Step 1 Express 2018-Pathology
Diunggah oleh
Pratik JadhavHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Step 1 Express 2018-Pathology
Diunggah oleh
Pratik JadhavHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
First Aid Express 2018 workbook: PATHOLOGY page 1
Pathology
Questions
CELLULAR INJURY
1. Define the following terms. (p 206)
A. Hyperplasia________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
B. Metaplasia _________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
C. Dysplasia __________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
2. Describe the fundamental differences between the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis.
Name two important similarities between the pathways. (p 208) ___________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
3. Describe the fundamental differences between apoptosis and necrosis. What are the six types of
necrosis? List an example of each. (pp 208-209)
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2018 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
page 2 First Aid Express 2018 workbook: PATHOLOGY
4. Name three organs that manifest irreversible ischemia with red infarcts. Name three that show pale
infarcts. (p 210) _________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
5. What conditions are associated with a low erythrocyte sedimentation rate? (p 212) ____________
______________________________________________________________________________
6. Which cells and proteins mediate the acute phase of inflammation? (p 212) __________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
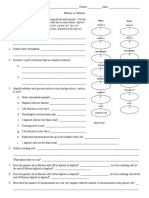
7. In the chart, compare and contrast the ligand-receptor interactions required for each step of leukocyte
extravasation. (p 213)
Ligand-Receptor
Endothelial Cells Leukocytes
Interaction
Rolling
Tight binding
Diapedesis
Migration
8. In cases of chronic inflammation, what types of cells infiltrate tissue? (p 214) What is the key cell of
granulomas? _________________
______________________________________________________________________________
9. What are the four ways that free radicals can be eliminated? Under what conditions might these
mechanisms fail? (p 216) _________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2018 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
First Aid Express 2018 workbook: PATHOLOGY page 3
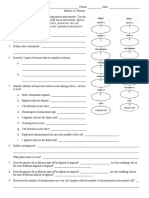
10. In the chart, compare and contrast the characteristics of transudates and exudates. (p 217)
Transudate Exudate
Causes
Cellularity
Protein level
NEOPLASIA
11. Compare and contrast the characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors. (p 220)
Characteristic Benign Tumor Metastatic Tumor
Differentiated?
Growth
Distinct boundaries?
Metastatic potential?
12. Describe the differences between tumor grade and tumor stage. (p 220) ____________________
______________________________________________________________________________
13. Match the neoplasm(s) to the condition(s) with which it is most commonly associated. (p 221)
_____ A. Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis 1. Acanthosis nigricans
_____ B. Cushing syndrome 2. Lymphoma
_____ C. Gastric adenocarcinoma 3. Neuroblastoma in children
_____ D. Hypercalcemia + elevated calcitriol level 4. Ovarian teratoma
_____ E. Myasthenia gravis 5. Pancreatic adenocarcinioma
_____ F. Opsoclonus-myoclonus ataxia syndrome 6. Renal cell carcinoma
_____ G. Polycythemia 7. Small cell lung cancer
_____ H. Trousseau syndrome 8. Thymoma
Copyright © 2018 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
page 4 First Aid Express 2018 workbook: PATHOLOGY
14. Oncogenes are associated with a ______ (gain/loss) of function and require damage to ______
(one/both) allele(s); examples include ________________________________________________.
In contrast, tumor suppressor genes are associated with a ______ (gain/loss) of function and require
damage to ______ (one/both) allele(s); examples include __________________________. (p 222)
15. A 40-year-old otherwise healthy man is diagnosed with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. He does not
smoke or drink. What is the most likely cause of his cancer? (p 223) _______________________
