(newborn) - 70
(adult) layers of elastic
membranes
Some smooth muscle cells, Few
collagen fibers, chondroitin sulfate
Fibers and amorphous material
e. Tunica Adventitia - [B in photo] relatively underdeveloped, elastic
and collagen fibers
2. Muscular (Distributing) medium to small
Note:Internal elastic membrane in photo
a. Large vessels that carry blood from the aorta
b. Nutrient arteries to organs, Directs flow, controls volume &
pressure
c. Tunica Intima - Internal Elastic
Membrane
d. Tunica Media - Thick muscular layer, to
40 layers of smooth muscle cells
e. Tunica Adventitia - External elastic
Membrane may be present (larger)
3. Arterioles (Resistance vessels)
a. Control blood flow to capillary beds.
b. Regulate volume and pressure in the arterial system
c. Tunica Intima - no sub endothelial layer
No (rarely) Internal Elastic Membrane
d. Tunica Media - 1 - 5 layers of smooth muscle
e. Tunica Adventitia - NO External Elastic Membrane
4. Metarterioles
1. Branch into capillaries
2. Discontinous layers of smooth muscle
3. Sphincter at junction of capillary
C. Capillary (exchange vessels)
1. Diffusion membrane = simple squamous epithelium (endothelial
tubes), with basal lamella
2. 7,000 sq meters in the adult, Not found in cartilage, hair, nails, cuticle,
or cornea of the eye
0. Tunica Intima, endothelium only
1. Tunica Media - None
2. Tunica Adventitia - None
3. Number and type vary with tissue type and metabolism
. Continuous (closed) blood brain barrier (brain, thymus, testicular,
ocular)
No pores through cells
Occluding (tight) Junctions, (zonula occludens)
a. Perforated (continuous with pores) = most capillary beds
Pores through cells
Some with sieve-like diaphragms
b. Sinusoidal capillary (discontinuous) = maximal exchange (Liver, bone
marrow, spleen)
Large diameter, discontinous vessel
gaps without cells, without basal lamella, with phagocytic cells
4. Pericyte = supportive cell of capillaries and small arterioles
with long cytoplasmic processes, undifferentiated connective tissue
cells
5. Endotheliun, possible contractility, microfillaments within cells, opens
cell junctions
6. pinocytotic vessicles cross cells in 2 - 3 minutes
7. Permeability varies, in kidney 100 times more permeable than muscle
capillaries
D. Venous system
1. Veins (Capacitance vessels) = Contain 75% of total blood volume
2. Venous return due to contraction of skeletal muscle
3. Large Veins
0. Tunica Intima - well developed
1. Tunica Media - Thin
2. Tunica Adventitia - Thickest, may contain longitudinal smooth muscle
4. Small & Medium Veins
. Valves, 2 semilunar folds,
elastic tissue lined with endothelium, Most numerous in limbs
prevent backflow of blood
a. Tunica Intima - thin endothelium
b. Tunica Media - few muscle cells
c. Tunica Adventitia - well developed collagenous layer
5. Venules thin walls
. Formed by coalescence of capillaries (Exchange vessels)
a. Tunica Intima - endothelium
b. Tunica Media - small bundles of smooth muscle cells mixed with
collagen
c. Tunica Adventitia - well developed collagenous layer
6. Heart Anatomy
. Two hearts (pumps in one): Right heart, Left heart
a. Heart Structure = Atria and Ventricle,
b. Heart Layers = Epicardium, Myocardium, Endocardium
1. Endocardium (intima) endothelium with
subendothelial layer
2. Myocardium Heart (cardiac) muscle 2
populations of cells
1. Contractile cells, major myocardial
contractions
2. Conducting cells, (Purkinji cells )
reduced myofibrils, full of glycogen, gap
junctions at discs
Conduction System = Controls Heart
Beat
3. Epicardium, serous membrane with
subepicardial connective tissue(adipose tissue
accumulates
c. Fibrous Skeleton
1. Fibrous central region for attachment of
myocytes
2. Thick collagenous fibers in various directions
3. Nodules of fibrocartilage
d. Valves (Control direction of Blood Flow)
Tricuspid valve, Bicuspid valve (Mitral), Semilunar valves
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Epithelium SummaryDokumen7 halamanEpithelium SummaryElena ArvanitiBelum ada peringkat
- Digestive System IDokumen15 halamanDigestive System IElena Arvaniti100% (1)
- Epithelial TissuesDokumen86 halamanEpithelial TissuesElena ArvanitiBelum ada peringkat
- Characteristics of BoneDokumen5 halamanCharacteristics of BoneElena ArvanitiBelum ada peringkat
- Connective Tissue IDokumen8 halamanConnective Tissue IElena ArvanitiBelum ada peringkat
