COM413 - Principles of Communication
Diunggah oleh
Giing Fernandez0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
22 tayangan2 halamanpcom
Judul Asli
Part-I
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inipcom
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
22 tayangan2 halamanCOM413 - Principles of Communication
Diunggah oleh
Giing Fernandezpcom
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
COM413 – Principles of Communication
COMMUNICATION 1887 – Heinrich Hertz discovers radio waves and Guglielmo
is the process of exchanging of information from source to Marconi demonstrates wireless radio wave propagation.
destination. 1895 – Guglielmo Marconi discovered ground-wave radio signals.
refers to the sending, receiving and processing of information by 1903 – John Ambrose Fleming invented the two-electrode vacuum
electronic means. tube rectifier.
is a process whereby information is transferred from one point in 1905 – Guglielmo Marconi invented the directional radio antenna.
space and time, called the source, to another point, the destination. 1906 – Reginald Fessenden invented amplitude modulation (AM)
and demonstrates the first electronic voice communication.
TWO MAIN BARRIERS OF HUMAN COMMUNICATION 1906 – Lee De Forest invented the triode vacuum tube.
Language 1914 – Hiram Maxim founding of American Radio Relay League, the
Distance first amateur radio organization.
1918 – Major Edwin Armstrong develops the superheterodyne
MESSAGE / INFORMATION receiver.
1920 – Radio station KDKA broadcast the first regular licensed
is the physical manifestation of the information as produced by the
source. radio transmission out of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
1923 – Vladimir Zworykin invents and demonstrates television.
1931 – Major Edwin Armstrong invented frequency modulation
TWO TYPES OF SIGNALS
(FM).
1935 – Commercial FM radio broadcasting with monophonic
1. ANALOG SIGNAL – are time-varying voltages of currents that are
transmission.
continuously changing.
1937 – Alec Reeves invents binary-coded pulse-code modulation
(PCM).
2. DIGITAL SIGNAL – are voltages or currents that change in discrete
steps or levels. 1939 – NBC demonstrates television broadcasting. United States
was first use of two-way radio communications using “walkie-
talkies.”
HISTORY OF ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATIONS
1940 – Britain and US, invention and perfection of radar.
1946 – The AT&T Company was the first mobile telephone system
1830 – American scientist and professor Joseph Henry transmitted
for the public called MTS.
the first practical electrical signal.
1948 – John Von Neumann creates of the first stored program
1837 – Samuel F.B. Morse invented the telegraph.
electronic digital computer and Bell Laboratories invents the
1843 – Alexander Bain invented the facsimile. transistor.
1861 – Johann Phillip Reis completed the first nonworking 1953 – RCA / NBC was the first color TV broadcast.
telephone.
1957 – Russia launches the world’s first satellite.
1864 – James Clerk Maxwell released his paper “Dynamical Theory
1958 – Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce invented the integrated circuits
of the Electromagnetic Field”
(IC).
1866 – The United States and England was the first trans-Atlantic
1965 – First commercial communications satellite launched.
telegraph cable laid.
1970 – HDTV introduced in Japan.
1876 – Alexander Graham Bell and Thomas A. Watson invented the
1977 – First commercial use of optical fiber cables.
telephone.
1983 – Cellular telephone networks introduced in US.
1877 – Thomas Edison invented the phonograph.
1999 – DTV transmission begins in the United States.
1879 – George Eastman invented the photography.
1880 – Heinrich Hertz discovers electromagnetic waves.
Prepared by: ENGR. MARK JOMMEL S. NASOL
COM413 – Principles of Communication
ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 4. NOISE – random and unpredictable electrical signals from natural
- is the totality of mechanism that provides information link sources both internal and external to the system.
between source and destination.
ELEMENTS OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
1. TRANSMITTER (TX) - is a collection of electronic components and
circuits designed to convert the message into a signal suitable for
transmission in a communication medium.