16. A 70-year-old who eats smoked salmon every day presents with abdominal pain and loss of appetite.
Which diagnosis should be high on the differential? (p 223) _______________________________
17. A 55-year-old woman with a 40-pack-year history of cigarette smoking presents with new-onset
cough, hemoptysis, and oliguria. What diagnosis should be high on the differential? (pp 221, 223)
______________________________________________________________________________
18. How are tumor markers best used? (p 224) ___________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
19. An IV drug abuser who is being monitored for cirrhosis shows a sudden increase in his α-fetoprotein
level. For which disease is he at increased risk? (p 224) _________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2018 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
First Aid Express 2018 workbook: PATHOLOGY page 5
20. Match the site of metastatic tumor with the immunohistochemical stain used to locate its origin.
(p 225)
_____ A. Chromogranin and synaptophysin 1. Astrocytes
_____ B. Cytokeratin 2. Epithelial cells
_____ C. Desmin 3. Mesenchymal tissue
_____ D. GFAP 4. Muscle
_____ E. Neurofilament 5. Neural crest cells
_____ F. PSA 6. Neuroendocrine cells
_____ G. S-100 7. Neurons
_____ H. TRAP 8. Prostatic epithelium
_____ I. Vimentin 9. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase
21. Which cancers are most common in men? In women? What is the overall leading cause of death in
the United States? (p 226) ________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2018 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
page 6 First Aid Express 2018 workbook: PATHOLOGY
Answers
CELLULAR INJURY
1. A. Hyperplasia: increase in the number of cells.
B. Metaplasia: one type of cell is replaced by another.
C. Dysplasia: disordered, non-neoplastic cell growth.
2. The intrinsic pathway begins with changes in the levels of anti- and proapoptotic factors, leading to
increased mitochondrial permeability. The extrinsic pathway begins with ligand receptor interactions
or perforin/granzyme release. Similarities: both require ATP, and both ultimately activate caspases.
3. Apoptosis occurs without any inflammation, whereas necrosis causes local inflammation. The six
types of necrosis are coagulative (as occurs in the heart), liquefactive (bacterial abscess), caseous
(eg, due to systemic fungal infection), fat (saponification of pancreas), fibrinoid (as occurs in blood
vessels), and gangrenous (limb gangrene).
4. Red infarcts: liver, lungs, and intestine. Pale infarcts: heart, kidney, and spleen.
5. Sickle cell anemia, polycythemia, heart failure, microcytosis, and hypofibrinogenemia, among others.
6. Neutrophils, eosinophils, mast cells, basophils, toll-like receptors, arachidonic acid metabolites,
complement, and Hageman factor.
Copyright © 2018 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
First Aid Express 2018 workbook: PATHOLOGY page 7
7.
Ligand-Receptor
Endothelial Cells Leukocytes
Interaction
E-selectin Sialyl-LewisX
Rolling P-selectin Sialyl-LewisX
GlyCAM-1 L-selectin
ICAM-1 CD11/18 integrins
Tight binding
VCAM-1 VLA-4 integrins
Diapedesis PECAM-1 PECAM-1
C5a
IL-8
LTB4
Migration Various
Kallikrein
Platelet-activating
factor
8. Mononuclear cells, including macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells. The key cell of
granulomas is epitheloid macrophages.
9. By scavenging enzymes (catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase), by
spontaneous decay, by antioxidants (vitamins A, C, and E), and by certain metal carrier proteins
(transferrin and ceruloplasmin). Deficiencies in free radical elimination can occur in individuals with
genetic mutations that result in abnormal/absent enzymes, or with vitamin deficiencies.
10.
Transudate Exudate
Increased hydrostatic pressure Lymphatic obstruction
Causes Decreased oncotic pressure Inflammation
Sodium retention Malignancy
Cellularity Hypocellular Cellular
Protein level Low High
Copyright © 2018 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
page 8 First Aid Express 2018 workbook: PATHOLOGY
NEOPLASIA
11.
