CCNP Mind Map Chapter 6
Diunggah oleh
Zulhilmi Rosli0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
73 tayangan1 halamanThis is mind map note for CCNP chapter 6
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis is mind map note for CCNP chapter 6
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
73 tayangan1 halamanCCNP Mind Map Chapter 6
Diunggah oleh
Zulhilmi RosliThis is mind map note for CCNP chapter 6
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
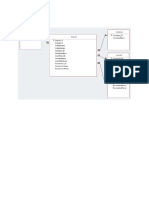
Network hosts are configured with a
single default gateway IP address
Layer 3 switches work together to present the
FHRP illusion of a single virtual router to the hosts on
the LAN
By sharing an IP address and a MAC (Layer 2)
address, two or more routers can act as a single
“virtual” router.
Overview of FHRP and
HSRP provides the mechanism for determining which
router should take the active role in forwarding
traffic
determining when that role must
be taken over by a standby
HSRP router.
The virtual router processes no physical
Virtual Router frames. There is one virtual router in an HSRP
group.
VRRP differs from HSRP in that it allows
you to use an address of one of the Configure and verify
First-Hop Router roles Active Router The active router physically forwards packets
sent to the MAC address of the virtual router.
physical VRRP group members as a virtual
IP address.
VRRP
Redundancy Take over as an Active Router when
Stand by Router there is no hello message from active
router
allows for automatic selection and simultaneous
use of multiple available gateways, in addition
to automatic failover between those gateways.
Members of a GLBP group elect
one gateway to be the AVG for that
group
Configure and verify The AVG assigns a virtual MAC
GLBP AVG (active virtual
GLBP address to each member of the GLBP
gateway)
group
The AVG listens to the ARP requests for the
default gateway IP and replies with a MAC
address of one of the GLBP group members
responsibility for forwarding packets that
GLBP AVF (active virtual
are sent to the virtual MAC address that is
forwarder)
assigned to that gateway by the AVG
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- FHRP First Hop Redundancy ProtocolDokumen3 halamanFHRP First Hop Redundancy ProtocolJack DannielsBelum ada peringkat
- FHRPDokumen6 halamanFHRPApril DaingBelum ada peringkat
- Implement High Availability Campus Networks with HSRP and VRRPDokumen24 halamanImplement High Availability Campus Networks with HSRP and VRRPMadhu SudhanBelum ada peringkat
- SWHSRPDokumen12 halamanSWHSRPWilfried Junior Njia NdzebeBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco First Hop Redundancy ProtocolsDokumen2 halamanCisco First Hop Redundancy ProtocolsRafi HussainBelum ada peringkat
- VRRP Cisco DasarDokumen32 halamanVRRP Cisco Dasardewi trisnowatiBelum ada peringkat
- Module 9: FHRP Concepts: Instructor MaterialsDokumen19 halamanModule 9: FHRP Concepts: Instructor MaterialsJohnBelum ada peringkat
- Configuring VRRP: Finding Feature InformationDokumen20 halamanConfiguring VRRP: Finding Feature Informationdisox14258Belum ada peringkat
- Discovery 12: Implementing HSRP: Task 1: Configure and Tune HSRPDokumen8 halamanDiscovery 12: Implementing HSRP: Task 1: Configure and Tune HSRPIonut StanciuBelum ada peringkat
- Module 9: FHRP Concepts: Switching, Routing and Wireless Essentials v7.0 (SRWE)Dokumen18 halamanModule 9: FHRP Concepts: Switching, Routing and Wireless Essentials v7.0 (SRWE)random studentBelum ada peringkat
- Configuring VRRP: Finding Feature InformationDokumen22 halamanConfiguring VRRP: Finding Feature Informationdisox14258Belum ada peringkat