2. TRANSMISSION CHANNEL or MEDIUM
- is the electrical connection between the transmitter and
receiver bridging the gap between the source and
destination.
3. RECEIVER (RX) – is a collection of electronic components and circuits
that accept the signal from the medium and convert it back into the
form of understandable by humans.
UNWANTED AND UNDESIRABLE EFFECTS ENCOUNTERED IN THE
MEDIUM
1. ATTENUATION – is a progressive decrease of signal power or power
density as distance increases.
2. DISTORTION – is a signal alteration due to imperfect response of the
system.
3. INTERFERENCE – extraneous signal usually man-made, that comes
into the system in the form similar to the original signal.
Prepared by: ENGR. MARK JOMMEL S. NASOL
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Communication 1Dokumen6 halamanCommunication 1Jade Dela PeñaBelum ada peringkat
- Milestones in The History of Electronic CommunicationDokumen2 halamanMilestones in The History of Electronic CommunicationChillie Bronzal Ullamot100% (1)
- Topic 0 History of Electronic CommunicationDokumen12 halamanTopic 0 History of Electronic CommunicationRoneline LizadaBelum ada peringkat
- Development of TelecommunicationDokumen3 halamanDevelopment of TelecommunicationDIANNE JOYBelum ada peringkat
- Tomasi Full Reviewer PDFDokumen159 halamanTomasi Full Reviewer PDFAdriane Patrick QuirosBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Electronic Communications: # Definitions TermsDokumen16 halamanIntroduction To Electronic Communications: # Definitions Termstsk2230Belum ada peringkat
- (Chapter 1) Introduction To Electronic Communication (1-18) PDFDokumen18 halaman(Chapter 1) Introduction To Electronic Communication (1-18) PDFgeorge ezar quiriadoBelum ada peringkat
- Tomasi Summary PDFDokumen197 halamanTomasi Summary PDFImtarid RacmanBelum ada peringkat
- Tomasi Book PDFDokumen191 halamanTomasi Book PDFJeremy JavierBelum ada peringkat
- History of Radio NewDokumen29 halamanHistory of Radio NewMarvie Caleon Delos SantosBelum ada peringkat
- History of Communication SystemDokumen3 halamanHistory of Communication SystemJOSHUA NEIL CARIGOBelum ada peringkat
- Tomasi PDFDokumen159 halamanTomasi PDFmiel_garrido82% (11)
- C CCC CCCC CCCCCCC CCC CCC CDokumen5 halamanC CCC CCCC CCCCCCC CCC CCC CMau Pots MuBelum ada peringkat
- History of CommunicationsDokumen3 halamanHistory of Communicationsedgardoelijah5Belum ada peringkat
- Historical Events in The Development of Telecommunication TechnologiesDokumen9 halamanHistorical Events in The Development of Telecommunication TechnologiesZaimon MaulionBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 NotesDokumen10 halamanChapter 5 Notescherilen gioBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom Industry: Telecom History Since 1842 Till Now .."Dokumen38 halamanTelecom Industry: Telecom History Since 1842 Till Now .."alok19886Belum ada peringkat
- Ece1: Electronics Devices and Circuits: HistoryDokumen10 halamanEce1: Electronics Devices and Circuits: HistoryAdriel JohnBelum ada peringkat
- History of Communication TechnologyDokumen11 halamanHistory of Communication TechnologyNurhikmah AzharBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics TimelineDokumen13 halamanElectronics TimelineDreian Calaoagan PalalayBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Acquisition and Retention at Bharti AirtelDokumen84 halamanCustomer Acquisition and Retention at Bharti AirtelAnonymous H6vlwbBelum ada peringkat