Characteristic Benign Tumor Metastatic Tumor
May be poorly
Differentiated? Well-differentiated
differentiated
Growth Slow Erratic
Distinct boundaries? Yes Diffuse or locally invasive
Metastatic potential? No Yes
12. Tumor grade is the degree of cellular differentiation within the tumor and is a characteristic of the
tumor itself. In contrast, tumor stage describes the extent of tumor spread within a patient, and thus
is a better indication of a patient’s prognosis than is tumor grade.
13. A-4, B-7, C-1, D-2, E-8, F-3, G-6, H-5.
14. Oncogenes are associated with a gain of function and require damage to only one allele for
expression; examples include c-myc (Burkitt lymphoma) and kras (colon carcinoma). Tumor
suppressor genes are associated with a loss of function and require damage to both alleles for
expression; examples include NF1 (neurofibromatosis type 1) and BRCA2 (breast cancer).
15. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
16. Gastric cancer. Smoked foods contain large amounts of nitrosamine.
17. Small cell lung carcinoma with paraneoplastic SIADH secretion.
18. To confirm a diagnosis, to check for tumor recurrence, and to monitor response to therapy.
19. Hepatocellular carcinoma. IV drug use and cirrhosis are associated with HCV, and HCV is associated
with hepatocellular carcinoma.
20. A-6, B-2, C-4, D-1, E-7, F-8, G-5, H-9, I-3
21. Prostate, lung, and colon/rectal cancers are the most common cancers in men; breast, lung, and
colon/rectal cancers are the most common in women. The overall leading cause of death in the
United States is cardiovascular disease.
Copyright © 2018 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Pathology: How To Use The Workbook With The VideosDokumen8 halamanPathology: How To Use The Workbook With The VideosDinhLinhBelum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Express 2018-ReproductiveDokumen13 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-ReproductivePratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Extended Response QuestionsDokumen29 halamanExtended Response QuestionsNoor MuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- ReproductiveDokumen8 halamanReproductiveMedSchoolStuffBelum ada peringkat
- ' GenetechnologiesPart2Dokumen49 halaman' GenetechnologiesPart2dfq67gtkqsBelum ada peringkat
- 3.8.2 Gene Expression - 26 MarksDokumen8 halaman3.8.2 Gene Expression - 26 MarksalaynasharleezBelum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Express 2018-Hematology and OncologyDokumen12 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-Hematology and OncologyPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- The Language of MedicineDokumen9 halamanThe Language of MedicineErnesto SilveiraBelum ada peringkat
- A Level Homework 5Dokumen4 halamanA Level Homework 5szyzypBelum ada peringkat
- paper-1-longer-answer-questionsDokumen26 halamanpaper-1-longer-answer-questionsaadilmiah2019Belum ada peringkat
- GenetechnologiesDokumen108 halamanGenetechnologiesdfq67gtkqsBelum ada peringkat
- ReproductiveDokumen16 halamanReproductiveCarla CentenoBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry: How To Use The Workbook With The VideosDokumen19 halamanBiochemistry: How To Use The Workbook With The VideosDewiBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry AtfDokumen26 halamanBiochemistry AtfDanielchowdary GarapatiBelum ada peringkat
- HWK 1Dokumen2 halamanHWK 1teemo no JutsuBelum ada peringkat
- BIO 202 Blood Lab 22S PDFDokumen2 halamanBIO 202 Blood Lab 22S PDFTraci GardnerBelum ada peringkat
- 2.4 The Immune System QPDokumen25 halaman2.4 The Immune System QPZarmina KhanBelum ada peringkat
- ImmunogyWorksheet MSDokumen14 halamanImmunogyWorksheet MSAngeleena ANTOBelum ada peringkat
- BiochemistryDokumen18 halamanBiochemistryMedSchoolStuff50% (2)