- Hot Standby Router Protocol Features and Functonality From CiscoDokumen14 halamanHot Standby Router Protocol Features and Functonality From CiscoargonautyBelum ada peringkat
- 0316 - HSRP States and Version ComparisonsDokumen2 halaman0316 - HSRP States and Version Comparisonsnetgame76Belum ada peringkat
- Hot Standby Router Protocol Features and Functionality: Document ID: 9234Dokumen14 halamanHot Standby Router Protocol Features and Functionality: Document ID: 9234Balaji RamanujamBelum ada peringkat
- Review of First Hop Redundancy Protocol and Their FunctionalitiesDokumen4 halamanReview of First Hop Redundancy Protocol and Their FunctionalitiesseventhsensegroupBelum ada peringkat
- Routing: Graphical User Interface Functional DescriptionDokumen1 halamanRouting: Graphical User Interface Functional Descriptionعلوم نوین امیرکبیرBelum ada peringkat
- M Configuring VRRP 922Dokumen28 halamanM Configuring VRRP 922nrBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Analysis of HSPR, VRRP and GLPB Network Redundancy ProtocolsDokumen7 halamanComparative Analysis of HSPR, VRRP and GLPB Network Redundancy ProtocolsMANTECH PublicationsBelum ada peringkat
- HSRP in CiscoDokumen12 halamanHSRP in Ciscoapi-3780069100% (1)
- SW HSRPDokumen13 halamanSW HSRPEmerson Barros RivasBelum ada peringkat
- Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) Configuration GuideDokumen38 halamanGateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) Configuration GuidejoaquimBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5-Dynamic Routing: Network AdministrationDokumen5 halamanChapter 5-Dynamic Routing: Network AdministrationRejean IsipBelum ada peringkat
- M Configuring HSRPDokumen8 halamanM Configuring HSRPAnagh SidhuBelum ada peringkat
- Configuring GLBP: Finding Feature InformationDokumen28 halamanConfiguring GLBP: Finding Feature InformationVictor HugoBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamic Routing Protocols ExplainedDokumen38 halamanDynamic Routing Protocols ExplainedArad RezaBelum ada peringkat
- Configure BGP routing and peeringDokumen7 halamanConfigure BGP routing and peeringnuBelum ada peringkat
- Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) Is A Cisco Proprietary Redundancy Protocol For Establishing A Fault-Tolerant DefaultDokumen4 halamanHot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) Is A Cisco Proprietary Redundancy Protocol For Establishing A Fault-Tolerant DefaultVidyun LambaBelum ada peringkat
- Glossary CCNP SwitchDokumen6 halamanGlossary CCNP SwitchSkynet9000Belum ada peringkat
- 01-02 ARP ConfigurationDokumen47 halaman01-02 ARP ConfigurationAdrian CarmonaBelum ada peringkat
- Configuring HSRPDokumen48 halamanConfiguring HSRPManishBelum ada peringkat
- VRRPDokumen20 halamanVRRPTanveer AkramBelum ada peringkat
- Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) : Speaker: Li-Wen Chen Date: 2010-08-12Dokumen12 halamanVirtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) : Speaker: Li-Wen Chen Date: 2010-08-12babeksfBelum ada peringkat
- l3 HSRPDokumen32 halamanl3 HSRPmouhannadn.alrightBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - HSRP PDFDokumen34 halamanChapter 2 - HSRP PDFCao Hồng MinhBelum ada peringkat
- Clase 21-Mod2Dokumen27 halamanClase 21-Mod2Alex Osores RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- UM Routing L3P 15 01 UsDokumen102 halamanUM Routing L3P 15 01 UsmiroBelum ada peringkat
- Distance Vector Routing Protocols ExplainedDokumen6 halamanDistance Vector Routing Protocols ExplainedAntonio BrandãoBelum ada peringkat
- 02 VRRP ConfigurationDokumen44 halaman02 VRRP Configurationmangla\Belum ada peringkat