- ModulationDokumen171 halamanModulationஏம்மனுஎல்லெ செலேச்டினோBelum ada peringkat
- Tomasi Chap 1Dokumen156 halamanTomasi Chap 1ReivenBelum ada peringkat
- Timeline: History of RadioDokumen4 halamanTimeline: History of Radioits yanaBelum ada peringkat
- EE 315 Module 1Dokumen10 halamanEE 315 Module 1Cedric Bernard100% (1)
- Living in The I.T. EraDokumen16 halamanLiving in The I.T. EraAira Mae CrespoBelum ada peringkat
- History of ElectronicsDokumen3 halamanHistory of ElectronicsEj Mar ManabatBelum ada peringkat
- History of ElectronicsDokumen3 halamanHistory of ElectronicsEj Mar ManabatBelum ada peringkat
- Communications: Refers To The Sending, Receiving and Processing of Information Through Electronic MeansDokumen90 halamanCommunications: Refers To The Sending, Receiving and Processing of Information Through Electronic MeansAngelicaBelum ada peringkat
- 1843-1923: From Electromechanics To ElectronicsDokumen11 halaman1843-1923: From Electromechanics To ElectronicsSheeraz MemonBelum ada peringkat
- History of Wireless Communications1 - 2015-07-22Dokumen4 halamanHistory of Wireless Communications1 - 2015-07-22salahberraBelum ada peringkat
- OBRADORDokumen1 halamanOBRADORLeslie Jean ObradorBelum ada peringkat
- OBRADORLJDokumen1 halamanOBRADORLJLeslie Jean ObradorBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution of TelevisionDokumen18 halamanEvolution of TelevisionArianne AtilasBelum ada peringkat
- 0 Compile-ECE05Dokumen166 halaman0 Compile-ECE05Canteen StirlingBelum ada peringkat
- To Study The Customer Satisfaction in AirtelDokumen77 halamanTo Study The Customer Satisfaction in AirtelSami Zama0% (1)
- History of Communication (Ian Guevarra)Dokumen3 halamanHistory of Communication (Ian Guevarra)ian jheferBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics Enrichment Activity Question 3Dokumen2 halamanElectronics Enrichment Activity Question 3Reyn CabarlesBelum ada peringkat
- Television HistoryDokumen5 halamanTelevision HistoryJaider Mercado López100% (1)
- "Television Cable and Other Multi-Channel Services": Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDokumen11 halaman"Television Cable and Other Multi-Channel Services": Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDexter CaroBelum ada peringkat
- Timeline of Radio HistoryDokumen4 halamanTimeline of Radio Historyits yanaBelum ada peringkat
- Telegraph and Telephone HistoryDokumen3 halamanTelegraph and Telephone HistoryBubacarr BahBelum ada peringkat
- Reviewer in StasDokumen113 halamanReviewer in StasALYSSA PERALTABelum ada peringkat
- Short HistoryDokumen4 halamanShort HistoryCaio FernandesBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics History TimelineDokumen2 halamanElectronics History TimelineJON LESTER CABANESBelum ada peringkat
- Communications: Refers To The Sending, Reception and Processing of Information by Electrical MeansDokumen171 halamanCommunications: Refers To The Sending, Reception and Processing of Information by Electrical MeansCye Kit100% (9)
- History of TelecommunicationDokumen21 halamanHistory of Telecommunicationdrnileshkarle5671Belum ada peringkat
- (Chapter 1) Introduction To Electronic Communication (1-18)Dokumen18 halaman(Chapter 1) Introduction To Electronic Communication (1-18)mia_bautista100% (1)
- Evolution of TVDokumen28 halamanEvolution of TVdakter esseBelum ada peringkat
- Communications PDFDokumen12 halamanCommunications PDFChester Kyles ColitaBelum ada peringkat
