CC2 - Electrolytes and Inorganic Ions
Diunggah oleh
johnjoseph.ermitano0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
92 tayangan4 halamanBasic notes for Electrolytes and Inorganic Ions.
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniBasic notes for Electrolytes and Inorganic Ions.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
92 tayangan4 halamanCC2 - Electrolytes and Inorganic Ions
Diunggah oleh
johnjoseph.ermitanoBasic notes for Electrolytes and Inorganic Ions.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 4
Electrolytes and Inorganic ions Increases sodium
Proximal Convoluted Tubules = Where 70% of
Electrolytes = Inorganic subs that dissociates into ions: cation anion the filtered sodium is passively reabsorbed
- They are charged - Atrial natriuretic peptide:
- It has different specialties CHF marker
Anion Gap Produced by the heart when it works too much.
Used for Electrolyte profile Natriuresis = sodium excretion in the urine
Makes use of 4 major electrolytes (water follows) that causes the blood volume to
- Sodium decrease that in turn alleviates its work load
- Potassium RAAS – Renin is produced in low BP (low salt
- Chloride concentration). In turn i will promote sodium
- Bicarbonate reabsorption at Distal Convoluted Tubules
Formula: [Na+] – [Cl- + HCO3] Related Imbalances:
Normal Value = 10-17mmol/L - Hypernatremia
Quality control purposes: low normal, normal, high for - Hyponatremia
electrolytes result - (plasma water has an effect in sodium levels in the
Cation = + ion blood;
Anion = - ion Hyponatremia
Electrical Neutrality = Electrolytes exists in the body with a - Overhydration = water retention.
0 net charge. - It is due to excessive loss
- In the body, electrical neutrality must be maintained - Dietary is not a quite significant cause
Sum of cation = sum of anion - Addison’s disease
- difference arise due to the presence of other Adrenal gland problem
electrolytes Primary Hypoadrenalism
We only use them for prob id esstimate = o Low Aldosterone production that causes
Increase in anion gap was observed in: decreased sodium conservation
- Uremia - It can be a result of diarrhea
- DM complication - Pseudohyponatremia
- Ketoacidosis Artefctual
- Dehydration High glucose, lipids and protein levels (especially
from DM patients, MM patients and
Decrease in anion gap was observed in:
dyslipidemia)
- Monoclonal and Polyclonal Gammopathies
- Electrolyte Exclusion Effect = Principles followed by
- Lithium toxicity
the electrolytes in the blood especially when it comes
- Hypermagnesemia
to their measurement
Electrolytes are only measured in the water
Functions:
phase of the plasma (93-95% of water), because
Maintain fluid balance (Mainly Na)
electrolytes are only found in water phase.
Acid base balance (Mainly HCO3)
All electrolytes measurements are in low
Production of action potential (Mainly K)
concentration due to the total volume of the
It can act as a cofactor for different enzyme systems (Mg = specimen.
most widely used activator) - Sodium is the most affected in imbalance
Maintenance of electrical neutrality Hypernatremia:
- Dehydration
Sodium (Na; Natrium) - High sodium levels
Maintains the fluid balance in the body. - Insulin therapy
It is the most abundant extracellular cation in the body. - Cushing syndrome and DM insipidus
- Monovalent cation Its hallmark is high sodium
- 1:12 intracellular:extracellular ratio Excessive aldosterone production
It controls osmosis of the water between different fluid Reference value: 135-150
compartments.
Analytical techniques:
Principal osmotic particle:
- Use serum as a specimen = no additives that might
- It is osmoticaly active which draws water (so as Cl)
interfere with the reaction performed
that creates osmotic pressure in the plasma.
- Almost half of the osmolality of the plasma water 11-30 min to clot
attributes to sodium. - Heparinized plasma is the second preferred specimen
~280-290 mOsmol/kg Specimen processing is faster
- Osmolality must be balanced to maintain blood You will not wait for clotting.
volume and blood pressure Sodium Heparin must not be used in Sodium
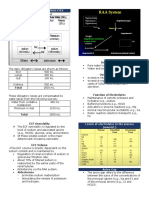
Regulation: measurement.