- IOS Interior Routing Protocols Cheat Sheet PDFDokumen1 halamanIOS Interior Routing Protocols Cheat Sheet PDFKurco BeinBelum ada peringkat
- TCP/IP Fundamentals to MPLS in X DaysDokumen6 halamanTCP/IP Fundamentals to MPLS in X Daysnipo809Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 QuestionsDokumen8 halamanChapter 4 Questionsahmed zuhdBelum ada peringkat
- EIGRP - Stub RoutingDokumen6 halamanEIGRP - Stub RoutingLinux NEBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco HSRP TroubleshootingDokumen52 halamanCisco HSRP TroubleshootingSivakonalarao MandalapuBelum ada peringkat
- Configuring HSRP Aware PimDokumen8 halamanConfiguring HSRP Aware PimCARLO ABREGOBelum ada peringkat
- RoutingDokumen8 halamanRoutingniravsoni001Belum ada peringkat
- Routing Overview - Static RouteDokumen20 halamanRouting Overview - Static RouteĐinh TúBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 2 - NET-351 Introduction To RoutingDokumen29 halamanChapter - 2 - NET-351 Introduction To RoutingPRASANG PRASANGBelum ada peringkat
- Configure and Test HSRP IP Route TrackingDokumen2 halamanConfigure and Test HSRP IP Route TrackingAdeyemi SamuelBelum ada peringkat
- 2 - RoutingDokumen54 halaman2 - RoutingNguyễn Phạm Thiên BảoBelum ada peringkat
- Routing Packet Switching ExplainedDokumen22 halamanRouting Packet Switching Explainedom tiwariBelum ada peringkat
- A Distance-Vector Multipath Routing ProtocolDokumen8 halamanA Distance-Vector Multipath Routing ProtocolquyhutcBelum ada peringkat
- CCNP Switch V7.1 Quiz - Chapter 5: Intervlan Routing and DHCPDokumen8 halamanCCNP Switch V7.1 Quiz - Chapter 5: Intervlan Routing and DHCPjohnBelum ada peringkat
- Internet RoutingDokumen52 halamanInternet Routingapi-26084493100% (1)
- HSRP, VRRP, GLBPDokumen11 halamanHSRP, VRRP, GLBPAmina BashirBelum ada peringkat
- First Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolDari EverandFirst Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolBelum ada peringkat
- HSDPA/HSUPA for UMTS: High Speed Radio Access for Mobile CommunicationsDari EverandHSDPA/HSUPA for UMTS: High Speed Radio Access for Mobile CommunicationsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONDari EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 1Dokumen2 halamanLab 1Zulhilmi RosliBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment CCNP1Dokumen9 halamanAssignment CCNP1Zulhilmi RosliBelum ada peringkat
- 6.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings Instructions PDFDokumen4 halaman6.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings Instructions PDFZulhilmi RosliBelum ada peringkat
- SBA CCNP Switch AnswerDokumen7 halamanSBA CCNP Switch AnswerVadan CorneliuBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Database 1Dokumen4 halamanAssignment Database 1Zulhilmi RosliBelum ada peringkat
- Ccnpv7.1 Switch Lab3-1 Vlan-trunk-Vtp StudentDokumen20 halamanCcnpv7.1 Switch Lab3-1 Vlan-trunk-Vtp StudentItamar Zimmerman0% (1)
- Real-Time Traffic Alerts Using VANETDokumen5 halamanReal-Time Traffic Alerts Using VANETZulhilmi RosliBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - Regression and Correlation (Student)Dokumen18 halamanChapter 2 - Regression and Correlation (Student)Zulhilmi RosliBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8: Switching Features and Technologies For The Campus NetworkDokumen1 halamanChapter 8: Switching Features and Technologies For The Campus NetworkZulhilmi RosliBelum ada peringkat
- How To Apply The Cashflow Quadrant ConceptDokumen2 halamanHow To Apply The Cashflow Quadrant ConceptZulhilmi Rosli100% (1)