- Exercise Recuperation IDokumen3 halamanExercise Recuperation IAlexandra IstvanBelum ada peringkat
- Cord Blood Stem Cells: A Lifesaving GiftDokumen3 halamanCord Blood Stem Cells: A Lifesaving GiftJulio MoreiraBelum ada peringkat
- Module 6Dokumen4 halamanModule 6Leah LlobellBelum ada peringkat
- MD II Material Pentru 10.03.2020Dokumen4 halamanMD II Material Pentru 10.03.2020Irina Panciu StefanBelum ada peringkat
- Immune System REVISION AnswersDokumen22 halamanImmune System REVISION Answersinder191100% (1)
- LAB 8 Chromosomal Abnormalities Gene Regulation 3Dokumen4 halamanLAB 8 Chromosomal Abnormalities Gene Regulation 3Christina NgwakoBelum ada peringkat
- A03 Data AnalysisDokumen19 halamanA03 Data Analysisleocarlton0700Belum ada peringkat
- Parasitology NematodesDokumen28 halamanParasitology NematodesJoshua Richard Jr Tubiano PayopaninBelum ada peringkat
- Comprehension QuestionsDokumen20 halamanComprehension QuestionsNoor MuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- Cell DivisionDokumen15 halamanCell DivisionShin3 KimBelum ada peringkat
- Year 10 Science Set 2 Part 2 160559226Dokumen30 halamanYear 10 Science Set 2 Part 2 160559226osasnelly2006Belum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Express 2018-BiochemistryDokumen26 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-BiochemistryPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Ap - BloodDokumen13 halamanAp - BloodJustine May Balinggan DelmasBelum ada peringkat
- Mitosis Vs Meiosis WorksheetDokumen2 halamanMitosis Vs Meiosis WorksheetFabian Andres Paez Velandia100% (1)
- Student Exploration: Cell Division: Vocabulary: Cell Division, Centriole, Centromere, Chromatid, Chromatin, ChromosomeDokumen5 halamanStudent Exploration: Cell Division: Vocabulary: Cell Division, Centriole, Centromere, Chromatid, Chromatin, ChromosomeBecka RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Rajeem Outlaw Wright - Mitosis Vs Meiosis BiologyDokumen2 halamanRajeem Outlaw Wright - Mitosis Vs Meiosis BiologyRajeem Outlaw WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 8 Assessment BookletDokumen32 halamanTopic 8 Assessment BookletjingBelum ada peringkat
- ParasitologyDokumen8 halamanParasitologyJoshua Richard Jr Tubiano PayopaninBelum ada peringkat
- Recuperare 2Dokumen3 halamanRecuperare 2Mihnea TurcuBelum ada peringkat
- Tremujori 2 Test Grupi ADokumen3 halamanTremujori 2 Test Grupi AgertaBelum ada peringkat
- Mitosis & MeiosisDokumen8 halamanMitosis & MeiosisamaraadomaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 6: Genetic Change: OutcomesDokumen8 halamanModule 6: Genetic Change: OutcomesSorour KashbaBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Review 1Dokumen4 halamanBiology Review 1Mehakpreet GillBelum ada peringkat
- Seventh Grade "Cell Division and Genetics" AssessmentDokumen11 halamanSeventh Grade "Cell Division and Genetics" AssessmentBrenda L. CarrasquilloBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Terminology AssignmentDokumen4 halamanMedical Terminology AssignmentBeverly GraciousBelum ada peringkat
- Organisation HTDokumen17 halamanOrganisation HTjane byersBelum ada peringkat
- The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and Cancer: in Depth: About This WorksheetDokumen8 halamanThe Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and Cancer: in Depth: About This WorksheetddhhdhdhdBelum ada peringkat
- NUMC 101 Module 1 Cardiovascular System Blood Lab ExerciseDokumen10 halamanNUMC 101 Module 1 Cardiovascular System Blood Lab ExerciseHannah Vannerie AlanguiBelum ada peringkat
- Renal: QuestionsDokumen15 halamanRenal: QuestionsMedStudent MedStudentBelum ada peringkat
- 8.2 Epigenetics and RNA interference QPDokumen10 halaman8.2 Epigenetics and RNA interference QPthere4per410Belum ada peringkat