- ADH (vasopressin) - secreted from the posterior - Ion Selective Electrode
pituitary gland. It promotes water absorption. Potentiometry = method of choice. It measures
It affects sodium balance if imbalance. electrode that binds to the electrolyte.
- Aldosterone – secreted by adrenal cortex. It promotes o Glass electrode must be used in sodium
sodium reabsorption.
- 2 types of ISE (2 modes of operation). o Acidosis = Potassium is pushed out of the
Direct cell and hydrogen comes in which causes
o No specimen dilution high potassium levels
o The risk of pseudohyponatremia will not be - As seen in Insulin therapy where potassium comes
a problem along as the glucose comes in.
o Most oftenly used - Potassium loss
- Asssociated with GI and Renal due to massive
Indirect
excretion
o Specimen dilution.
Diuretic = potassium decrease
o Electrolyte exclusion effect o Potassium sparring diuretic which prevents
o More prone in pseudohyponatremia. potassium loss
o Hemolysis specimen = Most common cause Remedy: Eat foods rich in Potassium
of pseduhyponatremia Hyperkalemia
Ruptured RBC can lead to - high potassium
electrolytes increase. - Opposite reasons
False decrease in sodium and - Acidosis
chloride, due to dilution. - Cell damage
- Flame photometry for sodium measurement; - Renal failure
Obsolete - Mineralocorticoid deficiency
Performs dilution Deficiency in Aldosterone which promotes
potassium excretion
Sodium = yellow flame
o If the aldosterone levels are high the
- Spectrophotometric and Colorimetric Method
potassium level decreases
Uses Bradbury method (Yellow end color)
o If deficient the potassium level increases
Adopted in: - Pseudohyperkalemia
o Albanese Lein - Zinc urinylacetate Artefactual
o Maruna Trinder - Mg uranylacetate False hyperkalemia
- Enzymatic Sodium Method o Potassium is collection sensitive
Uses beta-galactosimase o Most significantly affected in hemolysed
Sodium act as an activator samples
- Atomic absorption RBC contains ~105 mmol/L of
Gold standard Potassium against in serum that
Reference method contains only 3.85 - 5.5 mmol/L
Reference Values: o Excessive tourniquet time
- Serum= 135 - 150 mmol/L o Excessive clenching of fist
- CSF= 136 - 150 mmol/L o Delayed separation and refrigeration can
- Urine= 40 - 220 mmol/day (24-hr urine) result to pseudohyperkalemia due to
- Conversion of mmol/L to mEQ/L is based on the cellular activity
number of valence. o The same is true if the specimen is high
platelet count
Potassium (K; Kalium) When the blood clots the platelets will
Potassium balance. rapture and potassium will be release.
Generation of action potential. Remedy: use plasma
Involved in muscle contraction and nerve impulse Serum potassium is a little higher
transmission due to clotting process than
Most important in normal cardiac function plasma potassium val has a diff.
- Too much or little can make the heart stop beating Barter syndrome
- If not that extreme, only the muscles will be affected. - Low sodium
Most abundant intracellular cation - Low potassium
- 23:1 intracellular:extracellular ratio Analytical technique:
Low levels in blood serum. - Potassium Ion Selective Electrode
Levels are controlled by aldosterone in an opposite Uses liquid membrane electrode with
manner valinomycin incorporated as a potassium binder.
- Potassium excretion = decreases potassium in the Valinomycin is part of the electrode that serves
body as potassium binder
Hypokalemia - Flame photometry
- Due to potassium shift from extracellular Potassium = Violet flame
compartment to intracellular compartment as seen in - Spectrophotometric technique
alkalosis Lockhead and Purcell
Potassium replaces hydrogen as it goes out of o Old method
the cell to compensate alkalosis o Blue violet to violet
o Electrical neutrality = Hydrogen needs - Turbidimetric
replacement to balance the charges Hillman and Beyer
o Uses sodium tetraphenylboron which
produces turbidity
- Atom Absorption Spectroscopy o Sodium is also elevated
Gold standard o Elevation of chloride = 60mmol/L or higher
Reference Value: sweat chloride in CF.