- Histology Is The Study of TissuesDokumen87 halamanHistology Is The Study of TissuesElena ArvanitiBelum ada peringkat
- Endoderm - Mesoderm - Ectoderm and OrgansDokumen1 halamanEndoderm - Mesoderm - Ectoderm and OrgansElena ArvanitiBelum ada peringkat
- 2005 EJHG PragueDokumen1 halaman2005 EJHG PragueElena ArvanitiBelum ada peringkat
- CRT NotesDokumen7 halamanCRT NotesElena ArvanitiBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Race TheoryDokumen3 halamanCritical Race TheoryElena Arvaniti100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Lipoproteins in Diabetes Mellitus: Alicia J. Jenkins Peter P. Toth Timothy J. Lyons EditorsDokumen468 halamanLipoproteins in Diabetes Mellitus: Alicia J. Jenkins Peter P. Toth Timothy J. Lyons EditorsFELELBelum ada peringkat
- Karbohidrat: Gula, Pati & SeratDokumen20 halamanKarbohidrat: Gula, Pati & SeratAlfi Syahrin SiregarBelum ada peringkat
- Arendi v. GoogleDokumen16 halamanArendi v. GooglePriorSmartBelum ada peringkat
- Carnatic Music NotationDokumen6 halamanCarnatic Music Notationksenthil kumar100% (1)
- How To Perform A Financial Institution Risk Assessment: Quick Reference GuideDokumen15 halamanHow To Perform A Financial Institution Risk Assessment: Quick Reference GuideYasmeen AbdelAleemBelum ada peringkat
- IEEE 802.1adDokumen7 halamanIEEE 802.1adLe Viet HaBelum ada peringkat
- BMW I3 Wheel Airbag RemovalDokumen6 halamanBMW I3 Wheel Airbag RemovalAjmaster.ltBelum ada peringkat
- Febryruthwahyuni Lds g1718 Bilphy MRDokumen11 halamanFebryruthwahyuni Lds g1718 Bilphy MRfebry sihiteBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Information For Attempted MurderDokumen3 halamanSample Information For Attempted MurderIrin200Belum ada peringkat
- Short Question: Computer Science For 9 Class (Unit # 3)Dokumen5 halamanShort Question: Computer Science For 9 Class (Unit # 3)Yasir MehmoodBelum ada peringkat
- MBA Advantage LRDokumen304 halamanMBA Advantage LRAdam WittBelum ada peringkat
- Kumpulan Soal UPDokumen16 halamanKumpulan Soal UPTriono SusantoBelum ada peringkat
- Italian CuisineDokumen29 halamanItalian CuisinekresnayandraBelum ada peringkat
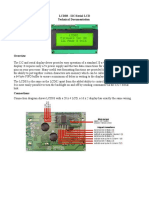
- Datasheet lcd03 20x4 B PDFDokumen8 halamanDatasheet lcd03 20x4 B PDFFrancis100% (1)
- Apollo Hospital Chennai: NO: 16, BSNL TELESHOPPE, Greams Road 044 2999 1606Dokumen9 halamanApollo Hospital Chennai: NO: 16, BSNL TELESHOPPE, Greams Road 044 2999 1606Manas ChandaBelum ada peringkat
- TorqueArm PDFDokumen186 halamanTorqueArm PDFanush_swaminathanBelum ada peringkat
- Different Varieties of English C1 WSDokumen5 halamanDifferent Varieties of English C1 WSLaurie WBelum ada peringkat
- The Great Psychotherapy Debate PDFDokumen223 halamanThe Great Psychotherapy Debate PDFCasey Lewis100% (9)
- SLS Ginopol L24 151-21-3-MSDS US-GHSDokumen8 halamanSLS Ginopol L24 151-21-3-MSDS US-GHSRG TBelum ada peringkat
- My Cook BookDokumen66 halamanMy Cook BookAkshay KumariBelum ada peringkat
- (Promotion Policy of APDCL) by Debasish Choudhury: RecommendationDokumen1 halaman(Promotion Policy of APDCL) by Debasish Choudhury: RecommendationDebasish ChoudhuryBelum ada peringkat
- Mps Item Analysis Template TleDokumen11 halamanMps Item Analysis Template TleRose Arianne DesalitBelum ada peringkat
- Derivative Pakistan PerspectiveDokumen99 halamanDerivative Pakistan PerspectiveUrooj KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Solved MCQS For Mid Terms Papers Solved by JUNAID MALIK and TeamDokumen23 halamanSolved MCQS For Mid Terms Papers Solved by JUNAID MALIK and TeamUrwa RiazBelum ada peringkat
- 1416490317Dokumen2 halaman1416490317Anonymous sRkitXBelum ada peringkat
- Maths-Term End Examination-2020-2021 (2020-2021, MATHS)Dokumen6 halamanMaths-Term End Examination-2020-2021 (2020-2021, MATHS)Venkat Balaji0% (1)
- A Daily Miracle2Dokumen1 halamanA Daily Miracle2LizZelencichBelum ada peringkat
- Collec The PassportDokumen2 halamanCollec The PassportvijikaBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding The School Curriculum Close Encounter With The School Curriculum SPARK Your InterestDokumen12 halamanUnderstanding The School Curriculum Close Encounter With The School Curriculum SPARK Your InterestJoshua Lander Soquita CadayonaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 Listening SkillDokumen7 halamanUnit 2 Listening SkillSbgacc SojitraBelum ada peringkat