- Application of Knowledge QuestionsDokumen16 halamanApplication of Knowledge QuestionsElllie TattersBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Worksheet Magnification and Cell PartsDokumen15 halamanBiology Worksheet Magnification and Cell PartsMemmy KidnaBelum ada peringkat
- 3.8.4.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Revision Questions - 25marksDokumen8 halaman3.8.4.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Revision Questions - 25marksalaynasharleezBelum ada peringkat
- InfectionandResponseHT (Copy)Dokumen13 halamanInfectionandResponseHT (Copy)jane byersBelum ada peringkat
- Inheritance 7 9 6Dokumen22 halamanInheritance 7 9 6Philip VuuBelum ada peringkat
- MicrobiologyDokumen20 halamanMicrobiologyMedSchoolStuff75% (4)
- Endocrine System Group 2 QuizDokumen4 halamanEndocrine System Group 2 QuizYanna LozanoBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 4 Exam QuestionsDokumen7 halamanTopic 4 Exam Questionsgul pinarBelum ada peringkat
- Ds90-Sol Sim Monohybrid Cross PracticeDokumen6 halamanDs90-Sol Sim Monohybrid Cross Practiceapi-110789702Belum ada peringkat
- Clinical Embryology Exam I, 2004Dokumen3 halamanClinical Embryology Exam I, 2004lucky mbaselaBelum ada peringkat
- Wound Healing: Stem Cells Repair and Restorations, Basic and Clinical AspectsDari EverandWound Healing: Stem Cells Repair and Restorations, Basic and Clinical AspectsBelum ada peringkat
- HGJKK PDFDokumen2 halamanHGJKK PDFPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- HGJKK PDFDokumen2 halamanHGJKK PDFPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Pathoma RuntimesDokumen6 halamanPathoma RuntimesaloverofdanceBelum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Express 2018-Neurology and Special SensesDokumen20 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-Neurology and Special SensesPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Express 2018-RespiratoryDokumen16 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-RespiratoryPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Express 2018-Musculoskeletal Skin and Connective TissueDokumen16 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-Musculoskeletal Skin and Connective TissuePratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Express 2018-ImmunologyDokumen12 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-ImmunologyPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Express 2018-CardiovascularDokumen23 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-CardiovascularPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Express 2018-Hematology and OncologyDokumen12 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-Hematology and OncologyPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Express 2018-MicrobiologyDokumen33 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-MicrobiologyPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Express 2018-RenalDokumen14 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-RenalPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Express 2018-EndocrineDokumen13 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-EndocrinePratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Express 2018-GastrointestinalDokumen13 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-GastrointestinalPratik Jadhav100% (1)
- Step 1 Express 2018-BiochemistryDokumen26 halamanStep 1 Express 2018-BiochemistryPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- F.A2016 12WeekUSMLESchedule PDFDokumen5 halamanF.A2016 12WeekUSMLESchedule PDFPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- DaefasfadsfdsDokumen1 halamanDaefasfadsfdsPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Book 1Dokumen2 halamanBook 1Pratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- F.A2016 12WeekUSMLESchedule PDFDokumen5 halamanF.A2016 12WeekUSMLESchedule PDFPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- New Workout For Indian OnlyDokumen1 halamanNew Workout For Indian OnlyPratik JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Lemna Minor 1Dokumen11 halamanLemna Minor 1Fitrah AbdiarsahBelum ada peringkat