- Serum = 3.8-5.5 mmo/L How to collect the sweat?
- Urine = 25-125 mmol/day o Use Pilocarpine Iontophoresis
Devised by Gibson Coolie
Chloride Uses pilocarpine nitrate to induce
Counter-ion of sodium sweating (so does increase salivation
- Regulates osmotic pressure and water balance but this is not we are up to), then
together with sodium. collected in goose pad then pathlab
Has a role in acid-base balance chlorinometer.
- Chloride shift Reference Values:
Bicarbonate acts as its reciprocal ion. - Serum = 98-106 mmol/L
Serves as its “Kapalitan” to preserve electrical - Urine = 110-250 mmol/day
neutrality - Sweat = 5-45mmol/L (Higher than 60 implies Cystic
Bicarbonate is an important base if it needs to Fibrosis)
cross the membranes and go other places, the
chloride take its place. Calcium
Reciprocal in relationship 5th most abundant mineral element in the body
Most abundant extracellular anion Lower than potassium
Hyperchloridemia 98% is found in the bones in the form of hydroxylapatite
- Metabolic alkalosis crystals
- Respiratory acidosis 2% is left for the other parts of the body
Hypochloridemia Ca is also a clotting factor
- Metabolic acidosis For muscle contraction
- Respiratory alkalosis Regulated by PTH produced by the parathyroid hormone
Analytical techniques: - PTH can cause blood calcium levels elevation by a
- Ionic Selective Electrode process called bone resorption
Uses Silver chloride 1% of bone calcium is exchangeable in the
- Colorimetric method plasma then calcium will go to the plasma which
Schales and Schales causes calcium elevation
o Uses mercurimetric titration - PTH promoting calcium absorption in the kidneys
Mercury has high affinity for chloride. - Promotes vitamin D synthesis
Chloride and Mercury will react to - Elevates calcium due to intestinal absorption of
produce HgCl, titrated with calcium and phosphorous:
diphenylcarabazome to a blue end Acetone, came from thyroid gland, has an
point opposite effect which decreases blood calcium.
- Skeggs modification It has different forms in the blood
Uses mercuric thiocyanate - Not exclusively ions compared to others.
o Mercuric thiocyanate will react with Some fractions cannot be measured by ISE due to its many
chloride to produce HgCl. forms:
o Then thiocyante ions are liberated (this is - 10% anion bound (not a subject to ISE)
we are up to), - 50% - free or ionized form (active form)
o Ferric iron is reacted to thiocyante to - 40% - protein bound (bound to albumin)
produce a red or reddish brown complex of - Ionization of calcium is pH dependent
ferric thiocyanate: Increase in pH
- Colometric ampherometric o Decrease ionized fraction
Gold standard Decrease in pH
Cotlove chlorinometer o Increase in ionized fraction
o Electrochemical technique like ISE Ionization and pH has an Inversely
o An electrode is used that will produce silver proportional relationship
ions then it will react with the chloride in Analytical techniques:
the specimen producing silver chloride - 2 Types of Calcium testing:
precipitate (basis). Ion Selective Electrode
o The instrument will correlate the timed o Ionized fraction measurement
elapse from the start to the end of the silver Specimen consideration:
chloride production Closed system – don’t open the
Correlated in chloride concentration. tube unless for testing. It will be
- Sweat chloride determination at risk for aerosol contamination,
Special area in chloride testing hence a false results will be
Specifically designed to detect Cystic Fibrosis generated.
o Mucoviscidosis For ionized calcium, if the
The patient has viscous secretions to tube was left open, the pH
the point that the internal organs are will increase due to
affected (e.g pancreas, lungs). liberation of CO2.