- The Radio: Creation of The Human BeingDokumen9 halamanThe Radio: Creation of The Human BeingSthepan NoseBelum ada peringkat
- 1.discovery of Electricity PresentationDokumen12 halaman1.discovery of Electricity PresentationangelitoBelum ada peringkat
- History of Telecom & ElectronicsDokumen90 halamanHistory of Telecom & ElectronicsRajuraji100% (1)
- REVIEWER in Electronic Communications System by Wayne TomasiDokumen112 halamanREVIEWER in Electronic Communications System by Wayne TomasiShe San100% (2)
- 5.2 Building TelecommunicationDokumen15 halaman5.2 Building TelecommunicationJohn Rhey Almojallas BenedictoBelum ada peringkat
- Communication Using Media Instructor'S Notes: History of TelevisionDokumen9 halamanCommunication Using Media Instructor'S Notes: History of TelevisionAlanBelum ada peringkat
- Radio Broadcasting: A History of the AirwavesDari EverandRadio Broadcasting: A History of the AirwavesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5)
- Fernandez, Joe Mari Navera Purok 4, Patubig, Dampol, Plaridel, Bulacan, PhilippinesDokumen1 halamanFernandez, Joe Mari Navera Purok 4, Patubig, Dampol, Plaridel, Bulacan, PhilippinesGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
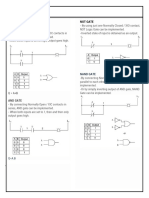
- Boolean Algebra or Gate: Jessa Fernandez PCEIT-03-801ADokumen2 halamanBoolean Algebra or Gate: Jessa Fernandez PCEIT-03-801AGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- April 7 2022 Grab E-ReceiptDokumen2 halamanApril 7 2022 Grab E-ReceiptGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- April 7 2022 Grab E-ReceiptDokumen2 halamanApril 7 2022 Grab E-ReceiptGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- EntrepDokumen11 halamanEntrepGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- May 24 - Grab E-ReceiptDokumen2 halamanMay 24 - Grab E-ReceiptGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- April 7 2022 Grab E-ReceiptDokumen2 halamanApril 7 2022 Grab E-ReceiptGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Library Management System: Bacarra, Rachel Anne H. Fernandez, Jessa NDokumen7 halamanLibrary Management System: Bacarra, Rachel Anne H. Fernandez, Jessa NGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Thai Foreign Business ActDokumen21 halamanThai Foreign Business ActaroonpardedeBelum ada peringkat
- Technological Institute of The Philippines On-The-Job Training / Practicum Weekly ReportDokumen6 halamanTechnological Institute of The Philippines On-The-Job Training / Practicum Weekly Reportjun dee83% (6)
- Rizal Technological UniversityDokumen2 halamanRizal Technological UniversityGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- LAB 1-Intro To Asmbly Lang ToolsDokumen14 halamanLAB 1-Intro To Asmbly Lang ToolsGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- PP02Dokumen3 halamanPP02Giing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Budget PropossalDokumen1 halamanBudget PropossalGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Output in FilipinoDokumen1 halamanOutput in FilipinoGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- BPI RoiDokumen2 halamanBPI RoiGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine MapDokumen36 halamanPhilippine MapGiing Fernandez100% (1)
- Part IIDokumen4 halamanPart IIGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Romel Mañaol Aquino: Career Objective ContactDokumen1 halamanRomel Mañaol Aquino: Career Objective ContactGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- CSAIS Documentation (Original) CDokumen109 halamanCSAIS Documentation (Original) CGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Eula 2Dokumen3 halamanEula 2norafiraBelum ada peringkat