- DLL SHS STEM Grade 12 - General Biology1 Quarter1 Week2 .DocxDokumen17 halamanDLL SHS STEM Grade 12 - General Biology1 Quarter1 Week2 .Docxjoan100% (4)
- Biological aspects of the dangerous jellyfish Physalia physalisDokumen19 halamanBiological aspects of the dangerous jellyfish Physalia physalisbakin muBelum ada peringkat
- Live Broadcasting Raising Dragons in The Interstellar (Unknown) (Z-Library)Dokumen702 halamanLive Broadcasting Raising Dragons in The Interstellar (Unknown) (Z-Library)mddgrcvfBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar Pustaka 2011sam-8Dokumen6 halamanDaftar Pustaka 2011sam-8Deanty ChairunnisaBelum ada peringkat
- DinosaursDokumen80 halamanDinosaursMelania VladBelum ada peringkat
- Inactivation of Viruses: June 2011Dokumen13 halamanInactivation of Viruses: June 2011Iqbal Muhammad Yaa-BegitulahBelum ada peringkat
- Snake Rescue Guideline EnglishDokumen8 halamanSnake Rescue Guideline Englishdipak thakurBelum ada peringkat
- Science Process Skills: Observe Classify Measure Infer Predict Credits Extensions About The AuthorDokumen21 halamanScience Process Skills: Observe Classify Measure Infer Predict Credits Extensions About The AuthorSharmaine TuazonBelum ada peringkat
- Verb classes and types in English and UkrainianDokumen16 halamanVerb classes and types in English and UkrainianАнастасия ДобровольскаяBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Poultry Chicken NC IiDokumen34 halamanLecture Poultry Chicken NC IiNichole Kyla Enriquez100% (1)
- Stem Cell Dan Produknya Di UnnesDokumen56 halamanStem Cell Dan Produknya Di UnnesemyBelum ada peringkat
- How to Make Homemade BaconDokumen11 halamanHow to Make Homemade Baconpilapil_j100% (1)
- Natural History 16 A Meru of TDokumen602 halamanNatural History 16 A Meru of Tacademo misirBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of Neurological InvolvementDokumen11 halamanClassification of Neurological InvolvementGyandeep B. GohainBelum ada peringkat
- Open and Closed Packed Positions of JointsDokumen1 halamanOpen and Closed Packed Positions of JointsRaymond100% (4)
- Test 5Dokumen7 halamanTest 550premahuBelum ada peringkat
- Ivan Petrovic PavlovDokumen3 halamanIvan Petrovic PavlovNazreen Ayein Shukor100% (1)
- Xii - Vivential ExamDokumen4 halamanXii - Vivential ExamKatherin Rodriguez ZavaletaBelum ada peringkat
- Don A. Samuelson. Textbook of Veterinary HistologyDokumen534 halamanDon A. Samuelson. Textbook of Veterinary HistologyYare Hernández88% (8)
- DR Lojpurr First Aid To The InjuredDokumen27 halamanDR Lojpurr First Aid To The InjuredbillrocksBelum ada peringkat
- Somali Folktales 1-19Dokumen36 halamanSomali Folktales 1-19Ak 47Belum ada peringkat
- Quarter 3, Week 1 English Inkay - PeraltaDokumen47 halamanQuarter 3, Week 1 English Inkay - PeraltaPatrick EdrosoloBelum ada peringkat
- Characteristics of Life Long TestDokumen5 halamanCharacteristics of Life Long TestMichelle Ramirez Co-GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of LiverDokumen22 halamanAnatomy of Liversiewv_1Belum ada peringkat
- Aulia Rahmatun Nufus Raihanun Nisa Dinur Sri RizkiDokumen18 halamanAulia Rahmatun Nufus Raihanun Nisa Dinur Sri RizkiFauzan JakfarBelum ada peringkat
- Hemodinamik Monitoring ModifDokumen34 halamanHemodinamik Monitoring ModifDea AjhaBelum ada peringkat
- Preksha Meditation GuideDokumen34 halamanPreksha Meditation GuideRam MadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Black Bellied TernDokumen11 halamanBlack Bellied TernPravalika SarvadevabhatlaBelum ada peringkat
- Talking Turkey Final ReportDokumen29 halamanTalking Turkey Final ReportDavid CarrBelum ada peringkat