Atomic absorption Magnesium
o Total calcium methodology 2nd most abundant intracellular cation
- Colorimetric method for total calcium 4th most abundant cation in the body
Clark and Collip Forms in the Blood: Free or Ionized (2/3) and Protein
o Calcium is treated with ammonium oxalate Bound (1/3) with Albumin.
then calcium oxalate is precipitated this Acts as an activator
then converts calcium oxalate to oxalic acid. Analytical Method:
After which we titrate with potassium - Atomic absorption spectroscopy
permanganate (purple end color; but its Reference method
endpoint is colorless (colorless manganese)) - Flame photometry
- EDTA titration Magnesium = blue flame
Bachra,Dawer & Sobel - Colorimetric and Spectrophotometric method
Use of indicator called Calcin red (pinkish), then Titan yellow
place a drop in the solution with calcium, afterso o A yellow dye that becomes red in the
it will form a yellowish green fluorescence. Apply presence of magnesium.
EDTA. o Not that sensitive
It will compete with calcin red via chelation so Calmalite green formazan with methylene blue
that calcin red will be degraded. After (dye binding)
degradation it will form salmon pink end color Cynidil blue (dye binding is the most common in
- Spectrophotometry Mg and Ca)
Dye binding
O-cresolpthalein complex method Bicarbonate
o It turns into a violet solution Acid base balance maintenance, act as an important base
o Has an additional reagent, 8- 2nd most abundant in extracellular anion
Hydroxyguinoline to prevent magnesium Could be a part in Blood Gas analysis (collected in arterial
interference. blood)
Because calcium and magnesium - Venous blood has a higher bicarbonate levels than
interfere with each other’s’ arterial
reaction. Because bicarbonate originates in carbon dioxide
- Atomic absorption which is a waste product of cellular metabolism.
Has AAS but it has phosphate. Acidifying the specimen
o This is the reason why we add lanthanum - All the bicarbonate will be converted into gaseous
chloride which prevents phosphorous to Carbon dioxide which then measured using pCO2
interact with calcium producing Calcium Electrode
phosphate
Anion that measures partial pressure of CO2
- If alkalinized = enzymatic
Phosphorous
Coupled enzyme assay
It has inverse relationship with Calcium in the body o Uses 2 enzymes:
Influenced by PTH, Calcitonin and Vitamin D phospoinolpyruvate carboxylase
For structural support mallate dehydrogenase as copling
Energy generation and storage enzyme
Majority of which is found in the bone in the form of
hydroxyapatite crystals around 85%;
Widely distributed
Analytical Techniques:
- Colorimetric
Fiske and Subarrow Method
o inorganic P (PI) is reacted with ammonium
molybdate which produces
phosphomolybdic/date acid (colorless) read
in 340nm. It could be continued to a visible
method, just add reducing agents:
Ascorbic acid
Stannous chloride
P-aminonapthtolsulfonic acid
And it will turn to a colored end product
called phospomolybdenum blue – blue and
red at 600nm wavelength
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Understanding Sodium, Potassium, and the Anion GapDokumen4 halamanElectrolyte Imbalances: Understanding Sodium, Potassium, and the Anion Gapjohnjoseph.ermitanoBelum ada peringkat
- Fe Finals NotesDokumen23 halamanFe Finals NoteshanhananicasBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Chemistry Midterm Lecture 1 ElectrolytesDokumen4 halamanClinical Chemistry Midterm Lecture 1 ElectrolytesMichelle San Miguel FeguroBelum ada peringkat