- PhilippinesDokumen35 halamanPhilippinesGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Letter CutDokumen2 halamanLetter CutGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- CrashDokumen1 halamanCrashGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- CrashDokumen1 halamanCrashGiing FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- CDMA and LTE Zero Bufferzone (SRAN12.1 - 02)Dokumen40 halamanCDMA and LTE Zero Bufferzone (SRAN12.1 - 02)waelq2003Belum ada peringkat
- WorkZone Install Guide 3700136CDokumen2 halamanWorkZone Install Guide 3700136COscar Acevedo MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Blockphone 120 Jammer enDokumen4 halamanBlockphone 120 Jammer enpaulmazziottaBelum ada peringkat
- Pinout RNS EDokumen2 halamanPinout RNS EPascaru Bogdan100% (1)
- 90 1114 3.1 505 CGSDokumen2 halaman90 1114 3.1 505 CGSJuan RimachiBelum ada peringkat
- Operating Manual (Deh-2550ui) - Eng-Esp-Por PDFDokumen108 halamanOperating Manual (Deh-2550ui) - Eng-Esp-Por PDFOssian Valera PinedaBelum ada peringkat
- Hi Fi Aiwa Cs Naj54u CX nbl54lh PDFDokumen28 halamanHi Fi Aiwa Cs Naj54u CX nbl54lh PDFpitomoyaBelum ada peringkat
- Rohde Schwarz SMIQ6GHZ R Service Manual 6 GHZ Extension PDFDokumen56 halamanRohde Schwarz SMIQ6GHZ R Service Manual 6 GHZ Extension PDFgonnos28106Belum ada peringkat
- AD829AQ-High Speed Video OpampDokumen13 halamanAD829AQ-High Speed Video OpamphariharanccetBelum ada peringkat
- 5951JDokumen2 halaman5951Jscribd_wamr87Belum ada peringkat
- ZTE UMTS UR15 Voice Service Optimization For Multi-RAB Feature Guide - V1.1Dokumen80 halamanZTE UMTS UR15 Voice Service Optimization For Multi-RAB Feature Guide - V1.1Hunter100% (1)
- Triacs and DiacsDokumen4 halamanTriacs and Diacsssami670Belum ada peringkat
- 4065 Data SheetDokumen30 halaman4065 Data SheetDwp BhaskaranBelum ada peringkat
- Huawei Active Antennas Design Guideline v05 VF-ESDokumen35 halamanHuawei Active Antennas Design Guideline v05 VF-ESestebanarca100% (2)
- RD 15 HVF 1Dokumen8 halamanRD 15 HVF 1zaxmavBelum ada peringkat
- AEX ME 1 - EnglpdfDokumen2 halamanAEX ME 1 - EnglpdfkmleongmyBelum ada peringkat
- Communications Receivers PDFDokumen2 halamanCommunications Receivers PDFWarrenBelum ada peringkat
- UMTS900 Refarming Deployment Strategy V1 0Dokumen67 halamanUMTS900 Refarming Deployment Strategy V1 0Latycia ChalistyBelum ada peringkat
- CS1 - Unit 1 - FMDokumen34 halamanCS1 - Unit 1 - FMAjay ABelum ada peringkat
- Sbs A300 QuickstartDokumen1 halamanSbs A300 Quickstartchitti409Belum ada peringkat
- CD4553 Datasheet OKDokumen13 halamanCD4553 Datasheet OKCong ThoBelum ada peringkat
- Seven SegmentDokumen3 halamanSeven SegmentSamar SahooBelum ada peringkat
- 21WHS3BN Tda9381Dokumen59 halaman21WHS3BN Tda9381Luís Francisco PérezBelum ada peringkat
- Datasheet 4017Dokumen12 halamanDatasheet 4017Sinaí PerezBelum ada peringkat
- SiSonic Design GuideDokumen30 halamanSiSonic Design Guidekarthikp94Belum ada peringkat
- Radio Coverage Boosting Solutions PDFDokumen62 halamanRadio Coverage Boosting Solutions PDFslipargolokBelum ada peringkat
- MT8888CDokumen16 halamanMT8888CShivbraham Singh RajawatBelum ada peringkat
- System 5Dokumen58 halamanSystem 5OMBBelum ada peringkat
- Icom Ic-R3Dokumen2 halamanIcom Ic-R3sl1ck50Belum ada peringkat
- LC100-A Users ManualDokumen6 halamanLC100-A Users ManualLaurentiu IacobBelum ada peringkat