Wave Guides
Diunggah oleh
Hikaru Hitachiin0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
43 tayangan3 halamanAntenna
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniAntenna
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
43 tayangan3 halamanWave Guides
Diunggah oleh
Hikaru HitachiinAntenna
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 3
Technological Institute of the Philippines
Electronics Engineering Department
Waveguides
Group Assignment #
OBJECTIVES:
1. Explain the basic theory of operation and construction of a
waveguide.
Reference: Chapter 10
Kennedy, Electronic Communication Systems, 4 th edition, Tata
McGraw-Hill, 1999
Course Code/Section: ECE503 / ECE51FC1
Members: Signature
Canaya, Regina Marie V.
Magadia, Morris Jay
Nicolas, Jo Malyn
Tapales, Miguel
Date Conducted:
Engr. Dennis Jefferson Amora
Instructor
Questions:
1. What are waveguides
2. At what frequencies waveguides are used?
3. How are waveguides constructed?
4. Describe the behavior of electromagnetic waves in waveguide?
5. How are electromagnetics wave propagated in a waveguide?
6. What is skin effect?
7. Differentiate transverse electric and transverse magnetic modes in
waveguides
8. What is meant by dominant mode of operation?
9. Search the internet and submit some pictures of an actual waveguides
Answers:
1. Any pipe with a sort of cross section can be considered as a waveguide
which we can conclude that waveguide is a device that confines and
conveys microwaves. Waveguides are preferred to transmission lines
because they are have less loss at the highest frequencies.
2. The frequencies waveguides are used are from 1.21GHz to 325GHz. It is
more widely used in higher frequency (e.g. 300GHz) because compare to
coaxial cable, it has a maximum higher operating frequency with
minimum loss.
3. A transmission line can be transformed into a waveguide by
connecting multiple quarter-wave shorted stubs. In a similar way, a pipe
with any sort of cross section could be used as a waveguide, but the
simplest cross sections are preferred.
4. The electromagnetic waves in the waveguide reflect in the wall and
moves in a zig zag fashion. The walls have nothing to short-circuit, and
they do not interfere with the wave pattern set up between them. Thus
propagation is not hindered.
5. The electromagnetic wave propagates in the waveguide by reflecting
on the walls.
6. Skin effect is the tendency where an alternating current (AC) flow
mostly near the outer surface of an electrical conductor, such as metal
wire. As the frequency increases, the effect becomes more and more
apparent.
7. A waveguide can be classified into transverse electric (TE) mode and
transverse magnetic (TM) mode. For the TE mode, there is no electric field
in the direction of the propagation; thus leaving only the magnetic field
in the direction of propagation. However, for TM mode, there are no
magnetic fields in the direction of propagation; thus, only an electric
field is present along the direction of propagation.
8. A dominant mode operation is the mode having the lowest cutoff
frequency in a waveguide. In this mode, the wave is propagated with the
minimum degradation. It can also support more than one propagation
mode.
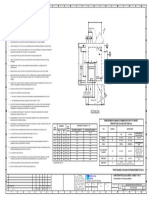
9.
Figure 1: An example of a RF waveguide
Figure 2: The behavior of the electromagnetic waves inside the waveguide
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Technological Institute of The Philippines: Impedance Matching Using Smith ChartDokumen8 halamanTechnological Institute of The Philippines: Impedance Matching Using Smith ChartHikaru HitachiinBelum ada peringkat
- (Hand Out) (New) P - Ece113 - w1Dokumen18 halaman(Hand Out) (New) P - Ece113 - w1Hikaru HitachiinBelum ada peringkat
- Bill of Materials - Design 1 Pre-Made Rectifier and Load Balancing Circuit Component Details Qty Price Per PC AmountDokumen6 halamanBill of Materials - Design 1 Pre-Made Rectifier and Load Balancing Circuit Component Details Qty Price Per PC AmountHikaru HitachiinBelum ada peringkat
- Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDokumen4 halamanTechnological Institute of The PhilippinesHikaru HitachiinBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- IMCI Chart BookletDokumen43 halamanIMCI Chart Bookletmysticeyes_17100% (1)
- Peer PressureDokumen13 halamanPeer PressuremightymarcBelum ada peringkat
- Mosfet Irfz44Dokumen8 halamanMosfet Irfz44huynhsang1979Belum ada peringkat
- Catedral de SevillaDokumen28 halamanCatedral de SevillaAnonymous LkgNmKeBelum ada peringkat
- CL57T V4.0Dokumen14 halamanCL57T V4.0dimitriBelum ada peringkat
- Oxford EAP B1 Pre-Intermediate Student - S Book 2Dokumen167 halamanOxford EAP B1 Pre-Intermediate Student - S Book 2Thư Dương Thị AnhBelum ada peringkat
- Buried PipelinesDokumen93 halamanBuried PipelinesVasant Kumar VarmaBelum ada peringkat
- SweetenersDokumen23 halamanSweetenersNur AfifahBelum ada peringkat
- Configuring BGP On Cisco Routers Lab Guide 3.2Dokumen106 halamanConfiguring BGP On Cisco Routers Lab Guide 3.2skuzurov67% (3)
- Baseline Scheduling Basics - Part-1Dokumen48 halamanBaseline Scheduling Basics - Part-1Perwaiz100% (1)
- Government College of Nursing Jodhpur: Practice Teaching On-Probability Sampling TechniqueDokumen11 halamanGovernment College of Nursing Jodhpur: Practice Teaching On-Probability Sampling TechniquepriyankaBelum ada peringkat
- BrochureDokumen3 halamanBrochureapi-400730798Belum ada peringkat
- Modlist - Modlist 1.4Dokumen145 halamanModlist - Modlist 1.4Tattorin vemariaBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen216 halamanUntitledMONICA SIERRA VICENTEBelum ada peringkat
- How To Configure PowerMACS 4000 As A PROFINET IO Slave With Siemens S7Dokumen20 halamanHow To Configure PowerMACS 4000 As A PROFINET IO Slave With Siemens S7kukaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2 MANA ECON PDFDokumen5 halamanModule 2 MANA ECON PDFMeian De JesusBelum ada peringkat
- Miguel Augusto Ixpec-Chitay, A097 535 400 (BIA Sept. 16, 2013)Dokumen22 halamanMiguel Augusto Ixpec-Chitay, A097 535 400 (BIA Sept. 16, 2013)Immigrant & Refugee Appellate Center, LLCBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Education Thesis TopicsDokumen4 halamanPhysics Education Thesis TopicsPaperWriterServicesCanada100% (2)
- Shakespeare Sonnet EssayDokumen3 halamanShakespeare Sonnet Essayapi-5058594660% (1)
- PDFDokumen10 halamanPDFerbariumBelum ada peringkat
- Sociology As A Form of Consciousness - 20231206 - 013840 - 0000Dokumen4 halamanSociology As A Form of Consciousness - 20231206 - 013840 - 0000Gargi sharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Perancangan Crushing Plant Batu Andesit Di PT Nurmuda Cahaya Desa Batujajar Timur Kecamatan Batujajar Kabupaten Bandung Barat Provinsi Jawa BaratDokumen8 halamanPerancangan Crushing Plant Batu Andesit Di PT Nurmuda Cahaya Desa Batujajar Timur Kecamatan Batujajar Kabupaten Bandung Barat Provinsi Jawa BaratSutan AdityaBelum ada peringkat
- Caspar Hirschi - The Origins of Nationalism - An Alternative History From Ancient Rome To Early Modern Germany-Cambridge University Press (2012)Dokumen255 halamanCaspar Hirschi - The Origins of Nationalism - An Alternative History From Ancient Rome To Early Modern Germany-Cambridge University Press (2012)Roc SolàBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment of The Genitourinary System: GeneralDokumen2 halamanAssessment of The Genitourinary System: GeneralMaharani UtamiBelum ada peringkat
- Notes:: Reinforcement in Manhole Chamber With Depth To Obvert Greater Than 3.5M and Less Than 6.0MDokumen1 halamanNotes:: Reinforcement in Manhole Chamber With Depth To Obvert Greater Than 3.5M and Less Than 6.0Mسجى وليدBelum ada peringkat
- Durex 'S Marketing Strategy in VietnamDokumen45 halamanDurex 'S Marketing Strategy in VietnamPham Nguyen KhoiBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Information and Communication Technology 0417/13 May/June 2022Dokumen15 halamanCambridge IGCSE™: Information and Communication Technology 0417/13 May/June 2022ilovefettuccineBelum ada peringkat
- WBDokumen59 halamanWBsahil.singhBelum ada peringkat
- Canoe Matlab 001Dokumen58 halamanCanoe Matlab 001Coolboy RoadsterBelum ada peringkat
- Economic Review English 17-18Dokumen239 halamanEconomic Review English 17-18Shashank SinghBelum ada peringkat