- ELECTROLYTES (Na & K)Dokumen3 halamanELECTROLYTES (Na & K)Alondra SagarioBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolyte 1Dokumen8 halamanElectrolyte 1Ylooner QuitsBelum ada peringkat
- Hyponatremia: ElectrolytesDokumen5 halamanHyponatremia: ElectrolytesCyreen Jill Aliling100% (1)
- Electrolytes Part 2 11Dokumen3 halamanElectrolytes Part 2 11Joshoua MalanaBelum ada peringkat
- tranzDokumen22 halamantranzMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolytes SummaryDokumen23 halamanElectrolytes SummaryDjdjjd SiisusBelum ada peringkat
- Fluids & Electrolytes: Thirst Reflex Triggered byDokumen7 halamanFluids & Electrolytes: Thirst Reflex Triggered byGummie Akalal SugalaBelum ada peringkat
- Disorders of Sodium: Presenter: DR Bharath Kumar P Moderator: DR Ramesh K NDokumen41 halamanDisorders of Sodium: Presenter: DR Bharath Kumar P Moderator: DR Ramesh K NBharath Kumar PamulapatiBelum ada peringkat
- CCHM 312: Week 4 & 5: Water Balance and ElectrolytesDokumen7 halamanCCHM 312: Week 4 & 5: Water Balance and ElectrolytesJanine Alicia VargasBelum ada peringkat
- Week12 13 RENAL PhysiologyDokumen41 halamanWeek12 13 RENAL Physiologyirwan kastellaBelum ada peringkat
- Kuliah S2 Dasar Air-ElekDokumen38 halamanKuliah S2 Dasar Air-ElekViany RehansyahBelum ada peringkat
- LP3 NCM 112 Electrolytes2021 UpdatedDokumen57 halamanLP3 NCM 112 Electrolytes2021 UpdatedJade CentinoBelum ada peringkat
- Hypovolemic hyponatremia causes and diagnosisDokumen6 halamanHypovolemic hyponatremia causes and diagnosisNobita DoraemonBelum ada peringkat
- ELECTROLYTES Edited Semi Finals XDDokumen52 halamanELECTROLYTES Edited Semi Finals XDzerachiel zephyrBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolytes Handout 1Dokumen6 halamanElectrolytes Handout 1dkBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolytes Water Balance PH Balance Trace MetalsDokumen21 halamanElectrolytes Water Balance PH Balance Trace MetalsJohn Kevin Carl SaligumbaBelum ada peringkat
- Na K and CL Profame and Diasys Summary CC2Dokumen3 halamanNa K and CL Profame and Diasys Summary CC2maja.amora.swuBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolytes To Phosphorus PPTsDokumen99 halamanElectrolytes To Phosphorus PPTsMarvin SimbulanBelum ada peringkat
- Water BalanceDokumen9 halamanWater BalanceKim Mae ComendadorBelum ada peringkat
- Ajo Poster-06072017Dokumen1 halamanAjo Poster-06072017api-383596435Belum ada peringkat
- Chloride and Calcium LevelsDokumen8 halamanChloride and Calcium LevelsOrhan AsdfghjklBelum ada peringkat
- CC2 ElectrolytesDokumen22 halamanCC2 ElectrolytesCyril Llego ManuelBelum ada peringkat
- Aubf - Renal Functions & TestsDokumen5 halamanAubf - Renal Functions & TestsBSMT Kharylle divine FuentibellaBelum ada peringkat
- Hypon at R em Ia: ST Epw Ise Appr Oach T o Diagn Osis: Ser U M Sodiu M 135 M M Ol/ LDokumen1 halamanHypon at R em Ia: ST Epw Ise Appr Oach T o Diagn Osis: Ser U M Sodiu M 135 M M Ol/ LMaría José GalvisBelum ada peringkat
- Sodium and PotassiumDokumen4 halamanSodium and PotassiumLUALHATI VILLASBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolytes New - 1Dokumen186 halamanElectrolytes New - 1Annamae Therese MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Perioperative Care Acid Base ElectrolytesDokumen7 halamanPerioperative Care Acid Base ElectrolytesIlyas HarunBelum ada peringkat
- Intra and Intradialytic Hypotension and Hypertension InrigDokumen29 halamanIntra and Intradialytic Hypotension and Hypertension InrigMonica HerreraBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolytes ACID BASE BALANCEDokumen11 halamanElectrolytes ACID BASE BALANCEimbendo.cvtBelum ada peringkat