- Trigonometri Notes Add Math Form 5Dokumen5 halamanTrigonometri Notes Add Math Form 5Zulhilmi Rosli100% (3)
- CP R77 Gaia AdminGuideDokumen234 halamanCP R77 Gaia AdminGuideAgnelo RodriguesBelum ada peringkat
- iS5Com Application Note VRRPDokumen8 halamaniS5Com Application Note VRRPFrancisco Antonio Bolaño CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- Etherchannel and Trunking QuestionsDokumen48 halamanEtherchannel and Trunking QuestionsyasserBelum ada peringkat
- Enterprise FW 04-High AvailabilityDokumen39 halamanEnterprise FW 04-High AvailabilityMarcos Vinicios Santos Corrêa100% (1)
- ZXR10 M6000 Carrier-Class Router Product DescriptionDokumen110 halamanZXR10 M6000 Carrier-Class Router Product DescriptionHarishBelum ada peringkat
- StoneGate Firewall Installation Guide v5-1Dokumen145 halamanStoneGate Firewall Installation Guide v5-1Riteesh AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Virtual Link Trunking in Dell EMC OS10 Enterprise Edition: Reference ArchitectureDokumen49 halamanVirtual Link Trunking in Dell EMC OS10 Enterprise Edition: Reference Architecturelyax1365Belum ada peringkat
- H3C MSR 20-30-50 User GuideDokumen60 halamanH3C MSR 20-30-50 User GuidePramod VijayBelum ada peringkat
- Implementing VRRP CiscoDokumen34 halamanImplementing VRRP CiscoJames OmaraBelum ada peringkat
- Mikrotik VRRP and Load SharingDokumen12 halamanMikrotik VRRP and Load SharingCarlosBelum ada peringkat
- 300-115 Exam DumpsDokumen2 halaman300-115 Exam DumpsNedu RaduBelum ada peringkat
- Jncda Quiz1Dokumen13 halamanJncda Quiz1Akaki Surguladze100% (1)
- Extreme Switch ManualDokumen26 halamanExtreme Switch ManualNst WahyudiBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Proposal For IGW HUAWEI - LATESTDokumen46 halamanTechnical Proposal For IGW HUAWEI - LATESTMunazil Rahman100% (1)
- 350-401 Ppwy Premium Exam 336qDokumen164 halaman350-401 Ppwy Premium Exam 336qsajjad gayyemBelum ada peringkat
- Brocade To Cisco Reference PDFDokumen31 halamanBrocade To Cisco Reference PDFSajeer RehmanBelum ada peringkat
- CSWcore02 SecIP v1Dokumen57 halamanCSWcore02 SecIP v1Doan Le Minh TuBelum ada peringkat
- Dell Networking Installation and Configuration Course Lab Guide v1b PDFDokumen202 halamanDell Networking Installation and Configuration Course Lab Guide v1b PDFrsalazar71Belum ada peringkat
- BCMSN30SG Vol.2 PDFDokumen394 halamanBCMSN30SG Vol.2 PDFShemariyahBelum ada peringkat
- Linux Virtual Server High Availability using VRRPv2Dokumen5 halamanLinux Virtual Server High Availability using VRRPv2Fredy PantiBelum ada peringkat
- Protocolos TotalesDokumen37 halamanProtocolos Totaleseduardo cerronBelum ada peringkat
- Teletronik DASANDokumen16 halamanTeletronik DASANosamaokokBelum ada peringkat
- Passed H12Dokumen13 halamanPassed H12Anonymous cs4BLczE0% (1)
- Networking RackSwitch G8316Dokumen16 halamanNetworking RackSwitch G8316afto_busBelum ada peringkat
- B 163 Consolidated 3850 CGDokumen3.082 halamanB 163 Consolidated 3850 CGKalan KlBelum ada peringkat
- ASR9000 Feature NavigatorDokumen9 halamanASR9000 Feature Navigatormountaineer07Belum ada peringkat
- Boughaz - ENCOR 350-401 PDFDokumen67 halamanBoughaz - ENCOR 350-401 PDFNilNirjoneBelum ada peringkat
- HP Switching and Routing Technologies: Web-Based Training Course CompanionDokumen102 halamanHP Switching and Routing Technologies: Web-Based Training Course CompanionivanovBelum ada peringkat
- Nokia Secure IP Networks A Multilayer, Embedded Approach To IP Network SecurityDokumen16 halamanNokia Secure IP Networks A Multilayer, Embedded Approach To IP Network SecuritySilvio SantosBelum ada peringkat
- First Hop RedundancyDokumen1 halamanFirst Hop RedundancyWA LidBelum ada peringkat