- Fluids PDFDokumen26 halamanFluids PDFLeogalvez BedanoBelum ada peringkat
- Fluids & ElectrolytesDokumen18 halamanFluids & ElectrolytesBiway RegalaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolytes - KBM - PPT 2017 MLS 3Dokumen77 halamanElectrolytes - KBM - PPT 2017 MLS 3Charles BagendaBelum ada peringkat
- Hyponatremia: Causes, Classification and ManagementDokumen40 halamanHyponatremia: Causes, Classification and Managementarchana p sBelum ada peringkat
- PHS CVSDokumen25 halamanPHS CVStewogbadeomobuwajo005Belum ada peringkat
- Supplementary Information To Chapter 30: Overview of Electrolyte BalanceDokumen11 halamanSupplementary Information To Chapter 30: Overview of Electrolyte BalanceAaron JoseBelum ada peringkat
- Fluids and Electrolytes: PGI Pat JacintoDokumen21 halamanFluids and Electrolytes: PGI Pat JacintoPat JacintoBelum ada peringkat
- CC Lec Mod 3Dokumen13 halamanCC Lec Mod 38wgmhh9ks9Belum ada peringkat
- Hyponatremia in DCLDDokumen27 halamanHyponatremia in DCLDGowtham KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolytes, Trace Elements and VitaminsDokumen67 halamanElectrolytes, Trace Elements and VitaminsFatima MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- CLINICAL CHEMISTRY ELECTROLYTESDokumen77 halamanCLINICAL CHEMISTRY ELECTROLYTESGrayBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Chemistry 2 LAB: Electrolytes, Sodium, Potassium, ChloridesDokumen2 halamanClinical Chemistry 2 LAB: Electrolytes, Sodium, Potassium, ChloridesEmiaj Francinne Mendoza100% (1)
- Diuretics TableDokumen6 halamanDiuretics TableVie TBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Physiology ReviewDokumen7 halamanRenal Physiology ReviewHOD AnesthesiaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolytes IDokumen4 halamanElectrolytes IRed AnthonyBelum ada peringkat
- Correcting Electrolyte Abnormalities in the Emergency DepartmentDokumen57 halamanCorrecting Electrolyte Abnormalities in the Emergency Departmentdrnado_82Belum ada peringkat
- Hypernatremia: Kidney Case Conference: How I TreatDokumen3 halamanHypernatremia: Kidney Case Conference: How I TreatJulian ViggianoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 15: ElectrolytesDokumen6 halamanChapter 15: ElectrolytesTelle AngBelum ada peringkat
- K (Anion Gap 12) (Anion Gap 12) Acute Asthma Hypovolemia: - Vomit - Pyloric StenosisDokumen4 halamanK (Anion Gap 12) (Anion Gap 12) Acute Asthma Hypovolemia: - Vomit - Pyloric StenosisAhmad Asyraf AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- M1 - F&eDokumen2 halamanM1 - F&ejuiceBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 14 - ElectrolytesDokumen10 halamanLesson 14 - ElectrolytesLUZVIMINDA GORDOBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Lecture 1aDokumen34 halamanRenal Lecture 1atyhbbhhBelum ada peringkat
- LP 8 Fluid and Electrolyte Disorders - PPSXDokumen57 halamanLP 8 Fluid and Electrolyte Disorders - PPSXCamelia A. ParuschiBelum ada peringkat
- 0618 Ecosolrllactatedringershartmannssolution PDFDokumen2 halaman0618 Ecosolrllactatedringershartmannssolution PDFninaBelum ada peringkat
- Directions for IV SolutionDokumen2 halamanDirections for IV SolutionIfah 'eii' FlainBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid and Electrolyte Management of The Surgical PatientDokumen56 halamanFluid and Electrolyte Management of The Surgical Patientsjmc.surgeryresidentsBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolytes: M. Zaharna Clin. Chem. 2009Dokumen35 halamanElectrolytes: M. Zaharna Clin. Chem. 2009Ahmed GaberBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisDari EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Avh p6050dvd EngDokumen119 halamanAvh p6050dvd EngcaimanaterBelum ada peringkat
- Ross 308 AP Broiler PO2019-EN PDFDokumen16 halamanRoss 308 AP Broiler PO2019-EN PDFJORGE GALVISBelum ada peringkat
- Unchained MelodeeDokumen93 halamanUnchained MelodeeRafael Cornholio RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- ABB Price Book 714Dokumen1 halamanABB Price Book 714EliasBelum ada peringkat
- MR 20 Nissan PDFDokumen1.639 halamanMR 20 Nissan PDFFREDYRUFO AZA MORALES83% (6)
- Hypnotherapy GuideDokumen48 halamanHypnotherapy Guides_e_bell100% (2)
- Operational Transconductance Amplifier ThesisDokumen6 halamanOperational Transconductance Amplifier ThesislaurahallportlandBelum ada peringkat
- Adobe Scan 12 Aug 2022Dokumen3 halamanAdobe Scan 12 Aug 2022surabhi kalitaBelum ada peringkat
- User Manual HDL 30 ADokumen36 halamanUser Manual HDL 30 AAgung KurniandraBelum ada peringkat
- Pancreatic NekrosisDokumen8 halamanPancreatic Nekrosisrisyda_mkhBelum ada peringkat
- CalderaDokumen56 halamanCalderaEsteban TapiaBelum ada peringkat
- MEETING 7 OPINIONSDokumen2 halamanMEETING 7 OPINIONSLeonie Irina MutiaraBelum ada peringkat
- Brosur Sy135cDokumen9 halamanBrosur Sy135cDenny KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- WHO Blocks Nanosilver Shipments to Treat Ebola in AfricaDokumen2 halamanWHO Blocks Nanosilver Shipments to Treat Ebola in AfricaTamas ZefferBelum ada peringkat
- Perreaux E220 200W Stereo Power Amplifier from 1994Dokumen2 halamanPerreaux E220 200W Stereo Power Amplifier from 1994joaoraffa raffaBelum ada peringkat
- The Anglican Digest - Winter 2022Dokumen64 halamanThe Anglican Digest - Winter 2022The Anglican Digest100% (1)
- AWWA M28 Rehabilitation of Water Mains 3rd Ed 2014Dokumen133 halamanAWWA M28 Rehabilitation of Water Mains 3rd Ed 2014millini67% (3)
- Moisture ManagementDokumen5 halamanMoisture ManagementSombis2011Belum ada peringkat
- October 14, 2011 Strathmore TimesDokumen28 halamanOctober 14, 2011 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesBelum ada peringkat
- Elimination - Nursing Test QuestionsDokumen68 halamanElimination - Nursing Test QuestionsRNStudent1100% (1)
- ArduinoDokumen15 halamanArduinoAlvarez TomasBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of SwimmingDokumen7 halamanFundamentals of SwimmingSheila Mae Lira100% (1)
- Tyco TY8281 TFP680 - 03 - 2023Dokumen17 halamanTyco TY8281 TFP680 - 03 - 2023First LAstBelum ada peringkat
- Vietnam & Angkor Wat (PDFDrive) PDFDokumen306 halamanVietnam & Angkor Wat (PDFDrive) PDFChristine TranBelum ada peringkat
- P198 Software and Atlases For Evaluating Thermal Bridges 0Dokumen10 halamanP198 Software and Atlases For Evaluating Thermal Bridges 0cm08909Belum ada peringkat
- Smart Asthma ConsoleDokumen35 halamanSmart Asthma ConsoleMohamad Mosallam AyoubBelum ada peringkat
- Vedic Astrology OverviewDokumen1 halamanVedic Astrology Overviewhuman999100% (8)
- Systematic Literature Review and Mapping of The Prediction of Pile CapacitiesDokumen12 halamanSystematic Literature Review and Mapping of The Prediction of Pile CapacitiesCaio Augusto Lemke CostaBelum ada peringkat
- The Focus Shooting Method CourseDokumen48 halamanThe Focus Shooting Method CourseKobiXDBelum ada peringkat
- Research Article (Lavandula Angustifolia) Essential Oil On: Effect of Lavender Acute Inflammatory ResponseDokumen10 halamanResearch Article (Lavandula Angustifolia) Essential Oil On: Effect of Lavender Acute Inflammatory ResponseAndreeaBelum ada peringkat